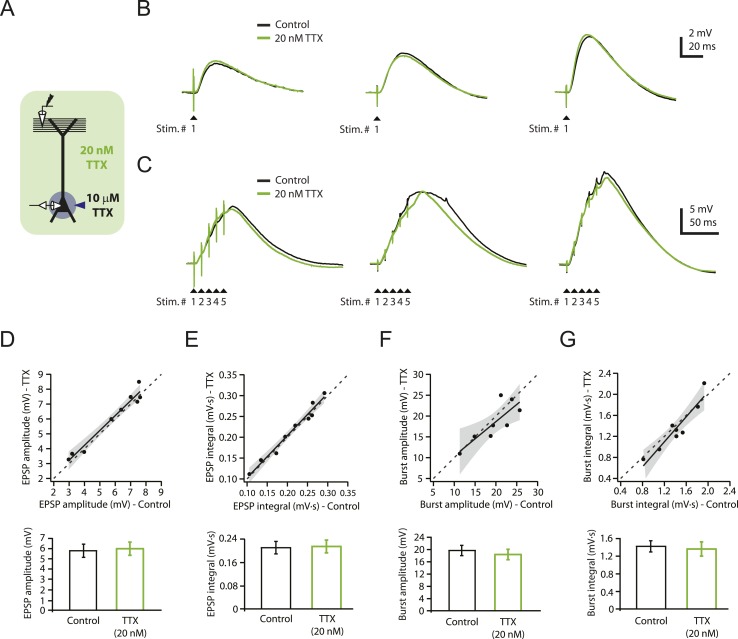
Figure 1. Reducing Nav channel availability with 20 nM TTX does not affect synaptic transmission at PP → CA1tuft synapses.
(A) Experimental configuration showing somatic whole-cell recording with presynaptic stimulation of the perforant pathway (PP), 10 µM TTX locally applied to the soma, and bath application of 20 nM TTX. (B, C) Representative traces of somatically recorded voltage in response to single-shock stimulation (B) or high-frequency burst stimulation (5 stimuli at 100 Hz; C) in control and 20 nM TTX. Traces are from three different cells. (D–G) Summary of effects of 20 nM TTX on EPSP amplitude and integral (D, E, single-shock, n = 9; F, G, burst, n = 8). Top. Scatter plots of the amplitude or integral of responses in 20 nM TTX vs control. Each point represents data from one cell. Solid lines represent a linear fit to data points, with shaded areas representing the 95% confidence band of the fit. Dashed lines are the unity line. Bottom. Bar graphs of the amplitude or integral of responses in control and 20 nM TTX.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.06414.003