Abstract
Vibrio anguillarum causes a fatal hemorrhagic septicemia in marine fish that leads to great economical losses in aquaculture world-wide. Vibrio anguillarum strain NB10 serotype O1 is a Gram-negative, motile, curved rod-shaped bacterium, isolated from a diseased fish on the Swedish coast of the Gulf of Bothnia, and is slightly halophilic. Strain NB10 is a virulent isolate that readily colonizes fish skin and intestinal tissues. Here, the features of this bacterium are described and the annotation and analysis of its complete genome sequence is presented. The genome is 4,373,835 bp in size, consists of two circular chromosomes and one plasmid, and contains 3,783 protein-coding genes and 129 RNA genes.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s40793-015-0060-7) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Vibrio anguillarum, Fish pathogen, Vibriosis, Marine fish, Genome comparisons
Introduction
Vibrio anguillarum is a marine pathogen that causes a fatal hemorrhagic septicemia, termed vibriosis, in cultured and wild fish as well as in mollusks and crustaceans [1, 2]. Vibrio anguillarum is also known under the name Listonella anguillarum [3], which is a later heterotypic synonym [4]. Twenty-three serotypes of V. anguillarum are reported and of these, only serotypes O1, O2, and to a lesser extent O3, are the main causes of vibriosis in fish [5–7]. Although vaccines and other preventive measures are in use, vibriosis still has a devastating economical impact on the contemporary larviculture and aquaculture industry worldwide [1, 2].
Despite a significant body of research, our understanding of the virulence mechanisms of V. anguillarum is far from complete [2, 8]. A recent assessment of 15 serotypes O1, O2, and O3 isolates in a sea bass larvae model indicated that the virulence of V. anguillarum is highly complex requiring multiple instead of a few crucial virulence determinants [9]. Whole genome sequencing of different isolates will further our research to elucidate the vital factors this pathogen utilizes to cause disease.
Recently, the complete genome sequences of two V. anguillarum serotype O1 strains have been determined. Strain 775 is an isolate from Coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) in the United States Pacific coast and strain M3 was isolated in China from Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) [10, 11]. In this study, the complete genome sequence of V. anguillarum NB10, a virulent, serotype O1 strain, isolated from diseased fish on the Swedish coast of the Gulf of Bothnia, is presented [12].
Organism information
Classification and features
Vibrio anguillarum strain NB10 belongs to the class of Gammaproteobacteria as part of the Vibrionaceae family (Table 1 and Additional file 1: Table S1). The cells display the characteristic curved, rod-shaped morphology of the Vibrio genus (Fig. 1) and possess a single polar, sheathed flagellum that is required for colonization of rainbow trout [13–15]. Cells are typically 1-2 microns long and 0.5 microns in width. Colony morphology on tryptone soy agar containing 0.5 % NaCl is a cream-colored, round colony that may sector into translucent and opaque colony types, which may be due to alterations in the expression of outer membrane proteins [16]. The bacterium forms yellow colonies on the vibrio-selective medium thiosulfate-citrate-bile-sucrose agar indicating the fermentation of sucrose. This strain grows at 15-30 oC but does not survive at 37 oC; in 0.5-4 % NaCl with optimum growth occurring at 1 % NaCl in rich media (unpublished data, D.L. Milton). Strain NB10 is highly virulent for at least two species of fish: rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) [13, 17]. Numerous genetically encoded virulence factors have been identified, such as iron transport systems, flagellum/motility, hemolysins, metalloproteases, lipopolysaccharides, exopolysaccharides, repeat toxins, outer membrane proteins, and a type IV pilus [1, 8]. Figure 2 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of V. anguillarum NB10 in a 16S ribosomal RNA based tree.
Table 1.
Classification and general features of Vibrio anguillarum NB10 according to MIGS recommendations [54]
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence codea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [55] | |
| Phylum Proteobacteria | TAS [56] | ||
| Class Gammaproteobacteria | TAS [57, 58] | ||
| Order ‘Vibrionales’ | TAS [56] | ||
| Family Vibrionaceae | TAS [59–61] | ||
| Genus Vibrio | TAS [59, 60, 62–64] | ||
| Species Vibrio anguillarum | TAS [4, 60, 64] | ||
| Strain: NB10 | TAS [12, 18] | ||
| Serotype O1 | IDA | ||
| Gram stain | Negative | IDA | |
| Cell shape | Curved rod (vibroid) | TAS [13] | |
| Motility | Motile | TAS [13] | |
| Sporulation | Non-sporeforming | IDA | |
| Temperature range | Mesophile 15-30 °C | IDA | |
| Optimum temperature | 24 °C | IDA | |
| pH range; Optimum | pH 6 - pH 9; pH 7 | NAS | |
| Carbon source | Highly diverse | NAS | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | Marine fish | TAS [12, 18] |
| MIGS-6.3 | Salinity | Slightly halophilic, optimum 1 % NaCl | IDA |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | Aerobe and facultative anaerobe | IDA |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | Parasitic | TAS [12, 18] |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | Pathogen, marine fish | TAS [18] |
| Biosafety level | 1 | NAS | |
| Isolation | Diseased fish | TAS [12] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Gulf of Bothnia, Norrbyn, Sweden | TAS [12, 18] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection | 1986 | TAS [12, 18] |
| MIGS-4.1 | Latitude | 63° 34' 0'' N | TAS [12, 18] |
| MIGS-4.2 | Longitude | 19° 49' 0'' E | TAS [12, 18] |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | 3 m | TAS [12, 18] |
aEvidence codes - IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay; TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [65]
Fig. 1.
