Abstract
AIM: To establish the methylation profile of the promoter CpG islands of 31 genes that might play etiological roles in colon carcinogenesis.
METHODS: The methylation specific PCR in conjunction of sequencing verification was used to establish the methylation-profile of the promoter CpG islands of 31 genes in colorectal cancer (n = 65), the neighboring non-cancerous tissues (n = 5), colorectal adenoma (n = 8), and normal mucosa (n = 1). Immunohistochemically, expression of 10 genes was assessed on the home-made tissue microarrays of tissues from 58 patients. The correlation of tumor specific changes with each of clinical-pathologic features was scrutinized with relevant statistic tools.
RESULTS: In comparison with the normal mucosa of the non-cancer patients, the following 14 genes displayed no tumor associated changes: breast cancer 1, early onset (BRCA1), cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) (CDH1), death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1), DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), melanoma antigen, family A, 1 (directs expression of antigen MZ2-E) (MAGEA1), tumor suppressor candidate 3 (N33), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1) (p21WAF1), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) (p27KIP1), phosphatase and tensin homolog (mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1) (PTEN), retinoic acid receptor, beta (RAR- , Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family 1 C (RASSF1C), secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (Sorsby fundus dystrophy, pseudoinflammatory) (TIMP3), and von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL). The rest 17 targets exhibited to various extents the tumor associated changes. As changes in methylation of the following genes occurred marginally, their impact on the formation of colorectal cancer were trivial: adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) (8%, 5/65), Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family 1A (RASSF1A) (3%, 2/65) and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, alternated reading frame (p14ARF) (6%, 4/65). The following genes exhibited moderate changes in methylation: O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) (20%, 13/65), mutL homolog 1, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 2 (E. coli) (hMLH1) (18%, 12/65), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (melanoma, p16, inhibits CDK4) (p16INK4a ) (10%, 10/65), methylated in tumor 1 (MINT1) (15%, 10/65), methylated in tumor 31 (MINT31) (11%, 7/65). The rest changed greatly in the methylation pattern in colorectal cancer (CRC): cyclin A1 (cyclin a1) (100%, 65/65), caudal type homeobox transcription factor 1 (CDX1) (100%, 65/65), RAR-(85%, 55/65), myogenic factor 3 (MYOD1) (69%, 45/65), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B (p15, inhibits CDK4) (p15INK4b) (68%, 44/65), prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (COX2) (72%, 47/65), cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) (CDH13) (65%, 42/65), CAAX box 1 (CXX1) (58%, 38/65), tumor protein p73 (p73) (63%, 41/65) and Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) (58%, 38/65). However, no significant correlation of changes in methylation with any given clinical-pathological features was detected. Furthermore, the frequent changes in methylation appeared to be an early phase event of colon carcinogenesis. The in situ expression of 10 genes was assessed by the immunohistochemical approach at the protein level: CDH1, CDH13, COX2, cyclin A1, hMLH1, MGMT, p14ARF, p73, RAR- , and TIMP3 genes in the context of the methylation status in colorectal cancer. No clear correlation between the hypermethylation of the promoter CpG islands and the negative expression of the genes was established.
CONCLUSION: The methylation profile of 31 genes was established in patients with colon cancer and colorectal adenomas, which provides new insights into the DNA methylation mediated mechanisms underlying the carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer and may be of prognostic values for colorectal cancer.
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is the third most common malignancy in the developed countries, with an annual incidence approximately 35-50/100000[1,2]. The risk factors of CRC include Western diet (low fiber, high fat diet), family history, smoking, obesity and inflammatory colorectal diseases. As a whole, China falls into the low incidence country in the world, with the relative incidence of CRC rates being the 4th-6th of the total malignances and the 2nd-3rd of those in the digestive system in China. However, CRC occurrence exhibits an increasing trend, with an average 4.2% increase per year in the last two decades[3]. CRC is the 3rd common malignancy in Shanghai and occurs more frequently in China (http://www.caca.org.cn/zlyy/shanghai/index.asp). Clinically and pathologically, CRC has been grouped as the sporadic (approximately 80% cases) and hereditary types of diseases (roughly 20% in the total).
Both activation of proto-oncogenes (e.g. the CDH13 gene) and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes (e.g. the APC, p53 and genes responsible for the mismatch repaired activity in cells) attributed to genetic defects have been proved instrumental to carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. The well-known adenoma-carcinoma sequence of the genetic defects by Volgestein has gained both experimental supports and general recognition. However, the predicted accumulation of genetic events has not been substantiated in sporadic colorectal adenocarcinomas, and the expected increase in the number of genetic events in aging tissues has not materialized[4]. Both observations are indeed at odds with the exponential increase in the incidence of colorectal cancer with age. Therefore, alternative mechanisms must be accounted for such a shortfall, which is associated with DNA methylation mediated control of the expression of critical genes overseeing cell growth, apoptosis, as well as cell cycle progression.
Addition of the methyl group at the fifth carbon of cytosine of CpGs is the only covalent DNA modification in vertebrate[5]. Such epigenetic signatures in parental cells are passed to the daughter cells at high fidelity, by a similar semi-conserved mechanism during duplication of the genetic information. The hypermethylated status of CpGs can affect the DNA-protein interaction by eliminating the otherwise occurring DNA-protein interactions involved with the methylation-sensitive transcription factors, while unfolding a cascade of reactions toward the condensed chromatin that is initiated with binding to the methylated CpG by members of the methylated CpG binding protein family[6]. Cancer specific changes in methylation occur widely in all the cancers tested[7]. The global demethylation of DNA has been linked to the increased genome instability as the otherwise transcription-/ transposition-silenced repetitive sequences in normal cells are reactivated by DNA demethylation[8,9]. Paradoxically, local hypermethylation (at the promoter CpG island) has been well established for inactivation of tumor suppressor genes and caught great attention. However, the local demethylation in human tumors has also been recently reported to be associated with transcription reactivation of the silenced genes in normal tissues, such as the MAGEA1 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma[10]. In view of the fact that the majority of the promoter CpG island containing genes (50% of the protein-coding genes fall into this category) have not been properly looked in the context of the tumor biology, methylation profiling remains valuable for new insights into the etiological mechanism.
CRC is one of the first few types of cancers for methylation profiling[11,12]. Learnt from the rather extensive survey with more than 30 targets, a so called “CpG island methylation (CIM)” phenomenon has been reported, i.e., a clustering occurrence of multiple hypermethylated targets including upto a dozen of tumor suppressor genes[11]. In this study, we recruited 65 CRC tissues, eight colorectal adenomatous tissues, five neighboring non-cancerous tissues and one normal mucosa tissue from Shanghai Cancer Hospital for a middle scale methylation profiling with the promoter CpG islands of 31 genes, aiming, to establish the methylation profile of CRC patients in China, and to assess the association between the methylation status and expression profile of the genes in situ. Our results presented in this report should provide some new insights into the role of the epigenetic mechanism in CRC carcinogenesis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical-pathological profiles of CRC patients
With the informed consent of all patients and approval of the ethics committee, tumor tissues were obtained during surgery from 65 CRC patients at the Cancer Hospital of Fudan University in 1996-2003. They were 39 patients with sporadic colorectal cancer (SCRC), 10 with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) fulfilling Amsterdam criteria of IGC and Japanese criteria, and 16 in the category of Bethesda CRC. In addition, tissues were taken from the neighboring non-cancerous mucosa (at least 5-10 cm away from the tumorous lesions) of five patients. A cecum sample was obtained from a 68-year old female patient with inflammatory pseudotumor. In addition, Bethesda CRC concomitant adenomatous samples from six patients and sporadic colon adenomatous samples (one was cancer concomitant) from two patients were taken.
