Abstract
AIM: To determine whether the combination of platelet count (PLT) with spleen volume parameters and right liver volume (RV) measured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could predict the Child-Pugh class of liver cirrhosis and esophageal varices (EV).
METHODS: Two hundred and five cirrhotic patients with hepatitis B and 40 healthy volunteers underwent abdominal triphasic-enhancement MRI and laboratory examination of PLT in 109/L. Cirrhotic patients underwent endoscopy for detecting EV. Spleen maximal width (W), thickness (T) and length (L) in mm together with spleen volume (SV) and RV in mm3 were measured by MRI, and spleen volume index (SI) in mm3 was obtained by W × T × L. SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RV × PLT/SV (RVPS) were calculated and statistically analyzed to assess cirrhosis and EV.
RESULTS: SV/PLT (r = 0.676) and SI/PLT (r = 0.707) increased, and PLT (r = -0.626) and RVPS (r = -0.802) decreased with the progress of Child-Pugh class (P < 0.001 for all). All parameters could determine the presence of cirrhosis, distinguish between each class of Child-Pugh class, and identify the presence of EV [the areas under the curve (AUCs) = 0.661-0.973]. Among parameters, RVPS could best determine presence and each class of cirrhosis with AUCs of 0.973 and 0.740-0.853, respectively; and SV/PLT could best identify EV with an AUC of 0.782.
CONCLUSION: The combination of PLT with SV and RV could predict Child-Pugh class of liver cirrhosis and identify the presence of esophageal varices.
Keywords: Cirrhosis, Spleen, Hepatic lobe, Magnetic resonance imaging, Platelet count
Core tip: This study determined whether and how the combination of platelet count (PLT) with spleen volume (SV) and right liver volume (RV) by MRI could predict the Child-Pugh class of liver cirrhosis and esophageal varices (EV). We confirmed that the ratio of SV/PLT increased with the progress of Child-Pugh class, PLT and RVPS (RV × PLT/SV) decreased with the progress of Child-Pugh class. As a new combined parameter, RVPS can be an optimized marker to identify the occurrence of cirrhosis and differentiate the Child-Pugh class. SV/PLT could be recommended for identifying the presence of EV.
INTRODUCTION
Post-hepatitis cirrhosis is a frequent disorder worldwide, and could lead to severe complications such as esophageal varices (EV) and liver failure, which are directly related to the mortality of cirrhosis patients[1-2]. The new concept in management of cirrhosis patients is early intervention to stabilize disease progression, and to avoid or delay clinical decompensation[1]. Therefore, noninvasive and reliable evaluation of the severity of cirrhosis is critically important for management. The modified Child-Pugh classification system (CPS) has been confirmed as an important predictive index for cirrhotic patients, and is an extensively used and reported system in assessment of the severity of cirrhosis[3-5]. However, CPS has several drawbacks which could be influenced by a variety of internal and external factors in cirrhosis patients. For example, all patients with bilirubin > 51 μmol/L were considered to have a score of three in the CPS, despite that they may have different prognosis[6]. Better dynamic and repeatable non-invasive tools are needed to monitor and classify the severity of cirrhosis.
Recently, the most commonly reported parameters for assessing cirrhosis include low platelet count (PLT) and large spleen size on ultrasound as well as high Child-Pugh score[7-10], and there were increasing numbers of studies for evaluating the severity of cirrhosis using the spleen function and splenomegaly[11,12]. Furthermore, the novel index by the combined PLT to spleen diameter ratio was reported to identify cirrhotic patients with EV, which was based on the routine laboratory and ultrasound examinations[13]. However, none of the above-mentioned methods were accurate enough. For example the assessment of the spleen size by ultrasound was always affected by the position of the spleen or bowel gas[14].
With recent advances in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is safe and repeatable, it plays a progressively more significant role in evaluation of cirrhosis[15-17]. Previous research showed that the decrease of right liver lobe volume (RV) was positively correlated with the severity of cirrhosis and prognosis[18]. However, the combination of RV, spleen volume parameters and PLT in a single score has not been tested for assessing cirrhosis. This study aimed at determining whether the combination of PLT with spleen volume parameters and RV measured by MRI is associated with the severity of cirrhosis and EV.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
This study was reviewed and approved by the Committee for Ethical Review of Research involving Human Subjects of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College.
