Abstract
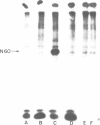
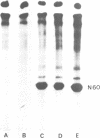
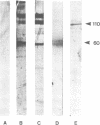
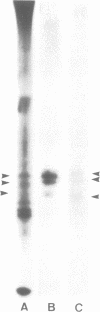
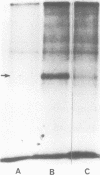
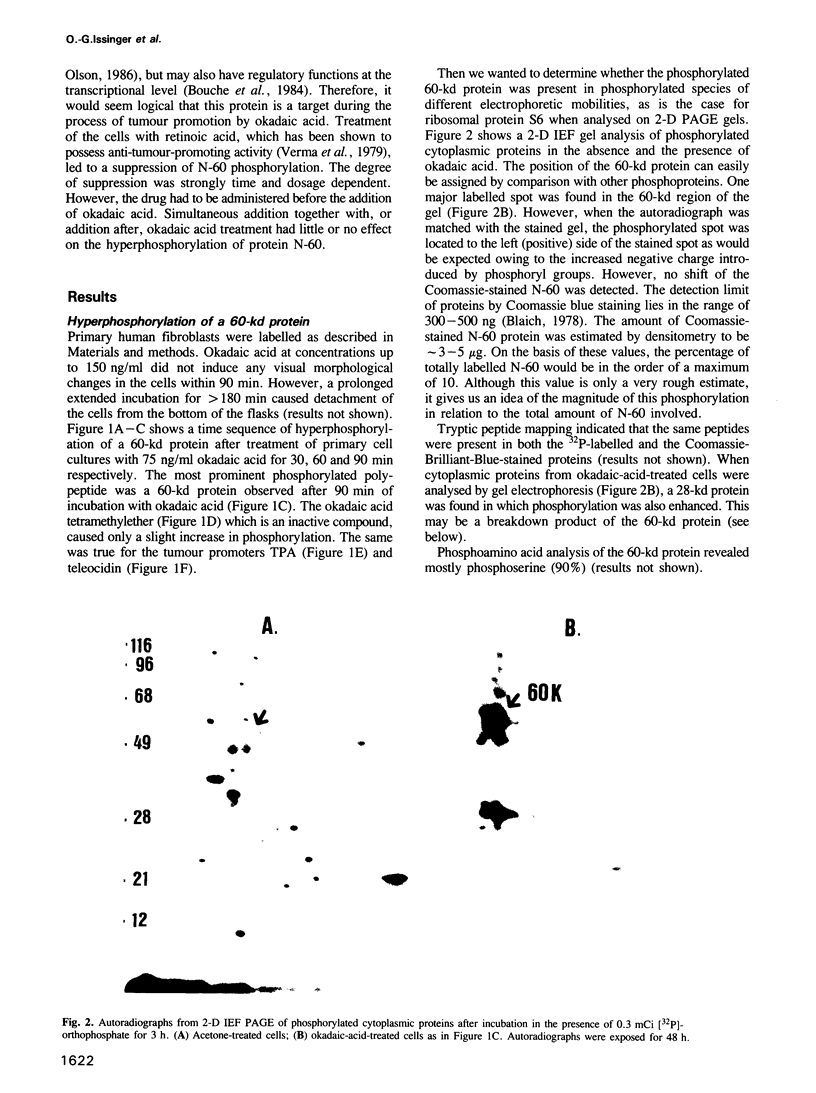
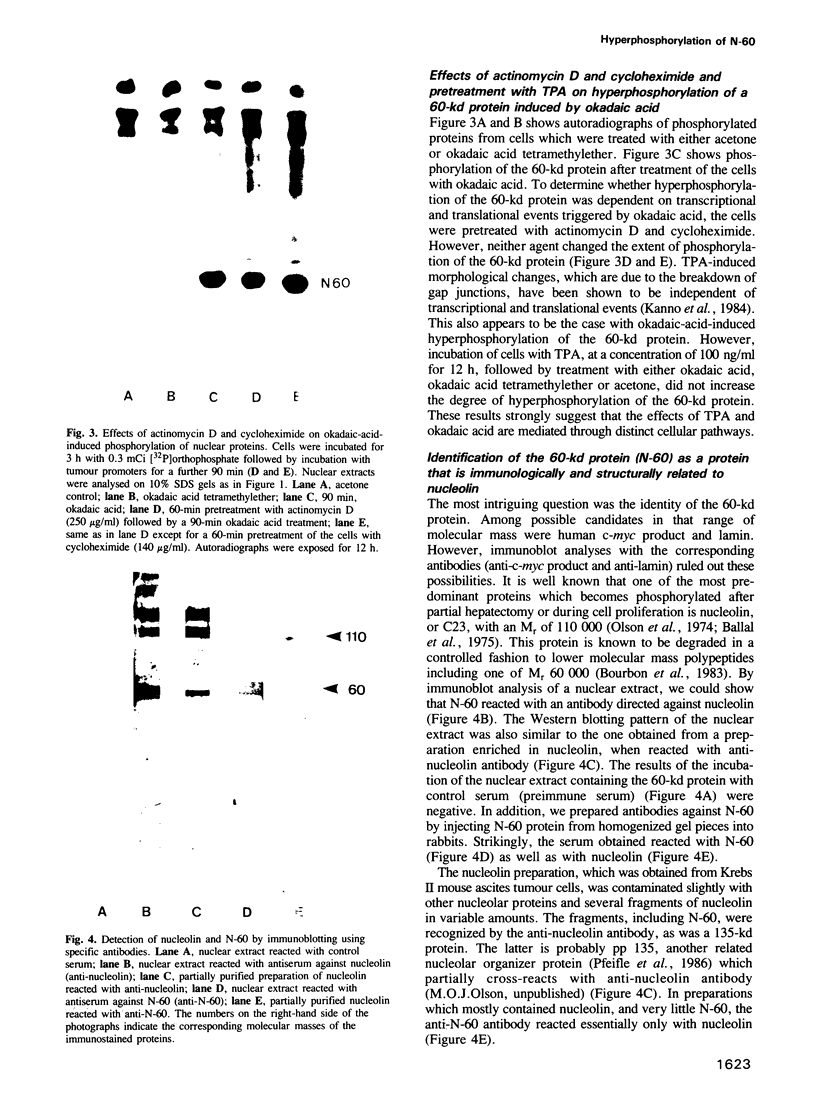
Okadaic acid, a non-TPA-type tumour promoter, induces hyperphosphorylation of a 60-kd protein in primary human fibroblasts. Treatment with TPA-type tumour promoters (e.g. TPA and teleocidin) did not cause this hyperphosphorylation. Phosphorylation of this protein was not seen at times earlier than 90 min after the addition of 75 ng/ml okadaic acid to the proliferating cell cultures. The presence of inhibitors such as actinomycin D and cycloheximide, did not significantly influence the level of hyperphosphorylation induced by okadaic acid treatment. By immunoblotting using an antibody anti-nucleolin, the 60-kd protein was identified as a fragment of nucleolar protein, nucleolin. Similarly, antibodies against the 60-kd protein cross-reacted with nucleolin. Furthermore peptide mapping, using staphylococcal V8 protease, showed that the 60-kd protein phosphorylated by casein kinase II in vitro and the okadaic-acid-induced hyperphosphorylated 60-kd protein exhibited identical phosphopeptide maps, indicating that there is also structural relatedness between N-60 and nucleolin. Hyperphosphorylation of the nucleolin fragment (N-60) was suppressed by anti-tumour promoter retinoic acid.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballal N. R., Kang Y. J., Olson M. O., Busch H. Changes in nucleolar proteins and their phosphorylation patterns during liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5921–5925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Phosphorylation of the ribosomal protein S6 is elevated in cells transformed by a variety of tumor viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):966–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.966-969.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bugler B., Amalric F. Interrelations between the maturation of a 100 kDa nucleolar protein and pre rRNA synthesis in CHO cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3025–3035. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H., Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F. Role of phosphorylation on the maturation pathways of a 100 kDa nucleolar protein. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caizergues-Ferrer M., Belenguer P., Lapeyre B., Amalric F., Wallace M. O., Olson M. O. Phosphorylation of nucleolin by a nucleolar type NII protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7876–7883. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Harrison M. L. Induction of a substrate for casein kinase II during lymphocyte mitogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 19;804(2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Kleppe K., Lillehaug J. R. Changes in polypeptide synthesis and glycosylation in mouse embryonic fibroblast C3H/10T1/2 Cl 8 cells caused by the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 19;889(3):334–345. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Boutwell R. K. Studies on the mechanism of skin tumor promotion. Cancer Res. 1970 Feb;30(2):312–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera A. H., Olson M. O. Association of protein C23 with rapidly labeled nucleolar RNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6258–6264. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan G. At the heart of the nucleolus. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):489–490. doi: 10.1038/329489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Enomoto T., Shiba Y., Yamasaki H. Protective effect of cAMP on tumor promoter-mediated inhibition of cell-cell communication. Exp Cell Res. 1984 May;152(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Nucleolin, the major nucleolar protein of growing eukaryotic cells: an unusual protein structure revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Richards R. L., Busch R. K., Busch H. Localization of phosphoprotein C23 to nucleolar structures and to the nucleolus organizer regions. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Nov;136(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamrack M. D., Olson M. O., Busch H. Amino acid sequence and sites of phosphorylation in a highly acidic region of nucleolar nonhistone protein C23. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3381–3386. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G., Simsiman R. C., Boutwell R. K. Induction of the polyamine-biosynthetic enzymes in mouse epidermis by tumor-promoting agents. Cancer Res. 1975 Jul;35(7):1662–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Guetzow K., Busch H. Localization of phosphoprotein C23 in nucleoli by immunological methods. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Oct;135(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Orrick L. R., Jones C., Busch H. Phosphorylation of acid-soluble nucleolar proteins of Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2823–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifle J., Boller K., Anderer F. A. Phosphoprotein pp135 is an essential component of the nucleolus organizer region (NOR). Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jan;162(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90422-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowald K., Fischer H., Issinger O. G. Enhanced casein kinase II activity in human tumour cell cultures. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance A. J., Thönnes M., Issinger O. G. Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation and morphological changes in response to the tumour promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in primary human tumour cells, established and transformed cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 30;847(1):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. V., Mamrack M. D., Olson M. O. Localization of phosphorylated highly acidic regions in the NH2-terminal half of nucleolar protein C23. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15035–15041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter W. W., Issinger O. G. Differential heat shock response of primary human cell cultures and established cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter W. W., Zang K. D., Issinger O. G. Influence of hyperthermia on the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 from human skin fibroblasts and meningioma cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80620-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. R., Reichert G. H., Issinger O. G. Enhanced casein kinase II activity during mouse embryogenesis. Identification of a 110-kDa phosphoprotein as the major phosphorylation product in mouse embryos and Krebs II mouse ascites tumor cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):733–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Krebs E. G. Induction of casein kinase II during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3839–3843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P., Becker H. Control of macromolecular synthesis in proliferating and resting Syrian hamster cells in monolayer culture. I. Ribosome function. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Feb;77(1):31–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Hirota M., Nakayasu M., Ojika M., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Sugimura T. Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi R., Mihara K., Maeda S., Yamaguchi T., Chen H. L., Aoyama N., Murao S., Hatanaka M., Sugiyama T. Secondary activation of c-abl may be related to translocation to the nucleolar organizer region in an in vitro cultured rat leukemia cell line (K3D). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A., Bialojan C., Troschka M., Rüegg J. C. Smooth muscle myosin phosphatase inhibition and force enhancement by black sponge toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unteregger G. Spermine induced phosphorylation of a 42 kD/pI 5.9 nuclear protein in different human tumor cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):700–707. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Shapas B. G., Rice H. M., Boutwell R. K. Correlation of the inhibition by retinoids of tumor promoter-induced mouse epidermal ornithine decarboxylase activity and of skin tumor promotion. Cancer Res. 1979 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):419–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Weinstein I. B. Tumour promotor induces plasminogen activator. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):232–233. doi: 10.1038/259232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth P. J., Yuspa S. H., Thorgeirsson S. S., Hennings H. Induction of common patterns of polypeptide synthesis and phosphorylation by calcium and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in mouse epidermal cell culture. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2831–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]