All samples were freshly obtained and cut into two parts. One was buried into an optimal cutting temperature compound (OCT, Miles Inc, USA), and put into fluid nitrogen for storage. The rest was fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin and then cut into 4-5 µm sections for routine pathological diagnosis.
Clinical-pathological features including the age and gender of patients, the tumor site histological type, Duke’s stages, differentiation grades (only moderate and poor differentiation), lymph node metastasis status, and more than 3 years follow-up results (36 cases) are shown in Table 1. The clinical-pathologic data of the eight adenomas are shown in Table 2.
Table 1.
Clinical-pathologic profiles of the CRC cases in this study
| Clinical-pathologic features | Number of cases | |
| Gender | Male | 37 |
| Female | 28 | |
| Age (yr) | Median | 60 |
| Range | 28-85 | |
| Tumor site | Left colon and rectum | 43 |
| Right colon | 22 | |
| Histological | Adenocarcinoma | 51 |
| types | Mucinousi carcinoma | 5 |
| Other types combined1 | 9 | |
| Differentiation Moderate | 51 | |
| Poor | 14 | |
| Follow-up | Survival | 27 |
| (3 yr) | Deceased | 9 |
| Duke’s stage | A | 6 |
| B | 15 | |
| C | 30 | |
| D | 14 | |
Other types combined included the mixed squamous cell carcinoma, carcinoid carcinoma, etc.
Table 2.
Clinical-pathologic profiles of adenomas and neigh-boring tumor-free mucosae
| Clinical-pathologic features | Adenoma | Mucosa | |
| Gender | Male | 4 | 2 |
| Female | 4 | 4 | |
| Age (yr) | Median | 60 | 68 |
| Range | 34-83 | 47-76 | |
| Tumor site | Left colon | 6 | 4 |
| Right colon | 2 | 2 | |
| Histological | Tubular | 3 | |
| type | Tubulovillous | 5 | |
| Dysplasia | Light-moderate | 8 | |
DNA preparation and methylation specific PCR analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from frozen tissues by the protein precipitation method[13]. Frozen tissue block was cut into 10-20 μm sections, put into a 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube, and then incubated at 37 °C in the cellular lysis buffer with proteinase K (SABC, Shanghai) for a final concentration of 100 μg/mL. The digestion was carried out at 55 °C for at least 2 h. After centrifuged, the upper liquid was collected and the protein precipitation mix was added. After centrifuged, 1:1 isopropanol was added. The deposition was washed with 750 mL/L ethanol, and naturally dried. The DNA pellet was washed once with 700 mL/L ethanol and dissolved with TE (10 mmmol/L Tris HCl, pH 7.4 and 1 mmol/L EDTA), and stored at a concentration of 1 mg/mL at 4 °C.
The primers for methylation specific PCR (MSP) (Table 3) were adopted as the previously published works[10,14] or designed with the assistance of the web server for the CpG islands identification (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/emboss/cpgplot/index.html) and the primer design software (http://micro-gen.ouhsc.edu/ cgi-bin/primer3_www.cgi). DNA treatment and PCR reaction were carried out by the previously described method[10,14,15]. In detail, 10 μg DNA in 50 μL TE was incubated with 5.5 μL of 3 mol/L NaOH at 37 °C for 10 min, followed by a 16 h treatment at 50 °C after 30 μL of freshly prepared 10 mmol/L hydroquinone and 520 μL of freshly prepared 3.6 mol/L sodium-bisulfite at pH 5.0 were added. The DNA was desalted using a home dialysis system with 10 g/L agarose. The DNA in the desalted sample (approximately 100 μL in volume) was denatured at 37 °C for 15 min with 5.5 μL of 3 mol/L NaOH followed by ethanol precipitation with 33 μL 10 mol-L NH4OAc and 300 μL ethanol. After washed with 700 mL/L ethanol, the gently dried DNA pellet was dissolved with 30 μL TE at 65 °C for 10 min. DNA samples were finally stored at -20 °C until further use. The sample of 50 ng of DNA was reserved for PCR reaction. PCR reaction was carried out in a volume of 15 μL with 50 ng or less template DNA with FastStart Taq polymerase (Roche, Germany) as follows. After an initial denaturing step for 3 min at 94 °C, 35 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, at varying temperatures with primer pairs for 30 s and at 72 °C for 30 s, were carried out. The PCR products were separated by 12 g/L ethidium bromide containing agarose gel electrophoresis with 1 × TAE and visualized under UV illumination. To verify the PCR results, representative bands from each target were gel-purified. Then the PCR products were sequenced directly or cloned into T-vector (Promega, USA) followed by automatic DNA sequencing provided by Bioasia (Shanghai, China). Only verified results were presented in this report.
Table 3.
