Abstract
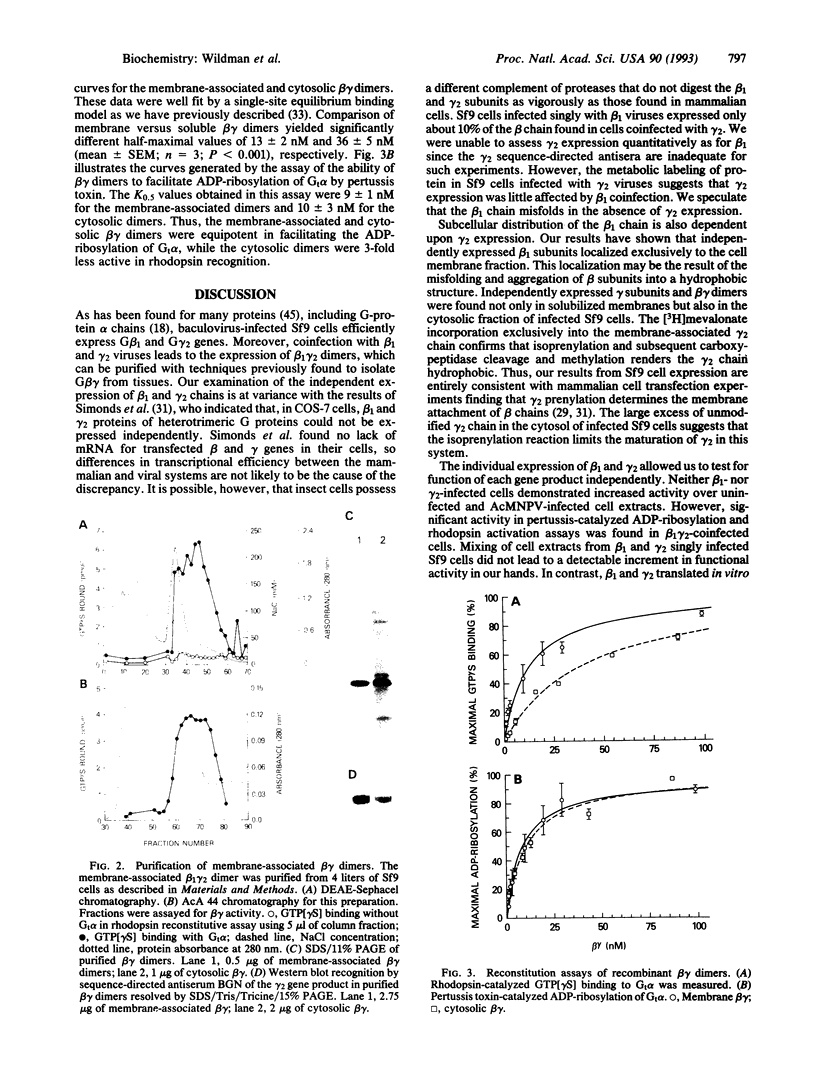
Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein (G protein) beta gamma dimers that were active in reconstitution assays were produced in insect cells using the baculovirus/Sf9 insect cell expression system. Sf9 cells were infected either singly or in combination with recombinant baculoviruses containing a human G-protein beta 1 gene or a bovine G-protein gamma 2 gene. It was possible to express the beta 1 and gamma 2 gene products independently of each other in this system, as determined by using immunological and metabolic labeling techniques. Further, the ability of recombinant beta and/or gamma chains to function in defined biochemical assays of beta gamma activity was assessed for membrane extracts and supernatant fractions from infected Sf9 cells. Extracts of cells expressing beta or gamma chain alone were inactive in these assays, whereas those from cells coinfected with beta 1 and gamma 2 did display activity. These assays were used to identify recombinant beta gamma dimer migration during chromatographic purification, and the recombinant dimers were purified to near homogeneity. Both the membrane-associated and soluble beta gamma dimers facilitated rhodopsin-catalyzed guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate binding to Gt alpha, the GTP-binding subunit of the retinal G protein transducin (K0.5 of 13 +/- 2 and 36 +/- 5 nM, respectively). Both recombinant beta gamma dimers also facilitated the pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of Gt alpha with equal potency (K0.5 of 9 +/- 1 and 10 +/- 3 nM for membrane and soluble dimers, respectively). [3H]Mevalonolactone labeling showed that the gamma 2 subunits of membrane-associated beta gamma dimers incorporated radiolabel, whereas in the soluble form they did not. Thus, prenyl modification of gamma 2 directs the membrane association of the beta 1 gamma 2 dimer and increases its apparent affinity for receptor, but it is not required for the functional interaction(s) of the dimer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Fong N. M., Stempien M. M., Wormsted M. A., Caput D., Ku L. L., Urdea M. S., Rall L. B., Sanchez-Pescador R. Human epidermal growth factor precursor: cDNA sequence, expression in vitro and gene organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8427–8446. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Graziano M. P., Gilman A. G. G protein beta gamma subunits from bovine brain and retina: equivalent catalytic support of ADP-ribosylation of alpha subunits by pertussis toxin but differential interactions with Gs alpha. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):611–616. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawzi A. B., Fay D. S., Murphy E. A., Tamir H., Erdos J. J., Northup J. K. Rhodopsin and the retinal G-protein distinguish among G-protein beta gamma subunit forms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12194–12200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawzi A. B., Northup J. K. Guanine nucleotide binding characteristics of transducin: essential role of rhodopsin for rapid exchange of guanine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 17;29(15):3804–3812. doi: 10.1021/bi00467a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher K. J., Aronson N. N., Jr Characterization of the cDNA and genomic sequence of a G protein gamma subunit (gamma 5). Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1585–1591. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Mechanisms of muscarinic receptor action on Go in reconstituted phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3909–3915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Birren B. W., Simon M. I. Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3792–3796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Gilman A. G. Mutations of GS alpha designed to alter the reactivity of the protein with bacterial toxins. Substitutions at ARG187 result in loss of GTPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21907–21914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada Y., Takao T., Ohguro H., Yoshizawa T., Akino T., Shimonishi Y. Farnesylated gamma-subunit of photoreceptor G protein indispensable for GTP-binding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):658–660. doi: 10.1038/346658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. I. Separation and reconstitution of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10495–10502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao B., Gilman A. G., Robishaw J. D. A second form of the beta subunit of signal-transducing G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6122–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam N., Northup J., Tamir H., Simon M. I. G protein diversity is increased by associations with a variety of gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7973–7977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber S. G., Figler R. A., Garrison J. C. Expression and purification of functional G protein alpha subunits using a baculovirus expression system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1271–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman M., Holzhöfer A., Gierschik P., Im M. J., Jakobs K. H., Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Regulation of signal transfer from beta 1-adrenoceptor to adenylate cyclase by beta gamma subunits in a reconstituted system. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):431–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Risinger R., Birnbaumer L. Identification of a gamma subunit associated with the adenylyl cyclase regulatory proteins Ns and Ni. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2039–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Neer E. J. Subunit interactions of native and ADP-ribosylated alpha 39 and alpha 41, two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1105–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Neer E. J. Subunit interactions of native and ADP-ribosylated alpha 39 and alpha 41, two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1105–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai R. K., Perez-Sala D., Cañada F. J., Rando R. R. The gamma subunit of transducin is farnesylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7673–7677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Smallwood P. M., Moen P. T., Jr, Helman L. J., Ahn T. G. Molecular cloning of beta 3 subunit, a third form of the G protein beta-subunit polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2329–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Gutowski S., Sternweis P. C. G protein gamma subunits contain a 20-carbon isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5873–5877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz K. H., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G., Mumby S. M. Influence of gamma subunit prenylation on association of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins with membranes. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):49–61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon S. E., Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. Mechanism and effects of cholera toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6686–6693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The guanine nucleotide activating site of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Identification by ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11416–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution, activity, and properties of the 35,000-dalton (beta) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11361–11368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohguro H., Fukada Y., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Yoshizawa T., Akino T. Carboxyl methylation and farnesylation of transducin gamma-subunit synergistically enhance its coupling with metarhodopsin II. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3669–3674. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohguro H., Fukada Y., Yoshizawa T., Saito T., Akino T. A specific beta gamma-subunit of transducin stimulates ADP-ribosylation of the alpha-subunit by pertussis toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1235–1241. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90656-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Lipkin V. M., Shuvaeva T. M., Bogachuk A. P., Shemyakin V. V. Complete amino acid sequence of gamma-subunit of the GTP-binding protein from cattle retina. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Kalman V. K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A. Existence of two gamma subunits of the G proteins in brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M. Signal sorting and amplification through G protein-coupled receptors. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Neer E. J. In vitro synthesis of G protein beta gamma dimers. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4538–4544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Butrynski J. E., Gautam N., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. G-protein beta gamma dimers. Membrane targeting requires subunit coexpression and intact gamma C-A-A-X domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5363–5366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamir H., Fawzi A. B., Tamir A., Evans T., Northup J. K. G-protein beta gamma forms: identity of beta and diversity of gamma subunits. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3929–3936. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vialard J., Lalumière M., Vernet T., Briedis D., Alkhatib G., Henning D., Levin D., Richardson C. Synthesis of the membrane fusion and hemagglutinin proteins of measles virus, using a novel baculovirus vector containing the beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):37–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.37-50.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane H. K., Farnsworth C. C., Xie H. Y., Howald W., Fung B. K., Clarke S., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Brain G protein gamma subunits contain an all-trans-geranylgeranylcysteine methyl ester at their carboxyl termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5868–5872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki A., Bartucca F., Ting A., Bitensky M. W. Reciprocal effects of an inhibitory factor on catalytic activity and noncatalytic cGMP binding sites of rod phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3702–3706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Weizsäcker E., Strathmann M. P., Simon M. I. Diversity among the beta subunits of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins: characterization of a novel beta-subunit cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91650-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]