Abstract
Subinhibitory doses of antibiotics have been shown to cause changes in bacterial morphology, adherence ability, and resistance to antibiotics. In this study, the effects of subinhibitory doses of aminoglycoside antibiotics on Mycobacterium abscessus were investigated. The treatment of M. abscessus cells with subinhibitory doses of amikacin was found to change their colony from a smooth to a rough morphotype and increase their ability to adhere to a polyvinylchloride plate, aggregate in culture, and resist phagocytosis and killing by macrophages. M. abscessus cells treated with a subinhibitory dose of amikacin also became more potent in Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2) stimulation, leading to increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) production by macrophages. The MAB_3508c gene was shown to play a role in mediating these phenotypic changes, as its expression in M. abscessus cells was increased when they were treated with a subinhibitory dose of amikacin. In addition, overexpression of MAB_3508c in M. abscessus cells caused changes similar to those induced by subinhibitory doses of amikacin, including a switch from smooth to rough colony morphology, increased ability to aggregate in liquid culture, decreased motility, and increased resistance to killing by macrophages. These findings suggest the importance of using sufficient doses of antibiotics for the treatment of M. abscessus infections.
INTRODUCTION
Antibiotics have been widely used to treat infectious diseases. However, at subinhibitory concentrations, antibiotics may act as signal molecules and modulate bacterial phenotypes such as virulence, colony morphology, and biofilm formation (1, 2). Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal that subinhibitory doses of antibiotics can cause significant changes in gene expression profiles in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1, 3–5).
Mycobacterium abscessus is a rapid-growing nontuberculosis mycobacterium. It is a common cause of infections in patients after tympanostomy tube placement and in those with surgical wounds or cystic fibrosis (6–10). Prolonged antibiotic therapy is generally required for treatment of infections caused by M. abscessus because of its intrinsic and acquired resistance to multiple antibiotics. Commonly used antibiotics for M. abscessus infections include clarithromycin, cefoxitin, tigecycline, and amikacin (AMK) (11).
Amikacin is an aminoglycoside and is the most effective bactericidal antibiotic for M. abscessus. We have found that subinhibitory doses of amikacin can convert colonies of M. abscessus from a smooth to a rough morphotype. Because colony morphology is related to virulence, we investigated the effects of subinhibitory doses of amikacin on various activities of M. abscessus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacteria and culture media.
The M. abscessus cs1c-S strain used in this study is an attenuated variant derived from the clinical isolate cs1c-R (12). M. abscessus cells were grown at 37°C on Middlebrook 7H11 (Difco, USA) agar plates supplemented with 10% oleic acid-bovine albumin-dextrose-catalase (OADC) (Becton Dickinson, USA) or in Middlebrook 7H9 broth (Difco) containing 10% OADC, 0.2% glycerol, and 0.05% Tween 80. The colony morphology was examined by light microscopy.
Sliding motility assay.
One colony of M. abscessus was inoculated in the center of a 7H9 plate with 0.3% agar; the plate was incubated at 37°C for 5 days. The sliding distance of the inoculated M. abscessus cells was measured in millimeters.
Aggregation assay.
M. abscessus cells were adjusted to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.1, and 100 μl of this cell suspension was inoculated into 5 ml of 7H9 broth in a tube. The culture was incubated with shaking at 37°C for 3 days. After standing still at room temperature for 10 min, the upper portion of the culture containing dispersed cells was removed, and its OD600 value was determined. The OD600 value of the bottom portion of culture was measured after the aggregated cells had been completely suspended by vortexing with glass beads of 4.5 mm in diameter (Biospec, USA) as described previously (13–15). The aggregation index of each culture was calculated as the ratio of the OD600 value of aggregated cells to that of dispersed cells.
Adherence assay.
M. abscessus cells were adjusted to an OD600 of 0.1 in 7H9 broth, and 100 μl of this cell suspension was placed in each well of a sterile 96-well polyvinylchloride (PVC) plate (Becton Dickinson). Following incubation for 6 days, the medium in each well was discarded, and the wells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to remove planktonic cells. The adhered cells in each well were then stained with 0.1% (wt/vol) crystal violet for 1 h. After the cells were washed with PBS, the crystal violet associated with the adhered cells in each well was dissolved in 95% ethanol, and the OD595 value of the resulting solution was determined.
Cord formation.
Examination of cord formation was performed by inoculating M. abscessus cells into 7H9 broth at an OD600 of 0.1. After incubation at 37°C for 5 days, M. abscessus cells were collected, stained with crystal violet, and examined at ×400 magnification under a light microscope as previously described (16).
Treatment of M. abscessus cells with subinhibitory concentrations of amikacin.
M. abscessus cells were grown to stationary phase in 7H9 broth at 37°C; 100 μl of this cell suspension was inoculated into 5 ml of 7H9 broth with or without a subinhibitory concentration (SIC) (1 μg/ml) of amikacin and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The bacteria were then washed and resuspended in PBS at a concentration of 4 × 108 CFU/ml.
Survival in macrophages.
THP-1 cells, derived from a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line, were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, USA) at 37°C in a humidified CO2 incubator. THP-1 cells were differentiated into adherent macrophages by adding phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma, USA) to the culture to a final concentration of 500 ng/ml. For investigation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) release, THP-1-derived macrophages were cocultured with M. abscessus cells at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 2 days after PMA addition. Twenty-four hours after M. abscessus infection, TNF-α levels in culture supernatants were measured using the DuoSet enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) development system kit (R&D Systems, USA). Some THP-1 cells were treated with anti-Toll-like receptor 2 (anti-TLR-2) antibody or isotype control antibody (eBioscience, USA) for 30 min before infection with M. abscessus. ELISA plates were analyzed using an Emax microplate reader (Molecular Devices, USA) at 450 nm. To examine macrophage-mediated killing, THP-1-derived macrophages were infected with M. abscessus at an MOI of 0.1 at 37°C. At 1, 2, and 3 days after infection, THP-1 macrophages were lysed with 1% Triton X-100. Each cell lysate was plated on 7H11 agar plates to determine the CFU of the surviving bacteria.
Phagocytosis assay.