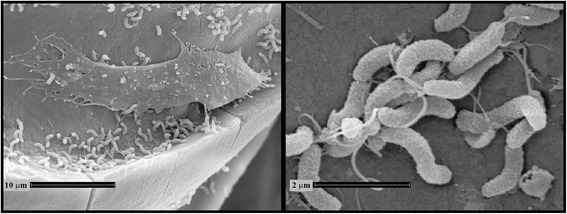
Scanning electron microscopy of V. anguillarum NB10 attached to a scale from an infected rainbow trout. The left image was taken at a 3,500× magnification and shows that the bacterium colonizes the groove of a growth ring. A highly motile skin epithelial cell called a keratocyte is shown above the growth ring and V. anguillarum evades internalization by the keratocytes [51]. The right image is a higher magnification (20,500×) of V. anguillarum cells attached to the surface of the fish scale. In this image, the curved, rod-shape of the bacterium is visible as well as the single polar flagellum. To obtain samples, rainbow trout, 15 g in weight, were infected with V. anguillarum NB10 via bathing in infected seawater. At 48 h post-infection at 22 °C, scales were removed from lesions that formed on the skin, washed 3× in phosphate buffered saline, and fixed in 2.5 % gluteraldehyde. Electron micrographs were taken using a Cambridge Stereoscan 360 iXP scanning electron microscope at the Electron Microscopy Platform at the Umeå University Core Facility for Electron Microscopy
Fig. 2.
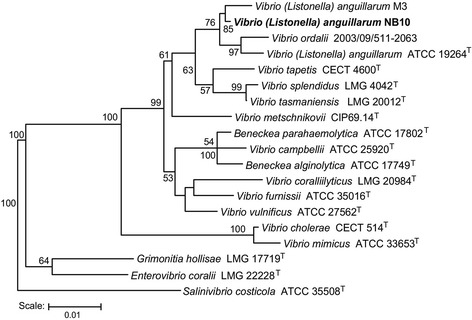
Phylogenetic tree of 16S RNA sequences highlighting the V. anguillarum NB10 position relative to other Vibrio and Beneckea strains. Type strains are indicated with a superscript "T". The strains and their corresponding GenBank accession numbers for 16S rRNA genes are: V. anguillarum M3, AY035897; V. anguillarum NB10 (chromosome 1, 233,624-235,167 bp), V. ordalii 2003/09/511-2063, AY530930; V. anguillarum ATCC 19264T, X16895; V. ordalii ATCC 33509, NR_044851; V. tapetis CECT 4600T, Y08430; V. splendidus LMG 4042T, AJ515230; V. tasmaniensis LMG 20012T, AJ316192; V. metschnikovii CIP 69.14T, X74711; B. parahaemolytica ATCC 17802T, AF388386; V. campbellii ATCC 25920T, X56575; B. alginolytica ATCC 17749T, X74690; V. coralliilyticus LMG 20984T, AJ440005; V. furnissii ATCC 35016T, X76336; V. vulnificus ATCC 27562T, X76333; V. cholerae CECT 514T, X76337; and V. mimicus ATCC 33653T, X74713. For outgroup strains, Grimonitia hollisae LMG 17719T, AJ514909; Enterovibrio coralii LMG 22228T, AJ842343; and Salinivibrio costicola ATCC 35508TT, X74699 were used. The tree uses sequences aligned by the RDP aligner, and uses the Jukes-Cantor corrected distance model to construct a distance matrix based on alignment model positions without the use of alignment inserts, and uses a minimum comparable position of 200. The tree is built with RDP Tree Builder, which uses Weighbor [52] with an alphabet size of 4 and length size of 1000. The building of the tree also involves a bootstrapping process repeated 100 times to generate a majority consensus tree [53]. Bar equals 1% sequence difference. Only significant bootstrap values are indicated
Genome sequencing information
Genome project history
Vibrio anguillarum strain NB10 is highly virulent for marine fish and was isolated from the Gulf of Bothnia, a brackish sea off the coast of Norrbyn, Sweden [12, 18]. Genome sequencing was performed by Eurofins MWG GmbH and the Norwegian Sequencing Centre. Finishing and annotation of the genome was performed at the Department of Molecular Biology at Umeå University and at the Department of Chemistry at UiT:The Arctic University of Tromsø, respectively. The genome project has been deposited at the European Nucleotide Archive under the ID number 251627 and accession number PRJEB5701. The accession number for plasmid p67-NB10 is LK021128, for chromosome 1 is LK021130, and for chromosome 2 is LK021129. A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2 and Table S1.
Table 2.