Target CpG islands and the primers for MSP
| Gene | GenBank No. |
Primer |
Location to transcription start | Size (bp) | |
| Sense (5’-3’) | Anti-sense (5’-3’) | ||||
| APC | U02509 | (U) GTGTTTTATTGTGGAGTGTGGGTT | CCAATCAACAAACTCCCAACAA | -17 147 to -17 050 | 108 |
| (M) TATTGCGGAGTGCGGGTC | TCGACGAACTCCCGACGA | -17 153 to -17 046 | 97 | ||
| BRCA1 | L78833 | (U) GGTTAATTTAGAGTTTTGAGAGATG | TCAACAAACTCACACCACACAATCA | -320 to -138 | 182 |
| (M) GGTTAATTTAGAGTTTCGAGAGACG | TCAACGAACTCACGCCGCGCAATCG | -320 to -138 | 182 | ||
| CDH1 | NM_004938 | (U) GGTGGGTGGGTTGTTAGTTTTGT | AACTCACAAATCTTTACAATTCCAAC | -266 to -93 | 172 |
| (M) GTGGGCGGGTCGTTAGTTTC | CTCACAAATACTTTACAATTCCGACG | -265 to -93 | 172 | ||
| CDH13 | AB001090 | (U) TTGTGGGGTTTGTTTTTTGT | AACTTTTCATTCATACACACA | -267 to -24 | 243 |
| (M) TCGCGGGGTTCGTTTTTCGC | GACGTTTTCATTCATACACGCG | -267 to -24 | 243 | ||
| CDX1 | NT_029289 | (U) TGATTGGGTTGTTGTTTATGG | TACCACCACCACCTCCAA | +290 to +522 | 233 |
| (M) CGATTGGGTCGTCGTTTA | CCGCATCCACTCGTAAAA | +290 to +491 | 202 | ||
| COX2 | NT_004487 | (U) TTGTTTGTTGTTGTGATGTTTG | TCCAAACTCTTTCCCAAATC | -119 to -324 | 206 |
| (M) GTTCGTCGTTGCGATGTT | CCAAACTCTTTCCCAAATCA | -121 to -323 | 203 | ||
| CXX1 | NT_011786 | (U) TTAGGTTGGTTTTTGTGGATATG | CACCCAACCATCCATCAC | -24 to +92 | 117 |
| (M) AGGTCGGTTTTCGTGGAT | GATCGATATCGCCGTCAA | -22 to +192 | 215 | ||
| Cyclina1 | AF124143 | (U) GGGTAGTTTTGTTGTGTTTTAGTTG | AACCACTAACAACCCCCTCT | -762 to -565 | 199 |
| (M) TCGTCGCGTTTTAGTCGT | ACCCGTTCTCCCAACAAC | -755 to -550 | 206 | ||
| DAPK1 | NM_004938 | (U) GGATAGTTGGATTGAGTTAATGTC | CAAATCCCTCCCAAACACCAA | -332 to -229 | 103 |
| (M) GGATAGTCGGATCGAGTTAACGTC | CCCTCCCAAACGCCGA | -332 to -234 | 98 | ||
| DNMT1 | NT_011176 | (U) GGGTGGTAGATGTTGTTTTTGT | CACCCTACCTATCCCCCTAA | -359 to -130 | 230 |
| (M) CGTCGTTTTCGTTTATCGTT | ATACCTACCGCCTACGAACA | -320 to -140 | 181 | ||
| hMLH1 | AB017806 | (U) TTTTGATGTAGATGTTTTATTAGGGTTGT | ACCACCTCATCATAACTACCCACA | -526 to -654 | 118 |
| (M) ACGTAGACGTTTTATTAGGGTCGC | CCTCATCGTAACTACCCGCG | -531 to -655 | 124 | ||
| MAGEA1 | U82670 | (U) GTTTGGTTGAAGGAATTTGA | ACCCACAACCCTCCCTCTTA | +24 to +347 | 324 |
| (M) GTTCGGTCGAAGGAATTTGA | CCACAACCCTCCCTCTTAAA | +24 to +345 | 322 | ||
| MGMT | AL355531 | (U) TTTGTGTTTTGATGTTTGTAGGTTTTTGT | AACTCCACACTCTTCCAAAAACAAAACA | -451 to -266 | 209 |
| (M) TTTCGACGTTCGTAGGTTTTCGC | GCACTCTTCCGAAAACGAAACG | -469 to –261 | 186 | ||
| MINT1 | AF135501 | (U) TATTTTTGAAGTGTTTGTTTGGTGT | TCCCTCTCCCCTCTAAACTTC | 202 | |
| (M) TTCGAAGCGTTTGTTTGG | CGCCTAACCTAACGCACA | * | 160 | ||
| MINT31 | AF135531 | (U) GGGTGGGAATTGAGATGATT | CATCACCACCCCTCACTTTA | 131 | |
| (M) GCGGGAATTGAGACGATT | ACGCTTACGCCACTACGA | * | 176 | ||
| MYOD1 | NT_009307 | (U) ATTTGATGGTTTTTGATGGTTT | CACACACATACTCATCCTCACA | +206 to +418 | 213 |
| (M) GACGGTTTTCGACGGTTT | GCCCGAAACCGAATACAC | +210 to +393 | 184 | ||
| N33 | NT_030737 | (U) TTTGGTGAATTGGATGTTTTG | CACCCAACTCCTACCACACAC | +20 to +169 | 150 |
| (M) TTTTCGGTGAATCGGATG | TACGCGCCCAACTCCTA | +18 to +173 | 156 | ||
| p14ARF | L41934 | (U) TGAGTTTGGTTTTGGAGGTGG | AACCACAACAACAAACACCCCT | +97 to +262 | 165 |
| (M) GTCGAGTTCGGTTTTGGAGG | AAAACCACAACGACGAACG | +95 to +255 | 160 | ||
| p15INK4b | NM_004936 | (U) TGTGATGTGTTTGTATTTTGTGGTT | CCATACAATAACCAAACAACCAA | -318 to -164 | 154 |
| (M) GCGTTCGTATTTTGCGGTT | CGTACAATAACCGAACGACCGA | -312 to -165 | 147 | ||
| p16INK4a | NM_000077 | (U) TTATTAGAGGGTGGGGTGGATTGT | CAACCCCAAACCACAACCATAA | -80 to +71 | 151 |
| (M) TTATTAGAGGGTGGGGCGGATCGC | ACCCCGAACCGCGACCGTAA | -80 to +69 | 149 | ||
| p21WAF1 | NT_007592 | (U) TTTTTGTAGTATGTGAGGTTTTGG | AACACAACTCAACACAACCCTA | -200 to -1 | 200 |
| (M) TGTAGTACGCGAGGTTTCG | TCAACTAACGCAACTCAACG | -196 to +5 | 202 | ||
| p27KIP1 | AB003688 | (U) TGTGATTTTGATGTTGGTAAGGT | CAAACCACAACCCAAACTCT | -363 to -141 | 223 |
| (M) CGACGTCGGTAAGGTTTG | AAACGCGCAAAAACTACG | -355 to -163 | 193 | ||
| p73 | AB031234 | (U) TGGGTGTTTGGTTTGTAGGT | CCAACTCTCAACTCCCAAAA | -1 725 to -1 505 | 221 |
| (M) GCGTTCGGTTCGTAGGTT | CTCAACTCCCAAAACCCAA | -1 722 to -1 511 | 212 | ||
| PTEN | NM_000314 | (U) TGGTTTTTTGAGGTGTTTG | TTCCATCATAACTACAACTTCCA | -979 to -812 | 167 |
| (M) GGTTTTTCGAGGCGTTCG | CGCCTCACAACGACTCAACT | -978 to -786 | 192 | ||
| RAR-β | NM_016152 | (U) TTGAGAATGTGAGTGATTTGA | AACCAATCCAACCAAAACAA | -343 to -197 | 146 |
| (M) TCGAGAACGCGAGCGATTCG | GACCAATCCAACCGAAACGA | -343 to -197 | 146 | ||
| RASSF1A | NT_022517 | (U) TTTGGTTGGAGTGTGTTAATGTG | CAAACCCCACAAACTAAAAACAA | +70 to +178 | 108 |
| (M) GTGTTAACGCGTTGCGTATC | AACCCCGCGAACTAAAAACGA | +82 to +176 | 94 | ||
| RASSF1C | NT_022517 | (U) GGAGTTTGGATTGTTGGTTTTG | CACCCCCAAAAATAACCTCAT | -370 to -137 | 187 |
| (M) AGTTTGGATTGTCGGTTTCG | TCACAAACCCCACCTACCAC | -370 to -137 | 187 | ||
| SFRP1 | NT_008251 | (U) GTTTTGTGGTTGTAAGTTGTTGTT | AAACCCCACACACTCCAA | -180 to +19 | 199 |
| (M) TCGCGGTCGTAAGTTGTT | CGCACTCCAACCCTACAA | -177 to +11 | 188 | ||
| TIMP3 | NM_000362 | (U) TTTTGTTTTGTTATTTTTTGTTTTTGGTTTT | CCCCCAAAAACCCCACCTCA | -454 to -335 | 119 |
| (M) CGTTTCGTTATTTTTTGTTTTCGGTTTC | CCGAAAACCCCGCCTCG | -451 to -335 | 116 | ||
| VHL | AF010238 | (U) GTTGGAGGATTTTTTTGTGTATGT | CCCAAACCAAACACCACAAA | -185 to -20 | 165 |
| (M) TGGAGGATTTTTTTGCGTACGC | GAACCGAACGCCGCGAA | -183 to -25 | 158 | ||
| WT1 | X74840 | (U) TGGGATTTGGGTGGTATTTG | CACCAACACCCACTACACCA | +295 to +510 | 216 |
| (M) GTTAGGCGTCGTCGAGGTTA | AAAACGCAAAATCCAACACC | +321 to +526 | 206 | ||
Immunohistochemistry analysis on a home made tissue microarray
The paraffin embedded tissues from 58 cancer cases were made into the tissue microarray paraffin blocks, followed by sectioning. For each sample, the H&E stained sections were first reviewed and marked for the picked point. At least 4 points of cancer tissue and 1 point of normal mucosa tissue were taken from the different positions on the paraffin block. The diameter of our tissue microarray punch was 1 mm. We put about 40-80 tissue dots in one array. To identify the tissue put into the array, all the made tissue microarray sections were stained with H&E and reviewed by two pathologists independently.
