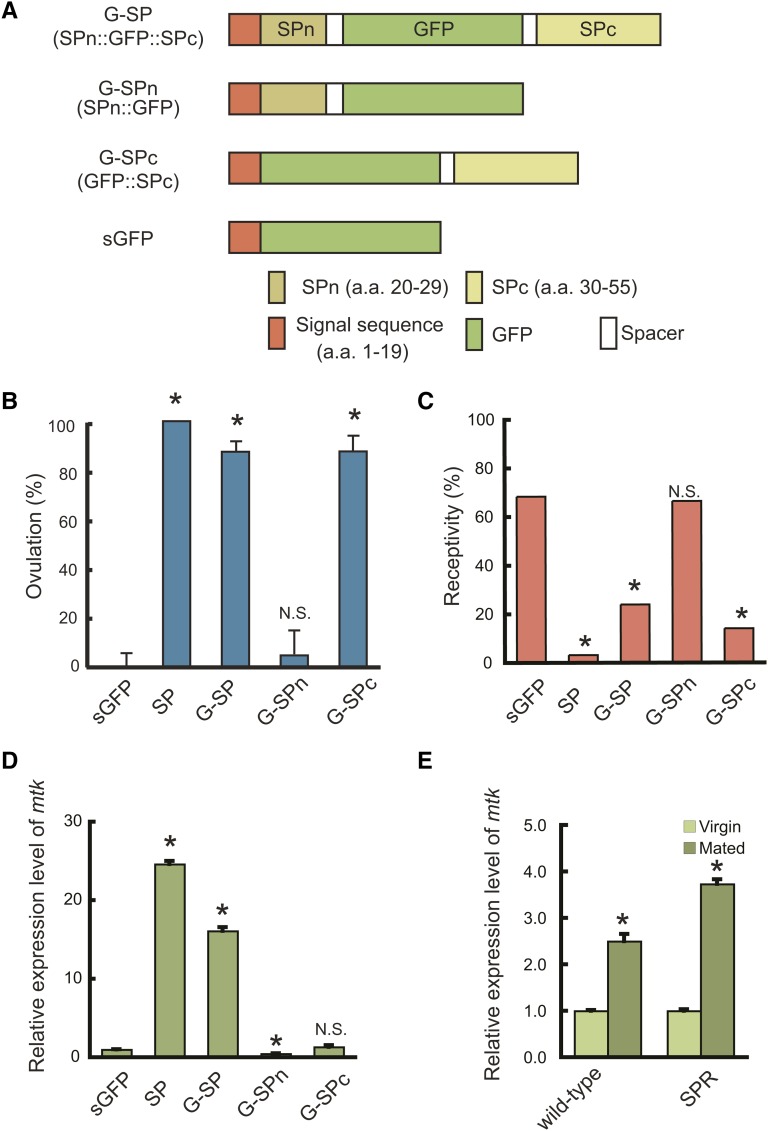
Figure 1.
Structure and biological activities of GFP-tagged SP (G-SP). (A) Schematic representation of G-SP fusion proteins. All fusion proteins contain the SP signal sequence (SP1–19) at their N termini and were expressed using the GAL4–UAS system. SPn and SPc indicate SP20–29 and SP30–55 of mature peptides, respectively. (B) Effects of fusion proteins on ovulation and (C) sexual receptivity, and (D) expression of an immune response gene, mtk. sca–GAL4 was used to induce ectopic expression of the fusion constructs. Wild-type SP was used as a positive control. mtk expression levels were determined by quantitative RT–PCR. G-SP and G-SPc stimulate ovulation and reduce receptivity, whereas no change was observed with G-SPn. G-SP also induces mtk expression, but no response was observed with G-SPn or G-SPc. (E) Mating-induced immune response in wild-type and SPR mutant females. SPR is not required for the mating-induced immune response. Values are the mean ±SEM of three experiments (*, P < 0.01; N.S., not significant).