Androgens stimulate neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells by nontranscriptional action of the endogenous androgen receptor (AR). AR is also required for NGF-induced neuritogenesis of PC12. Androgens or NGF trigger AR association with filamin and TrkA, TrkA interaction with PI3-K δ, and activation of PI3-K δ and Rac.
Abstract
Steroids and growth factors control neuronal development through their receptors under physiological and pathological conditions. We show that PC12 cells harbor endogenous androgen receptor (AR), whose inhibition or silencing strongly interferes with neuritogenesis stimulated by the nonaromatizable synthetic androgen R1881 or NGF. This implies a role for AR not only in androgen signaling, but also in NGF signaling. In turn, a pharmacological TrkA inhibitor interferes with NGF- or androgen-induced neuritogenesis. In addition, androgen or NGF triggers AR association with TrkA, TrkA interaction with PI3-K δ, and downstream activation of PI3-K δ and Rac in PC12 cells. Once associated with AR, filamin A (FlnA) contributes to androgen or NGF neuritogenesis, likely through its interaction with signaling effectors, such as Rac. This study thus identifies a previously unrecognized reciprocal cross-talk between AR and TrkA, which is controlled by β1 integrin. The contribution of FlnA/AR complex and PI3-K δ to neuronal differentiation by androgens and NGF is also novel. This is the first description of AR function in PC12 cells.
INTRODUCTION
Rat adrenal pheochromocytoma PC12 cells (Greene and Tischler, 1976) are widely used to study neuronal differentiation. They undergo differentiation upon nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulation and proliferate in response to epidermal growth factor (EGF; reviewed in Marshall, 1995). NGF, a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors (reviewed in Levi-Montalcini, 1987), initiates a cascade of events that arrests cell growth, induces expression of neuron-specific proteins, and leads to neurite extension (reviewed in Kaplan et al., 1997) through activation of the NGF tyrosine-kinase receptor TrkA (Kaplan et al., 1991).
Sex steroids regulate different functions of the nervous system. They contribute to sex-dependent regulation of the number of neuron and glial cells, as well as of the density of their processes (Spencer et al., 2008; Azcoitia et al., 2011). They also protect neurons against injury (Melcangi et al., 2011). Androgens and androgen receptor (AR) regulate neurite outgrowth and axon regeneration in motoneurons, (Fargo et al., 2008). Motoneurons in spinal cord are lost during the progression of Kennedy's syndrome, an X-linked motor neuropathy with a profile suggestive of hormonal resistance (Kennedy et al., 1968). Expression of abnormally long polyglutamine tract in the AR amino terminus underscores the importance of the receptor in this disease (La Spada et al., 1991). Androgen, in combination with NGF, triggers neuron-like changes in PC12 cells permanently transfected with human androgen receptor (hAR; Lustig et al., 1994). In addition, membrane androgen-binding sites have also been detected in PC12 cells, and hormone occupancy of these sites induces catecholamine release, whereas NGF reduces these sites (Alexaki et al., 2006). Expression of endogenous AR was reported in PC12 cells, although its role was not investigated (Meyer et al., 2009).
In addition to regulating gene expression, AR rapidly activates signaling pathways that transmit hormone signals from membrane inside the cells. This action, alone or integrated with the transcriptional activity of AR and/or other factors, regulates several cell functions, such as proliferation, apoptosis, and migration (reviewed in Migliaccio et al., 2011). Depending on the cellular context and ligand concentration, androgen-elicited nongenomic actions require recruitment by AR of different signaling effectors, including filamin A (FlnA), Src, and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3-K; reviewed in Giovannelli et al., 2012).
FlnA, a member of the Fln family of proteins (Fln A, B, and C), controls cell motility and differentiation through its interaction with actin and a large number of different effectors, some of which regulate cytoskeleton rearrangements (reviewed in Zhou et al., 2010). FlnA and its proteolytic fragments directly interact with AR. Fragments modulate the receptor nuclear import and gene expression as well as androgen dependence of prostate cancer LNCaP cells (reviewed in Savoy and Gosh, 2013). Full-length FlnA regulates migration and cell cycle modulated by androgens in fibroblasts and fibrosarcoma cells (Castoria et al., 2011, 2014).
Integrins control cell adhesion and cytoskeleton modifications in various stages of neuronal differentiation, including outgrowth and branching of axons and dendrites. Integrin β1–containing dimers are relevant to neuronal differentiation because they provide adhesive functions and a versatile platform mediating adhesion contact signaling (Moresco et al., 2005; Marrs et al., 2006). Integrin binding can be triggered through either an initial contact with a suitable substrate (“outside-in”) or alternative pathway activation (“inside-out”), which enhances adhesion by increasing the affinity and avidity of integrin surface receptors. This latter activation involves the intracellular association of integrins with membrane receptors, signaling effectors, and linkers (i.e., filamins, talins, and kindlins; reviewed in Harburger and Calderwood, 2009). In addition, β1 integrin links the AR/FlnA complex with adhesive/migratory pathway in androgen-treated fibroblasts and in fibrosarcoma cells (Castoria et al., 2011, 2014).
In the present article, we show that PC12 cells harbor low levels of classic AR. The receptor is predominantly localized in the extranuclear compartment of the cells and does not activate gene transcription, regardless of androgen stimulation. In the absence of significant proliferation, AR mediates both androgen- and NGF-induced neurite elongation. This process is regulated by cross-talk between AR, FlnA, and TrkA, leading to activation of the downstream PI3-K δ/Rac pathway. In cells stimulated with androgen or NGF, β1-integrin mediates the cross-talk between AR and TrkA, bridging the receptors. Our study provides new clues that might help in better understanding the complexity of AR and TrkA signaling in neuronal cells and, likely, other cell types.
RESULTS
PC12 cells harbor extranuclear AR
We first verified the responsiveness of PC12 cells to mitogenic and differentiative signals. These cells respond to NGF with morphological (Supplemental Figure S1A) and cytoskeletal changes (Supplemental Figure S1B) typical of a neuronal phenotype, whereas EGF does not significantly modify the phenotype (Supplemental Figure S1A) or cytoskeleton (Supplemental Figure S1B) of cells. In contrast, EGF robustly increases DNA synthesis (Supplemental Figure S1C) and transiently stimulates extracellular-regulated kinase (Erk) phosphorylation (Supplemental Figure S1D). As expected, NGF does not induce DNA synthesis (Supplemental Figure S1C) and activates Erk phosphorylation in sustained manner (Supplemental Figure S1D). These different kinetics of Erk activation have been associated with different cell fates (reviewed in Marshall, 1995).
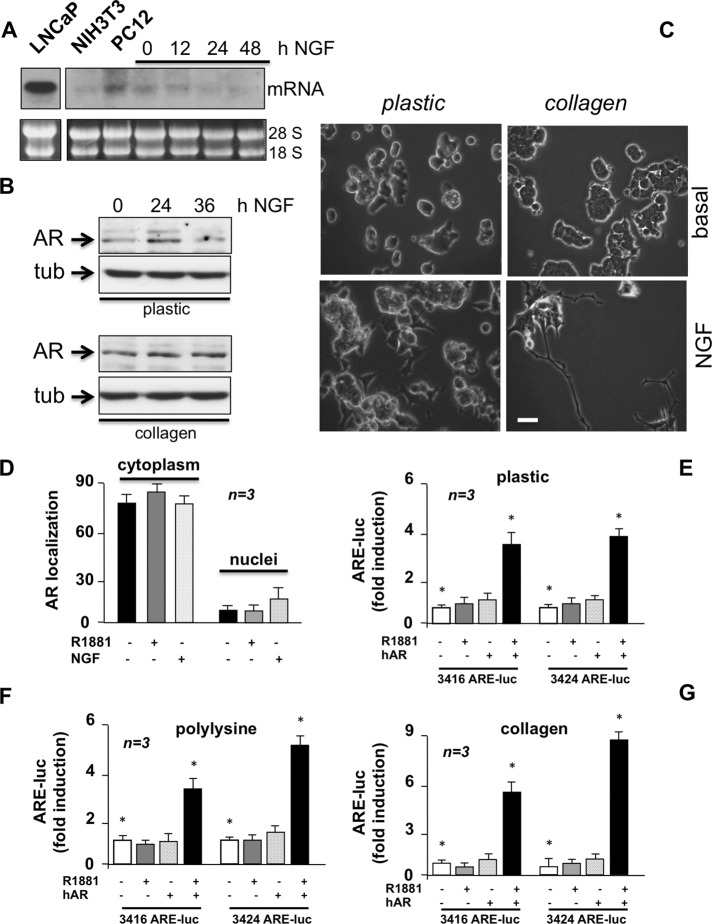
Under basal conditions, we detected by Northern blot a low amount of AR mRNA in plastic-plated PC12 cells, similar to that detected in NIH3T3 cells, which also express low amounts of classic AR (Castoria et al., 2003, 2011, 2014). The Northern blot of AR mRNA in LNCaP cells is shown for comparison (Figure 1A). NGF stimulation of PC12 cells does not increase, or even lowers, AR mRNA (Figure 1A), whereas it weakly and transiently increases AR protein levels in plastic-plated cells (Figure 1B, top). Thus, NGF likely controls AR expression and/or stability at posttranscriptional level. Phosphorylation, sumoylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination are reversible mechanisms affecting AR stability and localization or interactions of the receptor with other proteins (reviewed in Gioeli and Paschal, 2012). In addition to a major band migrating at 110 kDa, we detected a weaker AR band migrating slowly (at ∼112 kDa; Figure 1B, top) in plastic-plated cells. This might be due to posttranscriptional AR modifications induced by NGF. In contrast, in collagen-plated PC12 cells challenged with NGF, we detected only a single and stronger AR immunoreactive band migrating at 110 kDa (Figure 1B, bottom). Thus, signals from extracellular matrix (ECM) might overcome the effect of NGF in sustaining the AR stability. NGF-stimulated neurite elongation is stronger in collagen-plated PC12 cells than in the plastic-plated cells (Figure 1C), suggesting that NGF-dependent neuritogenesis requires stable and not transient AR expression. Findings in collagen-plated PC12 cells corroborate each other in suggesting a role for AR in PC12 cell differentiation.