Patients
Form October 2012 to May 2014, 218 consecutive cirrhotic patients treated in our institution were enrolled into the study according to the inclusion criteria as described in detail previously[15]: (1) cirrhosis resulting from hepatitis B was diagnosed according to practice guidelines of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD)[19]; (2) participants received available endoscopy for detection of EV, abdominal dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) scans, and available complete blood count and Child-Pugh score was calculated by ascites, albumin, prothrombin activity, bilirubin and encephalopathy; and (3) patients had no hepatocarcinoma, portal vein emboli, or hepatic vascular malformation based on clinical or image data. In this cohort, 133 cases were confirmed by liver biopsy, and the remaining 85 cases were diagnosed based on the AASLD guidelines because of the abnormal coagulation. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) previous or active gastrointestinal bleeding (n = 3); (2) receiving therapy for portal hypertension (n = 5); (3) hepatic schistosomiasis (n = 1) or hematologic disorders (n = 3); or (4) active alcohol abuse (n = 1). Consequently, two-hundred and five cirrhotic patients (127 men and 78 women; age range, 23-81 years) were enrolled into our study.
Each patient underwent MR scans, laboratory examination of PLT and Child-Pugh score calculation followed by endoscopy for demonstrating EV by the endoscopy operators within one week after admission. In this study, 32.7% (67/205) of patients had ascites, 7.8% (16/205) had EV, 35.1% (72/205) had EV and ascites, and 24.4% (50/205) had neither EV nor ascites. Based on Child-Pugh score calculation, 47, 95 and 63 patients were classified as having Child-Pugh Class A, B and C, respectively.
During the same research period, 40 (24 men and 16 women) randomly chosen consecutive healthy adults with no history of liver disease served as a reference group. The participants had negative findings on abdominal MRI and laboratory examinations at our institution.
MR technique
As described in detail previously[15], each participant underwent MRI scans supinely with a 3.0-T scanner (Signa; GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI) in an 8-channel phased array body coil after the establishment of respiratory signals. Unenhanced T1- and T2-weighted images were obtained with a single-shot fast SE sequence. Subsequently, each patient received an injection of Magnevist at a dose of 0.2 mmol/kg of body weight, and at an injection rate of 2 mL/s followed by 20-mL saline solution flush for axial enhanced three-dimensional gradient-echo sequence. The scanning coverage was from the diaphragm to the inferior border of spleen. The scanning parameters were: TR = 3.9 ms, TE = 1.8 ms, matrix = 256 mm × 224 mm, FOV = 34 cm × 34 cm, and thickness = 5.0 mm.
Image analysis
The analysis of MR images was performed on a GE workstation as described in detail previously[15]. The portal venous phase contrast-enhanced images were used for analysis, because they could be better than arterial or delayed phase images for depicting the outline of the liver and spleen[15]. On the enhanced images, two radiologists (Tian-Wu Chen and Xiao-Li Chen) independently measured RV and spleen volume (SV) without the knowledge of clinical data. To obtain RV, right liver lobe contour was manually traced excluding intrahepatic vasculature and the gallbladder. This measurement on each axial section was repeatedly until covering the whole liver lobe. The RV was then calculated by multiplying the sum of all the right liver lobe areas by the slice thickness[20]. SV was measured by the similar method to RV measurement (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
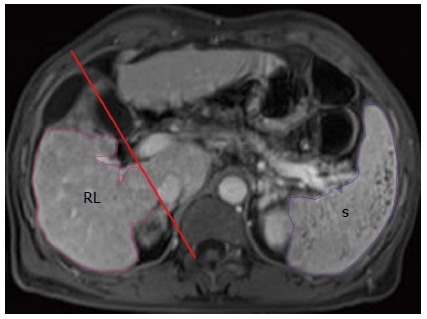
Outlines of right liver lobe (RL, in pink) and the spleen (S, in purple) are delineated on the axial enhanced magnetic resonance image.
