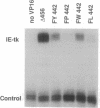
Abstract
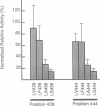
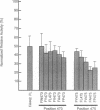
Structural features of the transcriptional activation domain of the herpes simplex virion protein VP16 were examined by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Extensive mutagenesis at position 442 of the truncated VP16 activation domain (delta 456), normally occupied by a phenylalanine residue, demonstrated the importance of an aromatic amino acid at that position. On the basis of an alignment of the VP16 sequence surrounding Phe-442 and the sequences of other transcriptional activation domains, we subjected leucine residues at positions 439 and 444 of VP16 to mutagenesis. Results from these experiments suggest that bulky hydrophobic residues flanking Phe-442 also contribute significantly to the function of the truncated VP16 activation domain. Restoration of amino acids 457-490 to various Phe-442 mutants partially restored activity. Although the pattern of amino acids surrounding Phe-473 resembles that surrounding Phe-442, mutations of Phe-473 did not dramatically affect activity; in fact, Phe-475 appears more sensitive to mutations than does Phe-473. We infer that the two regions of VP16 (amino acids 413-456 and 457-490) possess unique structural features, although neither is likely to be an amphipathic alpha-helix or an "acidic blob." These results, considered with previous in vitro activation and inhibition studies, suggest that the two subdomains of VP16 affect transcription by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger S. L., Cress W. D., Cress A., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Piña B., Silverman N., Marcus G. A., Agapite J., Regier J. L., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Genetic isolation of ADA2: a potential transcriptional adaptor required for function of certain acidic activation domains. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90100-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens D. J., Greaves R., Goding C. R., O'Hare P. The C-terminal 79 amino acids of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein, Vmw65, efficiently activate transcription in yeast and mammalian cells in chimeric DNA-binding proteins. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2337–2342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson L., Capone J. P. Purification and characterization of the carboxyl-terminal transactivation domain of Vmw65 from herpes simplex virus type 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1411–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Mutants of GAL4 protein altered in an activation function. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Transcription in yeast activated by a putative amphipathic alpha helix linked to a DNA binding unit. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):670–672. doi: 10.1038/330670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Eisenman R. N., McKnight S. L. Delineation of transcriptional control signals within the Moloney murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1948–1958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R., O'Hare P. Separation of requirements for protein-DNA complex assembly from those for functional activity in the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein Vmw65. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1641–1650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1641-1650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Tse L., Applegren N., Nicholas J., Veliuona M. A. The Epstein-Barr virus R transactivator (Rta) contains a complex, potent activation domain with properties different from those of VP16. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5500–5508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5500-5508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Shales M., Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J., Greenblatt J. Reduced binding of TFIID to transcriptionally compromised mutants of VP16. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):588–590. doi: 10.1038/351588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. RNA polymerase: regulation of transcript elongation and termination. FASEB J. 1991 Oct;5(13):2833–2842. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.13.1916107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Irresistible force meets immovable object: transcription and the nucleosome. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):833–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R., Haigh A. Direct combinatorial interaction between a herpes simplex virus regulatory protein and a cellular octamer-binding factor mediates specific induction of virus immediate-early gene expression. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4231–4238. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Williams G. Structural studies of the acidic transactivation domain of the Vmw65 protein of herpes simplex virus using 1H NMR. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):4150–4156. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. Postinitiation transcriptional control in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6041–6045. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler P. B. Transcriptional activation. Acid blobs and negative noodles. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):210–212. doi: 10.1038/333210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Transcription elongation and eukaryotic gene regulation. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):777–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., LaMarco K. L., McKnight S. L. Evidence of DNA: protein interactions that mediate HSV-1 immediate early gene activation by VP16. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):730–742. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werstuck G., Capone J. P. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus trans-inducing factor Vmw65. Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Q. L., Smith T. F., Lathrop R. H., Figge J. Acid helix-turn activator motif. Proteins. 1990;8(2):156–163. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]