Quantitative measurement of phagocytosis was performed by flow cytometry. M. abscessus cells were stained with the green fluorescent dye SYTO 9 (Molecular Probes, USA). The stained M. abscessus cells were incubated at an MOI of 10 with THP-1 macrophage cells for 1 h. The infected THP-1 cells were washed extensively with PBS to remove extracellular bacteria and then stained with trypan blue to quench the fluorescence of membrane-bound bacteria. Green fluorescence was measured at 525 nm after being excited with 488 nm light. Data acquisition and analysis were performed with BD CellQuest (BD Biosciences, USA).
Determination of mRNA levels by real-time RT-PCR and RNA-seq.
M. abscessus cells were suspended in TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA) and lysed with the aid of mechanical grinding using 0.1-mm silica-zirconium beads in a Mini-Beadbeater (Biospec, USA). Total RNA was then isolated using an RNA isolation kit (Bioman Scientific Co. Ltd., Taipei, Taiwan) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Reverse transcription was performed using the SuperScript III reverse transcription kit (Invitrogen, USA). Real-time reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) (quantitative PCR [qPCR]) was performed using Kapa SYBR FAST 2× qPCR master mix (Kapa Biosystems, USA). Primers used in this PCR included RT-MAB_3508c-F (5′-CCTGCTCAAGAATCTCACC-3′), RT-MAB_3508c-R (5′-CTGTGGTTCGCGGAAAC-3′), RT-16S rRNA-F (5′-GGACCACACACTTCATGGTG-3′), and RT-16S rRNA-R (5′-GAGTCTGGGCCGTATCTCAG-3′). The relative MAB_3508c mRNA level was determined as the ratio of the qPCR cycle threshold (CT) value of MAB_3508c mRNA to that of the 16S rRNA of each sample. For RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq), the libraries were prepared using a TruSeq Stranded mRNA sample preparation kit (Illumina Inc., USA). The libraries were sequenced on a MiSeq instrument (Illumina Inc.) to produce 75-bp paired-end reads. The sequences were analyzed by CLC Genomics Workbench v8.0 (CLC Bio).
Lipid extraction and analysis.
M. abscessus cells were inactivated by heating at 60°C for 1.5 h. After washing, lipids were extracted by treating 500 mg of bacteria (wet weight) with 2 ml of chloroform-methanol (2:1, vol/vol) at 56°C for 1 h. The organic phase of the extraction was collected and washed with water. The solvent was evaporated, and the dried lipid was weighed. The lipids were then dissolved in chloroform and subjected to thin-layer chromatography (TLC) on a Silica Gel60 TLC plate (Merck, Germany) using a solvent containing chloroform, methanol, and water at a ratio of 100:14:0.8 as previously described (16). To visualize lipids, the plate was sprayed with 10% H2SO4 and then charred with hot air until spots with hues characteristic of different lipid classes appeared. The mass of each lipid species was determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization−time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) with a pulse laser emitting at 337 nm as described previously (17). Samples were mixed with 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid as the matrix and analyzed in reflectron mode with an accelerating voltage of 25 kV.
Plasmid construction.
The DNA fragment containing the coding region of MAB_3508c was amplified by PCR using TaKaRa Ex Taq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa Corp., Shiga, Japan) and the primer pair MAB_3508c-F (5′-ATGGATCCATGATGACCGTTGAAGTGGA-3′) and MAB_3508c-R (5′-ATAAGCTTTCATGCCGCGGCGGTGTCGG-3′), containing BamHI and HindIII sites (underlined), respectively. The resulting MAB_3508c DNA fragment was cloned into pQE80L-pptr to generate pQE80L-pptr-MAB_3508c so that the MAB_3508c gene is driven by the ptr promoter (18). The DNA fragment containing the ptr promoter and MAB_3508c was cloned into the mycobacterial shuttle vector pMV261 (19), generating the plasmid pMN-pptr-MAB_3508c.
Statistical analysis.
All experiments were performed at least three times. Results are presented as means ± standard deviations. Statistical comparisons were performed using the Student t test.
RESULTS
M. abscessus colony morphotype changes induced by subinhibitory doses of aminoglycoside antibiotics.
To investigate changes in colony morphology in response to antibiotics, disc diffusion assays were performed. M. abscessus cells were inoculated at 200 to 500 CFU to form colonies on agar plates. As shown in Fig. 1A, the colonies of M. abscessus cs1c-S (smooth morphotype) exhibited a rough morphology near the disc containing the aminoglycoside antibiotic streptomycin, amikacin, or kanamycin, but a smooth morphology in areas distal to the disc. This colony morphology change was more profound in M. abscessus cells exposed to amikacin and kanamycin. An amikacin Etest showed that M. abscessus cs1c-S cells had a MIC of 2 μg/ml; the same MIC result was obtained with the microdilution assay (data not shown). The concentrations of amikacin that triggered a colony morphotype switch were 0.03 to 1 μg/ml. To investigate whether the morphotype switch caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics is reversible, the morphotype-switched M. abscessus cells were inoculated on another agar plate containing no antibiotics, and the colony morphology of these cells was found to switch from a rough back to a smooth form (data not shown).
FIG 1.
M. abscessus colony morphology switching induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. (A) Antibiotic disc diffusion assay. Cells of M. abscessus cs1c-S strain were plated at 200 to 500 CFU on a 7H11 agar plate. A disc containing streptomycin (100 μg), amikacin (20 μg), or kanamycin (20 μg) was then placed on the plate. Three-day-old M. abscessus colonies were examined for colony morphology. (B) Etest assay. An amikacin Etest strip was placed on a 7H11 plate inoculated with M. abscessus. The plate was incubated at 37°C for 3 days. The amikacin MIC and sub-MIC for M. abscessus are as indicated. The long arrow indicates the antibiotic diffusion direction.
Reduced sliding ability and increased aggregation and adherence by subinhibitory doses of amikacin.
Because the colony morphology of mycobacteria is related to their sliding, aggregation, and adherence abilities, we investigated the effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics on these phenotypes. The sliding motility assay was performed on agar plates with and without the presence of a subinhibitory dose (MIC50 [one-half of the MIC]) of antibiotics. As shown in Fig. 2A, M. abscessus cells were highly motile (16.2 ± 2.2 mm) on agar plates containing no antibiotics, but their motility was greatly decreased in the presence of a MIC50 of amikacin (9.1 ± 1.2 mm), streptomycin (5.9 ± 0.7 mm), or kanamycin (6.8 ± 0.9 mm).
FIG 2.