In addition, the two radiologists also independently measured spleen maximal width (W), thickness (T) and length (L) for obtaining the spleen volume index (SI = W × T × L) according to the previously described method[15,21]. Because SV or SI takes spleen maximal W, L and T into consideration, we think that SV or SI can be more accurate than spleen maximal width to assess spleen size. Therefore, based on SV, RV and PLT, the ratios of spleen volume parameters measured by MRI to PLT (including the SV/PLT and SI/PLT) were calculated in this study. Moreover, we combined PLT/SV with RV by multiplying both parameters into a single marker (RVPS = RV × PLT/SV) to assess liver cirrhosis.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS software (version 17.0, SPSS, Chicago, IL, United States). P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
The interobserver agreements in the RV or spleen size parameter measurements between two independent radiologists were evaluated using interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) combined with 95%CI as previously described[15].
The multiple pairwise comparisons were conducted with the Mann-Whitney U test for comparing parameters among the CPS classes of cirrhosis, and between patients with and without EV. Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was used to assess the correlation between modified Child-Pugh class and the possible noninvasive cirrhosis prediction parameters.
The cutoff values of prediction parameters were then determined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis for identification of the CPS classes of cirrhosis, and for predicting the presence of EV with an area under the ROC curve (AUC).
RESULTS
Interobserver measurement agreement
For the interobserver measurement agreement in this cohort, ICC was 0.96 (95%CI: 0.92-0.99) for the two observers’ measurements of W, 0.95 for T (95%CI: 0.90-0.99), 0.92 for L (95%CI: 0.86-0.98), 0.93 for SV (95%CI: 0.90-0.99), and 0.88 for RV (95%CI: 0.81-0.95). There was good agreement between the two observers’ measurements. Then the two observers’ measurements were averaged and used as the final results.
Comparisons of the combined variables and baseline characteristics of healthy volunteers and cirrhotic patients among modified Child-Pugh classes
The clinical characteristics including gender, body mass index, age, body weight, and the combined parameters including SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RVPS of all participants are shown in Table 1. The clinical characteristics between cirrhotic patients and healthy volunteers or among the CPS classes of cirrhosis had no significant difference (P > 0.05 for all).
Table 1.
The main clinical characteristics of healthy volunteers and cirrhotic patients with different modified Child-Pugh classes
| Variable | Healthy volunteers |
Cirrhotic patients (n = 205) |
P value | ||
| (n = 40) | Class A (n = 47) | Class B (n = 95) | Class C (n = 63) | ||
| Gender (M/F) | 24/16 | 24/23 | 60/35 | 43/20 | 0.816 |
| Age (yr) | 51.50 ± 2.31 | 58.13 ± 1.83 | 55.99 ± 1.18 | 54.38 ± 1.63 | 0.056 |
| Esophageal varices | Not appear | 17.02% (8/47) | 45.26% (43/95)1 | 58.73% (37/63)1 | < 0.001a |
| PLT (109/L) | 249.70 ± 5.71 | 178.29 ± 12.77 | 137.67 ± 22.171 | 82.44 ± 21.1412 | < 0.001a |
| SV/PLT | 0.56 ± 0.03 | 1.98 ± 0.25 | 5.23 ± 1.051 | 29.50 ± 13.5512 | < 0.001a |
| SI/PLT | 1.15 ± 0.06 | 4.07 ± 0.49 | 11.77 ± 2.081 | 67.39 ± 24.9112 | < 0.001a |
| RVPS | 1898.72 ± 138.12 | 686.34 ± 121.37 | 359.99 ± 41.371 | 80.06 ± 10.1012 | < 0.001a |
Different from Child-Pugh class A;
Different from Child-Pugh class B, and all the comparisons denote significance after Bonferroni correction (P < 0.05).
P value shows the difference between cirrhotic patients and healthy volunteers. BMI: Body mass index; SV: Spleen volume; SI: Spleen volumetric index; PLT: Platelet count; RV: Right liver lobe volume; RVPS: RV × PLT/SV; M: Male; F: Female.
SV/PLT and SI/PLT increased with the progress of CPS class (r = 0.676 and 0.707, respectively; P < 0.001 for all). Furthermore, SV/PLT and SI/PLT were greater in CPS class B compared with class A, and also greater in class C than in class B or A (P < 0.05 for all). PLT and RVPS decreased with the progress of CPS class (r = -0.626 and -0.802, respectively; P < 0.001 for all). PLT and RVPS between each class of CPS had significant differences (P < 0.05 for all).
