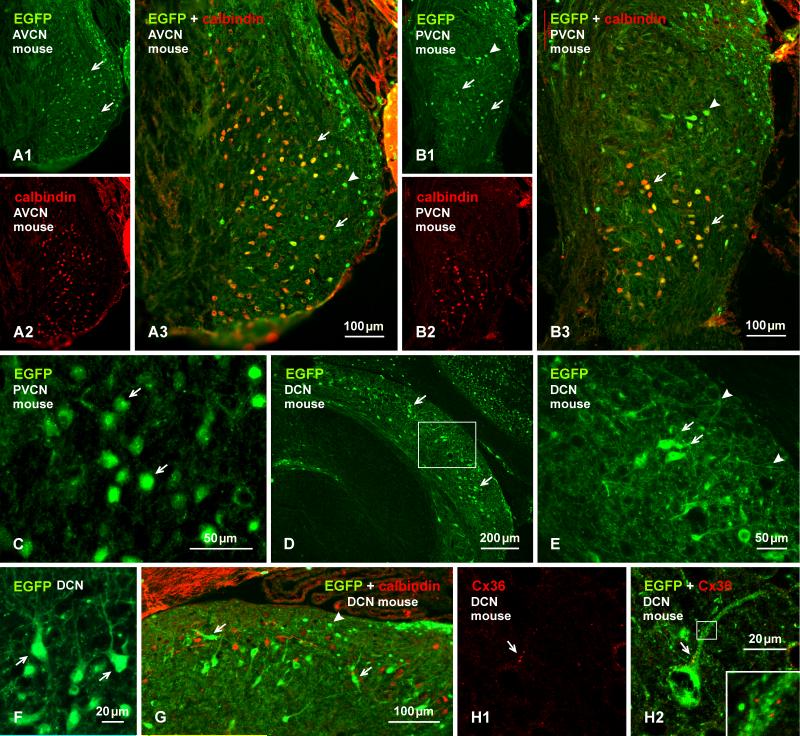
Fig. 4.
Immunofluorescence labelling of EGFP in combination with calbindin or Cx36 in adult EGFP-Cx36 mice. (A, B) The AVCN showing labelling for EGFP (A1) and calbindin (A2) in the same field and with overlay (A3) in an anterior region of the nucleus, and labelling for EGFP (B2) and calbindin (B2) in the same field and with overlay (B3) in the PVCN. EGFP-positive neurons are distributed in the AVCN (A1, arrows), and in the PVCN (B1), and many in both regions are calbindin-positive (A3,B3, arrows), but some in the dorsal PVCN are devoid of calbindin (B1, B3, arrowheads). (C) Labelling for EGFP is localized mainly to neuronal somata, including cellular nuclei (arrows). (D, E) Labelling for EGFP in the DCN, with the boxed area in (D) shown at higher magnification in (E). EGFP-positive neurons are seen throughout the nucleus, but are most concentrated near the border between the fusiform cell and molecular layer (D, arrow), with labelling in soma (E, arrows) and less so in dendritic processes (E, arrowheads). (F) Higher magnification of EGFP-positive neurons (arrows) in the fusiform cell layer with dendrites directed towards the molecular layer. (G) The DCN with immunolabelling of EGFP in combination with calbindin. Both large EGFP-positive cells in superficial regions of the fusiform cell layer (arrows) and small EGFP-positive cells in the molecular layer (arrowheads) are devoid of labelling for calbindin. (H) Immunolabelling of EGFP and Cx36 in the same field at the border between the fusiform and molecular layer, showing Cx36-puncta (H1, arrow) localized to the initial dendritic segment of an EGFP-positive neuron, as seen in overlay (H2, arrow) and at higher magnification (H2, inset).