Abstract
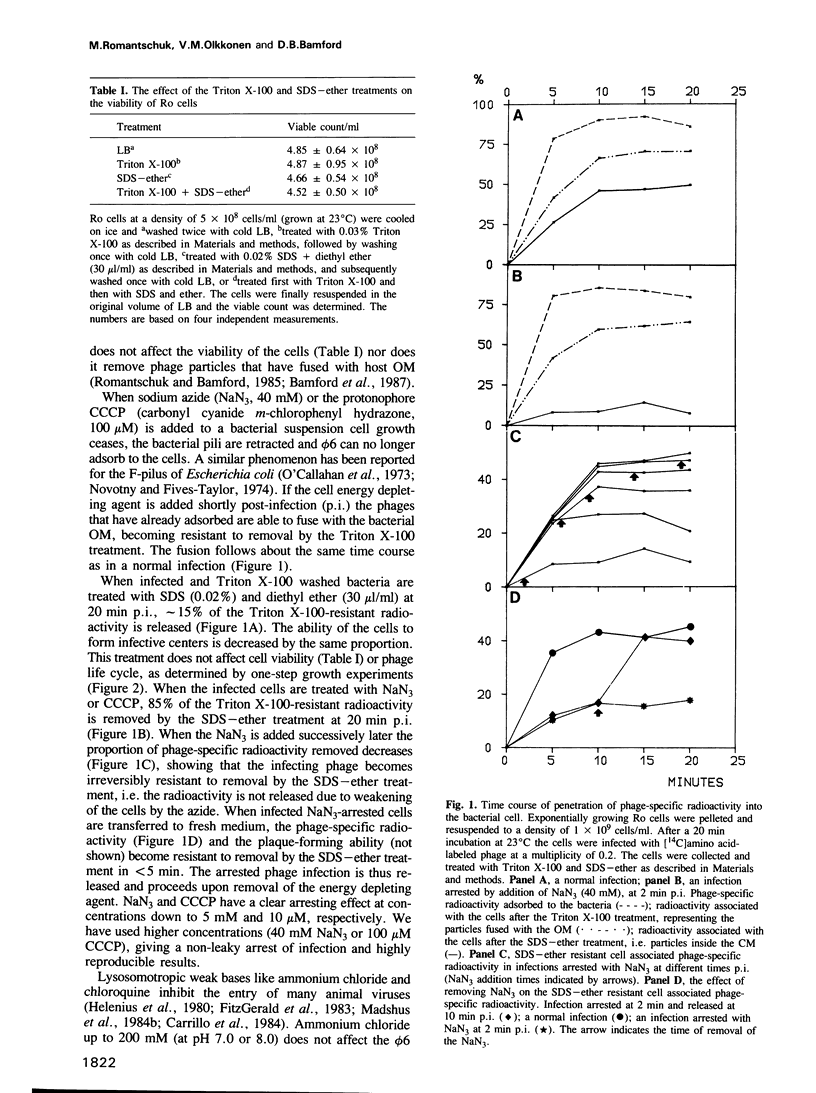
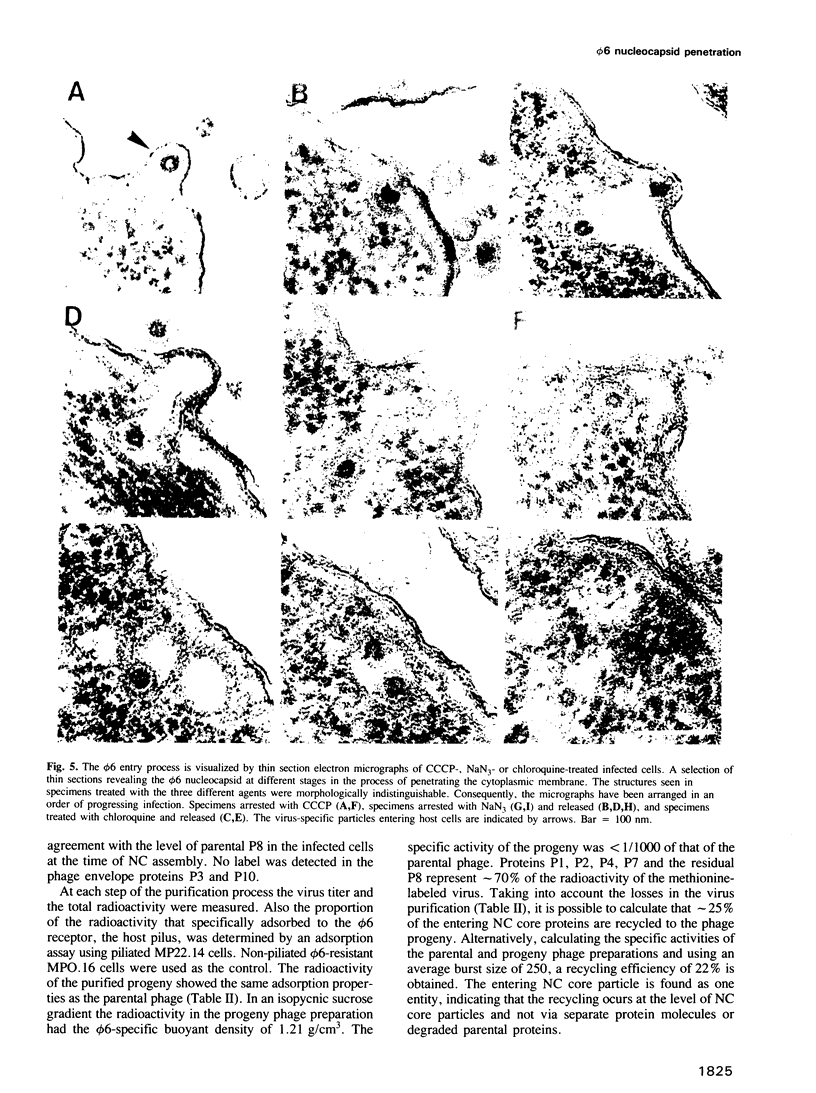
Bacteriophage phi 6 infects its host, the Gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas syringae, by a protein-targeted fusion of the virus envelope with the host outer membrane. In this investigation we present results suggesting that the phage nucleocapsid penetrates the host cytoplasmic membrane via a membrane invagination and an intracellular vesicle. This indicates that the prokaryotic plasma membrane might be more dynamic and have more common features with eukaryotic membrane systems than previously expected. Most of the nucleocapsid surface lattice protein is degraded in the cell, and the nucleocapsid core particle containing the viral dsRNA segments and the proteins necessary for the viral RNA polymerase activity can be isolated from the infected cells. The penetration is dependent on the energized state of the host cytoplasmic membrane. About 25% of the entering core particles are re-used in the progeny viruses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bamford D. H., Mindich L. Electron microscopy of cells infected with nonsense mutants of bacteriophage phi 6. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):222–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Palva E. T., Lounatmaa K. Ultrastructure and life cycle of the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. J Gen Virol. 1976 Aug;32(2):249–259. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Palva E. T. Structure of the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. Disruption by Triton X-100 treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 18;601(2):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90530-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Romantschuk M., Somerharju P. J. Membrane fusion in prokaryotes: bacteriophage phi 6 membrane fuses with the Pseudomonas syringae outer membrane. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1467–1473. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Kennedy K. Physical measurements on the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 17;633(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning W. M., Fields B. N. Ammonium chloride prevents lytic growth of reovirus and helps to establish persistent infection in mouse L cells. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):987–988. doi: 10.1126/science.6297010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo E. C., Giachetti C., Campos R. H. Effect of lysosomotropic agents on the foot-and-mouth disease virus replication. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):542–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Ball P. Transport of antibiotics into bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1982;23:183–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. A., Mindich L. The molecular weight of bacteriophage phi 6 and its nucleocapsid. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Iba H., Okada Y. Semi-conservative transcription of double-stranded RNA catalyzed by bacteriophage phi 6 RNA polymerase. J Biochem. 1980 Dec;88(6):1569–1575. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etten J. V., Lane L., Gonzalez C., Partridge J., Vidaver A. Comparative properties of bacteriophage phi6 and phi6 nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):652–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.652-658.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D. J., Padmanabhan R., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Adenovirus-induced release of epidermal growth factor and pseudomonas toxin into the cytosol of KB cells during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P., Metzger S., Romantschuk M., Carton J., Strassman J., Bamford D. H., Kalkkinen N., Mindich L. Nucleotide sequence of the middle dsRNA segment of bacteriophage phi 6: placement of the genes of membrane-associated proteins. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenawalt J. W., Whiteside T. L. Mesosomes: membranous bacterial organelles. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):405–463. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.405-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., van Dijk A. A., Els H. J. Uncoating of parental bluetongue virus to core and subcore particles in infected L cells. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):180–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ktistakis N. T., Lang D. The dodecahedral framework of the bacteriophage phi 6 nucleocapsid is composed of protein P1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2621–2623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2621-2623.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Different pH requirements for entry of the two picornaviruses, human rhinovirus 2 and murine encephalomyocarditis virus. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):346–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Mechanism of entry into the cytosol of poliovirus type 1: requirement for low pH. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Requirements for entry of poliovirus RNA into cells at low pH. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1945–1950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw T., Mindich L., Frangione B. Nucleotide sequence of the small double-stranded RNA segment of bacteriophage phi 6: novel mechanism of natural translational control. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):142–151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.142-151.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Hunt J. F., Beckwith J. Effects of signal sequence mutations on the kinetics of alkaline phosphatase export to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):160–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.160-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Cohen J., Weisburd M. Isolation of nonsense suppressor mutants in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):177–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.177-182.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Davidoff-Abelson R. The characterization of a 120 S particle formed during phi 6 infection. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):386–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Lehman J. Cell wall lysin as a component of the bacteriophage phi 6 virion. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):489–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.489-496.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Nemhauser I., Gottlieb P., Romantschuk M., Carton J., Frucht S., Strassman J., Bamford D. H., Kalkkinen N. Nucleotide sequence of the large double-stranded RNA segment of bacteriophage phi 6: genes specifying the viral replicase and transcriptase. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1180-1185.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Sinclair J. F., Cohen J. The morphogenesis of bacteriophage phi6: particles formed by nonsense mutants. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny C. P., Fives-Taylor P. Retraction of F pili. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1306–1311. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1306-1311.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan R. J., Bundy L., Bradley R., Paranchych W. Unusual arsenate poisoning of the F pili of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):76–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.76-81.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olkkonen V. M., Bamford D. H. The nucleocapsid of the lipid-containing double-stranded RNA bacteriophage phi 6 contains a protein skeleton consisting of a single polypeptide species. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2362–2367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2362-2367.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks L. C., Dicker D. T., Conger A. D., Daneo-Moore L., Higgins M. L. Effect of chromosomal breaks induced by x-irradiation on the number of mesosomes and the cytoplasmic organization of Streptococcus faecalis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):413–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Export of protein in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):290–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.290-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel H. R., Ewen M. E., Brusslan J., Pagratis N. Generation of cDNA clones of the bacteriophage phi 6 segmented dsRNA genome: characterization and expression of L segment clones. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):402–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romantschuk M., Bamford D. H. Function of pili in bacteriophage phi 6 penetration. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2461–2469. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth P., Fitzgerald D. J., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Role of a low-pH environment in adenovirus enhancement of the toxicity of a Pseudomonas exotoxin-epidermal growth factor conjugate. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):650–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.650-655.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth P., Fitzgerald D., Ginsberg H., Willingham M., Pastan I. Evidence that the penton base of adenovirus is involved in potentiation of toxicity of Pseudomonas exotoxin conjugated to epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1528–1533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Astell C., Levin D. H., Schonberg M., Acs G. The mechanisms of reovirus uncoating and gene activation in vivo. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Postma P. W. The energetics of bacterial active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:523–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Cohen J., Mindich L. The isolation of suppressible nonsence mutants of bacteriophage phi6. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):198–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Mindich L. RNA synthesis during infection with bacteriophage phi6. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steely H. T., Jr, Lang D. Electron microscopy of bacteriophage phi 6 nucleocapsid: two-dimensional image analysis. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):479–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.479-483.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturzenbecker L. J., Nibert M., Furlong D., Fields B. N. Intracellular digestion of reovirus particles requires a low pH and is an essential step in the viral infectious cycle. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2351–2361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2351-2361.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson U., Persson R. Entry of adenovirus 2 into HeLa cells. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.687-694.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson U. Role of vesicles during adenovirus 2 internalization into HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.442-449.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Brownstein B. H., Haselkorn R. Displacement of parental RNA strands during in vitro transcription by bacteriophage phi 6 nucleocapsids. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):855–862. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Sensitization of Gram-negative bacteria to antibiotics and complement by a nontoxic oligopeptide. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):526–528. doi: 10.1038/303526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten J. L., Burbank D. E., Cuppels D. A., Lane L. C., Vidaver A. K. Semiconservative synthesis of single-stranded RNA by bacteriophage phi 6 RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):769–773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.769-773.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K., Koski R. K., Van Etten J. L. Bacteriophage phi6: a Lipid-Containing Virus of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):799–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.799-805.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Lang D. Electron microscopy of bacteriophage phi 6 nucleocapsid: three-dimensional image analysis. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]