Project information
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS 31 | Finishing quality | Completed |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | 400-600-bp fragments (454), >10-kb fragments (PacBio) |
| MIGS 29 | Sequencing platforms | Roche 454 Life Sciences |
| Pacific Biotechnologies PacBio | ||
| MIGS 31.2 | Fold coverage | 60 × |
| MIGS 30 | Assemblers | Staden-gap4, Newbler (Roche/454 GS FLX), SMRTanalysis, version 2.0.1, HGAP module (Celera and Quiver) |
| MIGS 32 | Gene calling method | Glimmer3, tRNAscan-SE 1.21, Rfam, RNAmmer |
| Locus Tags | VANGcI, VANGcII, VANGp67 | |
| Genbank ID | GCA000786425 | |
| GenBank Date of Release | September 1, 2014 | |
| GOLD ID | Gp0102007 | |
| BIOPROJECT | PRJEB5701 | |
| MIGS 13 | Source Material Identifier | NB10 |
| Project relevance | Aquaculture, fish pathogen |
Growth conditions and genomic DNA preparation
Vibrio anguillarum NB10 was grown in tryptone soy broth containing 1 % sodium chloride with shaking at 24 oC overnight. For the Roche 454 and PacBio genomic sequencing, genomic DNA was extracted using the Qiagen DNeasy blood and tissue kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For gap closures, the genomic DNA, which was used as template for Sanger sequencing, was extracted using the Qiagen Blood and Cell Culture Midi Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using the Roche/454 GS FLX system equipped with Data Analysis Software Modules v.2.3 [19]. A total of 442,045 reads representing 20-fold coverage of the genome were assembled using the Roche genome assembler Newbler. The assembly resulted in 112 contigs >500 bp. Custom primers were designed to anneal to the ends of the contigs. Gaps between contigs were closed by PCR amplification followed by fragment sequencing. Several gaps could not be closed using this method due to long stretches of repeated sequences. Consequently, the total genome was sequenced a second time using the Pacific Biotechnologies PacBio RS II single-molecule, real-time sequencing technology. Library construction, which contains >10-kb fragments, and sequencing using the PacBio RS II system were performed according to Pacific Biosciences instructions, which may be found on their website [20]. A total of 60,000 reads with a genome coverage of 60-fold were obtained. The sequence reads were assembled using a hierarchical genome-assembly process module from Pacific Biosciences [21]. The HGAP module utilizes the Smrtanalysis, version 2.0.1 to assemble the raw sequence reads and corrects the longest reads utilizing the smaller reads to find a consensus sequence. The corrected reads were then assembled using the Celera Assembler and Quiver softwares resulting in two large contigs associating with chromosome 1 and 2 as well as one small contig representing the plasmid. Error rate of the completed genome sequence using the PacBio RS II system is less than 17 in 50,000 base pairs and the error rate for the Roche/454 GS FLX system is less than 1 in 100,000 base pairs.
Genome annotation
Coding sequences were predicted using the Glimmer3 program [22]. The numbering of CDSs for each chromosome follows clockwise from the end of the predicted origins of replication at 367 nt and 366 nt for chromosome 1 and 2, respectively. These CDSs were translated, and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information nonredundant database as well as the Uniprot and InterPro databases followed by manual curation to assign functional annotation. Using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool [23], homology searches of all CDSs were done against the Clusters of Orthologous Groups database [24] enabling the assignment of COG functional categories to the CDSs. The tRNAscan-SE 1.21 tool [25, 26] was used to identify tRNA genes; the RNAmmer 1.2 program [27] was used to identify rRNA genes; and the Rfam database [28] and manual curation was used to identify other non-coding RNAs. SignalP server versions 3.0 and 4.0 [29, 30] were used to predict proteins that have signal peptides utilized to target proteins for secretion. The TMHMM server version 2.0 [31] was used to predict transmembrane helices in the proteins. The PHAge Search Tool [32] was used to detect prophage sequences within the genomes. Potential genomic islands were identified using the IslandViewer web server [33] and putative insertion sequences were identified using ISFinder [34]. Putative chromosomal origins of replication were located using the Ori-Finder program [35] followed by manual curation with the help of V. cholerae studies that characterized the origins of replication for chromosome 1 [36–38] and chromosome 2 [36, 39, 40] in this organism.
Genome properties
The complete genome of V. anguillarum NB10 includes two circular chromosomes totaling 4,307,037 bp and one circular plasmid p67-NB10 totaling 66,798 bp, which together give a total genome size of 4,373,835 bp with an average GC content of 44.4 %. Putative oriC origins of replication were identified for both chromosomes. For chromosome 1, an oriCI region similar to that found in other γ-proteobacteria was found and spans 481 nucleotides (3,119,582 - 367 nt) [36–38]. For chromosome 2, an oriCII region similar to that of V. cholerae and other Vibrio species [36, 39, 40] was found and spans 366 nucleotides (1-366 nt). In addition, an incII incompatibility region similar to that of V. cholerae was found upstream of the oriCII region (1,186,667 - 1,187,342 nt). In V. cholerae, incII negatively regulates chromosome II replication [36, 39]. Of the 3,912 genes predicted, 3,783 encode proteins, 25 encode rRNAs, 91 encode tRNAs, and at least 13 encode ncRNAs. Fifty-five pseudogenes were found with 33 located on chromosome 1, 21 located on chromosome 2, and 1 located on p67-NB10. Of the predicted CDSs, a functional prediction was made for 84.8 % and 66.9 % were assigned a putative COG function with the remaining annotated as hypothetical proteins. The plasmid is a pJM1-like virulence plasmid that contains 58 protein-coding genes. Four new insertion sequences, named ISVa3, ISVa4, ISVa5, and ISVa6, were identified in this strain and were submitted to ISfinder database [41]. A total of 78 insertion elements were found: 34 on chromosome 1, 31 on chromosome 2, and 13 on p67-NB10. A putative 44.1-kb intact prophage was identified on chromosome 1 and this region is predicted to encode 69 proteins, of which most are phage-related proteins and 33 are hypothetical or uncharacterized proteins. In addition, one questionable prophage was found on chromosome 2 and an incomplete prophage was also found on chromosome 1. The properties and the statistics of the genome are summarized in Tables 3, 4 and 5 and in Figs. 3 and 4.
Table 3.
Summary of genome: two chromosomes and one plasmid
| Label | Size (Mb) | Topology | INSDC identifier | RefSeq ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosome 1 | 3.12 | Circular | LK021130 | NZ_LK021130.1 |
| Chromosome 2 | 1.19 | Circular | LK021129 | NZ_LK021129.1 |
| Plasmid p67-NB10a | 0.07 | Circular | LK021128 | NZ_LK021128.1 |
aThis plasmid is a pJM1-like virulence plasmid [42]
Table 4.
