Fig 1 is incorrect. The authors have provided a corrected version here. The publisher apologizes for the error.
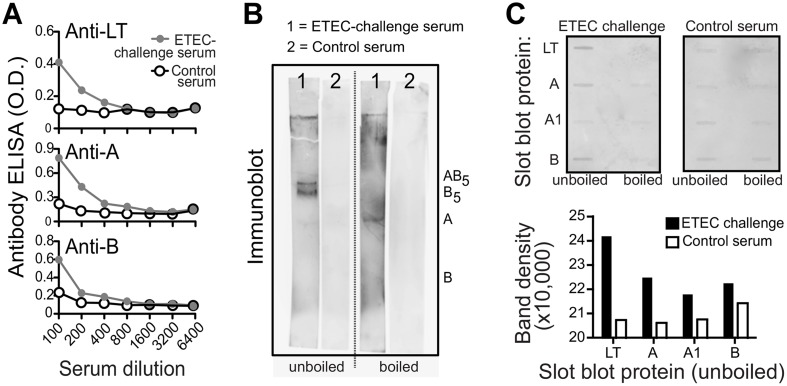
Fig 1. ETEC-challenged human serum pool contains antibodies to both A- and B-subunits of LT.
(A) ETEC challenge serum (pooled 10 days after oral H10407 challenge) anti-LT, anti-A, and anti-B antibody responses detected by ELISA (gray line, circles) compared to commercially purchased control sera (black lines, open circles) using dilutions of each sample. (B) ETEC-challenge serum (1) or control serum (2) immunoblot testing for anti-LT antibodies using unboiled LT-loaded lanes or boiled LT-loaded lanes. In unboiled SDS-PAGE gels, LT runs as an 84 kD polymeric protein, pentameric B-subunit (56 kD), and LT-A (28 kD). When boiled and subjected to SDS-PAGE, LT separates into LT-A (28 kD) and monomeric LT-B (11.5 kD). (C) ETEC-challenge serum or control serum anti-LT, anti-A, or anti-B responses detected with a modified Immunoblot using a slot blot apparatus to load 0.1 μg protein (LT, A, A1, or B) with raw images (top) and quantified band density of these images for unboiled, loaded proteins graphed (bottom).
Reference
- 1. Norton EB, Branco LM, Clements JD (2015) Evaluating the A-Subunit of the Heat-Labile Toxin (LT) As an Immunogen and a Protective Antigen Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). PLoS ONE 10(8): e0136302 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136302 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]