FIGURE 1:
PC12 cells harbor extranuclear classic AR. (A) Growing LNCaP, NIH3T3, and PC12 cells on plastic were used. PC12 cells were made quiescent for 12 h and then stimulated for the indicated times with NGF (100 ng/ml). mRNA was extracted and used for Northern blot of AR mRNA (top). The loading mRNA control (28S and 18S) was analyzed (bottom). (B) Plastic- or collagen-plated PC12 cells were made quiescent, then left untreated or treated for the indicated times with NGF (100 ng/ml). AR expression was detected by Western blot of lysate proteins. The filters were reprobed with anti-tubulin antibody as a loading control. (C) Plastic- or collagen-plated PC12 cells were made quiescent and then challenged for 24 h with NGF (100 ng/ml). Contrast phase images are representative of three different experiments, each performed in duplicate. Bar, 5 μM. (D) PC12 cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were made quiescent and then left untreated or treated for 1 h with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml). Cells were stained by IF for AR. Total nuclei were stained with Hoechst, and AR intracellular localization was analyzed. Data are represented as percentage of cells showing exclusively nuclear or cytoplasm AR staining. Data from at least 500 cells from each independent experiment were scored and are graphically presented. Means and SEM are shown; n represents the number of experiments. Growing PC12 cells plated on plastic (E), polylysine (F), or collagen (G) were transfected with either 3416 or 3424 ARE-Luc constructs with or without hAR-expressing plasmid. Cells were made quiescent and left unstimulated or stimulated for 18 h with 10 nM R1881. Luciferase activity was assayed, normalized using β-galactosidase as an internal control, and expressed as fold induction. Data from several independent experiments were analyzed. Means and SEM are shown; n represents the number of experiments. The statistical significance of results was also evaluated by paired t test in all the experiments (*p < 0.05). The difference in ARE-Luc induction between cells challenged with 10 nM R1881 and unstimulated cells was significant (*p < 0.05) only in cells cotransfected with hAR and 3416 ARE-Luc or 3424 ARE-Luc.
In the search for other functional properties of endogenous AR, we observed by both immunofluorescence (Figure 1D and Supplemental Figure S2A) and confocal microscopy (Supplemental Figure S2B) that irrespective of the primary antibody used (anti–C-terminal or anti–N-terminal AR), AR is predominantly cytoplasmic in PC12 cells, with a faint, background nuclear fluorescence. Androgen or NGF stimulation does not substantially modify such localization (Figure 1D and Supplemental Figure S2, A and B). AR remained predominantly cytoplasmic even upon 8 h of androgen stimulation, when the cells began to differentiate (Supplemental Figure S2B). In contrast, typical images of the androgen-induced AR nuclear translocation were captured by confocal microscopy from prostate cancer–derived LNCaP cells challenged with R1881. They are shown for comparison in Supplemental Figure S2C.
Consistent with data on AR localization, the receptor is devoid of transcriptional activity, as shown by gene reporter assay in PC12 cells plated on plastic (Figure 1E), polylysine (Figure 1F), or collagen (Figure 1G). In these conditions, overexpression of hAR confers androgen-dependent transcriptional responsiveness to PC12 cells (Figure 1, E–G). These results indicate that the failure of endogenous AR to mediate androgen-triggered gene transcription is not due to the intracellular milieu. Instead, the low level of endogenous receptor might hamper receptor dimerization (Giovannelli et al., 2012). On increase in the amount of transfected hAR (from 0 to 1000 ng), AR-negative Cos-7 cells became fully responsive to R1881 with gene transcription (Supplemental Figure S3A). Thus, when low AR amounts are expressed, as occurs in PC12 cells (present results) or other cell types (Castoria et al., 2003, 2011, 2014), the receptor level is not enough to stimulate gene transcription, although it is able to activate extranuclear signaling effectors (Castoria et al., 2003). A similar conclusion was reached with progesterone receptor (PR) in rat uterine stromal cells (Vallejo et al., 2005).
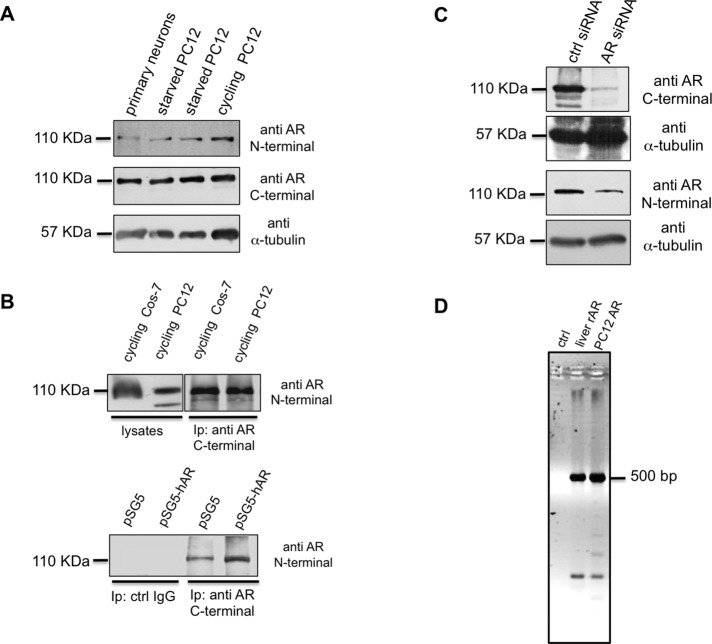
The possibility that PC12 cells harbor a precursor of AR or other nonclassic AR forms that fail to dimerize is excluded by the data in Figure 2A. They show that the anti-AR antibodies (N-20 or C-19, directed at NH2- and COOH-terminal sequences, respectively) react with a major band migrating with a molecular mass of ∼110 kDa in lysates from PC12 cells or mouse primary hippocampal neurons. The same migration in SDS–PAGE has been detected for mouse (Zhou et al., 2002) and rat (Hatanaka et al., 2014) AR. Further, the endogenous rat AR (rAR) immune-precipitated from PC12 cell lysates migrates like the human AR (hAR) immune-precipitated from lysates of Cos-7 cells ectopically expressing hAR (Figure 2B, top). Again, the endogenous rAR from PC12 cell lysates coimmunoprecipitates and comigrates with hAR overexpressed in the same cells (Figure 2B, bottom). Finally, the finding that small interfering RNA (siRNA) AR significantly reduces the 110-kDa receptor amounts, as shown by Western blot of PC12 lysate proteins with both N-20 and C-19 antibodies (Figure 2C), further indicates that PC12 harbor a classic AR.
FIGURE 2:
Characterization of endogenous AR in PC12 cells. (A) Primary neurons and starved and cycling PC12 cell lysates were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and resolved on SDS–PAGE using 10% acrylamide. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose filter and probed with the antibodies against N- or C-terminal domains of AR. The filter was reprobed using anti–α-tubulin antibody as a loading control. (B) Top, lysate proteins from cycling Cos-7 ectopically expressing hAR or PC12 cells were used for IP experiments using an antibody raised against the AR C-terminal domain. Bottom, cycling PC12 cells were transfected with pSG5 or pSG5-hAR plasmid as described in Materials and Methods. Lysate proteins (2 mg/ml) were used for IP experiments using an antibody raised against the AR C-terminal domain. Proteins from cell lysates and immune complexes were resolved on SDS–PAGE using 8% acrylamide, transferred to nitrocellulose filter, and probed with the antibody against the N-terminal domain of AR. (C) Cycling PC12 cells were transfected with control (ctrl) or AR siRNA, as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were made quiescent, and lysate proteins were resolved on SDS–PAGE, using 10% acrylamide. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose filter and probed with the antibodies against C- or N-terminal domains of AR. The filters were reprobed, using anti–α-tubulin antibody, as a loading control. (D) PCR products using the primers set indicated in Materials and Methods were amplified from rat liver genomic DNA (liver rAR), PC12 genomic DNA (PC12 AR), or water (ctrl) and separated by electrophoresis in 2% agarose in TBE. A PCR product of ∼500 base pairs corresponding to the size expected from a wild-type sequence (see also data in Supplemental Figure S3) was amplified from both genomic DNA samples.
To address this issue conclusively, however, we analyzed the genomic DNA from PC12 cells, using a set of oligos flanking the CAG repeats in rat AR (rAR; Supplemental Figure S3B). No difference in the size of the AR exon 1 PCR product was observed between the genomic DNA from control rat liver or PC12 cells (Figure 2D). In addition, the size of the product corresponds to that predicted by the wild-type rAR exon 1 sequence. Direct sequencing of the PCR products confirms that rAR exon 1 contains a normal number of repeats (i.e., n = 22 and 21 in wild-type liver and PC12 cells samples, respectively).
Taken together, our biochemical and genomic approaches point to the expression of a classic rAR in PC12 cells.
Androgen or NGF regulates neurite outgrowth through AR/TrkA cross-talk
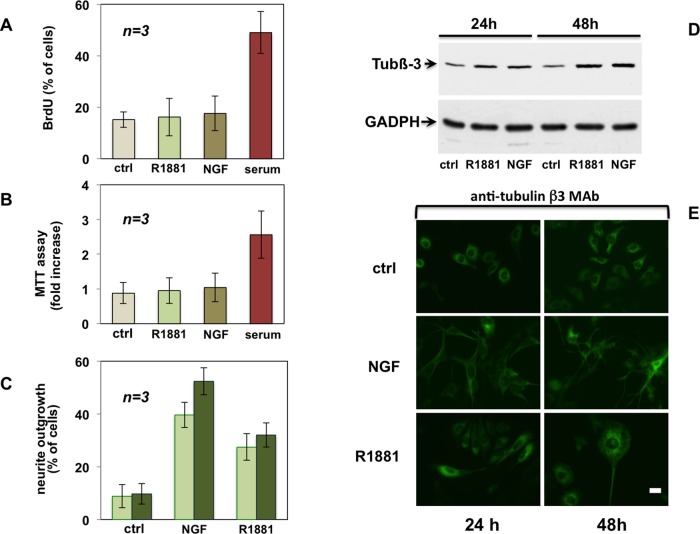
The foregoing findings point to a differentiative role for classic AR in PC12 cells. In addition, a negligible proliferative response was detected by both bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in androgen-stimulated PC12 cells. Such a response is comparable to that of NGF (Figure 3, A and B).
FIGURE 3:
Androgen does not stimulate proliferation but triggers differentiation of PC12 cells. Quiescent PC12 cells were used. (A) Cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were left unstimulated or stimulated for 24 h with R1881 (10 nM), NGF (100 ng/ml), or serum (at 20%). Cells were pulsed for 4 h with 100 μM BrdU (Sigma-Aldrich). BrdU incorporation was analyzed by IF and expressed as percentage of total cells. (B) Plastic-plated cells were left unstimulated or stimulated for 24 h with R1881 (10 nM), NGF (100 ng/ml), or serum (at 20%). After 24 h, MTT assay was performed. (C) Cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were left unstimulated or stimulated for 24 h (light green) or 48 h (dark green) with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml). Neurite outgrowth was analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and expressed as percentage of total cells. In A–C, data derive from several independent experiments. Means and SEM are shown. (D) Plastic-plated cells were left untreated (ctrl) or challenged for the indicated times with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml). Expression of tubulin β-III (tub β-III) was analyzed by Western blot of lysate proteins. Filters were reprobed with anti-GADPH as a loading control. (E) Cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were left untreated or treated for the indicated times with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml). Cells were analyzed by IF for tubulin β-III. Bar, 10 μM.
By analyzing neurite outgrowth, a classic differentiative process regulated by NGF in sympathetic neurons (Berkemeier et al., 1991), we compared the effect of androgen and NGF in PC12 cells. Figure 3C shows that the nonaromatizable R1881 induces stimulation of neurite outgrowth after 24 and 48 h, and similar results were observed using dihydrotestosterone (DHT; Supplemental Figure S4S). Stimulation of neurite outgrowth by NGF is consistently stronger (about twofold) than that observed in the presence of R1881 (Figure 3C) or DHT (Supplemental Figure S4S). Finally, we evaluated the effect of R1881 and NGF on a neuronal cytoskeleton antigen, the class III β-tubulin isotype (tub β-III). The expression level of this antigen is increased by R1881 or NGF, as assessed by Western blot in PC12 cells (Figure 3D). Its presence in differentiated cells was also analyzed by immunofluorescence (IF) analysis (Figure 3E). Thus androgens, R1881 or DHT, exert this differentiative effect in PC12 cells, whereas they do not affect DNA synthesis (Figure 3A) or in vitro cell growth (Figure 3B).