Genome statistics
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 4,373,835 | 100.0 |
| DNA coding (bp) | 3,762,570 | 86.0 |
| DNA G + C (bp) | 1,940,626 | 44.4 |
| DNA scaffolds | 3 | |
| Total genes | 3,912 | 100.0 |
| Protein coding genes | 3,783 | 96.7 |
| RNA genes | 129 | 3.3 |
| Pseudo genes | 55 | 1.4 |
| Genes in internal clusters | 447 | 11.4 |
| Genes with function prediction | 3,317 | 84.8 |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 2,620 | 66.9 |
| Genes with Pfam domains | 3,317 | 84.8 |
| Genes with signal peptides | 592 | 15.1 |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 1,037 | 26.5 |
| CRISPR repeats | 0 | 0.0 |
The total is based on either the size of the genome in base pairs or the total number of protein coding genes in the annotated genome
Table 5.
Number of genes associated with general COG functional categories
| Code | Value | % age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 180 | 4.8 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | 1 | 0.0 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 219 | 5.8 | Transcription |
| L | 157 | 4.2 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 0 | 0 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 34 | 0.9 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| V | 47 | 1.2 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 197 | 5.2 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 161 | 4.3 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 117 | 3.1 | Cell motility |
| U | 87 | 2.3 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion |
| O | 126 | 3.3 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 170 | 4.5 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 189 | 5.0 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 272 | 7.2 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 77 | 2.0 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 138 | 3.6 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 78 | 2.1 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 155 | 4.1 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 57 | 1.5 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 332 | 8.8 | General function prediction only |
| S | 234 | 6.2 | Function unknown |
| - | 1163 | 30.7 | Not in COGs |
The total is based on the total number of protein coding genes in the genome
Fig. 3.
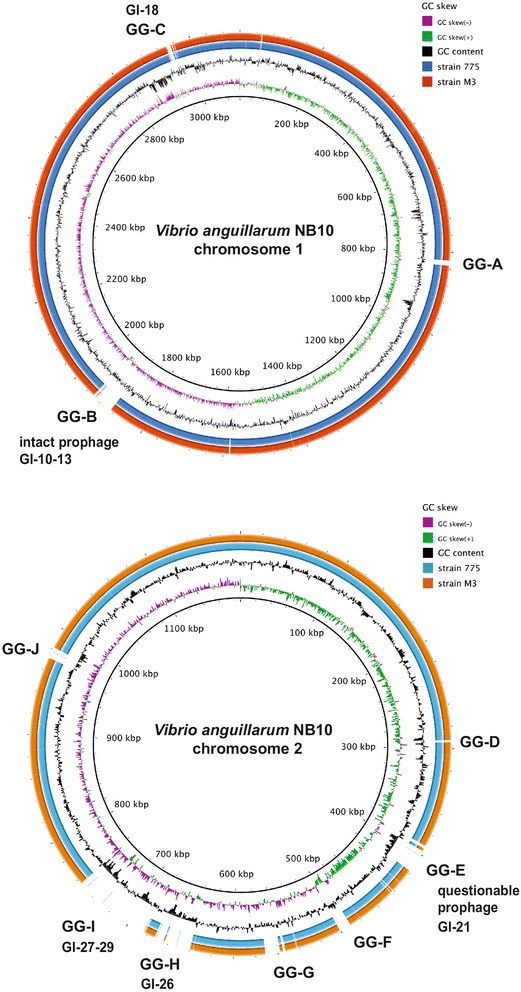
BRIG blast analyses of the two V. anguillarum serotype O1 chromosomes. The genome of strain NB10 was used as the reference genome (the inner circle) and compared to the sequenced genomes of strains 775 (blue circle) and M3 (orange circle). Regions showing genomic gaps (GGs) that are missing in strains 775 and M3 are uncolored and are labeled using GG-A to GG-J. In addition, the genomic islands (GIs) and the prophage that are embedded within these genomic gaps are indicated. Refer to Table 7 for exact locations and sizes of the prophages, GIs, and GGs
Fig. 4.
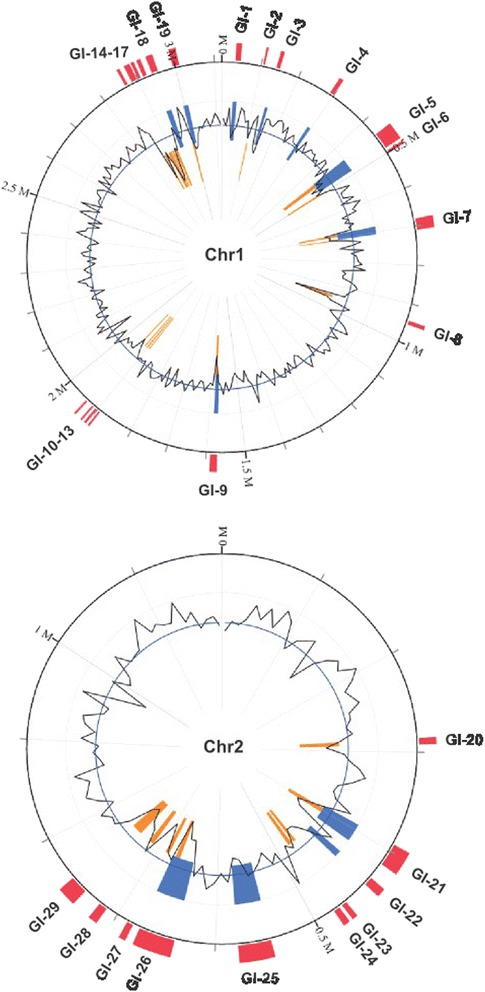
Genomic islands (GIs) of strain NB10 as predicted by the IslandViewer web server. Predicted GIs are colored within the circular image based on the tools used: SIGI-HMM, which predicts GIs based on a hidden Markov model (orange); IslandPath-DIMOB, which predicts GIs based on features associated with genomic islands, such as sequence bias, tRNAs, and integrases and transposases (blue), and an integration of three methods IslandPath-DIMOB, SIGI-HMM and IslandPick, which predicts based on comparative genomics (red). The black line represents the percent GC
Insights from the genome sequence
Comparison to other fully sequenced V. anguillarum serotype O1 strains
The genome of V. anguillarum strain NB10 was compared to the published genomes of V. anguillarum serotype O1 strains 775 and M3 [10, 11]. The results are summarized in Table 6. The origin of replication for chromosome 1 oriCI is identical in all three strains and for chromosome 2, the NB10 oriCII is 99 % identical to that of the 775 and M3. For NB10, we chose to start both chromosomes at their respective origins of replication. The compositional symmetry reflected in the chromosomal GC skews shown in Fig. 3 supports correct trimming of the NB10 replicons. The plasmids in all three strains differ by only a few hundred base pairs, are highly identical with each other, and encode a siderophore-based iron-utilization system that is required for virulence [42, 43]. Compared to strains 775 and M3, the NB10 chromosome 1 is larger by about 56,000 