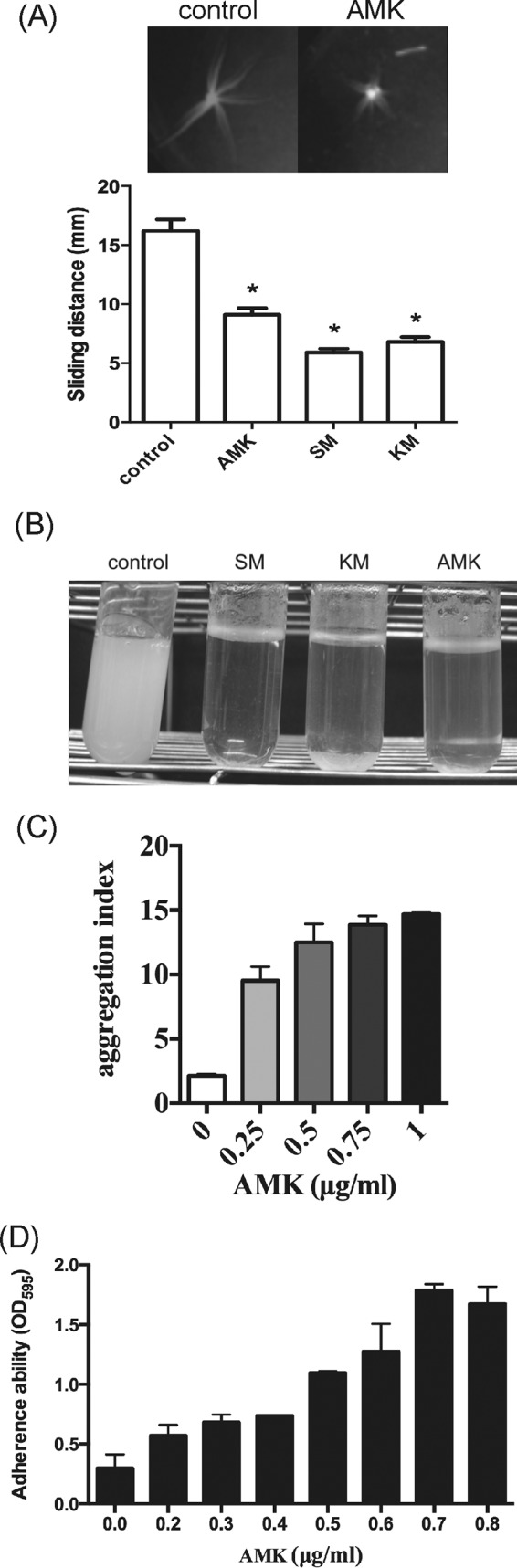
Alteration of M. abscessus cell surface-associated phenotypes by amino-glycoside antibiotics. (A) Sliding motility. M. abscessus cells were inoculated in the center of a 7H9 0.3% agar plate containing the MIC50s of the indicated antibiotics (control, no antibiotic; amikacin [AMK], 1 μg/ml; streptomycin [SM], 10 μg/ml; kanamycin [KM], 1 μg/ml). The sliding distance was measured in millimeters and plotted. (B) Bacterial aggregation ability. M. abscessus cells were cultured with low doses of antibiotics (SM, 10 μg/ml; KM, 1 μg/ml; AMK, 1 μg/ml) for 36 h at 37°C with shaking. Pictures of cultures were taken after the cultures were allowed to stand still for 10 min. (C) M. abscessus cells were cultured with various concentrations (0 to 1 μg/ml) of amikacin for 36 h at 37°C with shaking. The aggregation index of each culture was determined and plotted. (D) Adherence ability. Cultures of M. abscessus were grown in wells of a 96-well PVC plate containing the indicated concentrations (0 to 0.8 μg/ml) of amikacin for 6 days. The adhered bacteria in each well were washed and then stained with crystal violet. Optical density readings of the stain are presented as means ± standard deviations for three independent experiments. Data were analyzed by the Student t test. *, significant difference (P < 0.05).
To investigate the effect of subinhibitory doses of aminoglycosides on aggregation properties, M. abscessus cells were grown in liquid 7H9 medium with or without antibiotics at 37°C with shaking for 3 days. Results showed that M. abscessus cells exhibited a homogenously dispersed culture in the broth containing no antibiotics. In the presence of low concentrations (MIC50) of amikacin, streptomycin, or kanamycin, the cultures showed a clear supernatant with bacterial cells clumped in the bottom of the culture tubes (Fig. 2B). To quantify the aggregation ability, M. abscessus cells were grown in liquid 7H9 medium with various concentrations of amikacin (0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1 μg/ml). The cultures were incubated at 37°C for 3 days with shaking and then allowed to stand still for 10 min so that the bacterial cells settled to the bottom of the culture tubes. The OD600 values of the supernatant and the resuspended cell pellet were then measured to determine the aggregation index of each culture. As shown in Fig. 2C, the aggregation index of the culture without amikacin was approximately 2 but was increased to 10 to 15 in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of 0.25 to 1 μg/ml of amikacin. This result indicates that subinhibitory doses of aminoglycosides enhanced the aggregation property of M. abscessus cells.
The effect of subinhibitory doses of amikacin on adherence ability was then examined. M. abscessus cells were grown in wells of a 96-well PVC plate for 6 days. The adhered bacteria in each well were stained, and the intensity of the staining, which reflects the level of the adherence ability, was determined by measuring the OD595 of the dissolved stain. As shown in Fig. 2D, the adherence ability was increased by amikacin (0.2 to 0.7 μg/ml) in a dose-dependent manner.
Enhanced M. abscessus cord formation and antiphagocytosis ability by subinhibitory doses of amikacin.
Cord formation usually occurs in rough M. abscessus variants (16, 20). It is a mechanism of evading phagocytosis (21). Therefore, the possibility that subinhibitory doses of amikacin can trigger cord formation of M. abscessus cells and enhance their resistance to phagocytosis by macrophages was examined. As shown in Fig. 3A, microscopic examination of M. abscessus cs1c-S suspension cultures revealed no cord formation in the absence of amikacin. However, in the presence of a low dose (MIC50, 1 μg/ml) of amikacin, the cells formed cord-like structures. To perform the phagocytosis assay, M. abscessus cells were grown with or without a low dose (1 μg/ml) of amikacin to exponential phase, stained with SYTO 9, and then cocultured with THP-1 macrophages. The fluorescence intensity of the THP-1 cells containing phagocytosed SYTO 9-stained M. abscessus cells was determined. As shown in Fig. 3B, the fluorescence intensity of the THP-1 cells that phagocytosed amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells was significantly lower than that of those that phagocytosed untreated M. abscessus cells. These results indicate that M. abscessus cells gained antiphagocytosis ability after treatment with a subinhibitory dose of amikacin.