Comparisons of the measured parameters between cirrhotic patients with and without EV
Comparisons of the parameters including SV/PLT, SI/PLT, PLT and RVPS between cirrhotic patients with and without EV are illustrated in Table 2. The patients with EV had lower PLT and RVPS, and higher SV/PLT and SI/PLT than those without EV. PLT, SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RVPS between cirrhotic patients with and without EV had significant differences (P < 0.001 for all).
Table 2.
Comparison of the parameters between cirrhotic patients with and without esophageal varices
| Parameter |
Esophageal varices |
P value | |
| No (n = 117) | Yes (n = 88) | ||
| PLT (109/L) | 142.98 ± 81.45 | 99.33 ± 73.72 | < 0.001 |
| SV/PLT | 4.22 ± 5.98 | 14.58 ± 20.62 | < 0.001 |
| SI/PLT | 11.40 ± 16.73 | 48.33 ± 131.01 | < 0.001 |
| RVPS | 494.72 ± 650.52 | 160.62 ± 171.01 | < 0.001 |
PLT: Platelet count; SV: Spleen volume; SI: Spleen volumetric index; RV: Right liver lobe volume; RVPS: RV × PLT/SV.
ROC analysis of the measured parameters for differentiating Child-Pugh class of liver cirrhosis and predicting the presence of EV
The ROC analyses of each measured parameter for the differentiation between cirrhotic patients and healthy volunteers, or among different CPS classes of cirrhosis are shown in Table 3. All the measured parameters could identify the occurrence of cirrhosis, and differentiate the CPS classes (P < 0.05 for all) (Figure 2A-D). Among these combined parameters, RVPS was considered the best parameter for the differentiation between cirrhotic patients and healthy volunteers with an AUC of 0.973, and for differentiating each class of CPS (AUC = 0.740-0.976).
Table 3.
Receiver operating curve analysis of measured parameters for identifying the presence and Child-Pugh class of cirrhosis, and the presence of esophageal varices
| Parameter | Cutoff values | Differentiations | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
| PLT (109/L) | 217 | Normal liver vs cirrhosis | 0.903 | 97.5% | 86.8% |
| 140 | Child-Pugh class A vs B | 0.661 | 66.0% | 64.2% | |
| 114 | Child-Pugh class A vs C | 0.859 | 80.9% | 82.5% | |
| 96.5 | Child-Pugh class B vs C | 0.703 | 61.1% | 79.4% | |
| 99.5 | No varices vs varices | 0.678 | 61.5% | 60.2% | |
| SV/PLT | 0.83 | Normal liver vs cirrhosis | 0.952 | 91.2% | 97.5% |
| 2.99 | Child-Pugh class A vs B | 0.663 | 58.9% | 63.8% | |
| 5.19 | Child-Pugh class A vs C | 0.873 | 69.8% | 95.7% | |
| 5.40 | Child-Pugh class B vs C | 0.722 | 69.8% | 62.1% | |
| 4.13 | No varices vs varices | 0.782 | 72.7% | 68.4% | |
| SI/PLT | 2 | Normal liver vs cirrhosis | 0.967 | 93.7% | 97.5% |
| 6.08 | Child-Pugh class A vs B | 0.692 | 65.3% | 61.7% | |
| 12.55 | Child-Pugh class A vs C | 0.902 | 76.2% | 97.9% | |
| 13.01 | Child-Pugh class B vs C | 0.724 | 74.6% | 63.2% | |
| 11.08 | No varices vs varices | 0.773 | 72.7% | 70.1% | |
| RVPS | 883.90 | Normal liver vs cirrhosis | 0.973 | 97.5% | 92.7% |
| 330.98 | Child-Pugh class A vs B | 0.740 | 78.7% | 62.1% | |
| 175.72 | Child-Pugh class A vs C | 0.976 | 93.6% | 92.1% | |
| 129.36 | Child-Pugh class B vs C | 0.853 | 72.6% | 81.0% | |
| 226.46 | No varices vs varices | 0.758 | 64.1% | 79.5% |
PLT: Platelet count; SV: Spleen volume; SI: Spleen volumetric index; RV: Right liver lobe volume; RVPS: RV × PLT/SV; AUC: Area under the receiver operating curve.