The immunostaining was performed with each of 10 commercially available antibodies (Table 4) using DAKO Envision system/3,3-diaminoben-aidine (DAB) staining. The result was scored by conjunction with both staining intensity and the percentage of positive staining cells. Each sample was given an intensity score (0-3) and a percentage of cell positive score (0 = less than 5%, 1 = 5%-25%, 2 = 25%-50%, 3 = 50%-75%, 4 = more than 75%). An overall immunohistochemistry score was calculated by multiplying the intensity and percentage of cell positive scores. Scores of 1-4 were recorded as +, 6-8 as + +, and 9-12 as + + +.
Table 4.
Antibodies for immunohistochemical analysis
| Antibody name | Expression location | Company | Catalogue No. |
| CDH1 | Membrane/Cytoplasm | Antibody Diagnostica INC. | M-0536 |
| CDH13 | Cytoplasm | Santa Cruz | sc-7940 |
| COX2 | Cytoplasm | Santa Cruz | sc-1746 |
| Cyclin a1 | Nuclear | Novocastra Lab. | NCL-CYCLINA |
| hMLH1 | Nuclear | PharMingen | G168-15 |
| MGMT | Cytoplasm | DAKO | M3610 |
| p14ARF | Nulear/Cytoplasm | Santa Cruz | sc-8340 |
| p73 | Cytoplasm | Santa Cruz | sc-17823 |
| RAR | Nuclear/ Cytoplasm | Santa Cruz | sc-552 |
| TIMP3 | Cytoplasm | Oncogene | IM43T |
Statistical analysis
A comparison of the proportion was performed using Pearson 2 test or the Fisher’s exact method. Analysis of methylation status vs protein expression was performed using the contingency coefficient.
RESULTS
Among the 65 CRC patients, there were 39 SCRCs, 10 HNPCCs and 16 colorectal carcinoma in Bethesda category. In addition, eight colorectal adenomas, five non-cancerous mucosa tissues and one normal mucosa sample were also recruited for this study.
Twenty four genes among the 31 targets studied in this study were previously analyzed in liver cancer[10] and astrocytoma (unpublished data) in this and other laboratories. They were APC, BRCA1, CDH1, CDH13, DAPK1, hMLH1, p14ARF, p15INK4b , p16INK4a , p27KIP1, p73, PTEN, RAR-b, RASSF1A, RASSF1C, VHL and WT1. The CDX1, COX2, CXX1, MINT1, MINT31 and TIMP3 genes have also been studied in colon cancer, the methylation pattern of which was found altered in CRC[16] so that the relevant inter-study comparison of the methylation behaviors should be possible. In this list, there were genes with the proven roles in as well as those lacking any obvious association with the carcinogenesis of human tumors. For the later group, hypermethylation of the myogenetic lineage-specific transcription factor: MYOD1, occurs more frequently in aging tissues than its younger counterparts[17]. In the category of cancer associated genes, the tumor suppressor genes made up the major part. There were proteins operating in the RB1/p16INK4a pathway: p14ARF, p15INK4b and p16INK4a, as well as the three cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: p21WAF1, p27KIP1[18] and p57KIP2[19]. The rest in this subset were the p53 analogue, p73[18,20], the two alternative forms of a tumor suppressors in the Ras mediated signal transduction pathway: RASSF1A and RASSF1C[21], VHL[22], APC[23], PTEN[6], N33 as well as the Wilms tumor 1 gene, WT1[24]. Also included were the genes encoding the cell membrane proteins or nuclear receptors acting actively in intercellular interactions: e.g. melanoma specific antigen A1 (MAGEA1)[25], and cadherins, CDH1[26]and CDH13[26]. One gene implicated in signal transduction was cyclin A1[27]. The gene encoding O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase, MGMT[28] was also included, which plays a key role in the cellular responses to alkalyting agents and heavy metal stresses. The genes acting in DNA repair process were hMLH1[29] and BRCA1[30] as well as the gene acting in apoptosis, DAPK1[31].
Genes displayed no changes in methylation profile in tumor samples
As shown in Figure 1 and summarized in Figure 2, by comparing with the normal mucosa of non-cancerous samples, the following 14 genes did not display any tumor associated changes: BRCA1 (panel 2), CDH1 (panel 3), DAPK1(panel 9), DNMT1(panel 10), MAGEA1(panel 12), N33(panel 17), p21WAF1 (panel 21), p27KIP1 (panel 22), PTEN (panel 24), RAR- (panel 25), RASSF1C (panel 27), SFRP1 (panel 28), TIMP3 (panel 29) and VHL genes (panel 30). The MAGEA1 gene was the only target that tends to be demethylated and transcription-activated in tumors, as we previously demonstrated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[10]. But the hypermethylated state of its promoter CpG islands maintained in all the samples tested. The likely explanations for such no-change-type-observations were the following: no changes in expression of this set of genes occurred in CRC, and the changes in expression indeed occured, but the DNA methylation mediated mechanisms was not involved.
Figure 1.

Methylation profiles of the promoter CpG islands of 31 genes in CRC. Both electrophoretic patterns of the representa-tive PCR products of each of 31 targets (indicated respectively, at the top of figures) and the sequencing verification of the one representative PCR product are presented. To indicate the methylation status, the sequenced data are aligned with the wild-type sequence. 1Size markers, the bands of 250 bp and 100 bp are shown. U, the unmethylated; M, hypermethylated. Panels: 1, APC, 2, BRCA1, 3, CDH1, 4, CDH13, 5, CDX1, 6, COX2, 7,CXX1, 8, cyclin A1, 9, DPAK1, 10, DNMT1, 11, hMLH1, 12, MAGEA1, 13, MGMT, 14, MINT1, 15, MINT31, 16, MYOD1, 17, N33, 18, p14ARF, 19, p15INK4b, 20, p16INK4a 21, p21WAF1, 22, p27KIP1, 23, p73, 24, PTEN, 25, RAR-b, 26, RASSF1A, 27, RASSF1C, 28, SFRP1, 29, TIMP3, 30, VHL, and 31, WT1.