FIG 3.
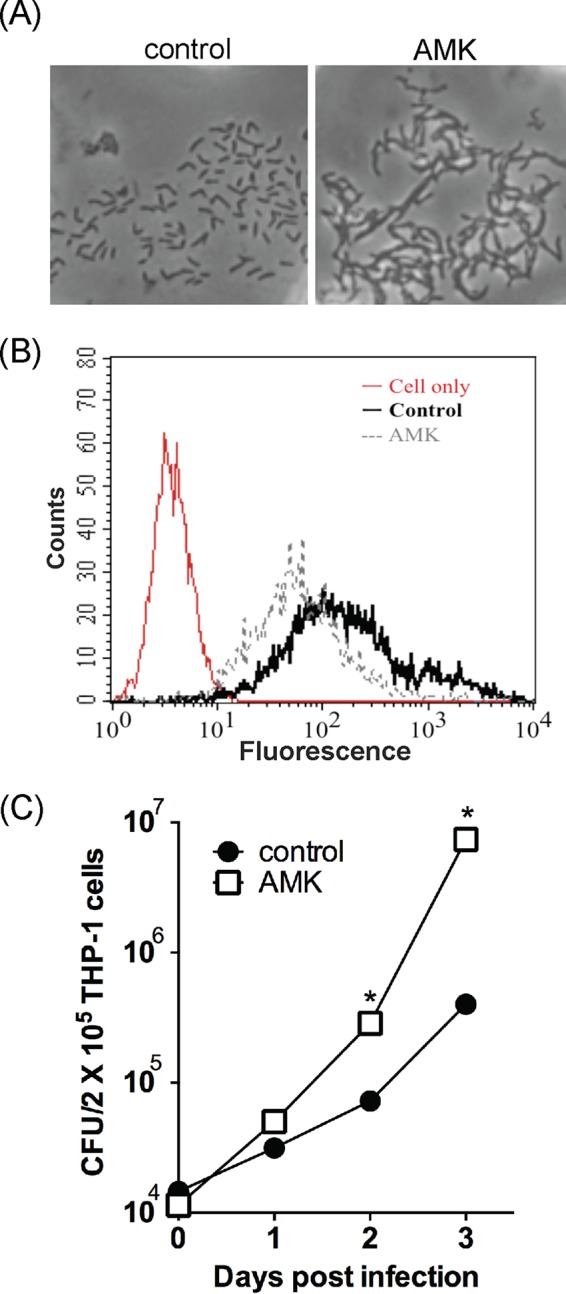
Virulence of the M. abscessus smooth variant enhanced by subinhibitory concentrations of amikacin. (A) Cord formation. M. abscessus cells were incubated in RPMI 1640 medium with or without a MIC50 (1 μg/ml) of amikacin for 2 days. The cells were collected, stained with crystal violet, and examined by microscopy. (B) Antiphagocytosis ability. M. abscessus cells were pretreated with a MIC50 of amikacin for 24 h, labeled with SYTO 9, and then cocultured with THP-1 macrophages at an MOI of 1 for 2 h. Bacterial uptake by the macrophages was determined by flow cytometry, and the fluorescence intensity of phagocytosed amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells was compared to that of phagocytosed non-amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells (control) and THP cells only (red curve). (C) Resistance against macrophage-mediated killing. M. abscessus cells were treated with or without a MIC50 of amikacin and then cocultured with THP-1 macrophages at an MOI of 1 for 1 h. THP-1 cells were lysed at the indicated time points after extensive washing with PBS. The cell lysates were plated for CFU determination. Data were analyzed by the Student t test. *, significant difference (P < 0.05).
Experiments were then performed to compare the tolerance of macrophage-mediated killing between untreated and amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells. THP-1-derived macrophages were infected with untreated or amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells. At 1, 2, and 3 days postinfection, the THP-1 macrophages were lysed, and the cell lysates were plated on agar plates. Results showed that the sample from THP-1 cells infected with amikacin-treated M. abscessus had a CFU of approximately 1 × 107, but that from those infected with untreated M. abscessus had a CFU of 5 × 105 (Fig. 3C). This result suggests that amikacin treatment increased the ability of M. abscessus to persist and replicate in THP-1 cells (Fig. 3C).
Increased TNF-α secretion by macrophages stimulated with amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells.
Since TNF-α is a potent proinflammatory cytokine and promotes aggregation of monocytes after Mycobacterium tuberculosis (22) and M. abscessus infection (16, 23), experiments were performed to determine whether, after amikacin treatment, M. abscessus cells induce more TNF-α release by macrophages. After pretreatment with a low dose (MIC50) of amikacin for 24 h, M. abscessus cells were cocultured with THP-1 macrophages for 1 day. As shown in Fig. 4A, TNF-α release was significantly higher by the THP-1 cells that were cocultured with amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells than those cocultured with untreated M. abscessus cells. To investigate whether Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2) plays a role in M. abscessus-simulated TNF-α secretion (24), THP-1 cells were treated with anti-TLR-2 antibody for 30 min and then were incubated with M. abscessus cells that were treated with or without a subinhibitory dose (1 μg/ml) of amikacin. Results showed that treatment with anti-TLR-2 antibody abrogated the ability of THP-1 cells to release TNF-α upon stimulation with amikacin-treated or untreated M. abscessus cells. However, THP-1 cells that were treated with control (isotype) antibody released approximately 30% more TNF-α when they were stimulated with amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells than those stimulated with untreated M. abscessus cells (Fig. 4B).
FIG 4.