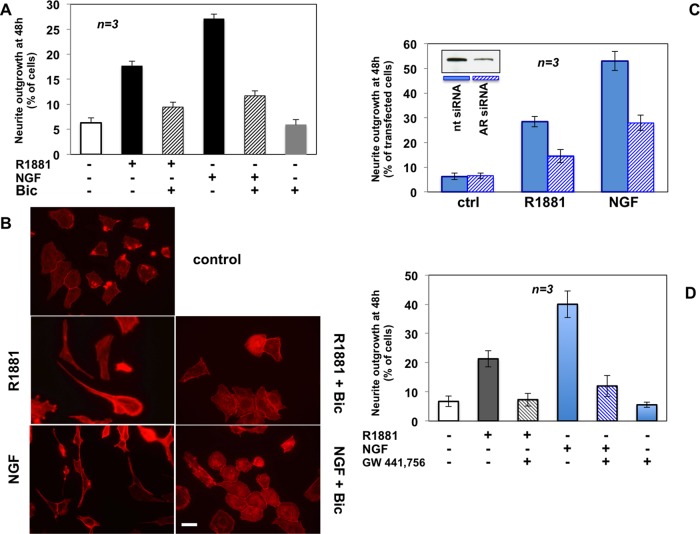
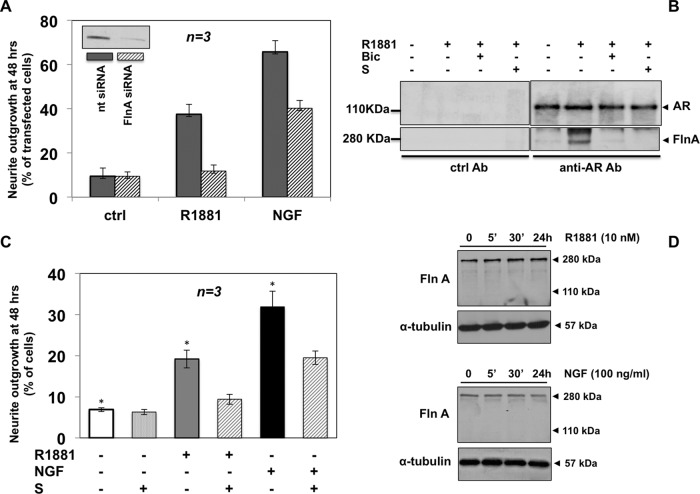
In addition to confirming the differentiative role of androgens, the findings in Figure 4A reveal a further and unexpected function for AR in neuritogenesis evoked by NGF. Using contrast phase microscopy, we found that 48 h of R1881 stimulation significantly increases the number of cells exhibiting neurite outgrowth, which is reduced to 27% by the androgen antagonist bicalutamide. Thus extranuclear AR regulates differentiative androgen action. Remarkably, bicalutamide also reduces the number of differentiated cells upon NGF stimulation, to 26% (Figure 4A), suggesting that NGF signaling engages AR to induce neuritogenesis in PC12 cells. IF images of cytoskeletal actin in Figure 4B confirm the results obtained by quantitative analysis in contrast phase microscopy (Figure 4A). Androgen and NGF induce significant changes in cell shape and neurite elongation. Bicalutamide restores the basal phenotype in both androgen- and NGF-treated PC12 cells (Figure 4B).
FIGURE 4:
Neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells stimulated by R1881 or NGF: functional cross-talk between AR and TrkA. PC12 cells were used. (A, B) Polylysine-plated cells were made quiescent and then left untreated or treated for 48 h with 10 nM R1881 or 100 ng/ml NGF in the absence or presence of 10 μM bicalutamide. (A) Neurite outgrowth expressed as percentage of total cells. (B) Actin stained using Texas red–phalloidin and analyzed by IF. Images are representative of two independent experiments. Bar, 10 μM. (C) Growing cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were transfected with AR or nt siRNA. Purified pEGFP (Amaxa) plasmid was included to help identification of transfected cells. Cells were made quiescent and then left unchallenged or challenged with R1881 or NGF. GFP-expressing cells were visualized by fluorescence microscopy and their neurite outgrowth analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and expressed as percentage of transfected cells. Several independent coverslips were analyzed, and data from at least 200 scored cells for each coverslip were collected and are graphically shown. Inset in C shows AR protein levels detected by Western blot of lysate proteins from PC12 cells transfected with nt or AR siRNA. About 30% of AR protein was still detected upon AR siRNA, as evaluated by ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). (D) Quiescent cells on polylysine were left untreated or treated for 48 h with R1881 or NGF in the absence or presence of the TrkA inhibitor GW441776 (1 μM). Neurite outgrowth was evaluated and expressed as percentage of total cells. In A, C, and D, means and SEM are shown.
Previous findings showed that dehydroepiandrosterone exerts its survival effect through direct binding with TrkA (Lazaridis et al., 2011; Gravanis et al., 2012). We did not detect the binding of radiolabeled R1881 with human TrkA in ligand-binding displacement assay (Supplemental Figure S5). Thus regulation of neuritogenesis by TrkA in androgen-stimulated PC12 cells does not seem to be caused by the direct binding of R1881 to TrkA.
However, to define conclusively the role of AR in mediating neuritogenesis triggered by androgen or NGF, we silenced AR in PC12 cells. We then evaluated neurite outgrowth induced by 48 h of treatment in cells transfected with AR siRNA and compared it with that observed in cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA (nt siRNA). The Western blot analysis in Figure 4C (inset) shows that residual AR expression after silencing was ∼30%, as calculated by ImageJ software (legend to Figure 4). Consistently, the number of PC12 cells exhibiting neurite outgrowth after AR silencing is reduced to ∼30% in cells differentiated by R1881 or NGF (Figure 4C).
Results in Figure 4, A–C, indicate a similar and strong dependence on AR of neuritogenesis stimulated by R1881 or NGF. Use of a specific TrkA inhibitor, GW441756 (Jung, 2008), not only prevents neuritogenesis in cells stimulated with NGF for 48 h but also impairs neurite outgrowth in cells stimulated with androgen, indicating that TrkA activity is also required for the R1881-induced differentiative action (Figure 4D). Again, the effects of bicalutamide and GW441756 are not additive, since the treatment of PC12 cells with both inhibitors (bicalutamide plus GW441756) does not significantly increase the effect observed by using either inhibitor alone (Supplemental Figure S6A).
These data, together with the previous observation that AR is needed for NGF action, point to AR/TrkA cross-talk bidirectionally regulated by NGF and R1881.
FlnA/AR complex controls neurite outgrowth triggered by androgen or NGF
FlnA controls brain development and directly interacts with AR (Zhou et al., 2010, and references therein). We therefore analyzed its role in neuritogenesis induced by androgen or NGF in PC12 cells. We first performed siRNA FlnA experiments in PC12 cells. On 48 h of R1881 stimulation, FlnA silencing to ∼20% of FlnA expressed in cells transfected with nt siRNA (inset in Figure 5A and legend to Figure 5) reduces the number of PC12 differentiated cells to 18% as compared with control cells transfected with nt siRNA (Figure 5A). The NGF-induced neuritogenic effect was reduced to 54% on FlnA silencing. Thus, in addition to androgens, NGF also uses FlnA to transmit its differentiative signal. Figure 5B shows that R1881 induces association of AR with FlnA, as revealed by FlnA coimmunoprecipitation by anti-AR antibodies in PC12 cells. Bicalutamide abolishes this effect.
FIGURE 5:
Role of FlnA and its association with AR in neurite outgrowth induced by R1881 or NGF. PC12 cells were used. (A) Growing cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were transfected with FlnA siRNA or nt siRNA. Purified pEGFP plasmid (Amaxa) was included to help identification of transfected cells. Cells were made quiescent and then left unchallenged or challenged for 48 h with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml). In GFP-expressing cells, neurite outgrowth was analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and expressed as percentage of transfected cells. Several coverslips were analyzed, and data from at least 150 scored cells for each coverslip were collected and are graphically shown. Inset in A shows FlnA protein levels detected by Western blot of lysate proteins from PC12 cells transfected with nt or FlnA siRNA. After silencing, residual FlnA expression was ∼20%, as calculated by ImageJ software. (B) Quiescent cells were left untreated or treated for 5 min with the indicated compounds: R1881 at 10 nM, bicalutamide (Bic) at 10 μM, and S peptide at 1 nM. Lysate proteins (2 mg/ml protein) were immunoprecipitated with nonspecific (ctrl Ab) or anti-AR antibodies (C-19 Ab). Proteins in immune complexes were analyzed using antibodies against the indicated proteins. The C-19 Ab was used to detect AR. (C) Quiescent cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were left untreated or treated for 48 h with 10 nM R1881 or 100 ng/ml NGF in the absence or presence of S peptide (1 nM). Neurite outgrowth in plastic-plated PC12 cells was evaluated and is expressed as percentage of total cells. In A and C, means and SEM are shown. In C, the statistical significance of results was also evaluated by paired t test. The difference in neurite outgrowth was significant (*p < 0.05) only between cells challenged with R1881 or NGF and unstimulated cells. (D) Quiescent cells were left untreated or treated for the indicated times with 10 nM R1881 (top) or 100 ng/ml NGF (bottom). Lysate proteins were analyzed using antibodies against the indicated proteins.
The hAR-deleted mutant (hAR Δ622–670) does not associate with FlnA in response to androgens (Loy et al., 2003; Castoria et al., 2011). From the hAR 628–646 sequence, an AC-stapled [A628S5, K632S5] amide peptide was synthesized in which Ala-628 and Lys-632 residues were each replaced with an olefinic amino acid that allows them to be cross-linked (Castoria et al., 2014; Supplemental Figure S6B). The stapled peptide is thus “locked” into its bioactive α-helical fold through the insertion of hydrocarbon staples. This modification increases affinity for targets as well as cell permeability and decreases degradation of the stapled peptide (Verdine and Hilinski, 2012). We evaluated the action of this peptide on androgen-induced association between AR and FlnA in PC12 cells. Figure 5B shows that 1 nM stapled peptide (S), like 10 μM bicalutamide, abolishes AR/FlnA association induced by androgen. At this concentration, the peptide reduces neuritogenesis in PC12 cells treated with R1881 to 20%. In cells stimulated with NGF, the peptide decreases the number of cells exhibiting neurite outgrowth to 50% (Figure 5C).
In sum, silencing of FlnA or use of the peptide similarly inhibits neurite outgrowth triggered by androgens or NGF in PC12 cells. Because the inhibitory effect is more evident in cells challenged with R1881 than with NGF-treated cells, FlnA and the AR/FlnA complex seem to play a more important role in androgen- than in NGF-induced neuritogenesis. In contrast, AR is similarly and strongly required for both R1881- and NGF-mediated differentiative signaling (Figure 4).
