Abstract
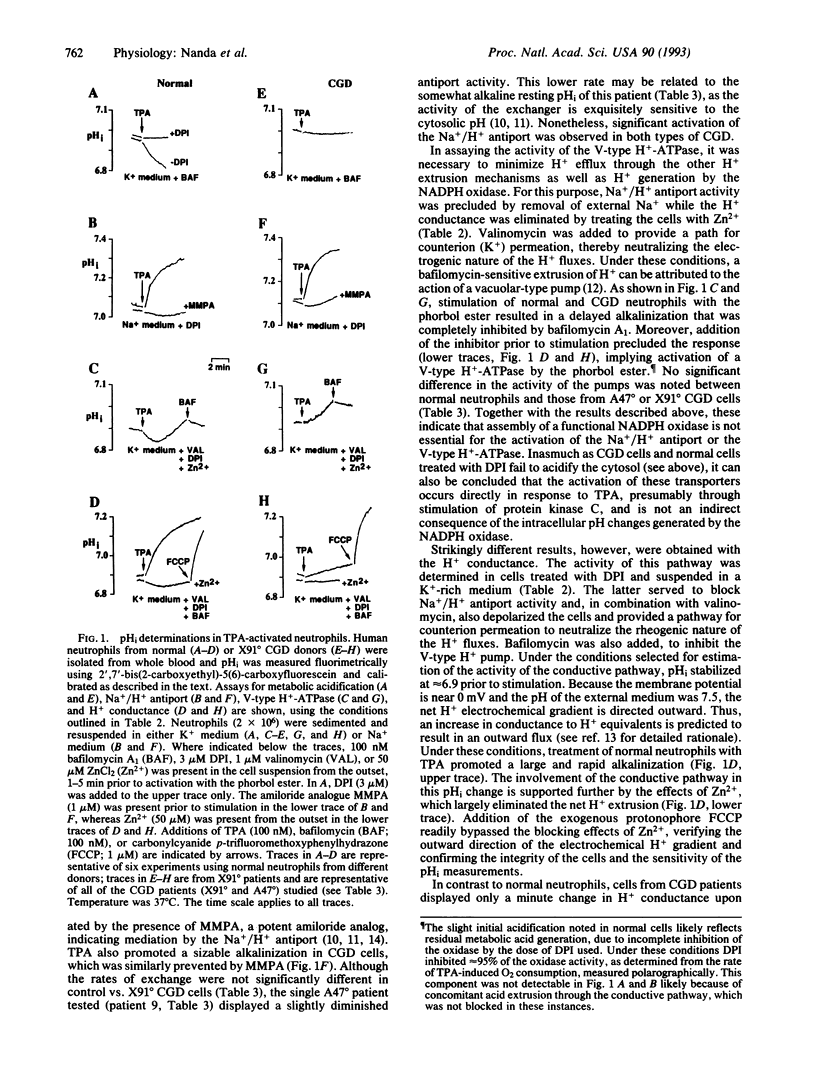
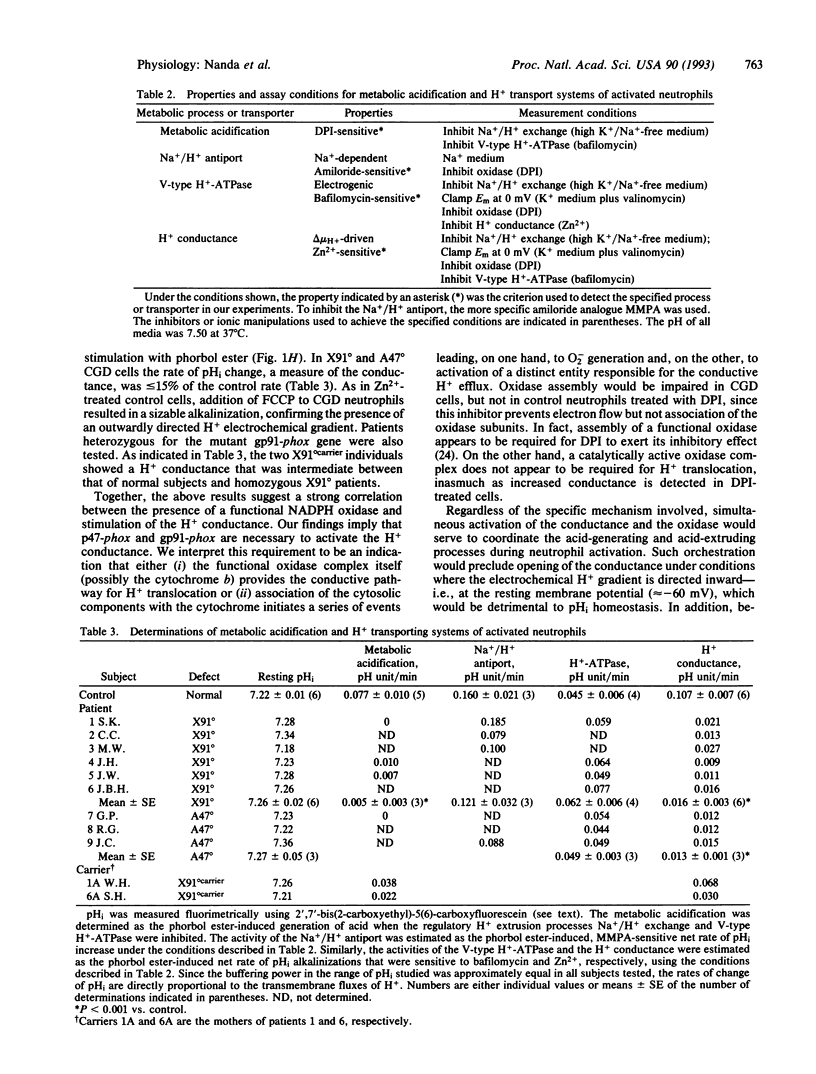
To combat bacterial infection, phagocytes generate superoxide (O2-) and other microbicidal oxygen radicals. NADPH oxidase, the enzyme responsible for O2- synthesis, is deficient in chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) patients. Although O2- generation is accompanied by a large burst of metabolic acid production, intracellular pH (pHi) remains near neutrality due to the concomitant stimulation of H+ extrusion. Three major pathways contribute to pHi regulation in activated phagocytes: Na+/H+ exchange, vacuolar-type H+ pumps, and a H+ conductance. The present study analyzed the relationship between activation of the NADPH oxidase and stimulation of the H+ extrusion mechanisms in human blood neutrophils. Phorbol ester-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange and H+ pumping occurred normally in cells from CGD patients. Unlike normal individuals, however, CGD patients were unable to activate the H+ conductive pathway. Thus, activation of the H+ conductance appears to be contingent on the assembly of a functional NADPH oxidase. These findings imply a dual role of the NADPH oxidase in O2- synthesis and in the regulation of pHi. The oxidase (or some components thereof) may itself undertake H+ translocation or, alternatively, may signal the activation of a separate H+ conducting entity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J., Siebers A., Altendorf K. Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. The human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1140–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Jones O. T. Enzymic mechanisms of superoxide production. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 6;1057(3):281–298. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Jones O. T. The effect of the inhibitor diphenylene iodonium on the superoxide-generating system of neutrophils. Specific labelling of a component polypeptide of the oxidase. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):111–116. doi: 10.1042/bj2370111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Berkow R. L., Roberts R. L., Shurin S. B., Scott P. J. Chronic granulomatous disease due to a defect in the cytosolic factor required for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):606–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI113360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Molecular basis of the autosomal recessive forms of chronic granulomatous disease. Immunodefic Rev. 1992;3(2):149–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund E. A., Marshall M., Gibbs J. B., Crean C. D., Gabig T. G. Resolution of a low molecular weight G protein in neutrophil cytosol required for NADPH oxidase activation and reconstitution by recombinant Krev-1 protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13964–13970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Dixon S. J. Ion transport, membrane potential, and cytoplasmic pH in lymphocytes: changes during activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):417–481. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W., Biggar W. D. Cytoplasmic pH regulation in normal and abnormal neutrophils. Role of superoxide generation and Na+/H+ exchange. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):512–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W. Characterization of the amiloride-sensitive Na+-H+ antiport of human neutrophils. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):C283–C291. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.2.C283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Heyworth P. G., Evans T., Curnutte J. T., Bokoch G. M. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac 2. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1512–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.1660188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Doussiere J., Vignais P. V. The superoxide-generating oxidase of phagocytic cells. Physiological, molecular and pathological aspects. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;201(3):523–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda A., Grinstein S. Protein kinase C activates an H+ (equivalent) conductance in the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10816–10820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda A., Gukovskaya A., Tseng J., Grinstein S. Activation of vacuolar-type proton pumps by protein kinase C. Role in neutrophil pH regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22740–22746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L. Chemotactic factor-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange in human neutrophils. II. Intracellular pH changes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13248–13255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Curnutte J. T. Molecular basis of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1991 Feb 15;77(4):673–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Meech R. W. Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurones. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):826–828. doi: 10.1038/299826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