bp and chromosome 2 is increased by about 199,000 bp. To determine if the extra 255,000 bp is unique to the NB10 strain, a BLAST comparison of the three genomes using the BRIG (Blast Ring Image Generator) program [44] and using NB10 as the reference strain was done (Fig. 3). Since horizontal transfer of DNA is a common method for acquiring new DNA in strains, we also screened the three genomes using similar parameters for genomic islands and prophages using the IslandViewer and PHAST search tools and the presence of integrons was determined by identifying attC sites, a feature of small mobile gene cassettes that are captured by integrons [45]. These data are summarized in Table 6 and predict that NB10 contains two prophages, a 44.1-kb intact and 45.7-kb questionable, that are not found in strains 775 and M3 and more GIs, of which many are unique, compared to strains 775 and M3. Table 7 presents the location, size, and predicted CDSs for each of the predicted prophages, GIs, and gaps of sequences that are missing in strain 775 and M3. These genomic differences are discussed in detail below.
Table 6.
Genome comparisons of sequenced V. anguillarum serotype O1 strains
| Strain | NB10 | 775 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosome 1 (bp) | 3,119,695 | 3,063,912 | 3,063,587 |
| Chromosome 2 (bp) | 1,187,342 | 988,135 | 988,134 |
| Plasmid (bp) | 66,798 | 65,009 | 66,164 |
| Total CDSsa | 3,782 | 3,880 | 3,824 |
| Prophage | |||
| intact | 44.1 kb | 0 | 0 |
| incomplete | 8.3 kb | 8.3 kb | 25.7 kb |
| 8.3 kb | |||
| questionable | 45.7 kb | 0 | 0 |
| Genomic Islandsb | |||
| Chr1 | 19 (208.2 kb) | 18 (209.5 kb) | 17 (211.6 kb) |
| Chr2 | 10 (147.0 kb) | 8 (74.3 kb) | 5 (62.5 kb) |
| Number of attC sitesc | 65 | 64 | 68 |
aAnnotation of the NB10 strain included fewer CDSs under 200 bp than that of strains 775 and M3
bNumbers represent all genomic islands detected by the IslandViewer tool irrespective of their size or content
cNumbers indicate attC sites found with a consensus sequence of 5'-TAACAAACGnnTCAAGAGGGAnnGnCAACGC-3'. This sequence makes up a repeat region at the 5’end of the 126-127-bp attC sites within the NB10 strain, (unpublished data, K.O. Holm) and indicates the number of integron-associated gene cassettes found in each strain [48]. The attC sites occur solely within chromosome 2 but are distributed differently in the three strains
Table 7.
Unique sequences in V. anguillarum NB10 identified by genome comparisons
| Base pairs | Size (kb) | CDSs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosome 1 | |||
| Prophage | |||
| Intact | 1,891,762…1,935,924 | 44.1 | 69 |
| Partial | 2,964,881…2,973,261 | 8.3 | 8 |
| Genomic Islands | |||
| GI-1 | 34,299…47,256 | 12.9 | 12 |
| GI-2 | 104,658…109,015 | 4.3 | 5 |
| GI-3 | 138,956…147,914 | 8.9 | 12 |
| GI-4 | 288,556…298,943 | 10.3 | 15 |
| GI-5 | 445,355…487,284 | 41.9 | 37 |
| GI-6 | 494,899…502,274 | 7.3 | 5 |
| GI-7 | 681,585…709,820 | 28.2 | 27 |
| GI-8 | 942,447…952,116 | 9.6 | 9 |
| GI-9 | 1,572,019…1,589,186 | 17.1 | 13 |
| GI-10-13 | 1,891,012…1,937,302 | 46.2 | 61 |
| GI-14-17 | 2,864,895…2,925,178 | 60.2 | 54 |
| GI-18 | 2,938,796…2,955,240 | 16.4 | 17 |
| GI-19 | 2,994,229…3,011,196 | 16.9 | 14 |
| Genome gaps a | |||
| GG-A | 820,080…832,800 | 12.7 | 12 |
| GG-B | 1,888,140…1,934,940 | 46.8 | 76 |
| GG-C | 2,938,440…2,951,880 | 13.4 | 13 |
| Chromosome 2 | |||
| Prophage | |||
| Questionable | 401,647…447,433 | 45.7 | 22 |
| Genomic Islands | |||
| GI-20 | 286,348…292,555 | 6.2 | 5 |
| GI-21 | 392,736…414,906 | 22.1 | 22 |
| GI-22 | 431,537…439,839 | 8.3 | 12 |
| GI-23 | 464,750…469,836 | 5.1 | 5 |
| GI-24 | 473,125…479,299 | 6.1 | 10 |
| GI-25 | 546,066…578,220 | 32.1 | 35 |
| GI-26 | 639,559…674,888 | 35.3 | 24 |
| GI-27 | 682,155…688,431 | 6.2 | 6 |
| GI-28 | 711,800…720,165 | 8.3 | 6 |
| GI-29 | 738,270…755,649 | 17.3 | 10 |
| Genome gaps a | |||
| GG-D | 292,140…294,360 | 1.9 | 3 |
| GG-E | 396,120…417,780 | 21.6 | 13 |
| GG-F | 489,780…500,880 | 11.1 | 19 |
| GG-G | 557,580…571,320 | 13.7 | 11 |
| GG-H | 643,380…673,560 | 34.0 | 22 |
| GG-I | 682,320…756,540 | 74.2 | 53 |
| GG-J | 971,280…981,740 | 10.5 | 9 |
aGaps indicate regions of the NB10 genome that are not found in the genomes of strains 775 and M3 as detected by BLAST searches using the BRIG program [44]
Prophage regions