FlnA proteolysis has been reported in various cell types and under different experimental conditions (Ozanne et al., 2000; Loy et al., 2003; Mooso et al., 2012). The possibility that AR interacts with a proteolytic fragment of FlnA in PC12 cells is excluded by the finding that neither R1881 nor NGF induces FlnA proteolysis (Figure 5D). In contrast, FlnA undergoes proteolysis in prostate cancer–derived LNCaP cells challenged with R1881. A 90-kDa fragment is detectable upon 30 min of hormonal stimulation in these cells, and FlnA degradation persists until 24 h of R1881 stimulation (Supplemental Figure S7A). Consistent with previous findings (Ozanne et al., 2000; Mooso et al., 2012), FlnA proteolysis induced by 30 min of R1881 treatment correlates with the appearance of FlnA nuclear spots, as shown by confocal microscopy in LNCaP cells (Supplemental Figure S7, B and C).
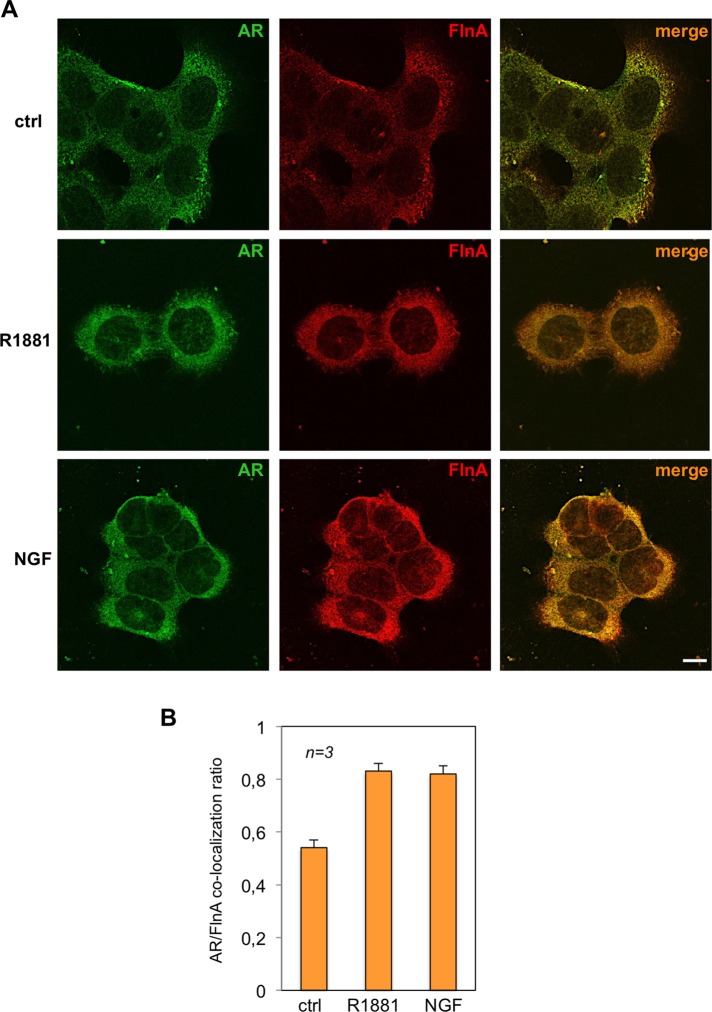
However, we further investigated the intracellular localization of the AR/FlnA complex by confocal microscopy in PC12 cells. Treatment of cells with R1881 or NGF increases within 30 min the AR/FlnA colocalization at extranuclear compartment (Figure 6A). Quantitative analysis from different experiments is presented in Figure 6B, which shows that 30 min of R1881 or NGF treatment of PC12 cells increases by about twofold the colocalization ratio between the two molecules.
FIGURE 6:
R1881 or NGF induces extranuclear AR/FlnA complex in PC12 cells. Quiescent PC12 cells were left untreated (ctrl) or treated for 5 min with 10 nM R1881 (R1881) or 100 ng/ml NGF (NGF). (A) Cells on coverslips were visualized by IF for AR and Fln A. Images captured by confocal microscope show the staining of AR (green) and Fln A (red). Right, merged images. Confocal microscopy analysis is representative of three independent experiments. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification and statistical analysis of these experiments. AR/FlnA colocalization ratio was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Data from several independent experiments were analyzed. Means and SEM are shown; n represents the number of experiments. The statistical significance of results was also evaluated by paired t test. The difference in AR/FlnA colocalization ratio between unstimulated (ctrl) and R1881-stimulated cells was significant (p < 0.001). Also significant (p < 0.001) was the difference in AR/FlnA colocalization ratio between control (ctrl) and NGF-stimulated cells.
In conclusion, this set of experiments shows that complexation of AR with the full-length FlnA in the extranuclear compartment of PC12 cells controls the androgen- or NGF-induced neuritogenesis. Interference in AR/FlnA complex assembly by FlnA siRNA or small stapled peptide inhibits this response.
Analysis of differentiative signaling activated by the TrkA/AR complex
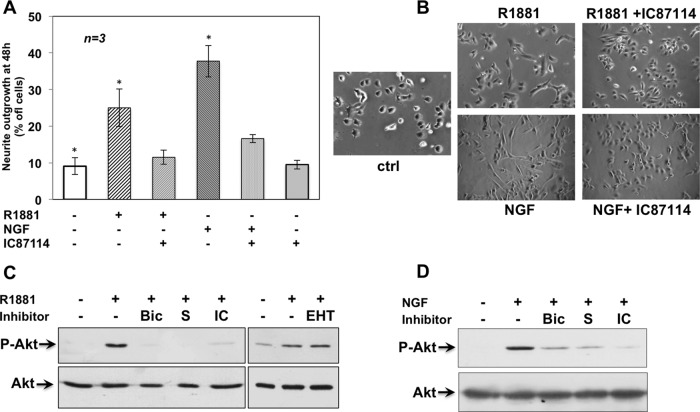
PI3-K is required for NGF-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells (Kimura et al., 1994), and the δ isoform of PI3-K (PI3-K δ) controls axonal growth and regeneration of sensory neurons (Eickholt et al., 2007). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis of Ammon's horn from adult mouse hippocampus shows that PI3-K δ is expressed with TrkA, AR, and FlnA, the three proteins regulating neuritogenesis in PC12 cells (Supplemental Figure S8). We then followed PC12 neurite outgrowth induced by 24-h stimulation with R1881 or NGF in the absence or presence of a p110 δ–selective small-molecule inhibitor, IC87114 (Sadhu et al., 2003). The inhibitor reduces androgen- or NGF-dependent neuritogenesis to 16 and 27% of total cells, respectively (Figure 7A). Contrast phase microscopy images (Figure 7B) confirm the inhibitory effect of IC87114 in neuritogenesis induced by R1881 or NGF.
FIGURE 7:
PI3-K δ regulates R1881- and NGF-induced neurite outgrowth. Quiescent PC12 cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were used. (A, B) Cells were left untreated or treated for 48 h with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of the PI3-K δ inhibitor IC87114 (5 μM). Neurite outgrowth was analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and expressed as percentage of total cells. Means and SEM are shown. The statistical significance of results was also evaluated by paired t test. The difference in neurite outgrowth was significant (*p < 0.05) only between cells challenged with R1881 or NGF and unstimulated cells. (B) Images from one experiment in A. Plastic-plated quiescent PC12 cells were used. Cells were left untreated or treated for 5 min with 10 nM R1881 (C) or 100 ng/ml NGF (D) in the absence or presence of the indicated compounds. Bicalutamide (Bic) was used at 10 μM; S peptide was used at 1 nM; IC87114 (IC) and EHT1864 were both used at 5 μM. Akt activation (P-Akt) was analyzed in lysate proteins using the anti–P-Ser-473 Akt Ab. Filters were reprobed with anti-Akt (Akt) Ab.
We then analyzed Ser-473–Akt phosphorylation as a readout for PI3-K activation. After a preliminary time-course activation assay, we observed that R1881 triggers transient Akt activation at 30 min. Stimulation by NGF is already detectable after 5 min. Bicalutamide, the S peptide, and the p110 δ inhibitor IC87114 inhibit Akt activation (Figure 7, C and D). Thus, in androgen or NGF signaling, PI3-K δ activation depends on AR and AR/FlnA association.
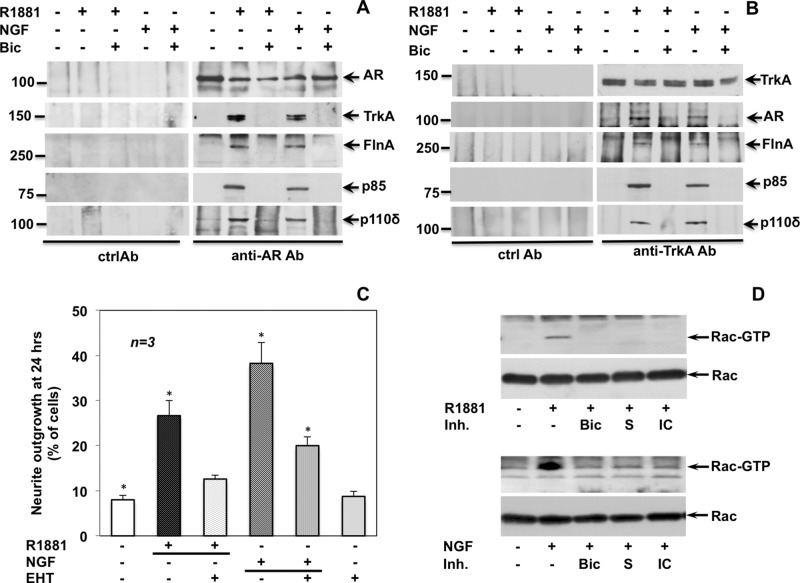
Coimmunoprecipitation experiments with anti-AR or anti-TrkA antibodies (Figure 8, A and B) show that the functional associations leading to neurite outgrowth follow rapid, physical association between AR, TrkA, FlnA, the regulatory subunit p85, and the catalytic subunit p110 δ. These associations are triggered by R1881 or NGF and inhibited by bicalutamide. In addition to AR, a lower immune-reactive band is observed in immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments presented in Figure 8, A and B. This likely represents a proteolytic fragment produced during the IP process.
FIGURE 8:
R1881 and NGF trigger association of a multiprotein complex and stimulate Rac-dependent neurite outgrowth. Quiescent PC12 cells were used. (A, B) Plastic-plated cells were left untreated or treated for 5 min with the R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of bicalutamide (Bic at 10 μM). Lysate proteins were immune-precipitated with C-19 anti-AR (A) or anti-Trk (B) antibodies or nonspecific immunoglobulin G (Ctrl Ab) as a control. Proteins in immune complexes were detected by Western blot, using the antibodies against the indicated proteins. The C-19 anti AR Ab was used to detect AR. (C) Cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were made quiescent and left untreated or treated for 24 h with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of EHT (5 μM). Neurite outgrowth was analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and is expressed as percentage of total cells. Means and SEM are shown. Asterisks indicate significantly different values as compared with control (p < 0.05). (D) Plastic-plated cells were left untreated or treated for 5 min with 10 nM R1881 (top) or 100 ng/ml NGF (bottom) in the absence or presence of the indicated compounds. Bicalutamide (Bic) was used at 10 μM, S peptide at 1 nM, and IC87114 (IC) at 5 μM. Rac activation was analyzed by pull-down assay. Active (Rac-GTP) or total Rac (Rac) was detected by Western blot.