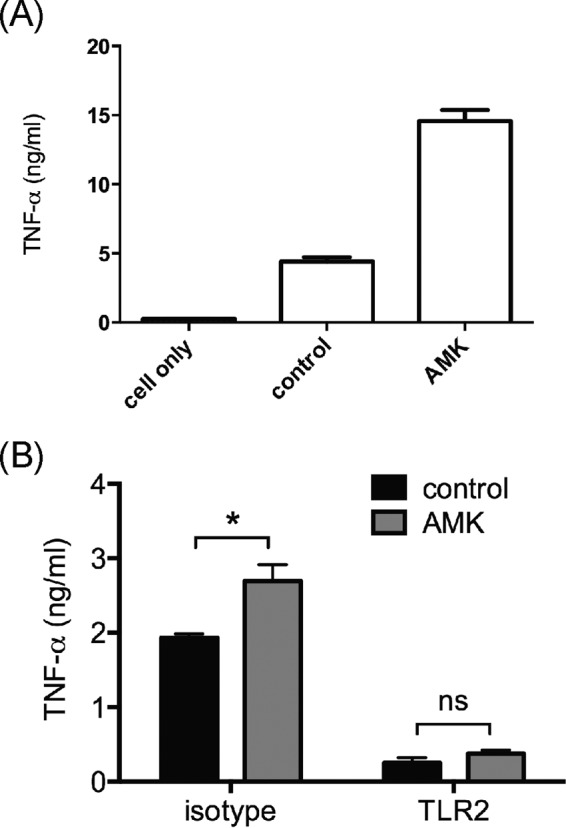
Enhanced TNF-α release through TLR-2 signaling by amikacin. (A) THP-1 macrophages were infected with untreated (control) M. abscessus cells or with M. abscessus cells treated with a MIC50 (1 μg/ml) of amikacin (AMK) at an MOI of 10 for 16 h. The levels of TNF-α in culture supernatants were determined by ELISA. (B) THP-1 macrophages were treated with anti-TLR-2 or isotype antibody for 30 min and then cocultured with untreated (control) or amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells for 24 h. The levels of TNF-α in culture supernatants were determined by ELISA. Data were analyzed by the Student t test. *, significant difference (P < 0.05); ns, no significant difference (P > 0.05).
No effect on glycopeptidolipid production of M. abscessus by subinhibitory amikacin treatment.
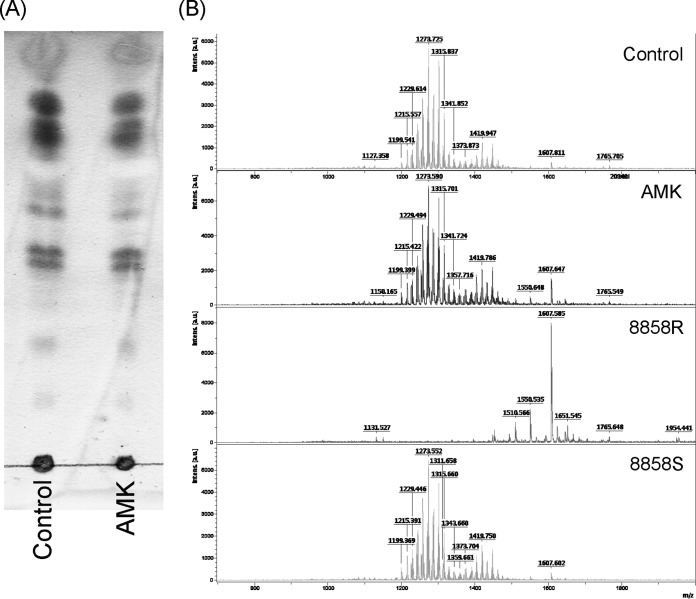
In previous studies, M. abscessus rough colony morphology was attributed to the lack of glycopeptidolipid (GPL) production (16, 25–27). To determine whether the smooth to rough colony morphotype change induced by amikacin was due to reduced GPL production, the GPL contents of M. abscessus cells with or without the treatment of subinhibitory doses of amikacin were analyzed. After pretreatment with the MIC50 of amikacin for 24 h, total lipids of M. abscessus cells were examined by TLC. Results showed that the GPL profile of amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells was similar to that of untreated control cells (Fig. 5A). Results of MALDI-TOF spectrometry revealed that the GPL profile of both untreated (control) and amikacin-treated M. abscessus cells was very similar to that of strain 8858S, which is a normal GPL producer (Fig. 5B).
FIG 5.
GPL contents of M. abscessus cs1c-S cells with or without treatment with a subinhibitory dose of amikacin. (A) TLC analysis. Equal weights of total lipid extracts from M. abscessus cs1c-S cells with or without amikacin treatment were resolved by thin-layer chromatography with CHCl3-CH3OH-H2O (100:14:0.8) and visualized with 1% 1-naphthol. (B) MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of total lipids from M. abscessus cs1c-S cells with or without amikacin treatment and control strains 8858R (GPL-deficient rough type) and 8858S (GPL-abundant smooth type).
To confirm that GPL production was not affected by treatment with subinhibitory doses of amikacin, the mRNA levels of genes involved in GPL production (28) were determined by RNA-seq. The ratios for mRNA levels of various GPL-associated genes of M. abscessus cells treated with subinhibitory doses of amikacin (AMK) versus untreated cells are listed in Table 1. These results showed that the expression of GPL-associated genes in M. abscessus cells was not significantly affected by subinhibitory doses of amikacin.
TABLE 1.
Ratios of mRNA levels of genes involved in the GPL biosynthesis of M. abscessus cells treated with subinhibitory doses of amikacin versus those of untreated (control) cells
| GPL gene | Gene name | AMKa/control |
|---|---|---|
| MAB_0934 | gap-like | 1.08 |
| MAB_0935c | fadD23 | 0.78 |
| MAB_0936c | pe | 0.85 |
| MAB_0937c | mmpL10 | 0.77 |
| MAB_0938c | papA3 | 0.81 |
| MAB_0939 | pks | 0.87 |
| MAB_4098c | mps2 | 1.13 |
| MAB_4099c | mps1 | 0.89 |
| MAB_4100c | mbtH | 0.82 |
| MAB_4103c | fmt | 1.21 |
| MAB_4104 | gtf | 1.53 |
| MAB_4105c | rmt3 | 1.43 |
| MAB_4110c | rmt2 | 1.29 |
| MAB_4111c | rmlB | 1.19 |
| MAB_4112c | gtf3 | 1.14 |
| MAB_4113 | rmlA | 1.06 |
| MAB_4114 | Rv1174 | 0.86 |
| MAB_4115c | mmpL4b | 0.75 |
| MAB_4116c | mmpL4a | 0.90 |
| MAB_4117c | mmpS4 | 1.25 |
| MAB_4454c | sap | 0.98 |
| MAB_4459c | ecf | 1.09 |
| MAB_4633 | Rv0926 | 1.04 |
AMK, amikacin.
