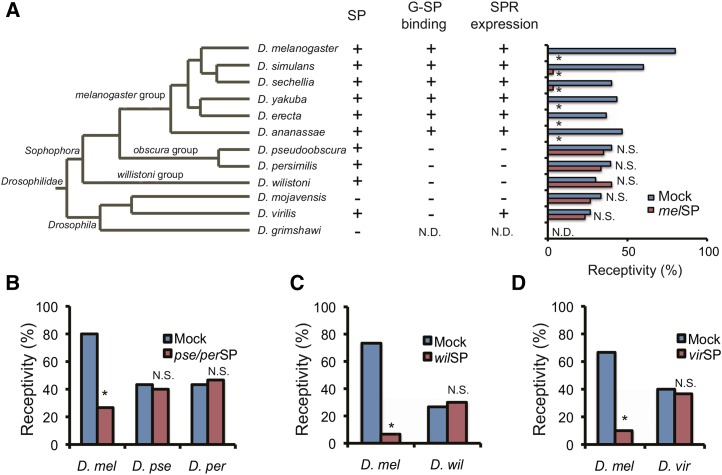
Figure 4.
Evolution of SP-dependent PMR in Drosophila. (A) The phylogenetic tree of 12 sequenced Drosophila species was adapted from http://flybase.org/blast/. Presence or absence of an SP-like sequence in each species is indicated by + or −, respectively (SP). Whether or not the D. melanogaster G-SP binding occurs in the common oviduct of each species is indicated by + or −, respectively (G-SP binding). Expression level of SPR orthologs in female reproductive tracts of each species is indicated by + (strong) or − (weak), respectively. Effects of D. melanogaster SP on sexual receptivity of virgin females from various species. The peptide was injected into virgin females of each species. At least 30 females were used for one assay. N.D. indicates not determined. Effects of SP orthologs from (B) D. pseudoobscura and D. persimilis, (C) D. willistoni, and (D) D. virilis on the receptivity of D. melanogaster and their conspecific females. None of the SP orthologs reduced receptivity in conspecific females, while they all reduced receptivity in D. melanogaster females. The amino acid sequences of SP orthologs are identical for D. pseudoobscura and D. persimilis. Therefore, the same peptide was used for both species (*; P < 0.01; N.S., not significant) .