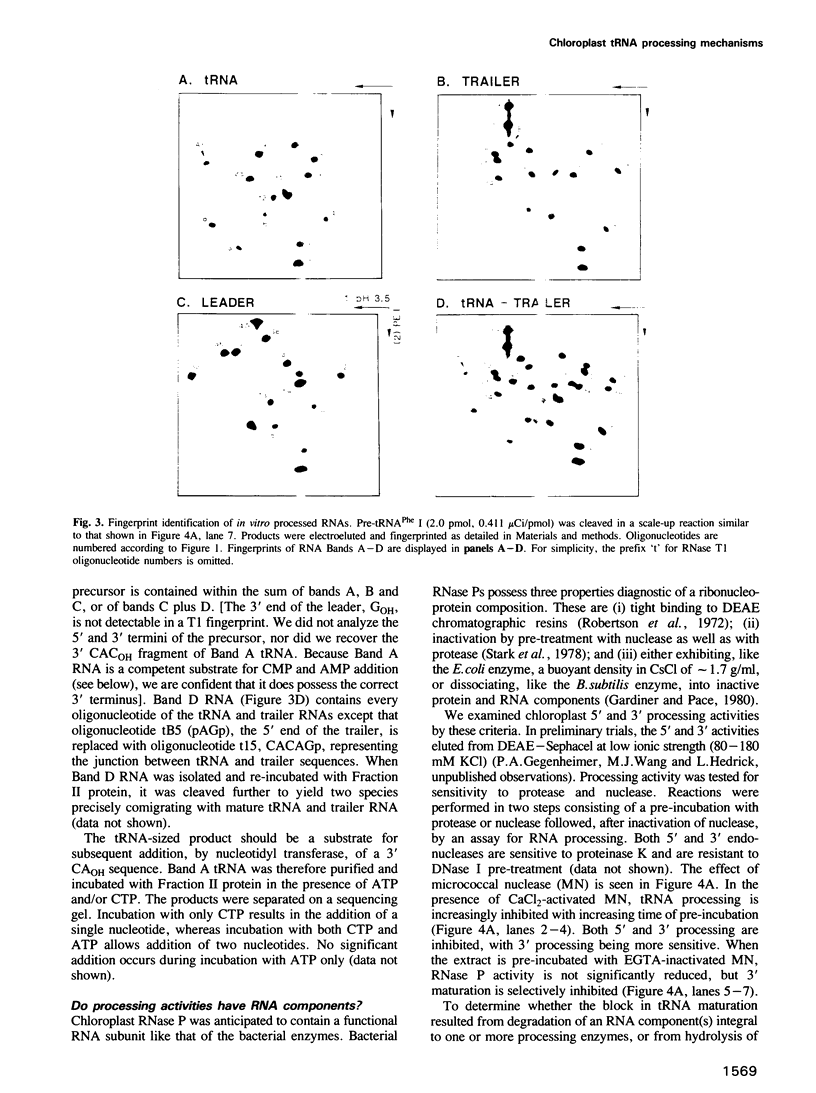
Abstract
Despite the prokaryotic origins of chloroplasts, a plant chloroplast tRNA precursor is processed in a homologous in vitro system by a pathway distinct from that observed in Escherichia coli, but identical to that utilized for maturation of nuclear pre-tRNAs. The mature tRNA 5' terminus is generated by the site-specific endonucleolytic cleavage of an RNase P (or P-type) activity. The 3' end is likewise produced by a single precise endonucleolytic cut at the 3' terminus of the encoded tRNA domain. This is the first complete structural characterization of an organellar tRNA processing system using a homologous substrate. In contrast to eubacterial RNase P, chloroplast RNase P does not appear to contain an RNA subunit. The chloroplast activity bands with bulk protein at 1.28 g/ml in CsCI density gradients, whereas E.coli RNase P bands as ribonucleoprotein at 1.73 g/ml. Chloroplast RNase P activity survives treatment with micrococcal nuclease (MN) at levels 10- to 100-fold higher than those required to totally inactivate the E.coli enzyme. The chloroplast system is sensitive to a suppression of tRNA processing, caused by binding of inactive MN to pre-tRNA substrate, which is readily overcome by addition of carrier RNA to the assay.