Prophages are bacteriophages that are integrated into the genome and that are diverse mobilizable elements that play a role in horizontal gene transfer. Three putative prophage regions were identified (Table 7 and Fig. 3). Chromosome 1 contains a partial 8.7-kb prophage (Phage_Bacill_G) that is also found in the 775 and M3 genomes and an intact prophage (Phage_Pseudo_vB_PaeS_PMG1) with a size of 44.1 kb that is unique to strain NB10 and that encodes 43 phage-related and 33 hypothetical proteins. Chromosome 2 contains a questionable 45.7-kb prophage (Phage_Stx2) that is also unique to strain NB10. In comparison, strain 775 contains no additional prophages; while, strain M3 contains a second partial 27.5-kb prophage (Phage_Entero_M13) on chromosome 2.
Genomic Islands (GIs)
Genomic islands (GIs) are clusters of genes, typically >8 kb in size, that likely originate from horizontal gene transfers and that often play a role in the adaptation of bacteria to their environment or host [46]. GIs impact bacterial evolution significantly and the identification of GIs within genomes provides insight into differences between bacterial species and strains. For strain NB10, 29 putative GIs that range from 4.2 kb to 41.9 kb were detected using the IslandViewer tool (Table 7). Of these, 19 are localized to chromosome 1 and 10 to chromosome 2 (Fig. 4). Twenty GIs contain genes that are often associated with the islands, such as tRNAs, transposases, integrases, and phage-related genes. Of the nine that do not contain these typifying genes, GI-4 contains CDSs encoding ribosomal proteins, while GIs-8,14-17 contain CDSs involved in O-antigen biosynthesis. Nineteen of the GIs are found in strains 775 and M3; while, 10 GIs are unique to strain NB10 and their genomic locations are shown in Fig. 3. Overall analyses of the CDSs within all GIs indicate that most encode hypothetical proteins. No obvious virulence genes were detected; however, 7 GIs carried CDSs for toxin-antitoxin systems, in particular that of hipAB, which plays a role in antibiotic tolerance and persistence [47].
Integrons
Integrons are genetic units that contain and disseminate small mobile elements called gene cassettes and thus contribute to genomic diversity [45]. Gene cassettes carry a gene, any gene, and an attC site, which is recognized by an integron enabling it to splice cassettes into its integration site. The integration of gene cassettes may occur over and over creating a string of gene cassettes. A consensus V. anguillarum NB10 attC site sequence repeat was predicted (5'-TAACAAACGnnTCAAGAGGGAnnGnCAACGC-3', unpublished data, K.O. Holm) [48] and used to identify integrons by localizing attC sites in the three different genomes. In all strains, attC sites were localized only in chromosome 2 and the number of attC sites did not differ much. However, in NB10, the location of the attC sites were all found within a 154.4-kb region, which represents 3.5 % of the genome and lends support to this location representing a putative superintegron with highly diverse gene cassettes of mostly unknown functions. In particular, this putative superintegron is highly similar to that characterized in the V. cholerae strain N16961 since the NB10 integrase shares identity with the V. cholerae VchIntIA integrase [48]. In contrast, for strains 775 and M3, the attC sites were found at 5 different locations distributed throughout chromosome 2. Whether this difference reflects putative geographical and/or different ancestral characteristics needs further investigation.
Genomic regions unique to strain NB10
The NB10 genome is around 255,000 bp larger than the genomes of strains 775 and M3. A comparative analysis using BRIG was performed to identify CDSs unique to NB10. Figure 3 indicates the location of 10 genomic gaps ranging from 1.9 kb to 74.2 kb in strains 775 and M3 compared to strain NB10. Table 7 gives the base pair coordinates for each gap. All but one genomic gap (GG-G), which was found on chromosome 1 of strains 775 and M3, contained CDSs unique to strain NB10. The majority of these CDSs encode hypothetical proteins. However, a few CDSs were identified that may provide strain NB10 an advantage either in its host or in its aquatic environment. The GG-A contains a CDS for a haem peroxidase that may play a role in oxidative stress aiding colonization of the host [49]. Numerous CDSs encode putative toxin-antitoxin systems, which have been reported to play a role in antibiotic tolerance, persistence, stress response, and virulence in some bacteria [50]. Many of the CDSs within these genomic gaps may be genes with not yet known functions, as they were not found within other bacterial species using a BLAST search.
