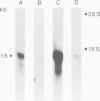
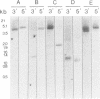
Abstract
IGF-I and IGF-II are growth-stimulating peptides with strong mitogenic properties. These polypeptide growth factors circulate in serum bound to specific binding proteins. We report the cloning and complete sequence of a cDNA encoding a low mol. wt IGF-binding protein from a human placenta cDNA library. We propose the designation IGF-binding protein 1 (IBP-1) for the gene and corresponding protein. Expression of the cDNA encoding IBP-1 in COS cells resulted in the synthesis of a 30-kd protein which binds IGF-I and is immunologically indistinguishable from the IGF-binding protein isolated from amniotic fluid or human serum. Northern blotting analysis demonstrated that expression of the IBP-1 gene is highly tissue specific and limited to placental membranes and fetal liver suggesting a rigid control. The IBP-1 gene is a single copy gene, located on chromosome 7. The results obtained suggest that most, if not all, lower mol. wt IGF-binding proteins originate from this gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulinlike growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI112742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Tyler M. I., Howden M. E. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human plasma differs from other human IGF binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Wood M. H. Two immunoreactive binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in human amniotic fluid: relationship to fetal maturity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Sep;65(3):423–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binoux M., Hossenlopp P., Hardouin S., Seurin D., Lassarre C., Gourmelen M. Somatomedin (insulin-like growth factors)-binding proteins. Molecular forms and regulation. Horm Res. 1986;24(2-3):141–151. doi: 10.1159/000180553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn H., Kraus W. Isolierung und Charakterisierung eines neuen plazentaspezifischen Proteins (PP12). Arch Gynecol. 1980;229(4):279–291. doi: 10.1007/BF02108579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra T., Stackhouse R., Kidd V. J., Woo S. L. Isolation and sequence characterization of a cDNA clone of human antithrombin III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1845–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Han V. K., Elgin R. G., D'Ercole A. J. Alterations in the synthesis of a fibroblast surface associated 35 K protein modulates the binding of somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 May;1(5):339–347. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-5-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J., Guyda H. J. Isolation of a somatomedin-binding protein from preterm amniotic fluid. Development of a radioimmunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):899–907. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J., Guyda H. J., Posner B. I. Immunoassay of a somatomedin-binding protein from human amniotic fluid: levels in fetal, neonatal, and adult sera. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):908–915. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Valiquette G., Guyda H. J., Corvol M. T., Posner B. I. Partial purification and characterization of a binding protein for insulin-like activity (ILAs) in human amniotic fluid: a possible inhibitor of insulin-like activity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Mar;90(3):505–518. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhtala M. L., Koistinen R., Palomäki P., Partanen P., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Biologically active domain in somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):263–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinen R., Huhtala M. L., Stenman U. H., Seppälä M. Purification of placental protein PP12 from human amniotic fluid and its comparison with PP12 from placenta by immunological, physicochemical and somatomedin-binding properties. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 May 15;164(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinen R., Kalkkinen N., Huhtala M. L., Seppälä M., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Placental protein 12 is a decidual protein that binds somatomedin and has an identical N-terminal amino acid sequence with somatomedin-binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1375–1378. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., MacDonald R. G., Brackett J. L., Mole J. E., Anderson J. K., Czech M. P. Purification and amino-terminal sequence of an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein secreted by rat liver BRL-3A cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11180–11188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Enberg G., Jörnvall H., Hall K. Isolation and characterization of a somatomedin-binding protein from mid-term human amniotic fluid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Isaksson M., Jörnvall H., Hall K. The somatomedin-binding protein isolated from a human hepatoma cell line is identical to the human amniotic fluid somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Póvoa G., Roovete A., Hall K. Cross-reaction of serum somatomedin-binding protein in a radioimmunoassay developed for somatomedin-binding protein isolated from human amniotic fluid. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Dec;107(4):563–570. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1070563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Goldfine I. D., Wells C. A. DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts: stimulation by insulin and by nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):512–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Koistinen R., Wahlström T., Bohn H., Ranta T., Seppälä M. Synthesis of placental protein 12 by human decidua. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1304–1309. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Menabawey M., Isaka K., Bohn H., Chard T., Grudzinskas J. G. Synthesis of placental protein 12 by decidua from early pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Sep;63(3):675–679. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-3-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Cowell J., Robertson M. E., Priestley L. M., Wadey R., Hopkins B., Pritchard J., Bell G. I., Rall L. B., Graham C. F. Insulin-like growth factor-II gene expression in Wilms' tumour and embryonic tissues. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):260–262. doi: 10.1038/317260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Structure of human hemopexin: O-glycosyl and N-glycosyl sites and unusual clustering of tryptophan residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2021–2025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuvel M., Bosveld I. J., Mooren A. A., Trapman J., Zwarthoff E. C. Properties of natural and hybrid murine alpha interferons. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2215–2222. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Underwood L. E., Hintz R. L., Clemmons D. R., Voina S. J., Weaver R. P. The somatomedins: a family of insulinlike hormones under growth hormone control. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1974;30(0):259–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Jagars G., Sand I., Grunwald J., Froesch E. R. Inhibition of the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity on isolated rat fat cells by binding to its carrier protein. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI109377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]