Figure 2.

Changes in methylation pattern of genes in CRC and other relevant tissues. The frequency (%) of the hypermethylated targets among the total cases was calculated, and the frequency of the changes in the methylation pattern is presented in the plot as well as in the attached table. Panels: 1, SCRC, 2, HNPCC, 3, Bethesda, 4, Adenoma, 5, Non-cancerous mucosa from CRC patients and 6, the normal mucosa from a non-cancerous patient.
It should be pointed out that our no change conclusion as to both N33 and TIMP3 genes was at odds with the previous report where both genes were hypermethylated rather frequently in CRC[32]. Whether it was attributed to the inherent difference between patient groups in different studies remains to be clarified.
Genes displayed changes in methylation profile in tumor samples
To score the changes in each CRC case, the methylated status in the mucosa tissue of the non-cancerous patients was taken as the reference, any deviation from which was scored as positive (increasing methylation extent) or negative (decrease in methylation extent).
Seventeen genes in this list displayed to various extents the tumor associated changes. As shown in Figures 1, 2, the changes of the following genes occurred marginally, and their impact on CRC looked trivial: APC (panel 1) (8%, 5/65), RASSF1A (3%, 2/65) (panel 26) and p14ARF (6%, 4/65) (panel 18). It was surprising to see that the extremely low frequency in hypermethylation of the RASSF1A gene in CRC, which was hypermethylated in a wide range of the human tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma[10,14], astrocytoma (unpublished results) and other tumors[33,34].
The following genes displayed significant alterations in methylation pattern deviated from that of the mucosa of the non-cancer tissues, including those with the moderate levels of changes: MGMT (20%, 13/65, panel 13), hMLH1 (18%, 12/65, panel 11), p16 INK4a(10%, 10/65, panel 20), MINT1 (15.4%, 10/65, panel 14), MINT31 (11%, 7/65, panel 15); and with a great level of changes: COX2 (72%, 47/65, (panel 6), cyclin A1 (100%, 65/65, panel 8) and CDX1 (100%, 65/65, panel 5), RAR- (85%, 55/65, panel 25), MYOD1 (69%, 45/65, panel 16), p15INK4b (68%, 44/65, panel 19), CDH13 (66%, 43/65, panel 4), CXX1 (58%, 38/65, panel 7), p73 (63%, 41/65, panel 23) and WT1 (58%, 38/65, panel 31, Figure 1). In this list, while changes in methylation pattern of the majority of targets, were compatible with the previously reported frequencies in CRC patients in the Western countries[7,11,35,36], there was a noticeable difference. For instance, we have found the p15INK4b was significantly methylated in CRC (68%, 44/65), while this gene was not methylated at all in a similar study in USA[35].
It was also our intention to correlate the methylation pattern with the clinical-pathological features of CRC patients. Subjected to the stringent statistic analysis (P < 5%), none of the comparisons displayed any significant correlation. For instance, there was no statistic significance between the methylation changes of any given genes among different subgroups of CRC: SCRC and HNPCC as well as against other cohorts of tissues, such as colorectal adenoma and adjacent mucosa. This was likely to attribute to the small sample size. Although there was a decent number for SCRC (n = 39), the sample sizes for other subgroups were rather small: 10 HNPCCs, 16 Bethesda CRCs, eight adenomas, five non-cancerous mucosae and one normal mucosa.
It has been well recognized that the so-called non-cancerous cells pathologically defined may have already suffered some genetic lesions as the corresponding cancerous tissues, the outcome of the earlier events of carcinogenesis. The scenario of the genetic events from the normal mucosa to the full-blown CRC within the context of the well defined clinical and pathological parameters has been well characterized[37]. In this study, we included samples of non-cancerous mucosa from five CRC patients, adenomatous samples from eight patients and tumorous tissues from 65 CRC cases including 39 SCRCs, 10HNPCCs and 16 Bethesda CRCs, which enabled us to determine whether the changes in methylation pattern in CRC were specific to the early or late phases of carcinogenesis. Judged by the no difference in methylation pattern between the non-cancerous mucosa and adenoma and /or CRC (Figure 1, Figure 2) (the same rationale used in our previous work on the hepatocellular carcinoma[10]), we suggested that the high frequent changes in methylation pattern of the genes might be the early rather than the late phase events during carcinogenesis of CRC.
CRC was among the first few types of human cancers subjected to the rather intensive DNA methylation profiling, where changes in methylation in tumor samples were classified as the aging related as well as the cancer specific[17,38,39]. For instance, the MYOD1 was found also hypermethylated more frequently in the aged healthy epithelia tissues than their younger counterparts[17]. Also from the studies of CRC, the concordant methylation profile of multiple genes was firstly reported, called “CpG island methylation phenotype (CIMP)”, short for CpG island methylator phenotype[11]. It implies that the unknown genetic mechanism (s) operating in CRC may contribute to the clustering profile of the DNA methylation of the multiple genes together. Among the 65 CRC cases, the distribution in occurrence of changes in the multiple genes was as following, 1, 3, 5, 7, 12, 11, 11, 7, 4, 1, and 3 cases, for assuming the methylation change of from 2, progressing step by step to 12 genes, respectively (Figure 3), with the 7 gene group as the peak.
Figure 3.

Concordant behavior of the multiple methylated loci in CRC.
In situ expression profile of 10 genes in CRC
Hypermethylation of the promoter CpG islands could reflect the transcriptional silencing status of the gene. However, exceptions also were reported, suggesting the involvement of other mechanisms in the control of the gene transcription. To verify this notion, we immunostained 10 target proteins in situ on the home-made tumor tissue arrays, where the tissue blocks from 58 CRC samples along with several controls of the non-cancerous mucosa from the cancer patients were present. The results were scored from the negative (-), to positive: ranging from + to + + +. With the expression level in the non-cancerous mucosa as reference, the relative level of expression of each protein in the context of the methylation state of the promoter CpG islands of the genes was assessed. As shown in Figure 4 and summarized in Table 5, the unmethylated states of the promoter CpG islands of the following genes were indeed positively correlated with the expression levels of the genes. Among the cases of the fully unmethylated targets, expression of each protein ≥ one + level occurred very frequently: for the CDH13, 73% (16/22); RAR-b, 100% (8/8); COX2, 80% (35/44); p73, 60% (12/20); hMLH1, 75% (35/47); p14ARF, 100% (51/51); TIMP3, 80% (46/58) and CDH1, 98% (57/58). The only exception was MGMT, only 25% (2/8) of the unmethylated cases expressed this protein, suggesting the mechanisms other than DNA hypermethylation being involved. For the CRC cases with the heterozygous methylated status (u/m), expression of each proteins was: CDH13, 50% (14/28); cyclin A1, 70% (37/53); RAR- , 79% (22/28); COX2, 100% (14/14); p73, 54% (19/35); MGMT, 24% (11/46); hMLH1, 36% (4/11) and p14ARF, 100% (2/2), respectively. For the CRC cases with the fully methylated targets, the expression profile of the genes was as the following: CDH13, 38% (33/58), cyclin A1, 80% (4/5), RAR- , 85% (17/20) and MGMT, 50% (2/4). Except for the CDH13, which expressed less frequently in the methylated than the unmethylated containing cases, the expression frequency was not significantly less prevalently in the methylated cases, even higher as far as the MGMT was concerned. Therefore, the correlation between the methylation status and level of expression of these 10 genes was not in a good agreement with the conventional notion.