Conclusions
In this study, the complete genome sequence of the V. anguillarum strain NB10 serotype O1, a virulent isolate from the Gulf of Bothnia, Norrbyn, Sweden, is presented. Genome comparisons were done with the complete genomes of two other virulent, O1 serotype V. anguillarum strains, M3 and 775. Although the genomes of M3 and 775 strains are quite similar in size, the genome from the NB10 strain was shown to contain an extra 255,000 bp that are unique to this strain. The extra DNA is predicted to contain two putative prophages as well as a number of GIs and genomic gaps, all of which are predicted to encode mostly hypothetical proteins with no obvious roles in virulence. The roles of the extra genomic sequences found in the V. anguillarum strain NB10 compared to strains 775 and M3 remain to be determined. However, a few genes were found in the extra DNA regions that may be predicted to aid the survival of strain NB10 in its host or its natural habitat, the brackish Baltic Sea, which contains both salty and fresh water [12]. Thus, in comparison to the M3 and 775 strains, which were isolated from different types of geographical regions [10, 11], it is tempting to speculate that the CDSs within the extra sequences may play a role in the ecology of strain NB10.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Per Hörstedt for performing the scanning electron microscopy techniques. This work was performed within the Umeå Centre for Microbial Research and within the Centre of Bioinformatics, Faculty of Science and Technology of UiT: Arctic University of Norway. These studies were supported by funding provided to DLM from the Swedish Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning (221-2O1 0–577), from the Swedish Research Council, and from the Natural Science Faculty of Umeå University and by funding from UiT: Arctic University of Norway and by support from The ELIXIR.NO project.
Abbreviations
- BRIG
Blast ring image generator
- GG
Genomic gaps
- GI
Genomic islands
- HAMAP
High-quality automated and manual annotation of proteins
- HGAP
Hierarchical genome-assembly process
- IS
Insertion elements
- Pfam
Protein families
- PHAST
Phage search tool
- PROSITE
Protein domains families and functional sites
- TMHMM
Tied mixture hidden markov model
Additional file
Associated MIGS record. (DOC 70 kb)
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
KOH, KN, and EH assembled contigs into a final genome sequence. KOH and EH annotated the genome and performed genomic comparisons and analyses. NPW and DLM conceived of and designed and coordinated the study. DLM and KOH drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Kåre Olav Holm, Email: kare.olav.holm@uit.no.
Kristina Nilsson, Email: kristina.nilsson@molbiol.umu.se.
Erik Hjerde, Email: erik.hjerde@uit.no.
Nils-Peder Willassen, Email: nils-peder.willassen@uit.no.
Debra L. Milton, Email: debra.milton@molbiol.umu.se
References
- 1.Frans I, Michiels CW, Bossier P, Willems KA, Lievens B, Rediers H. Vibrio anguillarum as a fish pathogen: virulence factors, diagnosis and prevention. J Fish Dis. 2011;34:643–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2011.01279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Actis LA, Tolmasky ME, Crosa JH. Vibriosis. In: Woo PTK, Bruno DW, editors. Fish Diseases and Disorders. Oxfordshire, UK: CABI International; 2011. pp. 570–605. [Google Scholar]
- 3.MacDonell MT, Colwell RR. Phylogeny of the Vibrionaceae, and recommendation of two new genera, Listonella and Shewanella. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:171–182. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(85)80051-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Thompson FL, Thompson CC, Dias GM, Naka H, Dubay C, Crosa JH. The genus Listonella MacDonell and Colwell 1986 is a later heterotypic synonym of the genus Vibrio Pacini 1854 (Approved Lists 1980)--a taxonomic opinion. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2011;61:3023–3027. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.030015-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pedersen K, Grisez L, van Houdt R, Tiainen T, Ollevier F, Larsen JL. Extended serotyping scheme for Vibrio anguillarum with the definition and characterization of seven provisional O-serogroups. Curr Microbiol. 1999;38:183–189. doi: 10.1007/PL00006784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sorensen UB, Larsen JL. Serotyping of Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986;51:593–597. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.593-597.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tiainen T, Larsen JL, Pelkonen S. Characterization of Vibrio anguillarum strains isolated from diseased fish in Finland. Acta Vet Scand. 1994;35:355–362. doi: 10.1186/BF03548308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Naka H, Crosa JH. Genetic determinants of virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Pathol. 2011;46:1–10. doi: 10.3147/jsfp.46.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Frans I, Dierckens K, Crauwels S, Van Assche A, Leisner J, Larsen MH, Michiels CW, Willems KA, Lievens B, Bossier P, et al. Does virulence assessment of Vibrio anguillarum using sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae correspond with genotypic and phenotypic characterization? PLoS One. 2013;8 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Naka H, Dias GM, Thompson CC, Dubay C, Thompson FL, Crosa JH. Complete genome sequence of the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum harboring the pJM1 virulence plasmid and genomic comparison with other virulent strains of V. anguillarum and V. ordalii. Infect Immun. 2011;79:2889–2900. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05138-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li G, Mo Z, Li J, Xiao P, Hao B. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio anguillarum M3, a serotype O1 strain isolated from Japanese flounder in china. Genome Announc. 2013;1:5. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00769-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rehnstam AS, Norqvist A, Wolf-Watz H, Hagstrom A. Identification of Vibrio anguillarum in fish by using partial 16S rRNA sequences and a specific 16S rRNA oligonucleotide probe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989;55:1907–1910. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1907-1910.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Milton DL, O'Toole R, Horstedt P, Wolf-Watz H. Flagellin A is essential for the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:1310–1319. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.5.1310-1319.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ormonde P, Horstedt P, O'Toole R, Milton DL. Role of motility in adherence to and invasion of a fish cell line by Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:2326–2328. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2326-2328.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McGee K, Horstedt P, Milton DL. Identification and characterization of additional flagellin genes from Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:5188–5198. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.17.5188-5198.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang SY, Lauritz J, Jass J, Milton DL. Role for the major outer-membrane protein from Vibrio anguillarum in bile resistance and biofilm formation. Microbiol. 2003;149:1061–1071. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Denkin SM, Nelson DR. Regulation of Vibrio anguillarum empA metalloprotease expression and its role in virulence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:4193–4204. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.7.4193-4204.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Norqvist A, Hagstrom A, Wolf-Watz H. Protection of rainbow trout against vibriosis and furunculosis by the use of attenuated strains of Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989;55:1400–1405. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1400-1405.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Roche 454 GS FLX system equipped with Data Analysis Software Modules v.2.3 [http://454.com/products/gs-flx-system/index.asp].