Rho-family GTPases (Rho, Rac, and Cdc42) control neuronal morphogenesis and axon growth (reviewed in Luo, 2000). The Rac inhibitor EHT1864 (Shutes et al., 2007) reduces neuritogenesis induced by 24 h of R1881 or NGF stimulation (Figure 8C), in good agreement with the finding that R1881 or NGF treatment rapidly (5 min) increases the amount of Rac-GTP in PC12 cells. Bicalutamide, the S peptide, and IC87114 prevent this effect (Figure 8D). Findings on Akt (Figure 7, C and D) and Rac (Figure 8D) regulation are similar, indicating that the two effectors are controlled upstream by both AR/FlnA complex and PI3-K δ. Because EHT1864 does not decrease R1881-triggered Akt phosphorylation (Figure 7C, top, right) and PI3-K δ is required for Rac activation (Figure 8D), it is unlikely that in PC12 cells androgens activate the Rac/PI3-K/Akt pathway previously described in macrophages and in lung epithelial cells (Chen, 2009; Lin et al., 2011).
These findings show that R1881 and NGF share the PI3-K δ/Rac pathway to induce neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.
Integrin β1 controls the recruitment of TrkA to AR and neurite outgrowth triggered by androgen or NGF
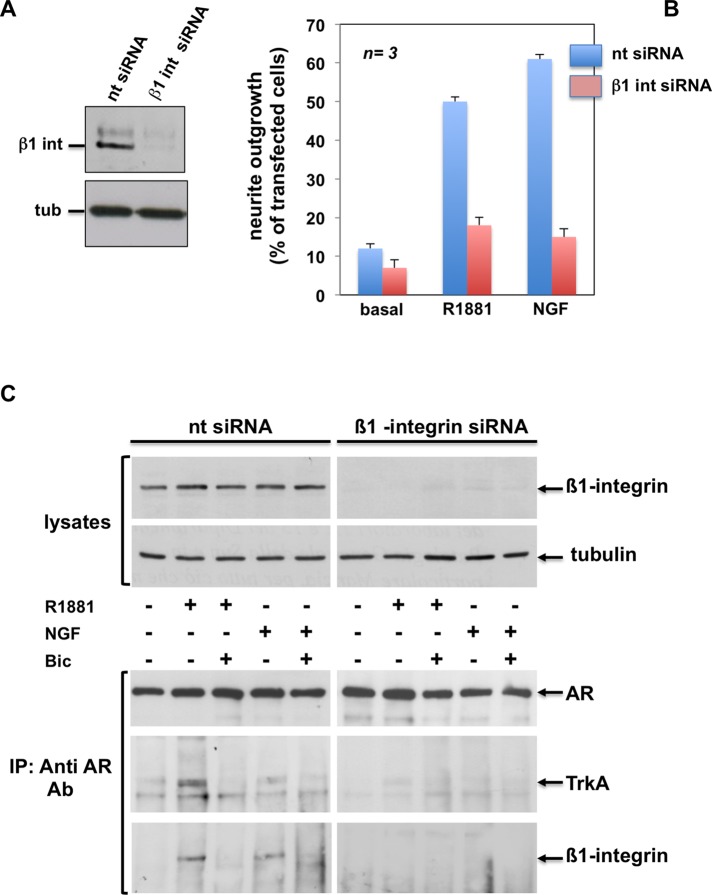
Results on AR/TrkA cross-talk in PC12 cells led us to focus our research on the mechanism responsible for AR/TrkA cross-talk during neuritogenesis. Integrin β1 links the AR/FlnA complex with adhesion machinery in androgen-treated fibroblasts, as well as in fibrosarcoma cells (Castoria et al., 2011). Therefore we hypothesized a role for β1 integrin in the mechanism of TrkA/AR cross-talk in PC12 cells. In a first attempt, we depleted PC12 cells of β1 integrin by the siRNA approach (Figure 9A). Thereafter we followed by contrast phase microscopy the neurite outgrowth stimulated by R1881 or NGF in PC12 cells transfected with β1 integrin or nontargeting siRNA. Irrespective of the ligand stimulation (R1881 or NGF), β1 integrin silencing drastically reduces the number of differentiated cells (Figure 9B). Finally, by coimmunoprecipitation experiments with anti-AR antibodies (Figure 9C, bottom), we observed association between AR, TrkA, and β1 integrin in PC12 cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA. These associations are triggered by R1881 or NGF and inhibited by bicalutamide (Figure 9C, bottom, left). Of note, depleting the cells of β1 integrin almost abolishes these associations (Figure 9C, bottom, right). The immunoblot of loaded lysate proteins from PC12 cells transfected with nontargeting or β1 integrin siRNAs is shown as a control (Figure 9C, top).
FIGURE 9:
Regulatory role of β1 integrin in androgen- or NGF-stimulated neuritogenesis of PC12 cells. PC12 cells were used. (A, B) Growing cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were transfected with β1 integrin or nt siRNA. Purified pEGFP plasmid (Amaxa) was included to help identification of transfected cells. Cells were made quiescent and then left unchallenged or challenged for 48 h with R1881 (10 nM) or NGF (100 ng/ml). In GFP-expressing cells, neurite outgrowth was analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and is expressed as percentage of transfected cells. Several coverslips were analyzed, and data from at least 200 scored cells for each coverslip were collected and graphically shown in B. The blot in A shows β1 integrin protein levels detected by Western blot of lysate proteins from PC12 cells transfected with nt siRNA or β1 integrin siRNA. (C) Growing plastic-plated cells were transfected with β1 integrin or nt siRNA. Quiescent cells were then left untreated or treated for 5 min with the indicated compounds: R1881 at 10 nM, bicalutamide (Bic) at 10 μM, and NGF at 100 ng/ml. Lysate proteins (2 mg/ml protein) were immune-precipitated with C-19 anti-AR antibodies. Proteins lysates or immune complexes were analyzed using antibodies against the indicated proteins. The C-19 anti AR Ab was used to detect AR.
In conclusion, it is conceivable from these data that β1 integrin links TrkA with AR in regulating the neuritogenesis triggered by androgens or NGF in PC12 cells.
DISCUSSION
The nervous system (NS) represents one of the major targets of androgenic steroids. These hormones regulate sexual, reproductive, and aggressive behaviors in the NS (Spencer et al., 2008) but also control several cognitive abilities, such as language tasks. Prenatal testosterone levels can predict spatial ability at age 7 yr (Grimshaw et al., 1995). This suggests that release of androgens in a specific temporal frame of fetal life determines aspects of brain development, leading to a “male” or “female” brain. In addition, androgens might be involved in the onset of some autistic spectrum–related disorders, considered as an expression of an “extreme male brain” (Baron-Cohen and Hammer, 1997). Organizational and many activational effects of androgens in NS involve the establishment of an appropriate neuronal connectivity through regulated neurite (dendritic and axonal) outgrowth (Fargo et al., 2008).
In the present study, we used PC12 cells as a model to analyze the differentiative action of androgens, and for the first time we identified by both biochemical and DNA sequencing approaches the expression of a classic AR in PC12 cells. The immune reactivity of a band migrating at ∼110 kDa with antibodies directed against different domains of AR and the somatic knockdown studies and molecular sequencing corroborate each other in supporting this conclusion. Again, the nonaromatizable androgen R1881 and DHT both induce neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells, and the AR antagonist bicalutamide inhibits this response. Some nonreproductive cells express sex steroid receptors at a low level (Giovannelli et al., 2012). Most of these receptors, as is the case of AR in PC12 cells, do not translocate into the nuclear compartment and do not activate steroid receptor–dependent gene transcription. Nevertheless, they activate extranuclear signaling pathways, supporting the view that receptor transcriptional and nontranscriptional actions can occur independently in target cells. NIH3T3 cells, mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs), human fibrosarcoma-derived HT1080 cells expressing endogenous AR (Castoria et al., 2011, 2014), and rat uterine stromal cells expressing PR (Vallejo et al., 2005) offer examples of this dichotomy.
Identification of scaffolds and/or effectors recruited by the ligand-activated extranuclear steroid receptor is a crucial step for the study of nontranscriptional hormone action. Recruitment of Src by AR and estradiol receptor (ER, α or β) triggers DNA synthesis and growth in mammary and prostate cancer cells stimulated in vitro or in xenografts by estradiol or androgen (Migliaccio et al., 2007; Varricchio et al., 2007). Association of FlnA with AR leads to cell migration and cell quiescence in fibroblasts and fibrosarcoma cells challenged with a physiological concentration of androgen (Castoria et al., 2003, 2014). In PC12 cells, R1881 induces association of AR with full-length FlnA at intermediate cytoskeleton filaments. Thus the full-length FlnA tethers AR to cytoskeleton sites, where the bipartite AR/FlnA complex commands the organization of the FlnA-dependent downstream effectors involved in neurite outgrowth stimulation by androgens or NGF. The absence of FlnA proteolysis, together with the predominant extranuclear FlnA localization, supports a role for cytoplasmic FlnA in PC12 cells. FlnA is expressed in distinct regions of the brain, where it regulates neuronal migration during embryogenesis. Mutations in FlnA gene cause brain developmental malformations, presumably due to severe defects in embryonic cell migration, associated with the failure of FlnA to interact with other proteins (Zhou et al., 2010). FlnA cross-links with cortical actin and interacts with the cytoplasmic β integrin domain, as well as with upstream and downstream regulators of GTPase (e.g., Trio-GEF, Fil-GAP, ROCK) and small GTP-binding proteins, including Rac (Zhou et al., 2010). In such a way, FlnA coordinates cytoskeleton modifications leading to motility, adhesion, and cell differentiation. Here, we show a novel and unexpected function of the AR/FlnA complex, which relies on neuritogenesis induced by androgen and partly by NGF. Thus the AR/FlnA complex might control neuronal differentiation, as indicated by the finding that a peptide dissociating the AR/FlnA complex reduces neuritogenesis of PC12 (Figure 5, B and C). Again, we observe by IHC that FlnA is expressed in mouse adult hippocampus (Supplemental Figure S8), a region of the limbic system involved in short- and long-term memory as well as spatial navigation. Hippocampus is the first brain region damaged by Alzheimer's disease (AD), which causes memory loss and disorientation. Of interest, FlnA is involved in AD pathogenesis, and a small FlnA-targeting molecule has been proposed as a potential therapeutic tool for this disease (Wang et al., 2012).