Characterization of MAB_3508c responsible for pleiotropic phenotype switch of M. abscessus.
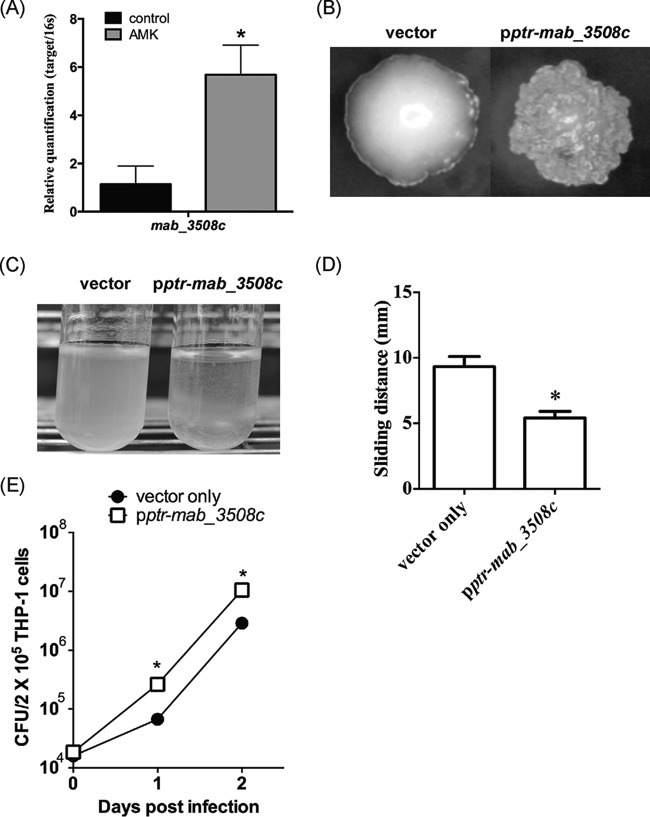
WhiB7 is a transcription factor that activates the intrinsic antibiotic resistance system of mycobacteria (29). We have found that the MAB_3508c gene of M. abscessus shares 55% amino acid sequence identity with whiB7 (our unpublished data). To determine whether amikacin has any effect on the expression of MAB_3508c, M. abscessus cells were treated with or without the MIC50 of amikacin and then examined for MAB_3508c mRNA levels. The results showed that amikacin treatment caused a 5-fold increase in MAB_3508c mRNA levels (Fig. 6A), compared to that of untreated cells.
FIG 6.
Role of M. abscessus MAB_3508c in amikacin-induced phenotype alterations. (A) MAB_3508c mRNA levels in untreated (control) and amikacin (1 μg/ml)-treated M. abscessus. (B to E) Colony morphology (B), aggregation in broth culture (C), sliding motility (D), and survival (E) of THP-1 macrophages of M. abscessus cs1c-s cells transformed with pMV-pptr-MAB_3508c or with the vector pMV261. Data were analyzed by the Student t test. *, significant difference (P < 0.05).
To investigate whether MAB_3508c plays a role in aminoglycoside-induced phenotype changes, the MAB_3508c gene was cloned and placed under the control of the constitutive promoter ptr from Streptomyces coelicolor for expression (18). The resulting construct was then introduced into M. abscessus cells. The transformed cells (designated pptr-MAB_3508c cells) were found to have a rough morphology, whereas M. abscessus cells containing the vector (pMV261) had a smooth morphology (Fig. 6B). Phenotype analyses showed that pptr-MAB_3508c cells had increased aggregation ability (Fig. 6C) and reduced sliding motility (Fig. 6D) than cells containing the vector. The sliding distance of M. abscessus cells transformed with the vector was 9.3 ± 2.6 mm and that of pptr-MAB_3508c cells was 5.4 ± 1.6 mm. The pptr-MAB_3508c cells were also found to be more resistant to phagocytosis by THP-1 cells as M. abscessus colony counts of THP-1 cells infected with pptr-MAB_3508c cells were higher (2.63 × 105 ± 0.63 × 105 at day 1 and 1.06 × 107 ± 0.13 × 107 CFU at day 2) than those of cells infected with M. abscessus containing the vector pMV261 (6.68 × 104 ± 1.55 × 104 at day 1 and 2.89 × 106 ± 0.58 × 106 CFU at day 2) (Fig. 6E).
DISCUSSION
In this study, we showed that subinhibitory concentrations of aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as amikacin, induced M. abscessus to change its colony morphology from a smooth to a rough morphotype. This change was associated with increased ability of M. abscessus cells to adhere to PVC, to aggregate in culture, and to resist phagocytosis and killing by macrophages. M. abscessus cells treated with a subinhibitory dose (1 μg/ml) of amikacin also became more potent in TLR-2 stimulation, leading to increased TNF-α production by macrophages and severity of lung inflammation.
The morphotype of M. abscessus cells is closely related to their glycopeptidolipid (GPL) biosynthesis (16). Previous studies showed that variations in the production of GPL by M. abscessus affect its colony morphology (23), and most rough M. abscessus strains were found to produce less GPL than smooth strains (16, 25–27). Deletion of the mmpl4b gene, which is involved in GPL biosynthesis, switched M. abscessus from a smooth to a rough morphotype (23). A genome-wide analysis of M. abscessus clinical isolates has identified a number of genetic mutations or deletions associated with the decrease in GPL production and the smooth to rough morphotype switching (25). Although GPL production is an important factor in the colony morphotype of M. abscessus, it may not be the sole determinant, as some smooth and rough strains of Mycobacterium smegmatis show no differences in GPL production (30). In the present study, we examined the surface lipids of smooth and antibiotic-induced rough M. abscessus strains by TLC and MALDI-TOF MS and found no differences in lipid profiles (Fig. 5). We also performed RNA-seq and found no significant differences in the mRNA levels of various genes involved in GPL biosynthesis (Table 1). Therefore, the antibiotic-induced morphotype switching may not be completely dependent on GPL biosynthesis. Further investigation is required to clarify this possibility.