Figure 2.
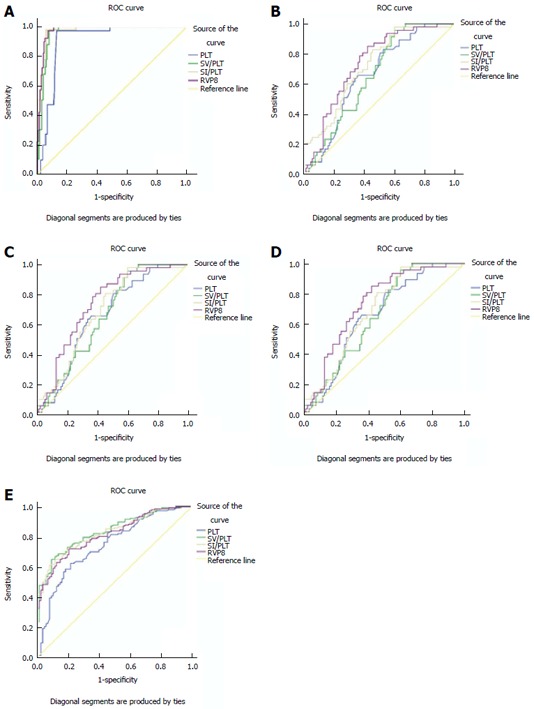
Right liver lobe volume × platelet count/spleen volume is better than platelet count, spleen volume/platelet count or spleen volume index/platelet count for distinguishing cirrhotic patients from healthy participants (A), Child-Pugh class A of cirrhosis from B, A from C, and B from C; and SV/PLT is better than PLT, RVPS or SI/PLT for identifying esophageal varices (E). RVPS: Right liver lobe volume × platelet count/spleen volume; PLT: Platelet count; SV/PLT: Spleen volume/platelet count; SI/PLT: Spleen volume index/platelet count.
The ROC analysis was also carried out to differentiate between cirrhotic patients with and without EV (Table 3). All the parameters might be indicators for differentiating cirrhotic patients with and without EV (Figure 2E). SV/PLT was the best predictor for identifying the presence of EV in patients with cirrhosis with an AUC of 0.782 (Figure 2E).
DISCUSSION
In cirrhotic patients, it is difficult to perform liver biopsy for monitoring the stage of cirrhosis every year or two. On the contrary, the noninvasive tools such as laboratory examination and imaging were secure, repeatable and useful in diagnosing chronic liver disease[22-24]. In view of the changes of both the liver or SV and PLT with the progress of cirrhosis, we combined the noninvasive variables including RV, SV or SI measured by MRI with PLT for determining whether and how the parameters are associated with the presence and severity of cirrhosis.
We combined spleen volume parameters with PLT into a single parameter (SV/PLT or SI/PLT) to assess liver cirrhosis for the first time this study. The previously reported studies found that SV and SI measured by MRI were closely related to the Child-Pugh class of cirrhosis[25,26]. Low PLT in cirrhosis patients is possibly a multifactorial event[22-23]. The accuracy may decrease when using PLT alone to diagnose cirrhosis for the increased false positive results[22]. We presumed that combination of the sensitive markers of splenomegaly and PLT might ameliorate the accuracy of single tests by assessing different pathophysiological components of liver cirrhosis. The ratio of PLT to spleen diameter, which represents an acceptable parameter of clinical relevance in patients with portal hypertension, could better reflect the hypersplenism compared with PLT[27-29]. Our study implied that the combination of SV or SI with PLT was clearly superior to the performance of PLT alone for differentiating the presence of cirrhosis and the CPS class.
Moreover, we combined PLT/SV with RV by multiplying both parameters into a single marker (RVPS) to assess cirrhosis. The first attempt at integrating empirical values was reported by multiplying spleen diameter and liver stiffness to platelet ratio to predict EV[30,31]. Similarly, we combined PLT/SV and RV into a single marker (RVPS), which could be an optimal marker to classify the CPS classes of cirrhosis. We did not combine PLT/SI and RV in our study because SV was more accurate to show spleen size than SI.
