Vol. 210 No. 2, July 20, 2015. Pages 333–346.
In Figure 5 A, the authors noticed the inadvertent duplication of one kymograph in the wt Ecad and cis Ecad panels. Below is the amended version of the figure containing the correct cis Ecad kymograph.
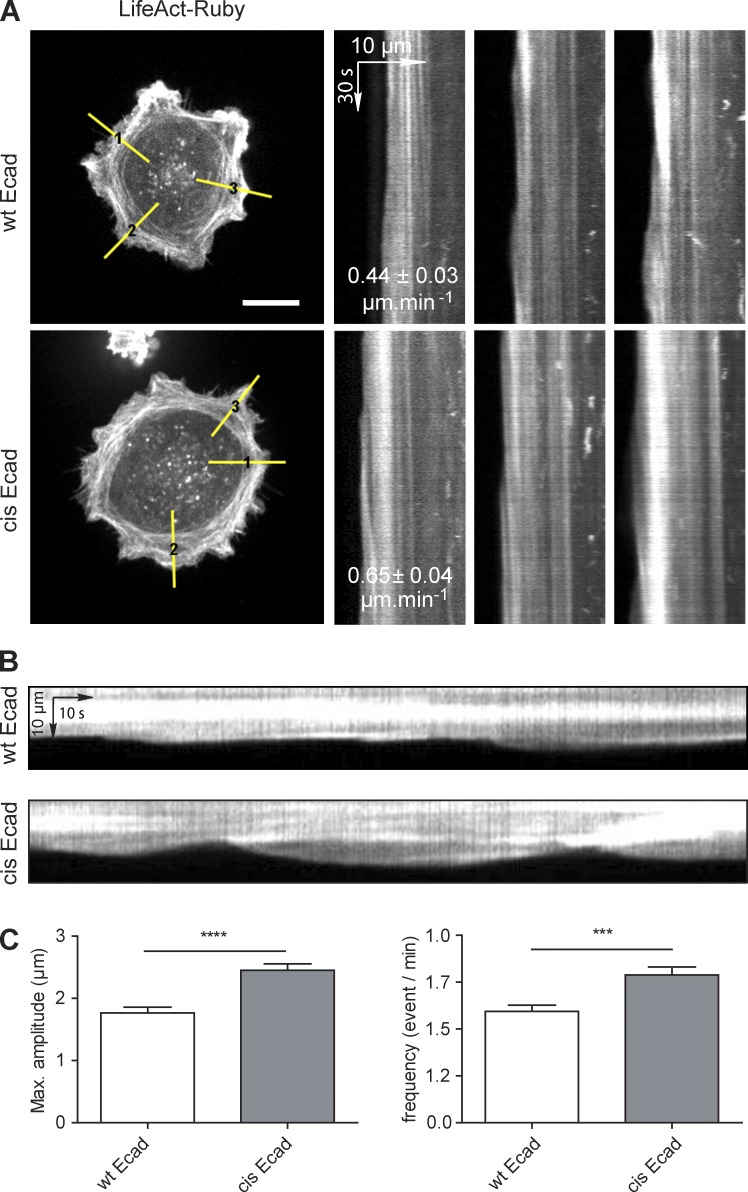
Figure 5.
Impairment of Ecad cis dimerization alters the actin dynamics of cells spread on Ecad-Fc. Cells coexpressing wt Ecad-GFP or cis-Ecad-GFP and LifeAct-Ruby were seeded on Ecad-Fc substrates for 2 h and then subjected to spinning disk live-cell imaging for 3 min at a frequency of one image per 500 ms. (A) Still Images of LifeAct-Ruby distribution. Bar, 25 µm. The actin retrograde flow was quantified by kymograph analysis (yellow lines 1–3, 1 pixel width, perpendicular to the cell membrane in Ecad dense region). Superimposed on the kymographs are the means of actin retrograde flow speed for wt Ecad (n = 156 kymographs from 26 cells) and cis-Ecad (n = 192 kymographs from 32 cells) cells. The actin retrograde flow was significantly faster for cis-Ecad expressing cells than for cells expressing wt Ecad (P ≤ 0.0002, Student’s t test). (B) Similar kymographs of the LifeAct-Ruby signal extending on a longer time window revealed the cyclic protrusion of the edge of wt Ecad and cis-Ecad expressing cells. (C) Quantification of the maximum amplitude and frequency of membrane protrusions (mean values ± SEM; n = 100 kymographs from 26 cells for wt Ecad cells and n = 130 kymographs from 32 cells for cis-Ecad expressing cells). ****, P ≤ 0.0001; ***, P ≤ 0.005, Student’s t test.
The HTML and PDF versions of this article have been corrected. The error remains only in the print version.