Figure 4.
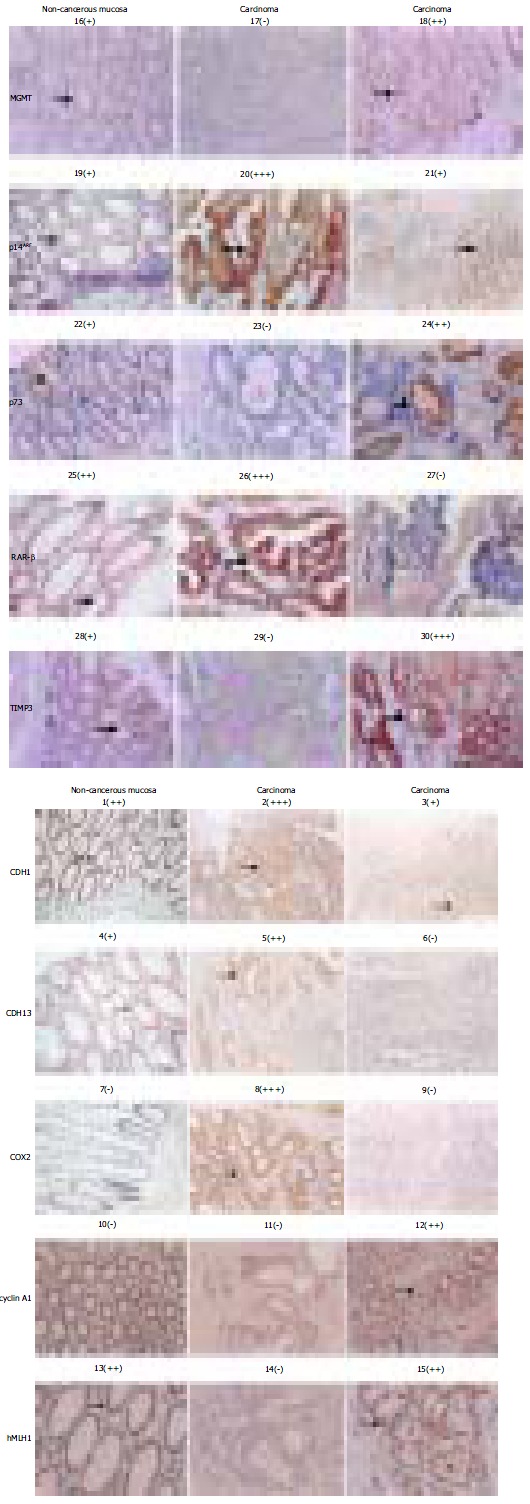
Immunochemical assessment of the expression level of each of 10 target genes. Both the protein targets (left site to) and sample identities (top down) of the immuno-chemical stained picture are indicated. The signs: -, +, + +, and + + + in bracket are used to provide the quantitative reference in pictures below. The areas pointed by the arrows are the regions showing the immunostaining data quantified.
Table 5.
Expression profile of the genes in the context of DNA methylation status
| Methylation status |
Positive rate % (Positive cases/the total cases) |
|||||||||
| CDH13 | Cyclin a1 | RAR- | COX2 | P73 | MGMT | hMLH1 | p14ARF | TIMP3 | CDH1 | |
| U | 73 (16/22) | / | 100 (8/8) | 81 (35/43) | 60 (12/20) | 24 (11/46) | 74 (35/47) | 100 (51/51) | 80 (46/58) | 98 (57/58) |
| U/M | 50 (14/28) | 70 (37/53) | 79 (22/28) | 93 (14/15) | 54 (19/35) | 25 (2/8) | 36 (4/11) | 100 (2/2) | / | / |
| M | 38 (3/8) | 80 (4/5) | 85 (17/20) | / | / | 50 (2/4) | / | / | / | / |
| Total | 57 (33/58) | 71 (41/58) | 84 (47/56) | 84 (49/58) | 53 (31/58) | 26 (15/58) | 67 (39/58) | 100 (53/53) | 79 (46/58) | 98 (57/58) |
| Non-cancerous mucosa | + | / | ++ | / | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ |
DISCUSSION
In this study, 31 targets were selected to be studied, 65 cases of CRC, 8 cases of adenoma, five cases of non-cancerous mucosa from the cancer patients and one case mucosa from the non-cancerous patient. As far as the number of genes was concerned, this study is rather extensive, and it is the first of such a kind with CRC patients in China, and in Shanghai in particular.
Changes in methylation pattern of the promoter CpG islands are very common in CRC
By taking the methylation profile of the mucosa from the non-cancerous patient as the reference, CRC associated changes in methylation pattern were a very extensive event, 17 among of 31 targets assumed the altered patterns, the following 14 changed in more than 20% of CRC cases as a whole: MGMT (20%, 13/65), hMLH1 (18%, 12/65), p16 INK4a (10%, 10/65), MINT1 (15.4%, 10/65), MINT31 (11%, 7/65), COX2 (72%, 47/65), cyclin A1 (100%, 65/65), CDX1 (100%, 65/65), RAR- (85%, 55/65), MYOD1 (69%, 45/65), p15INK4b (68%, 44/65), CDH13 (66%, 43/65), CXX1 (58%, 38/65), p73 (63%, 41/65) and WT1 (58%, 38/65) genes. Furthermore, there was only one case assuming the methylation changes with three genes (Figure 3), no less than 76.3 % of cases assumed changes in methylation more than seven targets (49/65), 86% more than six targets (56/65), 93.8% more than five targets (61/65). This observation indeed supports the concept, “CpG island methylator phenotype”, for that changes in methylation pattern in CRC indeed tend to be clustered. As a similar survey with the astrocytoma showed that less 26.4% patients assumed no more than two gene (among 31 targets being surveyed), and the occurrence of changes in methylation pattern for at least five, six and seven targets was 41.51%, 20.75 and 9.43% in a cohort of 56 astrocytoma patients (unpublished data). The high incidence of changes in CRC may be partly attributed to the fact that colorectal epithelial cells were much amenable to the environmental challenges.
Except for the genes that have been proved in the category of tumor associated genes, such as p16INK4a, p15CDKN4b, p14ARF, p27KIP1, WT1, VHL, RB, p73, APC, N33, PTEN and BRCA1, the MAGEA1 and RAR- genes have not been studied in CRC. While the MAGEA1 gene displayed the homozygously methylated state in all samples tested, the RAR- gene indeed changes its methylated state from the unmethylated in the normal mucosa toward the hypermethylated state at a significantly higher frequency in CRC, over 85% (55/65). The retinoic acid receptor (RAR) gene is a putative tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p24, where a high incidence of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) is detected in many types of tumors. Retinoic acid suppresses cancer cell growth through binding to RARs, especially RAR-, indicating a critical role in mediating anticancer effects. Selective loss or down-regulation of the RAR mRNA and protein has been reported in prostate cancers. The DNA methylation mediated silencing of this gene has been suggested as an etiological factor for carcinogenesis of prostate cancer[40]. This result indicates that the RAR- hypermethylation may be the mechanism of expression silencing in these tumor cells[41]. However, its etiological significance in carcinogenesis of CRC remains to be clarified.