We also found that treatment of M. abscessus cells with a subinhibitory concentration of amikacin increased the expression of MAB_3508c (Fig. 6A). Furthermore, overexpression of MAB_3508c in M. abscessus cells caused a switch from smooth to rough colony morphology, increased ability to aggregate in culture, decreased motility, and increased resistance to killing by macrophages (Fig. 6B to E). All of these properties of MAB_3508c-overexpressed M. abscessus cells are the same as those induced by a subinhibitory concentration of amikacin, suggesting that the effects of subinhibitory doses of aminoglycoside antibiotics on M. abscessus phenotype changes are mediated by MAB_3508c.
The MAB_3508c gene is homologous to the whiB7 gene of M. tuberculosis. WhiB7 has been shown to play a major role in the intrinsic antibiotic resistance of M. tuberculosis by activating the expression of a multidrug transporter (tap, Rv1258c) (31) and a ribosomal methyltransferase (erm, Rv1988) (32); whiB7-null mutants of M. tuberculosis are hypersusceptible to antibiotics. The expression of whiB7 in M. tuberculosis is inducible by antibiotics such as erythromycin, streptomycin, and tetracycline (33). WhiB7 also regulates the expression of eis (enhanced intracellular survival; Rv2416c), which has been shown to reduce the host immune response (34) and enhance mycobacterial survival in macrophages (33). The functions of MAB_3508c have not been characterized. The results of this study suggest that it regulates the phenotypic changes of M. abscessus cells when they are exposed to subinhibitory concentrations of amikacin. We are in the process of knocking out the MAB_3508c gene to confirm its function.
M. abscessus is the second most common cause of nontuberculosis mycobacterial infections in patients (6, 7). Only a limited number of antibiotics are effective for treatment of M. abscessus infections, including clarithromycin, kanamycin, amikacin, cefoxitin, and tigecycline (35, 36). Since most strains of M. abscessus are natively resistant or readily acquire resistance to multiple antibiotics, the doses of antibiotics used for prophylaxis or treatment of M. abscessus infections may be subinhibitory. This may make M. abscessus more virulent by the aforementioned mechanisms.
Subinhibitory doses of antibiotics may cause a wide variety of effects, such as increased mutation frequency, enhanced adhesion, and decreased protein secretion (1). Aminoglycosides are known to cause misreading errors during translation, leading to reduced growth rates (37), elongated cell morphology (38), and enhanced virulence in various bacteria. It has been shown that subinhibitory concentrations of tobramycin (an aminoglycoside) induce biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli (13). In P. aeruginosa, this effect is mediated by the aminoglycoside response regulator (arr), which regulates the levels of the second messenger cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP).
The results of this study might provide a guide for physicians in the treatment of M. abscessus infections. Sufficient concentrations of aminoglycoside antibiotics should be used for both prophylaxis and treatment. Investigations to determine whether subinhibitory concentrations of other nonaminoglycoside antibiotics also exacerbate the virulence of M. abscessus should be conducted, so that appropriate measures can be taken when these antibiotics are used.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Chao-Hung Lee for discussions and critical editing of the manuscript.
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (NSC102-2320-B-010-020-MY3) and the Ministry of Education (Aiming for the Top University Plan), Republic of China, to S.-T. Hu.
REFERENCES
- 1.Davies J, Spiegelman GB, Yim G. 2006. The world of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:445–453. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hoffman LR, D'Argenio DA, MacCoss MJ, Zhang Z, Jones RA, Miller SI. 2005. Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 436:1171–1175. doi: 10.1038/nature03912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lin JT, Connelly MB, Amolo C, Otani S, Yaver DS. 2005. Global transcriptional response of Bacillus subtilis to treatment with subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:1915–1926. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.1915-1926.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aminov RI. 2009. The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ Microbiol 11:2970–2988. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Subrt N, Mesak LR, Davies J. 2011. Modulation of virulence gene expression by cell wall active antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:979–984. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Galil K, Miller LA, Yakrus MA, Wallace RJ Jr, Mosley DG, England B, Huitt G, McNeil MM, Perkins BA. 1999. Abscesses due to Mycobacterium abscessus linked to injection of unapproved alternative medication. Emerg Infect Dis 5:681–687. doi: 10.3201/eid0505.990509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Villanueva A, Calderon RV, Vargas BA, Ruiz F, Aguero S, Zhang Y, Brown BA, Wallace RJ Jr. 1997. Report on an outbreak of postinjection abscesses due to Mycobacterium abscessus, including management with surgery and clarithromycin therapy and comparison of strains by random amplified polymorphic DNA polymerase chain reaction. Clin Infect Dis 24:1147–1153. doi: 10.1086/513656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Esther CR Jr, Esserman DA, Gilligan P, Kerr A, Noone PG. 2010. Chronic Mycobacterium abscessus infection and lung function decline in cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros 9:117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2009.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Roux AL, Catherinot E, Ripoll F, Soismier N, Macheras E, Ravilly S, Bellis G, Vibet MA, Le Roux E, Lemonnier L, Gutierrez C, Vincent V, Fauroux B, Rottman M, Guillemot D, Gaillard JL. 2009. Multicenter study of prevalence of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients with cystic fibrosis in France. J Clin Microbiol 47:4124–4128. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01257-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nessar R, Cambau E, Reyrat JM, Murray A, Gicquel B. 2012. Mycobacterium abscessus: a new antibiotic nightmare. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:810–818. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jarand J, Levin A, Zhang L, Huitt G, Mitchell JD, Daley CL. 2011. Clinical and microbiologic outcomes in patients receiving treatment for Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease. Clin Infect Dis 52:565–571. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gwan-Han S. 2007. The mycobacteria detection, molecular epidemiology and the drug susceptibility studies in Central Taiwan. Ph.D. dissertation. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stokes RW, Norris-Jones R, Brooks DE, Beveridge TJ, Doxsee D, Thorson LM. 2004. The glycan-rich outer layer of the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis acts as an antiphagocytic capsule limiting the association of the bacterium with macrophages. Infect Immun 72:5676–5686. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5676-5686.