Abstract
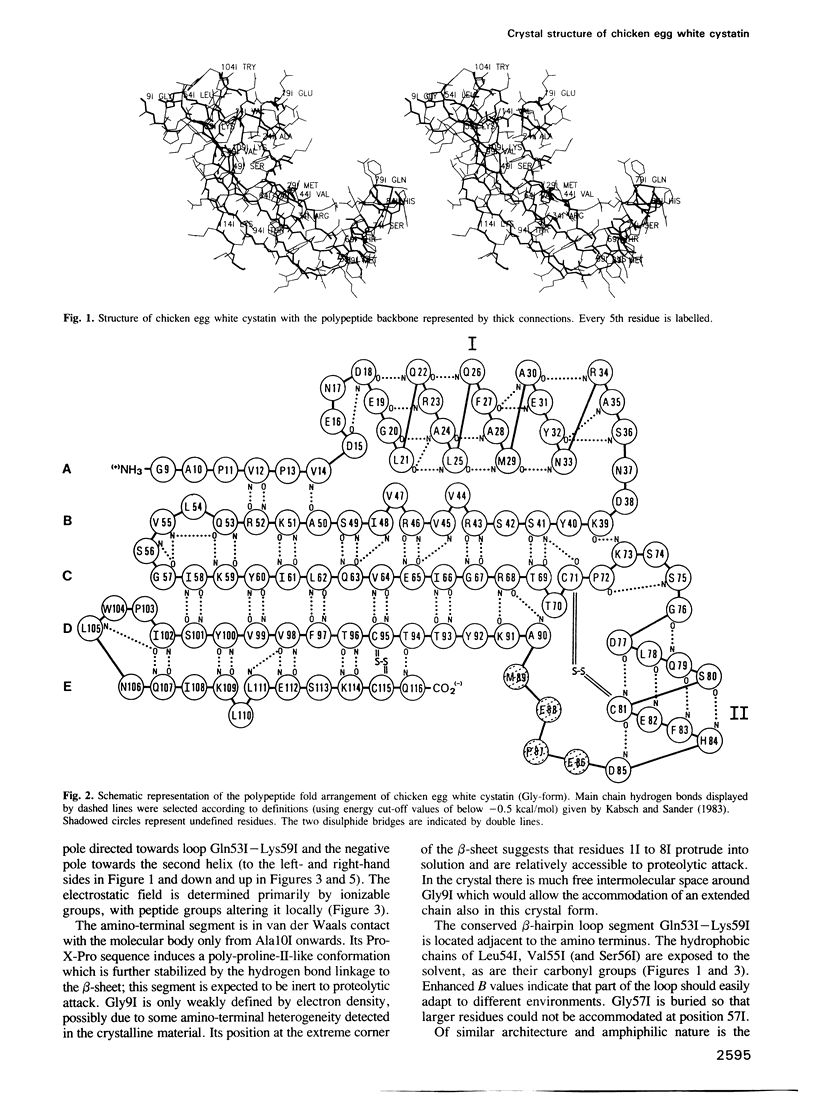
The crystal structure of chicken egg white cystatin has been solved by X-ray diffraction methods using the multiple isomorphous replacement technique. Its structure has been refined to a crystallographic R value of 0.19 using X-ray data between 6 and 2.0A. The molecule consists mainly of a straight five-turn alpha-helix, a five-stranded antiparallel beta-pleated sheet which is twisted and wrapped around the alpha-helix and an appending segment of partially alpha-helical geometry. The 'highly conserved' region from Gln53I to Gly57I implicated with binding to cysteine proteinases folds into a tight beta-hairpin loop which on opposite sides is flanked by the amino-terminal segment and by a second hairpin loop made up of the similarly conserved segment Pro103I - Trp104I. These loops and the amino-terminal Gly9I - Ala10I form a wedge-shaped 'edge' which is quite complementary to the 'active site cleft' of papain. Docking experiments suggest a unique model for the interaction of cystatin and papain: according to it both hairpin loops of cystatin make major binding interactions with the highly conserved residues Gly23, Gln19, Trp177 and Ala136 of papain in the neighbourhood of the reactive site Cys25; the amino-terminal segment Gly9I - Ala10I of bound cystatin is directed towards the substrate subsite S2, but in an inappropriate conformation and too far away to be attacked by the reactive site Cys25. As a consequence, the mechanism of the interaction between cysteine proteinases and their cystatin-like inhibitors seems to be fundamentally different from the 'standard mechanism' defined for serine proteinases and most of their protein inhibitors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson M., Ritonja A., Brown M. A., Grubb A., Machleidt W., Barrett A. J. Identification of the probable inhibitory reactive sites of the cysteine proteinase inhibitors human cystatin C and chicken cystatin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9688–9694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anastasi A., Brown M. A., Kembhavi A. A., Nicklin M. J., Sayers C. A., Sunter D. C., Barrett A. J. Cystatin, a protein inhibitor of cysteine proteinases. Improved purification from egg white, characterization, and detection in chicken serum. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 1;211(1):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj2110129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Fritz H., Grubb A., Isemura S., Järvinen M., Katunuma N., Machleidt W., Müller-Esterl W., Sasaki M., Turk V. Nomenclature and classification of the proteins homologous with the cysteine-proteinase inhibitor chicken cystatin. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):312–312. doi: 10.1042/bj2360312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Brzin J., Turk V. Crystallization of chicken egg white cystatin, a low molecular weight protein inhibitor of cysteine proteinases, and preliminary X-ray diffraction data. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly M. L. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):709–713. doi: 10.1126/science.6879170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Kalk K. H., Swen H. M. Binding of chloromethyl ketone substrate analogues to crystalline papain. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3731–3738. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum K., Whitaker J. R. Ficin and papain inhibitor from chicken egg white. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90672-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Bode W., Schwager P., Bartels K., Deisenhofer J., Steigemann W. Structure of the complex formed by bovine trypsin and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Crystallographic refinement at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):73–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamphuis I. G., Drenth J., Baker E. N. Thiol proteases. Comparative studies based on the high-resolution structures of papain and actinidin, and on amino acid sequence information for cathepsins B and H, and stem bromelain. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Barrett A. J. Inhibition of cysteine proteinases and dipeptidyl peptidase I by egg-white cystatin. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):245–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2230245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo I., Kurachi K., Takasawa T., Shiokawa H., Sasaki M. Isolation of a human cDNA for alpha 2-thiol proteinase inhibitor and its identity with low molecular weight kininogen. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5691–5697. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritonja A., Popović T., Kotnik M., Machleidt W., Turk V. Amino acid sequences of the human kidney cathepsins H and L. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe C., Anastasi A., Crow H., McDonald J. K., Barrett A. J. Cystatin. Amino acid sequence and possible secondary structure. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 1;217(3):813–817. doi: 10.1042/bj2170813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Towatari T., Katunuma N., Teller D. C., Titani K. Homology of amino acid sequences of rat liver cathepsins B and H with that of papain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teno N., Tsuboi S., Itoh N., Okamoto H., Okada Y. Significant effects of Z-Gln-Val-Val-OME, common sequences of thiol proteinase inhibitors on thiol proteinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):749–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk V., Brzin J., Kotnik M., Lenarcic B., Popović T., Ritonja A., Trstenjak M., Begić-Odobasić L., Machleidt W. Human cysteine proteinases and their protein inhibitors stefins, cystatins and kininogens. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1375–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk V., Brzin J., Lenarcic B., Locnikar P., Popović T., Ritonja A., Babnik J., Bode W., Machleidt W. Structure and function of lysosomal cysteine proteinases and their protein inhibitors. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;180:91–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk V., Brzin J., Longer M., Ritonja A., Eropkin M., Borchart U., Machleidt W. Protein inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. III. Amino-acid sequence of cystatin from chicken egg white. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Nov;364(11):1487–1496. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu N., Kominami E., Takio K., Katunuma N. Three forms of thiol proteinase inhibitor from rat liver formed depending on the oxidation-reduction state of a sulfhydryl group. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13832–13838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]