Abstract
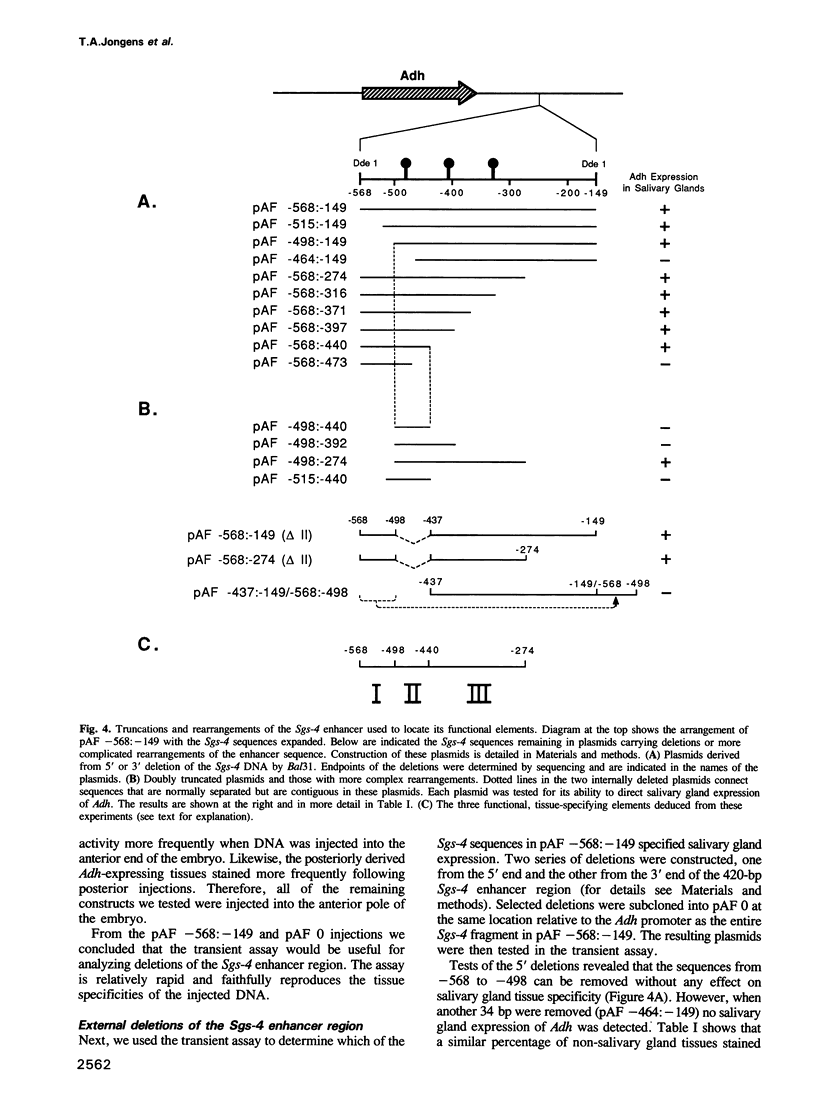
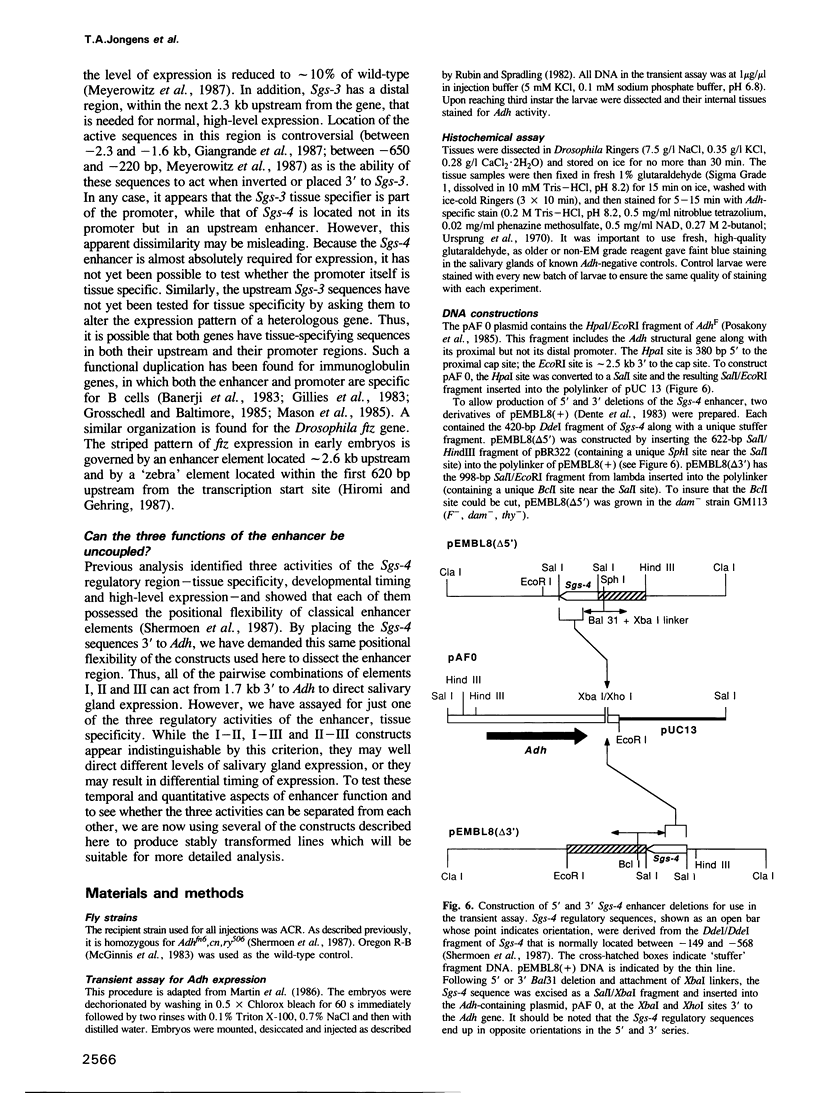
During the last day of larval development, the Sgs-4 glue gene of Drosophila melanogaster is expressed at high levels in a single tissue, the larval salivary glands. As shown by transformation experiments and by DNA sequence analysis of Sgs-4 underproducing strains, an essential regulatory region for Sgs-4 expression lies between 149 and 568 bp upstream from the transcribed part of the gene. This region shows the positional independence of a transcriptional enhancer and directs at least three regulatory activities: tissue specificity, developmental timing and high-level expression. Here we use a transient transformation assay to identify three elements within this enhancer that are involved in tissue specificity. For at least this regulatory activity the enhancer is internally redundant. Any pairwise combination of the three elements is sufficient to direct salivary gland expression, although none of the three can act alone.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckendorf S. K., Kafatos F. C. Differentiation in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of the glue proteins and their developmental appearance. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworniczak B., Seidel R., Pongs O. Puffing activities and binding of ecdysteroid to polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1050–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.2943018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Regulatory elements involved in Drosophila Adh gene expression are conserved in divergent species and separate elements mediate expression in different tissues. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Independent control elements that determine yolk protein gene expression in alternative Drosophila tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shepherd B. M., Wensink P. C. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer from the Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel M. D., Pruitt R. E., Meyerowitz E. M. DNA sequences, gene regulation and modular protein evolution in the Drosophila 68C glue gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):765–789. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giangrande A., Mettling C., Richards G. Sps-3 transcript levels are determined by multiple remote sequence elements. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3079–3084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A., Keinhorst A., Krumm A., Korge G. Regulatory sequences of the Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila melanogaster analysed by P element-mediated transformation. Chromosoma. 1987;96(1):8–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00285877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4550–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladiges W. C., Raff R. F., Brown S., Deeg H. J., Storb R. The canine major histocompatibility complex. Supertypic specificities defined by the primed lymphocyte test (PLT). Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00345410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Martin A., Osmani A., Sofer W. A transient expression assay for tissue-specific gene expression of alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1986 Oct;117(2):574–580. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Shermoen A. W., Heemskerk J., Beckendorf S. K. DNA sequence changes in an upstream DNase I-hypersensitive region are correlated with reduced gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1063–1067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNabb S. L., Beckendorf S. K. Cis-acting sequences which regulate expression of the Sgs-4 glue protein gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2331–2340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestril R., Schiller P., Amin J., Klapper H., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Heat shock and ecdysterone activation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp23 gene; a sequence element implied in developmental regulation. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1667–1673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. An expandable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variants lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Spradling A. C. Drosophila chorion gene amplification requires an upstream region regulating s18 transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4624–4633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for the regulation of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:515–520. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan K. V., Crosby M. A., Mathers P. H., Meyerowitz E. M. Sequences sufficient for correct regulation of Sgs-3 lie close to or within the gene. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3321–3326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. An ecdysone response element in the Drosophila hsp27 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3729–3734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. Gene regulation: why should DNA loop? Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):369–370. doi: 10.1038/327369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd B., Garabedian M. J., Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Developmental control of Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene by cis-acting DNA elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:521–526. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A complex of interacting DNAase I-hypersensitive sites near the Drosophila glue protein gene, Sgs4. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Jongens J., Barnett S. W., Flynn K., Beckendorf S. K. Developmental regulation by an enhancer from the Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore E. M., Guild G. M. Larval salivary gland secretion proteins in Drosophila structural analysis of the Sgs-5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Regulated expression of genes injected into early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):165–173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]