The following genes: CXX1, CDX1, SFRP1, MINT1 and MINT31 were initially identified as the CRC associated hypomethylated genes by an approach at the genome level[16]. Except for the SERP1 gene that was not methylated with all the samples being tested, the rest targets were indeed hypermethylated to varying extents in CRC (Figure 1, Figure 2). Tumor suppressor gene RASSF1A was inactivated predominantly by promoter methylation and rarely by somatic mutations. wagner et al[34] investigated RASSF1A promoter methylation in colorectal cancer and detected RASSF1A methylation in 80% (4/5) colorectal cancer cell lines and 45% (13/29) primary colorectal cancers. But we found that the frequency of RASSF1A methylation was extremely low in CRC although we previously found this gene was hypermethylated (100%) in HCC[14].
Does the methylation profile of the promoter CpG islands of the genes correlate with the expression of the genes?
Although it has been generally accepted that the hypermethylated status of the promoter CpG islands represents the long-term transcription silencing state of the genes, its credential has not been thoroughly checked in clinical samples, due to various limiting factors, including availability and inherent diversity of the cell types in the actual samples. In this study, we immuno-stained the genes with antibodies to assess the expression of 10 genes in a home-made tissue array. For both homozygously and heterozygously unmethylated samples, nine of 10 targets (except for MGMT) expressed at a detectable level of more than 60% cases. It was generally fit with the expectation. For the fully methylated CRC, only four targets were involved, among which the profile of the CDH13 gene met the expected profile. The expression frequency (38%, 3/8) in methylated samples was significantly lower than heterozygously methylated (50%, 14/28), and homozygously unmethylated (73%, 16/22). The profiles of the other three targets did not comply with the role at all. Both cyclin A1 and RAR- genes expressed equally well as the CRC samples of m/u type. Furthermore, it was paradoxically found that the MGMT gene expressed more prevalently in the methylated CRC cases (50%, 2/4) than its counterparts (u/m: 25%, 2/8 and u: 25%, 11/46). As we have previously shown in astrocytoma cell lines, the methylated status of the promoter CpG islands inversely correlated with the expression of the MGMT gene (unpublished data), this rather unexpected observation should be looked into further. In conclusion, despite the general roles that have been followed as to the inverse correlation between the methylation state of the promoter CpG islands and expression, the exception is also distinguishingly noticeable. Therefore, it should be very cautious in correlating the methylated status with the expression profile of the genes.
Demethylation of the COX2 gene correlates with the increased frequency in its expression
Cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX2), an inducible isoform of prostaglandin H synthase, which mediates prostaglandin synthesis during inflammation, and is selectively over-expressed in colon tumors, is thought to play an important role in colorectal carcinogenesis[42]. Its expression in the normal epithelial cells is low, but can be induced by a variety of stressing agents, including tumor promoters and inflammatory cytokines. In the list of the genes displaying changes in methylation, it was noticed that the COX2 gene was the only target that displayed CRC associated demethylation, i.e., from the heterozygous methylated state to fully demethylated in 47 among 65 cases being studies (72%) (Figure 1, Figure 2). The COX2 gene did not express in the control non-cancerous tissues, indicating that it seems less likely to have the physiological role in normal colon epithelial cells. Although there was no increase in the frequency of expression in CRC from the heterozygously to the fully unmethylated CRC cases (Figure 2), the fact that over 82% CRC cases expressed this gene was indeed supportive.
Tumor type specificity of the methylation profile
It has been well established that the methylation profile as an inheritable epigenetic signature in any given cells reflects both history of cell differentiation and the chronicle of aging, in addition to those closely associated with the biological profiles of tumors[6,43,44]. It is desirable to identify the changes, specific to one type of tumor from the others, otherwise our efforts to use the DNA methylation pattern, as the biomarkers for tumor diagnosis would be severely constrained. Therefore, we compared the methylation patterns in HCC[10,14] with those in CRC. As shown in Figure 5, there were methylation changes common to both HCC and CRC i.e., the p73 gene: 73% in HCC vs 62.5% in CRC and the MYOD1 gene: 57.8% in HCC vs 69.23% in CRC. The following changes were more prevalent in CRC than in HCC: the cyclin A1 gene: 100% in CRC vs 53.85% in HCC; the WT1 gene: 58.46% in CRC vs 30.77% in HCC; and the CDH13 gene: 64.62% in CRC vs 23.08% in HCC. The following two genes were more frequently hypermethylated in HCC than in CRC: the RASSF1A gene: 100% in HCC vs 2.08% in CRC; and the p16INK4a gene: 53.85% in HCC vs 15.38% in CRC. Although little is known about the mechanisms underlying the tumor specific methylation profiles of CRC vs those of HCC, the distinct profiles of CRC vs HCC should have the profound implication in the future diagnostic tools to differentiate these two common human cancers.
Figure 5.

Tumor specific methylation pattern: CRC verse HCC.
In conclusion, the altered promoter CpG island methylation patterns of 17 genes are the common and distinguished hallmarks specific to the early phase of colon carcinogenesis, although no significant correlation has been detected between the changes in the methylation patterns with any given clinical-pathological features. The correlation between the methylated state of the promoter CpG islands and the expression of the corresponding genes has not been proved as close as previously suggested. Our observations from this rather extensive methylation-profiling maneuver would provide new insights into the role of the DNA methylation mediated control in the colon carcinogenesis as well as the clues for the development of robust diagnostic and prognostic tools for colorectal cancer.