- 20.PacBio RS II system [http://www.pacificbiosciences.com/products/].
- 21.Chin CS, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, Clum A, Copeland A, Huddleston J, Eichler EE, et al. Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat Methods. 2013;10:563–569. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:673–679. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tatusov RL, Koonin EV, Lipman DJ. A genomic perspective on protein families. Science. 1997;278:631–637. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5338.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:955–964. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.5.0955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM. The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:W686–689. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rodland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:3100–3108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Griffiths-Jones S, Moxon S, Marshall M, Khanna A, Eddy SR, Bateman A. Rfam: annotating non-coding RNAs in complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:D121–124. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods. 2011;8:785–786. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:953–971. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol. 2001;305:567–580. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhou Y, Liang Y, Lynch KH, Dennis JJ, Wishart DS. PHAST: a fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W347–352. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Langille MG, Brinkman FS. IslandViewer: an integrated interface for computational identification and visualization of genomic islands. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:664–665. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Siguier P, Perochon J, Lestrade L, Mahillon J, Chandler M. ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D32–36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gao F, Zhang CT. Ori-Finder: a web-based system for finding oriCs in unannotated bacterial genomes. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Egan ES, Waldor MK. Distinct replication requirements for the two Vibrio cholerae chromosomes. Cell. 2003;114:521–530. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00611-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rajewska M, Wegrzyn K, Konieczny I. AT-rich region and repeated sequences - the essential elements of replication origins of bacterial replicons. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012;36:408–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Saha A, Haralalka S, Bhadra RK. A naturally occurring point mutation in the 13-mer R repeat affects the oriC function of the large chromosome of Vibrio cholerae O1 classical biotype. Arch Microbiol. 2004;182:421–427. doi: 10.1007/s00203-004-0708-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Venkova-Canova T, Saha A, Chattoraj DK. A 29-mer site regulates transcription of the initiator gene as well as function of the replication origin of Vibrio cholerae chromosome II. Plasmid. 2012;67:102–110. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2011.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yamaichi Y, Gerding MA, Davis BM, Waldor MK. Regulatory cross-talk links Vibrio cholerae chromosome II replication and segregation. PLoS Genet. 2011;7 doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.ISFinder database [https://www-is.biotoul.fr//].
- 42.Di Lorenzo M, Stork M, Tolmasky ME, Actis LA, Farrell D, Welch TJ, Crosa LM, Wertheimer AM, Chen Q, Salinas P, et al. Complete sequence of virulence plasmid pJM1 from the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum strain 775. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:5822–5830. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.19.5822-5830.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Crosa JH. A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature. 1980;284:566–568. doi: 10.1038/284566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:402. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hall RM. Integrons and gene cassettes: hotspots of diversity in bacterial genomes. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2012;1267:71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Langille MG, Hsiao WW, Brinkman FS. Detecting genomic islands using bioinformatics approaches. Nature Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:373–382. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Germain E, Castro-Roa D, Zenkin N, Gerdes K. Molecular mechanism of bacterial persistence by HipA. Mol Cell. 2013;52:248–254. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cambray G, Guerout AM, Mazel D. Integrons. Ann Rev Genet. 2010;44:141–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Welinder KG. Bacterial catalase-peroxidases are gene duplicated members of the plant peroxidase superfamily. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1080:215–220. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90004-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mutschler H, Meinhart A. Epsilon/zeta systems: their role in resistance, virulence, and their potential for antibiotic development. J Mol Med. 2011;89:1183–1194. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0797-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lindell K, Fahlgren A, Hjerde E, Willassen NP, Fallman M, Milton DL. Lipopolysaccharide O-antigen prevents phagocytosis of Vibrio anguillarum by rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skin epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2012;7 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bruno WJ, Socci ND, Halpern AL. Weighted neighbor joining: a likelihood-based approach to distance-based phylogeny reconstruction. Mol Biol Evol. 2000;17:189–197. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM. The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D169–172. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:541–547. doi: 10.1038/nbt1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Garrity GM, Holt JG. The Road Map to the Manual. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholtz RW, editors. Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. 2. New York: Springer; 2001. pp. 119–169. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Class III. Gammaproteobacteria class. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, editors. Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Part B, 2. New York: Springer; 2005. p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- 58.List-Editor Validation of publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSEM. List no. 106. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2005;55:2235–2238. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA. Approved lists of bacterial names. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1980;30:225–420. doi: 10.1099/00207713-30-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA. Approved lists of bacterial names amended. In: Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA, editors. Approved Lists of Bacterial Names (Amended) Washington DC: ASM Press; 1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Veron M. The taxonomic position of Vibrio and certain comparable bacteria. Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des seances de l'Academie des sciences Serie D: Sciences naturelles. 1965;261:5243–5246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pacini F. Osservazione microscopiche e deduzioni patologiche sul cholera asiatico. Gazette Medicale de Italiana Toscano Firenze. 1854;6:405–412. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shewan J, Veron M: Genus I. Vibrio Pacini 1854, 411. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE, editors. Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 8. Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Co; 1974. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bergman AM. Die rote Beulenkrankheit des Aals. Bericht aus der Koniglichen Bayerischen Versuchsstation. 1909;2:10–54. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