As shown in our study, with the increasing CPS class of cirrhosis, SV/PLT and SI/PLT increased, which was similar to the previous reports. Combining PLT and spleen size into a single parameter could be a good marker of portal hypertension[31]. The pressure of portal vein increased with the progress of cirrhosis, resulting in an increase in spleen size and a decrease in PLT[25,31]. With the progress of CPS class, RVPS also decreased. Our findings supported the previous finding that the spleen enlarged in cirrhosis with the rising splenic blood flow, and at the same time the liver volume diminished[32]. Among the 4 parameters, our study confirmed for the first time that RVPS could be best associated with CPS class of cirrhosis.
As shown in our study, PLT, SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RVPS could be used to identify the presence of cirrhosis and to differentiate the CPS classes. With a better AUC, the performance of RVPS was superior to PLT, SV/PLT or SI/PLT for indicating the presence of cirrhosis and to differentiate the CPS classes. Therefore, for identifying the presence of cirrhosis and to differentiate the CPS classes, RVPS could be suggested as an optimal parameter.
In addition, we determined how the combined parameters (SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RVPS) are associated with EV in cirrhosis patients. This protocol was referenced from the published report, in which the liver stiffness × spleen diameter/platelet ratio or the ratio of PLT to spleen diameter was used to identify cirrhotic patients with EV[30,31]. In the current study, the combined parameters were used to identify clinical EV in patients with compensated cirrhosis, which is potentially useful in that it might enable avoidance of endoscopy in some patients. The patients with EV had lower PLT and RVPS, and higher SV/PLT or SI/PLT than those without EV. In patients with cirrhosis, although PLT, SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RVPS could predict the presence of EV, SV/PLT was the best parameter. Although RVPS cannot be superior to SV/PLT for predicting EV, this combined parameter might decrease false positive results and improve the accuracy, for higher specificity can be obtained from RVPS than from SV/PLT.
There are several limitations in this study. First, the results were not tested prospectively on another group of patients with hepatitis B but without cirrhosis (such as no or mild fibrosis), but this study provided some positive suggestions that the combined parameters including SV/PLT, SI/PLT and RVPS could be used to identify the occurrence of cirrhosis, to differentiate the CPS classes, and to identify the presence of EV. Our further studies involving patients with hepatitis B but without cirrhosis will be performed to confirm these results. Second, some concerns could be raised in terms of costs. The avoidance of upper gastrointestinal endoscopies has to be challenged with the costs related with a routine use of MR in all patients with cirrhosis. Although MRI examination was more expensive than upper gastrointestinal endoscopies, most of patients, especially for these patients who cannot endure invasive upper gastrointestinal endoscopic examination, would like to receive non-invasive MRI other than upper gastrointestinal endoscopies. Third, we did not make a differential diagnosis between chronic hepatitis B and liver cirrhosis. In our future study, we will differentiate patients with chronic hepatitis B from those with liver cirrhosis.
In conclusion, SV/PLT and SI/PLT increased with the progress of Child-Pugh class, and PLT and RVPS decreased with the progress of Child-Pugh class. As a new combined parameter, RVPS can be an optimized marker to identify the occurrence of cirrhosis and differentiate the CPS class. SV/PLT could be recommended for identifying the presence of EV. We hope that the results of our study could be helpful to determine the appropriate treatment approach.
COMMENTS
Background
The noninvasive and reliable assessment of the severity of liver cirrhosis is critically important for management of cirrhosis patients. Many studies have reported that parameters for assessing cirrhosis include low platelet count and large spleen size on ultrasound as well as high Child-Pugh score for evaluating the severity of cirrhosis. Furthermore, previous research showed that the decrease of right liver lobe volume was positively correlated with the Child-Pugh class and cirrhosis prognosis. However, to date, none of the above-mentioned methods were accurate enough. Better dynamic and repeatable non-invasive tools are needed to monitor and classify the severity of cirrhosis.