Footnotes
Supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program), No. 2002AA2Z3352, the Science Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Government, No. 02DJ14056, and the Special Fund set up by the State-Key Laboratory for Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Cancer Institute, Shanghai Jiaotong University, This work was also supported by the Science Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Government to Xiang Du, No. 024119010 Co-first-authors: Xiao-Li Xu, Jian Yu, Hong-Yu Zhang
Edited by Xia HHX and Wang XL Proofread by Xu FM
References
- 1.DuBOIS RN. COX-2 in large bowel cancer: a one-sided story. Gut. 1999;45:636–637. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.5.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Landscaping the cancer terrain. Science. 1998;280:1036–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5366.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 1999;49:33–64, 1. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.49.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.DePinho RA. The age of cancer. Nature. 2000;408:248–254. doi: 10.1038/35041694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bird AP. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986;321:209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jaenisch R, Bird A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 2003;33 Suppl:245–254. doi: 10.1038/ng1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Feinberg AP. Cancer epigenetics takes center stage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:392–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.2.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen RZ, Pettersson U, Beard C, Jackson-Grusby L, Jaenisch R. DNA hypomethylation leads to elevated mutation rates. Nature. 1998;395:89–93. doi: 10.1038/25779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gaudet F, Hodgson JG, Eden A, Jackson-Grusby L, Dausman J, Gray JW, Leonhardt H, Jaenisch R. Induction of tumors in mice by genomic hypomethylation. Science. 2003;300:489–492. doi: 10.1126/science.1083558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yu J, Zhang HY, Ma ZZ, Lu W, Wang YF, Zhu JD. Methylation profiling of twenty four genes and the concordant methylation behaviours of nineteen genes that may contribute to hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cell Res. 2003;13:319–333. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Toyota M, Ahuja N, Ohe-Toyota M, Herman JG, Baylin SB, Issa JP. CpG island methylator phenotype in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:8681–8686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.15.8681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.van Rijnsoever M, Grieu F, Elsaleh H, Joseph D, Iacopetta B. Characterisation of colorectal cancers showing hypermethylation at multiple CpG islands. Gut. 2002;51:797–802. doi: 10.1136/gut.51.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cai Q, et al. Molecular genetics research of HNPCC in China, Departmetn of Pathology, Cancer Hosptital of Fudan University, Fudan University, Shanghai 2002 [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yu J, Ni M, Xu J, Zhang H, Gao B, Gu J, Chen J, Zhang L, Wu M, Zhen S, et al. Methylation profiling of twenty promoter-CpG islands of genes which may contribute to hepatocellular carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer. 2002;2:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-2-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Herman JG, Graff JR, Myöhänen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB. Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:9821–9826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.18.9821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Suzuki H, Gabrielson E, Chen W, Anbazhagan R, van Engeland M, Weijenberg MP, Herman JG, Baylin SB. A genomic screen for genes upregulated by demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in human colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2002;31:141–149. doi: 10.1038/ng892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ahuja N, Li Q, Mohan AL, Baylin SB, Issa JP. Aging and DNA methylation in colorectal mucosa and cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5489–5494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kibel AS, Christopher M, Faith DA, Bova GS, Goodfellow PJ, Isaacs WB. Methylation and mutational analysis of p27(kip1) in prostate carcinoma. Prostate. 2001;48:248–253. doi: 10.1002/pros.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li Y, Nagai H, Ohno T, Yuge M, Hatano S, Ito E, Mori N, Saito H, Kinoshita T. Aberrant DNA methylation of p57(KIP2) gene in the promoter region in lymphoid malignancies of B-cell phenotype. Blood. 2002;100:2572–2577. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-11-0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Watanabe T, Huang H, Nakamura M, Wischhusen J, Weller M, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H. Methylation of the p73 gene in gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2002;104:357–362. doi: 10.1007/s00401-002-0549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Agathanggelou A, Honorio S, Macartney DP, Martinez A, Dallol A, Rader J, Fullwood P, Chauhan A, Walker R, Shaw JA, et al. Methylation associated inactivation of RASSF1A from region 3p21.3 in lung, breast and ovarian tumours. Oncogene. 2001;20:1509–1518. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Linehan WM, Lerman MI, Zbar B. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene. Its role in renal cancer. JAMA. 1995;273:564–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Neibergs HL, Hein DW, Spratt JS. Genetic profiling of colon cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2002;80:204–213. doi: 10.1002/jso.10131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Laux DE, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Lubahn DB, Huang TH. Hypermethylation of the Wilms' tumor suppressor gene CpG island in human breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1999;56:35–43. doi: 10.1023/a:1006222803788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.De Smet C, De Backer O, Faraoni I, Lurquin C, Brasseur F, Boon T. The activation of human gene MAGE-1 in tumor cells is correlated with genome-wide demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:7149–7153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, Harada K, Miyajima K, Makarla P, Sathyanarayana UG, Yin J, Sato F, Shivapurkar N, Meltzer SJ, et al. Aberrant methylation of the CDH13 (H-cadherin) promoter region in colorectal cancers and adenomas. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3382–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Müller C, Readhead C, Diederichs S, Idos G, Yang R, Tidow N, Serve H, Berdel WE, Koeffler HP. Methylation of the cyclin A1 promoter correlates with gene silencing in somatic cell lines, while tissue-specific expression of cyclin A1 is methylation independent. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3316–3329. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.9.3316-3329.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Esteller M, Corn PG, Baylin SB, Herman JG. A gene hypermethylation profile of human cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3225–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Viswanathan M, Tsuchida N, Shanmugam G. Promoter hypermethylation profile of tumor-associated genes p16, p15, hMLH1, MGMT and E-cadherin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2003;105:41–46. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fearon ER. BRCA1 and E-cadherin promoter hypermethylation and gene inactivation in cancer-association or mechanism? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:515–517. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.7.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zöchbauer-Müller S, Fong KM, Virmani AK, Geradts J, Gazdar AF, Minna JD. Aberrant promoter methylation of multiple genes in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2001;61:249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Issa J. Genes Affected by Promoter CpG Island Methylation in Aging and/or Cancer. Available from: http://www.mdanderson.org/de-partments/methylation/dIndex.cfm?pn=D02B3250-57D7-4F61-88358636A8073A082001.
- 33.Maruyama R, Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, Harada K, Virmani AK, Zöchbauer-Müller S, Farinas AJ, Vakar-Lopez F, Minna JD, Sagalowsky A, et al. Aberrant promoter methylation profile of bladder cancer and its relationship to clinicopathological features. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8659–8663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wagner KJ, Cooper WN, Grundy RG, Caldwell G, Jones C, Wadey RB, Morton D, Schofield PN, Reik W, Latif F, et al. Frequent RASSF1A tumour suppressor gene promoter methylation in Wilms' tumour and colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2002;21:7277–7282. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Esteller M, Fraga MF, Guo M, Garcia-Foncillas J, Hedenfalk I, Godwin AK, Trojan J, Vaurs-Barrière C, Bignon YJ, Ramus S, et al. DNA methylation patterns in hereditary human cancers mimic sporadic tumorigenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:3001–3007. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.26.3001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Suh ER, Ha CS, Rankin EB, Toyota M, Traber PG. DNA methylation down-regulates CDX1 gene expression in colorectal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35795–35800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205567200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159–170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jubb AM, Bell SM, Quirke P. Methylation and colorectal cancer. J Pathol. 2001;195:111–134. doi: 10.1002/path.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rashid A, Shen L, Morris JS, Issa JP, Hamilton SR. CpG island methylation in colorectal adenomas. Am J Pathol. 2001;159:1129–1135. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61789-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nakayama T, Watanabe M, Yamanaka M, Hirokawa Y, Suzuki H, Ito H, Yatani R, Shiraishi T. The role of epigenetic modifications in retinoic acid receptor beta2 gene expression in human prostate cancers. Lab Invest. 2001;81:1049–1057. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3780316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Côté S, Momparler RL. Activation of the retinoic acid receptor beta gene by 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine in human DLD-1 colon carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 1997;8:56–61. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199701000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks RJ, Kaptein A, Farrow S, Howells L. Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene. 1999;18:6013–6020. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jones PA. Epigenetics in carcinogenesis and cancer prevention. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;983:213–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb05976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jubb AM, Quirke P, Oates AJ. DNA methylation, a biomarker for colorectal cancer: implications for screening and pathological utility. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;983:251–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb05980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