Analysis of androgen-induced neuritogenesis reveals a new and unexpected cross-talk between AR and TrkA and shows that NGF or androgens share the signaling pathways leading to neuritogenesis. In search for mechanistic insight into the regulation of AR/TrkA cross-talk, we hypothesized the involvement of integrins, since β1-family integrin receptors were identified as mediators of neurite outgrowth on extracellular matrix (ECM) many years ago (Reichardt and Tomaselli, 1991). Of greater importance, NGF induces accumulation of β1 integrins at the tips of growth cone filopodia of neurons grown in the absence of ECM substrate (Grabham and Goldberg, 1997). In addition to indicating a role for integrins in proper axonal navigation induced by NGF, these findings also suggested that integrins associate with other transmembrane receptors (Woods and Couchman, 2000). We recently observed that androgen stimulation rapidly induces the recruitment of β1 integrin to AR/FlnA complex, leading to focal adhesion changes in fibroblasts and fibrosarcoma cells (Castoria et al., 2011). Experiments of somatic knockdown suggest that β1 integrin represents the link between AR and TrkA. Again, β1 integrin involvement in the androgen action might also account for Erk activation detected in PC12 cells challenged with R1881 (Supplemental Figure S9). In sum, TrkA recruits β1 integrin and likely modifies its cytoplasmic tail in NGF-stimulated cells, thus attracting the FlnA/AR complex and enabling activation of the downstream pathway leading to neuritogenesis. In turn, in cells stimulated with androgens, the FlnA/AR complex might recruit β1 integrin cytoplasmic domain to plasma membranes and concentrate it close to TrkA. In such a way, the spatial organization of the signaling pathway involved in neuritogenesis is enabled. However, alternative possibilities cannot be excluded (reviewed in Alam et al., 2007).
PI3-K controls several processes, including neuronal differentiation in the NS (Arimura and Kaibuchi, 2005). Its activity has been implicated in pathogenesis of schizophrenia and proposed as a potential therapeutic target for psychiatric disorders (Law et al., 2012). The catalytic subunit of PI3-K δ, p110 δ, belongs to the class Ia PI3-K family (reviewed in Vanhaesebroeck et al., 2010). PI3-K δ is expressed in distinct brain regions of adult mouse, including hippocampus (Eickholt et al., 2007; Supplemental Figure S8). Results from pharmacological inhibition of PI3-K δ (Figure 7) indicate that its activity is required for both R1881- and NGF-regulated neuritogenesis. In addition, PI3-K δ (catalytic and regulatory subunits) undergoes association with TrkA in cells stimulated by androgen or NGF, as shown by coimmunoprecipitation experiments in Figure 8. Thus it is conceivable that such an association triggers the catalytic activity of PI3-K δ, thereby activating the PI3-K–dependent neuritogenic pathway, including Rac in PC12 cells stimulated with NGF or androgens.
On the basis of the experimental evidence presented in this study, we propose the model presented in Figure 10. Androgens or NGF induce through β1 integrin the assembly of AR with TrkA. FlnA participates in this complex through its direct interaction with β1 integrin (Loo et al., 1998) and interaction with AR (Castoria et al., 2011; the present results). TrkA then recruits PI3-K δ, likely through p85 (Obermeier et al., 1993). Rac activation and neurite elongation then follow.
FIGURE 10:
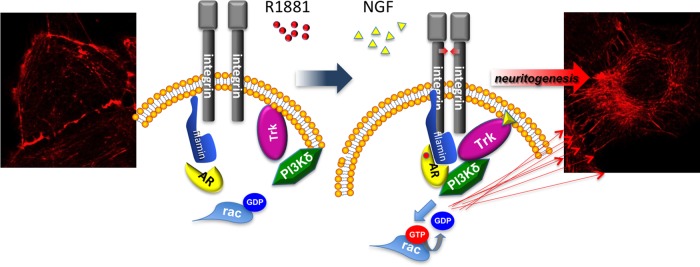
Model based on our experimental findings. Androgen or NGF induces association of TrkA/β1 integrin/AR/FlnA /PI3-K δ complex, which in turn triggers Rac activation and neuritogenesis in cells challenged with androgens or NGF. Images show the cytoskeleton changes induced by 10 nM R1881 in quiescent PC12 cells.
The observed redundancy of signals (androgen and NGF) triggering the same signaling pathway indicates that the functions regulated by this pathway are required by the cells even under unfavorable conditions, such as reduction or lack of a signal or a receptor dysfunction. It might also have implications for neurodevelopmental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemical reagents
The Rac inhibitor EHT1846 (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy) was used at 5 μM (final concentration). The PI-3K δ inhibitor IC87114 (Merck-Serono, Rockland, MA) was used at 5 μM (final concentration). The TrkA inhibitor GW441756 (Selleckhem, Houston, TX) was used at 1 μM (final concentration). The mitogen-activated kinase kinase inhibitor PD98050 (Alexis, San Diego, CA) was used at 10 μM (final concentration). R1881 and DHT (Sigma-Aldrich) were used at 10 nM. NGF (Calbiochem, Millipore/Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and EGF (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) were both used at 100 ng/ml. The antiandrogen bicalutamide (Sigma-Aldrich) was used at 10 μM.
Constructs
cDNA encoding wild-type hAR was in pSG5 (Chang et al., 1988). The 3416 construct, containing four copies of wild-type slp-HRE2 (5′-TGGTCAgccAGTTCT-3′) and the 3424 construct (5′-TGGACAgccAGTTCT-3′) were cloned in the NheI site in pTK-TATA-Luc (Verrijdt et al., 2000). cDNA encoding wild-type human TrkA was in pCMV (Addgene).
Cell culture, transfection, transactivation assays, and siRNA
Cos-7 and LNCaP cells from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA) were cultured and made quiescent as reported (Migliaccio et al., 2000). PC12 cells were a gift of B. J. Eickholt (Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Cluster of Excellence NeuroCure, and Institute of Biochemistry–Charité CrossOver Ebene, Berlin, Germany). The cells were cultured in Corning plates (Cosker and Eickholt, 2007), using F12K medium (ATCC) supplemented with 2.5% fetal calf serum (FCS; Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD), 15% horse serum (Life Technologies), streptomycin (Life Technologies) at 100 μg/ml, and penicillin (Life Technologies) at 100 U/ml. PC12 cells were made quiescent using phenol red–free DMEM (Life Technologies) containing 0.5% charcoal-treated FCS, antibiotics, and l-glutamine (Life Technologies) at 2 mM. Before transfection, PC12 cells were detached and counted using a Burker chamber. The cells (at 2 × 106) were transfected with the indicated plasmids or siRNAs. In transactivation assay, PC12 or Cos-7 cells were transfected using the Superfect reagent with 2 μg of 3416-pTK-TATA-Luc or 3424-pTK-TATA-Luc plasmids, alone or with the indicated amounts of pSG5-hAR-expressing plasmid. After 24 h, transfected cells were left unstimulated or stimulated with 10 nM R1881 (Perkin Elmer, Weiterstadt, Germany) for 18 h. Luciferase activity from lysates was measured using a luciferase assay system (Promega, Madison, WI), and values were corrected using CH110-expressed β-galactosidase activity (GE Healthcare, Milan, Italy). Values were obtained from several independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Unless otherwise stated, PC12 cells were transfected using a Nucleofector kit (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland), according to the manufacturer's instructions. For FlnA siRNA, a pool of three target-specific 20- to 25-nucleotide siRNAs (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX) was used. For AR siRNA, a pool of four target-specific 20- to 25-nucleotide siRNAs (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used. For β1 integrin siRNA, a pool of three to five target-specific 19- to 25-nucleotide siRNAs (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used. Nontargeting siRNA, containing a scrambled sequence, was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. When indicated, PC12 cells were cotransfected with 2 μg of enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)–cDNA (Lonza) to help identification of transfected cells. After 24 h, transfected cells were made quiescent for 6 h and then used.
Primary mouse hippocampal neurons
C57/BL6 mice from our in-house colony were fed with a standard diet and water and maintained on a 12-h light/dark cycle. Primary hippocampal neurons were generated from mouse embryos at 16.5 embryonic days as described (Cosker et al., 2008), using a cold Hank's balanced saline solution (Life Technologies) and enzymatic dissociation (37°C in 0.25% trypsin-EDTA for 15 min and 10 mg/ml DNase I for 1 min). Hippocampus was dissociated (Cosker et al., 2008) in phenol red high-glucose medium containing 10% horse serum, 2 mM l-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 U/ml streptomycin. The resulting suspension was filtered through a 40-mm strainer (Corning, Corning, NY) and used. Animal procedures were performed according to the Italian Legislative Decree 116/92 issued by the Italian Ministry of Health, as well as European Community laws.
Genomic DNA and PCR
Genomic DNA was extracted from rat liver or PC12 cells using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Milan, Italy) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The AR exon 1 region containing the CAG repeats was amplified by PCR using the oligonucleotide primers listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1:
Oligonucleotide primers used.
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Forward sequence 1 | 5′-GCTCTCCTCAAGCCCACATC-3′ |
| Reverse sequence 1 | 5′-AGGAATACTCAGCAGTCTCTT-3′ |
| Forward sequence 2 | 5′-TCCCGGAGCCTGGAGCTGCCA-3′ |
| Reverse sequence 2 | 5′-TGGGCAGCACGGCGGGTGGA-3′ |
A 100-ng amount of rat liver or PC12 genomic DNA was used in the amplification reaction as template. Water was used as control. PCR was performed using, in a final volume of 50 μl, a PCR mixture containing 5 μl of 10× PCR buffer; 5 μl of MgCl2, 25 mM; 2.5 μl of forward primer, 10 mM; 2.5 μl of reverse primer, 10 mM; 1 μl of PCR Nucleotide mix, 10 mM (Promega); and 0.25 μl of Taq Gold (Roche). The amplification was run for 40 cycles, using the following program: 95°C for 5 min; 95°C for 1 min; 64°C for 1 min; 72°C for 2 min; and a final elongation at 72°C for 15 min. The amplification products were analyzed on a 2% agarose gel in Tris/borate/EDTA (TBE) and then submitted to direct sequencing to determine the number of CAG repeats.
RNA extraction and Northern blot
Total RNA was extracted from growing LNCaP, NIH3T3, or PC12 cells using TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies). Northern blot for AR mRNA was performed using appropriate primers (Castoria et al., 2003).
Neurite outgrowth assay in PC12 cells
Growing cells were plated on polylysine- or collagen (type I from rat tail at 100 mg/ml; BD Biosciences)-precoated coverslips in Corning 60-mm dishes. Cells were made quiescent and then left untreated or treated with the indicated compounds for 24 or 48 h. Cells were then analyzed by contrast phase microscopy and counted for neurite outgrowth. A neurite outgrowth was defined as a process equal to or greater than two cell bodies in length.
Cytoskeleton changes, DNA synthesis, and MTT analysis
Cytoskeleton analysis was done (Castoria et al., 2003) using Texas red–labeled phalloidin (Sigma-Aldrich). For DNA synthesis, cells were made quiescent for 24 h and then left unstimulated or stimulated for 18 h with the indicated compounds. After an in vivo pulse with 100 μM BrdU (Sigma-Aldrich), the BrdU incorporation was analyzed by IF using diluted (1:50 in phosphate-buffered saline [PBS]) mouse monoclonal anti-BrdU antibody (clone BU-1; GE Healthcare). Diluted (1:200 in PBS) Texas red–conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody (Jackson Laboratories, West Grove, PA) was used as a secondary reagent. In vitro cell growth was analyzed by MTT assay (Castoria et al., 2014).