Keywords: chloroplast, RNA processing, RNase P, 3'endonuclease, micrococcal nuclease
Full text
PDF

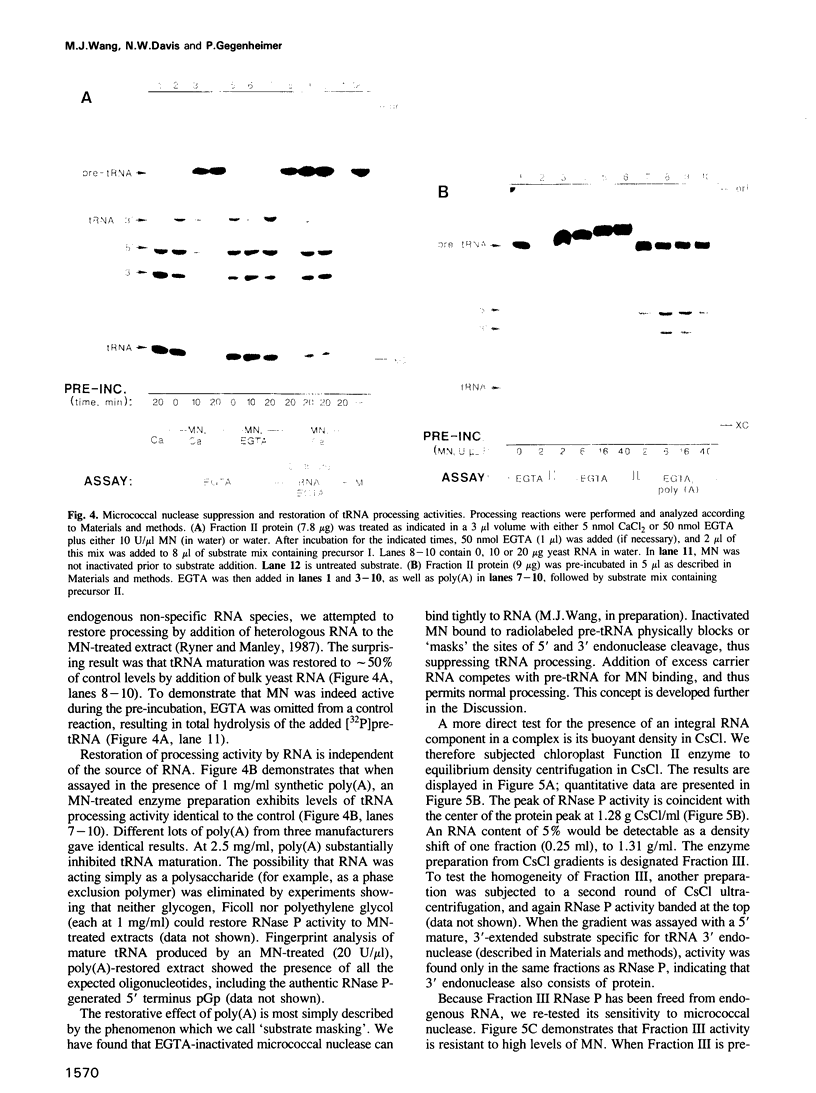
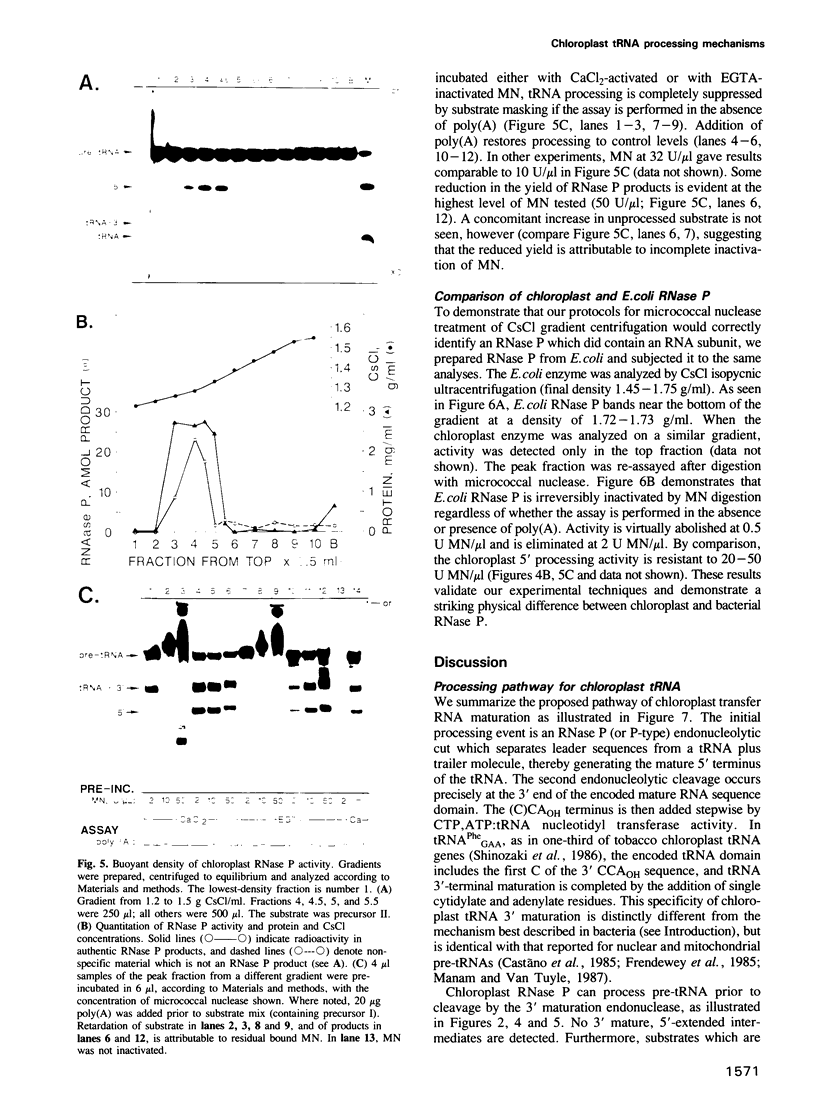



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaboshi E., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Veal heart ribonuclease P has an essential RNA component. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):831–837. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi D. G., Margarit I., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Structural alterations in mutant precursors of the yeast tRNALeu3 gene which behave as defective substrates for a highly purified splicing endoribonuclease. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3289–3297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikoff E. K., LaRue B. F., Gefter M. L. In vitro synthesis of transfer RNA. II. Identification of required enzymatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6248–6255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Ornberg R., Koster J. G., Tobian J. A., Zasloff M. Eukaryotic pre-tRNA 5' processing nuclease: copurification with a complex cylindrical particle. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Tobian J. A., Zasloff M. Purification and characterization of an endonuclease from Xenopus laevis ovaries which accurately processes the 3' terminus of human pre-tRNA-Met(i) (3' pre-tRNase). J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9002–9008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudny H., Deutscher M. P. Apparent involvement of ribonuclease D in the 3' processing of tRNA precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. Processing of tRNA in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(1):45–71. doi: 10.3109/10409238409110269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doersen C. J., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S., Attardi G. Characterization of an RNase P activity from HeLa cell mitochondria. Comparison with the cytosol RNase P activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5942–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Nucleolytic processing of a tRNAArg-tRNAAsp dimeric precursor by a homologous component from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1271–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier M. J., Ozeki H. Structure and organization of the transfer ribonucleic acid genes of Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):379–397. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.379-397.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Dingermann T., Cooley L., Söll D. Processing of precursor tRNAs in Drosophila. Processing of the 3' end involves an endonucleolytic cleavage and occurs after 5' end maturation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):449–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada K., Abelson J. DNA sequence of a T4 transfer RNA gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):377–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber R. L., Gage L. P. Transcription of a cloned Bombyx mori tRNA2Ala gene: nucleotide sequence of the tRNA precursor and its processing in vitro. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K. J., Marsh T. L., Pace N. R. Ion dependence of the Bacillus subtilis RNase P reaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5415–5419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Pace N. R. RNase P of Bacillus subtilis has a RNA component. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7507–7509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Apirion D. Processing of procaryotic ribonucleic acid. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):502–541. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.502-541.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Apirion D. Structural characterization and in vitro processing of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA transcripts containing 5- triphosphates, leader sequences, 16 S rRNA, and spacer tRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 5;143(3):227–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P. Electronic fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1799–1800. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Gabius H. J., Peebles C. L., Abelson J. An RNA ligase from wheat germ which participates in transfer RNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8365–8373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. A., Altman S. Reconstitution of RNAase P activity using inactive subunits from E. coli and HeLa cells. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90758-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Has the endosymbiont hypothesis been proven? Microbiol Rev. 1982 Mar;46(1):1–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.1.1-42.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Elsner-Menzel C., Latshaw S., Narita J. O., Schaffer M. A., Zurawski G. A subpopulation of spinach chloroplast tRNA genes does not require upstream promoter elements for transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7541–7556. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast gene expression and promoter identification in chloroplast extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:253–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Prescott D. M., Hallick R. B. Biosynthesis of chloroplast transfer RNA in a spinach chloroplast transcription system. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):815–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Larson D., Hall G. I., Sprague K. U. The primary transcription product of a silkworm alanine tRNA gene: identification of in vitro sites of initiation, termination and processing. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1217–1229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein associates with the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth M. J., Martin N. C. RNase P activity in the mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on both mitochondrion and nucleus-encoded components. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1058–1064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Liu J. S., Pace N. R. The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Sirdeskmukh R., Schlessinger D. Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):428–451. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.428-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline L., Nishikawa S., Söll D. Partial purification of RNase P from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5058–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole R., Baer M. F., Stark B. C., Altman S. E. coli RNAase P has a required RNA component. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):881–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Cherayil B., Frendewey D., Nishikawa S., Söll D. Two RNA species co-purify with RNase P from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1697–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence N. P., Richman A., Amini R., Altman S. Heterologous enzyme function in Escherichia coli and the selection of genes encoding the catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6825–6829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manam S., Van Tuyle G. C. Separation and characterization of 5'- and 3'-tRNA processing nucleases from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10272–10279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J., Schmidt O., Söll D. Dimeric transfer RNA precursors in S. pombe. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):509–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Moriya S., von Meyenburg K., Hansen F. G., Yoshikawa H. Conservation of genes and their organization in the chromosomal replication origin region of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Mullet J. E., Hanley-Bowdoin L., Chua N. H. In vitro transcription of chloroplast protein genes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:232–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Spiegelman S. The synthesis of infectious RNA with a replicase purified according to its size and density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1608–1615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. E., Baer M. F., Guerrier-Takada C., Donis-Keller H., Altman S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the RNA subunit (M1 RNA) of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich C., Gardiner K. J., Olsen G. J., Pace B., Marsh T. L., Pace N. R. The RNA component of the Bacillus subtilis RNase P. Sequence, activity, and partial secondary structure. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7888–7893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich C., Olsen G. J., Pace B., Pace N. R. Role of the protein moiety of ribonuclease P, a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):178–181. doi: 10.1126/science.3122322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Altman S., Smith J. D. Purification and properties of a specific Escherichia coli ribonuclease which cleaves a tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid presursor. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5243–5251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Requirements for accurate and efficient mRNA 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation of a simian virus 40 early pre-RNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):495–503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Contreras R., Takeya T., Khorana H. G. Total synthesis of a tyrosine suppressor transfer RNA gene. XVII. Transcription, in vitro, of the synthetic gene and processing of the primary transcript to transfer RNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5802–5816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark B. C., Kole R., Bowman E. J., Altman S. Ribonuclease P: an enzyme with an essential RNA component. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3717–3721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A. A., Krebbers E. T., Schwarz Z., Gubbins E. J., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequences of five maize chloroplast transfer RNA genes and their flanking regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5503–5511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vold B. S. Structure and organization of genes for transfer ribonucleic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.71-80.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]