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Byrd TF, Lyons CR. 1999. Preliminary characterization of a Mycobacterium abscessus mutant in human and murine models of infection. Infect Immun 67:4700–4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Davidson LB, Nessar R, Kempaiah P, Perkins DJ, Byrd TF. 2011. Mycobacterium abscessus glycopeptidolipid prevents respiratory epithelial TLR2 signaling as measured by HbetaD2 gene expression and IL-8 release. PLoS One 6:e29148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Howard ST, Rhoades E, Recht J, Pang X, Alsup A, Kolter R, Lyons CR, Byrd TF. 2006. Spontaneous reversion of Mycobacterium abscessus from a smooth to a rough morphotype is associated with reduced expression of glycopeptidolipid and reacquisition of an invasive phenotype. Microbiology 152:1581–1590. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Villeneuve C, Etienne G, Abadie V, Montrozier H, Bordier C, Laval F, Daffe M, Maridonneau-Parini I, Astarie-Dequeker C. 2003. Surface-exposed glycopeptidolipids of Mycobacterium smegmatis specifically inhibit the phagocytosis of mycobacteria by human macrophages. Identification of a novel family of glycopeptidolipids. J Biol Chem 278:51291–51300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306554200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Forti F, Crosta A, Ghisotti D. 2009. Pristinamycin-inducible gene regulation in mycobacteria. J Biotechnol 140:270–277. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stover CK, de la Cruz VF, Fuerst TR, Burlein JE, Benson LA, Bennett LT, Bansal GP, Young JF, Lee MH, Hatfull GF, Snapper SB, Barletta RG, Jacobs WR Jr, Bloom BR. 1991. New use of BCG for recombinant vaccines. Nature 351:456–460. doi: 10.1038/351456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sánchez-Chardi A, Olivares F, Byrd TF, Julian E, Brambilla C, Luquin M. 2011. Demonstration of cord formation by rough Mycobacterium abscessus variants: implications for the clinical microbiology laboratory. J Clin Microbiol 49:2293–2295. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02322-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bernut A, Herrmann JL, Kissa K, Dubremetz JF, Gaillard JL, Lutfalla G, Kremer L. 2014. Mycobacterium abscessus cording prevents phagocytosis and promotes abscess formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E943−E952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321390111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Byrd TF. 1997. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) promotes growth of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human monocytes. Iron-mediated growth suppression is correlated with decreased release of TNFalpha from iron-treated infected monocytes. J Clin Invest 99:2518–2529. doi: 10.1172/JCI119436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nessar R, Reyrat JM, Davidson LB, Byrd TF. 2011. Deletion of the mmpL4b gene in the Mycobacterium abscessus glycopeptidolipid biosynthetic pathway results in loss of surface colonization capability, but enhanced ability to replicate in human macrophages and stimulate their innate immune response. Microbiology 157:1187–1195. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.046557-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rhoades ER, Archambault AS, Greendyke R, Hsu FF, Streeter C, Byrd TF. 2009. Mycobacterium abscessus glycopeptidolipids mask underlying cell wall phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides blocking induction of human macrophage TNF-alpha by preventing interaction with TLR2. J Immunol 183:1997–2007. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pawlik A, Garnier G, Orgeur M, Tong P, Lohan A, Le Chevalier F, Sapriel G, Roux AL, Conlon K, Honore N, Dillies MA, Ma L, Bouchier C, Coppee JY, Gaillard JL, Gordon SV, Loftus B, Brosch R, Herrmann JL. 2013. Identification and characterization of the genetic changes responsible for the characteristic smooth-to-rough morphotype alterations of clinically persistent Mycobacterium abscessus. Mol Microbiol 90:612−629. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim BJ, Kim BR, Lee SY, Kook YH, Kim BJ. 2013. Rough colony morphology of Mycobacterium massiliense type II genotype is due to the deletion of glycopeptidolipid locus within its genome. BMC Genomics 14:890. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Catherinot E, Clarissou J, Etienne G, Ripoll F, Emile JF, Daffe M, Perronne C, Soudais C, Gaillard JL, Rottman M. 2007. Hypervirulence of a rough variant of the Mycobacterium abscessus type strain. Infect Immun 75:1055–1058. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00835-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ripoll F, Deshayes C, Pasek S, Laval F, Beretti JL, Biet F, Risler JL, Daffe M, Etienne G, Gaillard JL, Reyrat JM. 2007. Genomics of glycopeptidolipid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium abscessus and M. chelonae. BMC Genomics 8:114. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zheng F, Long Q, Xie J. 2012. The function and regulatory network of WhiB and WhiB-like protein from comparative genomics and systems biology perspectives. Cell Biochem Biophys 63:103–108. doi: 10.1007/s12013-012-9348-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Arora K, Whiteford DC, Lau-Bonilla D, Davitt CM, Dahl JL. 2008. Inactivation of lsr2 results in a hypermotile phenotype in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Bacteriol 190:4291–4300. doi: 10.1128/JB.00023-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ramón-García S, Mick V, Dainese E, Martin C, Thompson CJ, De Rossi E, Manganelli R, Ainsa JA. 2012. Functional and genetic characterization of the tap efflux pump in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:2074–2083. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05946-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Buriánková K, Doucet-Populaire F, Dorson O, Gondran A, Ghnassia JC, Weiser J, Pernodet JL. 2004. Molecular basis of intrinsic macrolide resistance in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:143–150. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.1.143-150.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Morris RP, Nguyen L, Gatfield J, Visconti K, Nguyen K, Schnappinger D, Ehrt S, Liu Y, Heifets L, Pieters J, Schoolnik G, Thompson CJ. 2005. Ancestral antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12200–12205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505446102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kim KH, An DR, Song J, Yoon JY, Kim HS, Yoon HJ, Im HN, Kim J, Kim DJ, Lee SJ, Kim KH, Lee HM, Kim HJ, Jo EK, Lee JY, Suh SW. 2012. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Eis protein initiates suppression of host immune responses by acetylation of DUSP16/MKP-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7729–7734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120251109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, Holland SM, Horsburgh R, Huitt G, Iademarco MF, Iseman M, Olivier K, Ruoss S, von Reyn CF, Wallace RJ Jr, Winthrop K. 2007. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:367–416. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200604-571ST. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Colin AA, Ali-Dinar T. 2010. Aerosolized amikacin and oral clarithromycin to eradicate Mycobacterium abscessus in a patient with cystic fibrosis: an 8-year follow-up. Pediatr Pulmonol 45:626–627. doi: 10.1002/ppul.21222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Davies J, Gilbert W, Gorini L. 1964. Streptomycin, suppression, and the code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Possoz C, Newmark J, Sorto N, Sherratt DJ, Tolmasky ME. 2007. Sublethal concentrations of the aminoglycoside amikacin interfere with cell division without affecting chromosome dynamics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:252–256. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00892-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]