Contrast phase microscopy, IF, confocal microscopy, and IHC
For neurite outgrowth, fields were randomly analyzed with a DMIRB inverted microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) using N-Plan 10×, 20×, and 40× objectives (Leica). Images were captured using a DC200 or DFC 450C camera (Leica) and acquired with IMI1000 or Application Suite (Leica) software. They are representative of at least three different experiments, each performed in duplicate. In IF analysis, cells on polylysine-coated coverslips were fixed and permeabilized (Castoria et al., 2003). Endogenous AR was visualized (Castoria et al., 2003) using diluted (1:100) rabbit polyclonal anti-AR antibodies (C-19 from Santa Cruz Biotechnology against the C-terminal domain of AR or Ab-2 from Neomarkers (Fremont, CA) against the N-terminal domain of AR). Diluted (1:200 in PBS containing 0.2% bovine serum albumin) anti-rabbit Texas red–conjugated or anti-rabbit fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated antibody (Jackson Laboratories) was used as a secondary reagent. Neuronal class III β-tubulin was revealed using diluted (1:500 in PBS) Alexa Fluor–labeled neuronal class III β-tubulin (TUJ1) monoclonal antibody (Covance, Pinceton, NJ). In PC12 cells, FlnA was stained using diluted (1:30 in PBS) goat polyclonal anti-FlnA (Ab11074; Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Goat antibody was detected using diluted (1:300 in PBS) rabbit anti-goat Texas red–conjugated antibody (Abcam). In LNCaP cells, FlnA was stained using diluted (1:50 in PBS) mouse monoclonal antibody MAB 1680 (Chemicon, Calbiochem, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Diluted (1:100 in PBS) goat anti-mouse Texas red–conjugated antibody (Jackson Laboratories) was used as a secondary reagent. When indicated, coverslips were stained with Hoechst 33258, inverted, and mounted in Mowiol (Calbiochem, Millipore/Merck KGaA). Fields were analyzed with a DMBL Leica fluorescence microscope using HCX PL Apo 63× oil and HCX PL Fluotar 100× oil objectives. Images were captured using a DC480 or DFC365FX camera (Leica) and acquired with FW4000 or Application Suite (Leica) software. Confocal microscopy analysis was done using a Zeiss LSM 510 laser scanning confocal microscope as reported (Lombardi et al., 2008). For AR/FlnA colocalization analysis, we used Argon2 (458, 477, 488, 514 nm) and HeNe1 (543 nm) excitation lasers, which were separately switched on to reduce cross-talk of the two fluorochromes. The green and the red emissions were separated by a dichroic splitter (FT 560) and filtered (515- to 540-nm band-pass filter for green and >610-nm long-pass filter for red emission). A threshold was applied to the images to exclude ∼99% of the signal found in control images. The weighted colocalization coefficient represents the sum of intensity of colocalizing pixels in channels 1 and 2 as compared with the overall sum of pixel intensities above threshold. This value could be 0 (no colocalization) to 1 (all pixels colocalize). Bright pixels contribute more than faint pixels. The colocalization coefficient represents the weighted colocalization coefficients of Ch1 (red) with respect to Ch2 (green) for each experiment (Manders et al., 1993). IHC analysis was carried out using C57/BL6 mice from our in-house colony, maintained as described. The appropriately aged mice were perfused with saline and fixative (2% paraformaldehyde in PBS). Meninges were removed from the cortex. The brain was separated by a sagittal cut along the midline and harvested and fixed in 4% Formalin and processed for paraffin embedding. Serial sagittal sections (50 μm) were cut on a vibratome. Paraffin-embedded and Formalin-fixed sections were rinsed in xylene, dehydrated through graded ethanol series, heated with citric acid/sodium salt mix (0.01 M, pH 6) for 30 min in a microwave oven at 99°C, and cooled for 20 min at room temperature for antigen retrieval. Endogenous peroxidase was inactivated in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 5 min at room temperature. AR was stained using diluted (1:100 in the antibody diluent solution [ADS]; DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) anti-AR (clone Ab 2; Neomarker) at room temperature for 3 h. FlnA was visualized using diluted (1:100 in ADS) anti-FlnA antibody (clone H-300; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) overnight at 4°C. TrkA expression was assessed using diluted (1:100 in ADS) anti-TrkA antibody (clone 763; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) at room temperature for 2 h. The p110 δ expression was assessed using diluted (1:200 in ADS) anti-p110 δ antibody (clone H-219; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) at room temperature for 3 h. The staining was performed using Envision System (DAKO) and DAB Chromogen (DAKO). Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Control sections were obtained by substituting the primary antibody (Ab) with nonspecific anti-rabbit Ab. Coverslips were mounted, and fields were analyzed with a BX43 microscope (Olympus, Milan, Italy), using 4×, 10×, 20×, and 40× Plan CN objectives. Images were captured using a DP21 Olympus camera and acquired with Ultra VNC software (Olympus). For IF, confocal microscopy, and IHC analysis, the image collection periods and exposures are identical in the different experimental conditions. All images are representative of at least two different experiments, each in duplicate.
Peptide synthesis
The stapled peptide was synthesized and modified as reported (Castoria et al., 2014). Crude peptide was purified using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) on a preparative C4 column (BioAdvantage Pro 300; Thomson Liquid Chromatography) with a water/acetonitrile solvent system containing trifluoroacetic acid. Purified peptide was characterized by matrix-associated laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI micro MX; Waters) and RP-HPLC on an analytical C18 column (Eclipse XDB-C18; Agilent). The purity of the peptide was found to be >95%.
AR ligand-binding displacement studies
Cos-7 cells were transfected with hAR or hTrkA encoding plasmid (1.5 μg) as described. Transfected cells were made quiescent (Migliaccio et al., 2000), and ligand-binding displacement studies were done (Guerrini et al., 2014). Briefly, cells at 70% confluence were incubated by adding 10 nM [3H]R1881 (98 Ci/mmol; PerkinElmer) to the medium in the absence or presence of the indicated excess of radio-inert compounds. After a 4-h incubation at 37°C, cells were washed three times with ice-cold PBS and collected by gently scraping in the cold room using 600 μl of ice-cold PBS containing 0.05% EDTA (wt/vol). The number of cells in an aliquot of 100 μl was counted. An aliquot (200 μl) of cell suspension was submitted in duplicate to the extraction of intracellular radioactivity using 500 μl of ice-cold ethanol (100%) for 1 h. After 24 h at 37°C, radioactivity was counted in a liquid scintillation counter. Nonspecific binding of [3H]R1881 was determined in separate wells by adding the indicated excess of unlabeled R1881 to the incubation medium.
Lysates, Rac assay, immunoprecipitation, and Western blot
The Rac pull-down assay was done (Castoria et al., 2003) using a Rac activation kit (Upstate Biotechnology) and lysate proteins at 1 mg/ml. In coimmunoprecipitation experiments, lysates containing 2 mg/ml protein were used. The rabbit polyclonal anti-AR antibody (C-19; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used to immune-precipitate AR (Castoria et al., 2011). TrkA was immunoprecipitated using the rabbit polyclonal anti-TrkA antibody (06-574; Millipore). SDS–PAGE (acrylamide 8 or 12%) was done as reported in Castoria et al. (1993), and Western blot analysis was performed as described in Migliaccio et al. (1998). The rabbit polyclonal anti-AR antibodies (C-19 or N-20; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were used to detect AR. FlnA was detected using the rabbit polyclonal anti-FlnA antibody (4762S; Cell Signaling). The rabbit polyclonal AB1952 antibody (Chemicon) was used to detect β1 integrin. The rabbit polyclonal anti-p85α antibody (clone 06-195) was from Millipore. The rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-p110δ (clone H219) was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Akt, P-Ser-473 Akt, Erk, and P-Tyr-204 Erk were detected using appropriate antibodies (Cell Signaling or Santa Cruz Biotechnology, respectively). TrkA was detected using the rabbit polyclonal anti-TrkA antibody (06-574; Millipore). Tubulin or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was detected using mouse monoclonal anti-tubulin or anti-GADPH antibodies (Sigma-Aldrich). The ECL system (GE Healthcare) was used to reveal immune- reactive proteins.
Statistical analysis
Differences between values observed after the various treatments were analyzed using the Student's t test for unpaired or paired observations. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank C. S. Chang, F. Claessens, B. J. Eickholt, and C. J. Loy for plasmids, cells, and reagents. This work was supported by grants from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (IG11520 to A.M.) and the Italian Ministry of University and Scientific Research (2010NFEB9L_002 to G.C.). M.D.D. is the recipient of PRIN Grant 2010-2011.
Abbreviations used:
- AR
androgen receptor
- BrdU
bromodeoxyuridine
- DHT
dihydrotestosterone
- Erk
extracellular-regulated kinase
- Fln
filamin
- hAR
human androgen receptor
- IF
immunofluorescence
- IHC
immunohistochemistry
- PI3-K
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- rAR
rat AR.
Footnotes
This article was published online ahead of print in MBoC in Press (http://www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1091/mbc.E14-09-1352) on June 10, 2015.
G.C., A.M., and F.A. contributed to the concept and design of the study and the writing of the article; E.A. contributed to the design and preparation of the S peptide; M.V.B. contributed to the design of experiments in IF and confocal microscopy; M.D.D., A.B., and A.A. contributed to the design of experiments and analysis of data; M.D.D., L.D., P.C., and M.A.O. performed experiments.
The authors declare that they do not have competing financial interests.