Research frontiers
The platelet count to spleen diameter ratio, a new combined index, was reported to identify cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices, which was based on the routine laboratory and ultrasound examinations. The current research hotspot is to determine whether and how the combination of platelet count with spleen volume and right liver volume measured by MRI are associated with Child-Pugh class of liver cirrhosis and esophageal varices in patients with hepatitis B.
Innovations and breakthroughs
The results of this research showed that the spleen volume/platelet count ratio increased with the progress of Child-Pugh class, which could be used to identify the Child-Pugh class of cirrhosis and the presence of esophageal varices. The combination of platelet count with spleen volume and right liver volume could identify the occurrence of cirrhosis and differentiate the Child-Pugh class.
Applications
As a new combined parameter (RVPS = right liver lobe volume × platelet count/spleen volume), the combination of platelet count with spleen volume and right liver volume can be an optimized marker to identify the occurrence of cirrhosis and to monitor or classify the severity of cirrhosis. The spleen volume/platelet count ratio could be recommended for identifying the presence of esophageal varices. The authors hope that the results of the study could be helpful to determine the appropriate treatment approach.
Terminology
The Child-Pugh classes include A, B, and C, which are calculated by ascites, albumin, prothrombin activity, bilirubin and encephalopathy.
Peer-review
The manuscript reports a retrospective study describing the ability of the combination of platelet count with spleen volume and right liver volume measured by magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose clinically and/or biopsy proven cirrhosis and esophageal varices in 205 HBV-positive patients.
Footnotes
Supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81050033; the Key Projects of Sichuan Province Science and Technology Pillar Program, No. 2011SZ0237; the Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Sichuan Province in China, No. 2010JQ0039; the Key Science and Technology Project of Chinese Ministry of Public Health, No. 2014114; and the Natural Science Key Project of North Sichuan Medical College, No. CBY12-A-ZD03.
Institutional review board statement: This study was reviewed and approved by the Committee for Ethical Review of Research involving Human Subjects of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China.
Informed consent statement: All study participants, or their legal guardian provided informed written consent prior to study enrollment.
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: April 2, 2015
First decision: June 2, 2015
Article in press: July 18, 2015
P- Reviewer: Desai ND, Mura VL, Tai DI S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: Wang TQ E- Editor: Liu XM
References
- 1.Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2014;383:1749–1761. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006;44:217–231. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Durand F, Valla D. Assessment of the prognosis of cirrhosis: Child-Pugh versus MELD. J Hepatol. 2005;42 Suppl:S100–S107. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Angermayr B, Cejna M, Karnel F, Gschwantler M, Koenig F, Pidlich J, Mendel H, Pichler L, Wichlas M, Kreil A, et al. Child-Pugh versus MELD score in predicting survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Gut. 2003;52:879–885. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Conn HO. A peek at the Child-Turcotte classification. Hepatology. 1981;1:673–676. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shi BM, Wang XY, Mu QL, Wu TH, Xu J. Value of portal hemodynamics and hypersplenism in cirrhosis staging. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:708–711. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kudo M, Zheng RQ, Kim SR, Okabe Y, Osaki Y, Iijima H, Itani T, Kasugai H, Kanematsu M, Ito K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of imaging for liver cirrhosis compared to histologically proven liver cirrhosis. A multicenter collaborative study. Intervirology. 2008;51 Suppl 1:17–26. doi: 10.1159/000122595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brown JJ, Naylor MJ, Yagan N. Imaging of hepatic cirrhosis. Radiology. 1997;202:1–16. doi: 10.1148/radiology.202.1.8988182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Witters P, Freson K, Verslype C, Peerlinck K, Hoylaerts M, Nevens F, Van Geet C, Cassiman D. Review article: blood platelet number and function in chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:1017–1029. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wehler M, Kokoska J, Reulbach U, Hahn EG, Strauss R. Short-term prognosis in critically ill patients with cirrhosis assessed by prognostic scoring systems. Hepatology. 2001;34:255–261. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.26522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shah SH, Hayes PC, Allan PL, Nicoll J, Finlayson ND. Measurement of spleen size and its relation to hypersplenism and portal hemodynamics in portal hypertension due to hepatic cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:2580–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Giannini E, Botta F, Borro P, Risso D, Romagnoli P, Fasoli A, Mele MR, Testa E, Mansi C, Savarino V, et al. Platelet count/spleen diameter ratio: proposal and validation of a non-invasive parameter to predict the presence of oesophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gut. 2003;52:1200–1205. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.8.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berzigotti A, Piscaglia F. Ultrasound in portal hypertension--part 1. Ultraschall Med. 2011;32:548–568; quiz 569-571. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1281856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen XL, Chen TW, Zhang XM, Li ZL, Zeng NL, Li T, Wang D, Li J, Fang ZJ, Li H, et al. Quantitative assessment of the presence and severity of cirrhosis in patients with hepatitis B using right liver lobe volume and spleen size measured at magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Fidler JL, Sanderson SO, Kamath PS, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance imaging of hepatic fibrosis: emerging clinical applications. Hepatology. 2008;47:332–342. doi: 10.1002/hep.21972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Taouli B, Ehman RL, Reeder SB. Advanced MRI methods for assessment of chronic liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193:14–27. doi: 10.2214/AJR.09.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Saygili OB, Tarhan NC, Yildirim T, Serin E, Ozer B, Agildere AM. Value of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for assessing severity of liver cirrhosis secondary to viral hepatitis. Eur J Radiol. 2005;54:400–407. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007;45:507–539. doi: 10.1002/hep.21513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mazonakis M, Damilakis J, Maris T, Prassopoulos P, Gourtsoyiannis N. Comparison of two volumetric techniques for estimating liver volume using magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15:557–563. doi: 10.1002/jmri.10109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rezai P, Tochetto SM, Galizia MS, Yaghmai V. Splenic volume model constructed from standardized one-dimensional MDCT measurements. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196:367–372. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.4453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Peck-Radosavljevic M. Thrombocytopenia in liver disease. Can J Gastroenterol. 2000;14 Suppl D:60D–66D. doi: 10.1155/2000/617428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Toghill PJ, Green S, Ferguson F. Platelet dynamics in chronic liver disease with special reference to the role of the spleen. J Clin Pathol. 1977;30:367–371. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.de Franchis R. Revising consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno V consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2010;53:762–768. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen XL, Chen TW, Li ZL, Zhang XM, Chen N, Zeng NL, Li H, Tang HJ, Pu Y, Li CP. Spleen size measured on enhanced MRI for quantitatively staging liver fibrosis in minipigs. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38:540–547. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ito K, Mitchell DG, Hann HW, Kim Y, Fujita T, Okazaki H, Honjo K, Matsunaga N. Viral-induced cirrhosis: grading of severity using MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999;173:591–596. doi: 10.2214/ajr.173.3.10470885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Giannini E, Botta F, Borro P, Malfatti F, Fumagalli A, Testa E, Podestà E, Chiarbonello B, Polegato S, Mamone M, et al. Relationship between thrombopoietin serum levels and liver function in patients with chronic liver disease related to hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:2516–2520. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.08665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Giannini EG, Zaman A, Kreil A, Floreani A, Dulbecco P, Testa E, Sohaey R, Verhey P, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Mansi C, et al. Platelet count/spleen diameter ratio for the noninvasive diagnosis of esophageal varices: results of a multicenter, prospective, validation study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:2511–2519. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.de Mattos AZ, de Mattos AA. Platelet count/spleen diameter ratio: can it replace endoscopy for the screening of esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;24:1113. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283551e22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim BK, Han KH, Park JY, Ahn SH, Kim JK, Paik YH, Lee KS, Chon CY, Kim do Y. A liver stiffness measurement-based, noninvasive prediction model for high-risk esophageal varices in B-viral liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:1382–1390. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Berzigotti A, Seijo S, Arena U, Abraldes JG, Vizzutti F, García-Pagán JC, Pinzani M, Bosch J. Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:102–111.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li H, Chen TW, Zhang XM, Li ZL, Zhang JL, Wang D, Li T, Wu JL, Guo X, Chen XL, et al. Liver lobe volumes and the ratios of liver lobe volumes to spleen volume on magnetic resonance imaging for staging liver fibrosis in a minipig model. PLoS One. 2013;8:e79681. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