REFERENCES
- Alam N, Goel HL, Zarif MJ, Butterfield JE, Perkins HM, Sansoucy BG, Sawyer TK, Languino LR. The integrin–growth factor receptor duet. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:649–653. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexaki VI, Dermitzaki E, Charalampopoulos I, Kampa M, Nifli AP, Gravanis A, Margioris AN, Castanas E. Neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells abolishes the expression of membrane androgen receptors. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:2745–2756. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimura N, Kaibuchi K. Key regulators in neuronal polarity. Neuron. 2005;48:881–884. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azcoitia I, Arevalo MA, De Nicola AF, Garcia-Segura LM. Neuroprotective actions of estradiol revisited. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011;22:467–473. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Cohen S, Hammer J. Parents of children with Asperger syndrome: what is the cognitive phenotype. J Cogn Neurosci. 1997;9:548–554. doi: 10.1162/jocn.1997.9.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkemeier LR, Winslow JW, Kaplan DR, Nikolics K, Goeddel DV, Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-5: a novel neurotrophic factor that activates trk and trkB. Neuron. 1991;7:857–866. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90287-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoria G, D'Amato L, Ciociola A, Giovannelli P, Giraldi T, Sepe L, Paolella G, Barone MV, Migliaccio A, Auricchio F. Androgen-induced cell migration: role of androgen receptor/filamin A association. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoria G, Giovannelli P, Di Donato M, Ciociola A, Hayashi R, Bernal F, Appella E, Auricchio F, Migliaccio A. Role of non-genomic androgen signalling in suppressing proliferation of fibroblasts and fibrosarcoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014;(5):e1548. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoria G, Lombardi M, Barone MV, Bilancio A, Di Domenico M, Bottero D, Vitale F, Migliaccio A, Auricchio F. Androgen-stimulated DNA synthesis and cytoskeletal changes in fibroblasts by a non-transcriptional receptor action. J Cell Biol. 2003;161:547–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200211099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoria G, Migliaccio A, Green S, Di Domenico M, Chambon P, Auricchio F. Properties of a purified estradiol-dependent calf uterus tyrosine kinase. Biochemistry. 1993;32:1740–1750. doi: 10.1021/bi00058a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang CS, Kokontis J, Liao ST. Structural analysis of complementary DNA and amino acid sequences of human and rat androgen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:7211–7215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen BC, Kang JC, Lu YT, Hsu MJ, Liao CC, Chiu WT, Yeh FL, Lin CH. Rac1 regulates peptidoglycan-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosker KE, Eickholt BJ. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling events controlling axonal morphogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:207–210. doi: 10.1042/BST0350207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosker KE, Shadan S, van Diepen M, Morgan C, Li M, Allen-Baume V, Hobbs C, Doherty P, Cockcroft S, Eickholt BJ. Regulation of PI3K signalling by the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein PITPalpha during axonal extension in hippocampal neurons. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:796–803. doi: 10.1242/jcs.019166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickholt BJ, Ahmed AI, Davies M, Papakonstanti EA, Pearce W, Starkey ML, Bilancio A, Need AC, Smith AJ, Hall SM, et al. Control of axonal growth and regeneration of sensory neurons by the p110delta PI 3-kinase. PLoS One. 2007;2:e869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargo KN, Galbiati M, Foecking EM, Poletti A, Jones KJ. Androgen regulation of axon growth and neurite extension in motoneurons. Horm Behav. 2008;53:716–728. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.01.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioeli D, Paschal BM. Post-translational modification of the androgen receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;352:70–78. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannelli P, Di Donato M, Giraldi T, Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Auricchio F. Targeting rapid action of sex-steroid receptors in breast and prostate cancers. Front Biosci. 2012;4:453–461. doi: 10.2741/e390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabham PW, Goldberg DJ. Nerve growth factor stimulates the accumulation of beta1 integrin at the tips of filopodia in the growth cones of sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1997;17:5455–5465. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-14-05455.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravanis A, Calogeropoulou T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Thermos K, Neophytou C, Charalampopoulos I. Neurosteroids and microneurotrophins signal through NGF induce receptors to prosurvival signaling in neuronal cells. Sci Signal. 2012;5:pt8. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene LA, Tischler AS. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976;73:2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimshaw GM, Sitarenios G, Finegan JA. Mental rotation at 7 years: relations with prenatal testosterone levels and spatial play experiences. Brain Cogn. 1995;29:85–100. doi: 10.1006/brcg.1995.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrini A, Tesei A, Ferroni C, Paganelli G, Zamagni A, Carloni S, Di Donato M, Castoria G, Leonetti C, Porru M, et al. A new avenue toward androgen receptor pan-antagonists: C2 sterically hindered substitution of hydroxy-propanamides. J Med Chem. 2014;57:7263–7279. doi: 10.1021/jm5005122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harburger DS, Calderwood DA. Integrin signalling at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:159–163. doi: 10.1242/jcs.018093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka Y, Hojo Y, Mukai H, Murakami G, Komatsuzaki Y, Kim J, Ikeda M, Hiragushi A, Kimoto T, Kawato S. Rapid increase of spines by dihydrotestosterone and testosterone in hippocampal neurons: dependence on synaptic androgen receptor and kinase networks. Brain Res. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.011. S0006-8993(14)01680-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung EJ, Kim CW, Kim DR. Cytosolic accumulation of gammaH2AX is associated with tropomyosin-related kinase A-induced cell death in U2OS cells. Exp Mol Med. 2008;40:276–285. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan DR, Martin-Zanca D, Parada LF. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991;350:158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan DR, Miller FD. Signal transduction by the neurotrophin receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:213–221. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(97)80065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy WR, Alter M, Sung JH. Progressive proximal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy of late onset: a sex-linked recessive trait. Neurology. 1968;18:671–680. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.7.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K, Hattori S, Kabuyama Y, Shizawa Y, Takayanagi J, Nakamura S, Toki S, Matsuda Y, Onodera K, Fukui Y. Neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells is suppressed by wortmannin, a specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:18961–18967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Spada AR, Wilson EM, Lubahn DB, Harding AE, Fischbeck KH. Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature. 1991;352:77–79. doi: 10.1038/352077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law AJ, Wang Y, Sei Y, O'Donnell P, Piantadosi P, Papaleo F, Straub RE, Huang W, Thomas CJ, Vakkalanka R, et al. Neuregulin 1-ErbB4-PI3K signaling in schizophrenia and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-p110d inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:12165–12170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206118109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaridis I, Charalampopoulos I, Alexaki VI, Avlonitis N, Pediaditakis I, Efstathopoulos P, Calogeropoulou T, Castanas E, Gravanis A. Neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone interacts with nerve growth factor (NGF) receptors, preventing neuronal apoptosis. PLoS Biol. 2011;9:e1001051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987;237:1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin CH, Cheng HW, Ma HP, Wu CH, Hong CY, Chen BC. Thrombin induces NF-kappaB activation and IL-8/CXCL8 expression in lung epithelial cells by a Rac1-dependent PI3K/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:10483–10494. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.112433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi M, Castoria G, Migliaccio A, Barone MV, Di Stasio R, Ciociola A, Bottero D, Yamaguchi H, Appella E, Auricchio F. Hormone-dependent nuclear export of estradiol receptor and DNA synthesis in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol. 2008;182:327–40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200712125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo DT, Kanner SB, Aruffo A. Filamin binds to the cytoplasmic domain of the beta1-integrin. Identification of amino acids responsible for this interaction. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23304–23312. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.36.23304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loy CJ, Sim KS, Yong EL. Filamin-A fragment localizes to the nucleus to regulate androgen receptor and coactivator functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:4562–4567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0736237100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo L. Rho GTPases in neuronal morphogenesis. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1:173–180. doi: 10.1038/35044547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig RH, Hua P, Smith LS, Wang C, Chang C. An in vitro model for the effects of androgen on neurons employing androgen receptor-transfected PC12 cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1994;5:587–596. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1994.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manders E, Verbeek F, Aten J. Measurement of co-localization of object in dual-colour confocal images. J Microsc. 1993;169:375–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs GS, Honda T, Fuller L, Thangavel R, Balsamo J, Lilien J, Dailey ME, Arregui C. Dendritic arbors of developing retinal ganglion cells are stabilized by beta 1-integrins. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006;32:230–241. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2006.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall CJ. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 1995;80:179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melcangi RC, Panzica G, Garcia-Segura LM. Neuroactive steroids: focus on human brain. Neuroscience. 2011;191:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer RP, Gehlhaus M, Schwab R, Bürck C, Knoth R, Hagemeyer CE. Concordant up-regulation of cytochrome P450 Cyp3a11, testosterone oxidation and androgen receptor expression in mouse brain after xenobiotic treatment. J Neurochem. 2009;109:670–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Auricchio F. Analysis of androgen receptor rapid actions in cellular signaling pathways: receptor/Src association. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;776:361–370. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-243-4_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Barone MV, Ametrano D, Zannini MS, Abbondanza C, et al. Steroid-induced androgen receptor–oestradiol receptor β–Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2000;19:5406–5417. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio A, Piccolo D, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Gong W, Beato M, Auricchio F. Activation of the Src/p21ras/Erk pathway by progesterone receptor via cross-talk with estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1998;17:2008–2018. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.7.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio A, Varricchio L, De Falco A, Castoria G, Arra C, Yamaguchi H, Ciociola A, Lombardi M, Di Stasio R, Barbieri A, et al. Inhibition of the SH3 domain-mediated binding of Src to the androgen receptor and its effect on tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26:6619–6629. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooso BA, Vinall RL, Tepper CG, Savoy RM, Cheung JP, Singh S, Siddiqui S, Wang Y, Bedolla RG, Martinez A, et al. Enhancing the effectiveness of androgen deprivation in prostate cancer by inducing Filamin A nuclear localization. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012;19:759–777. doi: 10.1530/ERC-12-0171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moresco EM, Donaldson S, Williamson A, Koleske AJ. Integrin-mediated dendrite branch maintenance requires Abelson (Abl) family kinases. J Neurosci. 2005;25:6105–6118. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1432-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier A, Lammers R, Wiesmüller KH, Jung G, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A. Identification of Trk binding sites for SHC and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase and formation of a multimeric signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22963–22966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne DM, Brady ME, Cook S, Gaughan L, Neal DE, Robson CN. Androgen receptor nuclear translocation is facilitated by the f-actin cross-linking protein filamin. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:1618–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.10.0541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt LF, Tomaselli KJ. Extracellular matrix molecules and their receptors: functions in neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:531–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu C, Masinovsky B, Dick K, Sowell CG, Staunton DE. Essential role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta in neutrophil directional movement. J Immunol. 2003;170:2647–2654. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.5.2647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoy RM, Ghosh PM. The dual role of filamin A in cancer: can't live with (too much of) it, can't live without it. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20:R341–R356. doi: 10.1530/ERC-13-0364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shutes A, Onesto C, Picard V, Leblond B, Schweighoffer F, Der CJ. Specificity and mechanism of action of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:35666–35678. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703571200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer JL, Waters EM, Romeo RD, Wood GE, Milner TA, McEwen BS. Uncovering the mechanisms of estrogen effects on hippocampal function. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2008;29:219–237. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo G, Ballaré C, Barañao JL, Beato M, Saragüeta P. Progestin activation of nongenomic pathways via cross talk of progesterone receptor with estrogen receptor beta induces proliferation of endometrial stromal cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:3023–3037. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:329–341. doi: 10.1038/nrm2882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varricchio L, Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Yamaguchi H, de Falco A, Di Domenico M, Giovannelli P, Farrar W, Appella E, Auricchio F. Inhibition of estradiol receptor/Src association and cell growth by an estradiol receptor α tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;11:1213–1221. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdine GL, Hilinski GJ. Stapled peptides for intracellular drug targets. Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:3–33. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00001-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijdt G, Schoenmakers E, Haelens A, Peeters B, Verhoeven G, Rombauts W, Claessens F. Change of specificity mutations in androgen-selective enhancers. Evidence for a role of differential DNA binding by the androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12298–12305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.16.12298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang HY, Bakshi K, Frankfurt M, Stucky A, Goberdhan M, Shah SM, Burns LH. Reducing amyloid-related Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis by a small molecule targeting filamin A. J Neurosci. 2012;32:9773–9784. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0354-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A, Couchman JR. Integrin modulation by lateral association. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:24233–24236. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R000001200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou AX, Hartwig JH, Akyürek LM. Filamins in cell signaling, transcription and organ development. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20:113–123. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou ZX, He B, Hall SH, Wilson EM, French FS. Domain interactions between coregulator ARA(70) and the androgen receptor (AR) Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:287–300. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.2.0765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.