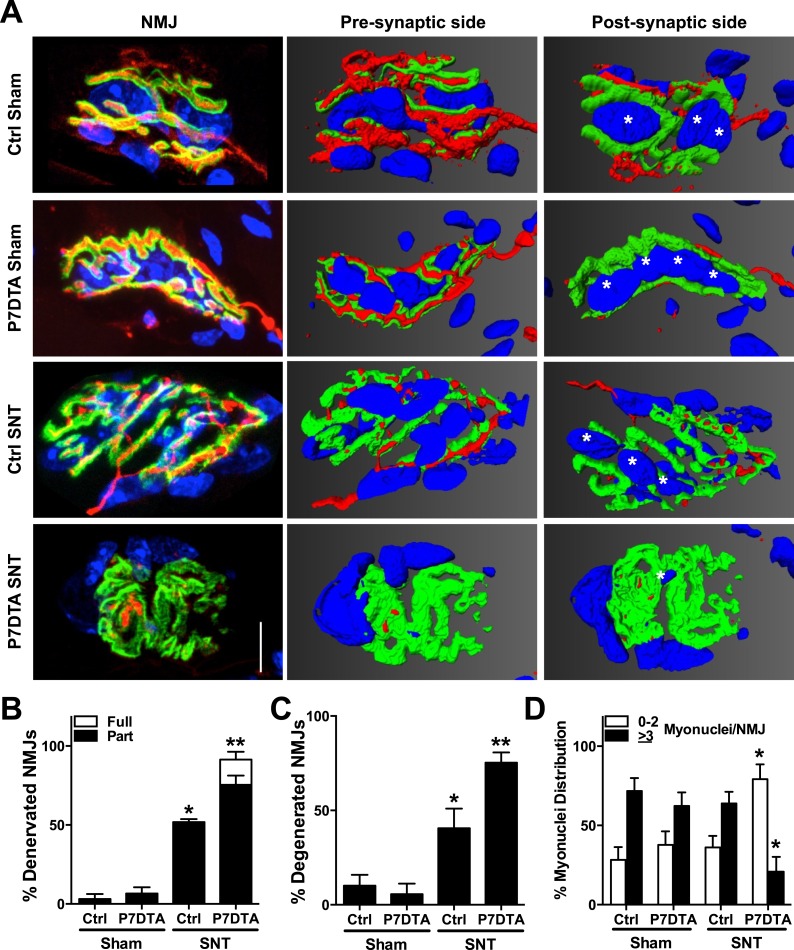
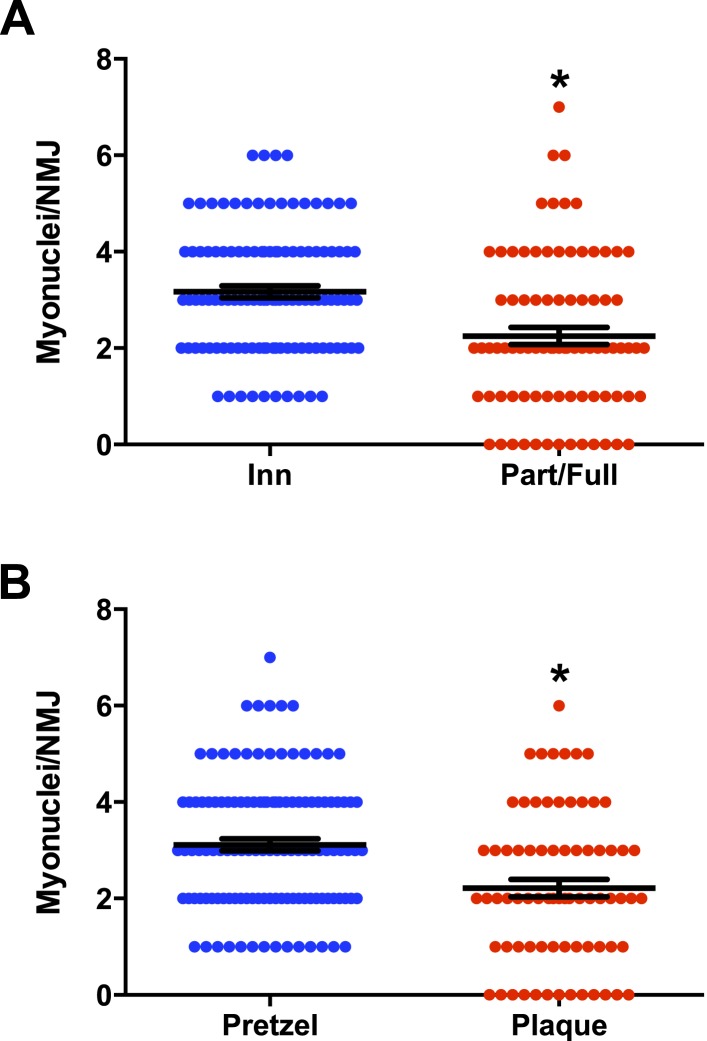
Figure 8. Reductions in NMJ reinnervation, post-synaptic morphology, and post-synaptic myonuclei in SC depleted skeletal muscle.
(A) Representative confocal IF images and 3-D Amira based reconstructions of Ctrl and P7DTA NMJs 6 weeks after sham or SNT surgery, stained for post-synaptic (AChRs labeled with Btx, green), pre-synaptic markers (SV2, Syt-2, neurofilament, red) and myonuclei (DAPI, blue). Post-synaptic myonuclei are indicated with asterisks. (B) Quantification of NMJ reinnervation: partially dennervated (Part) and fully denervated (Full). (C) Quantification of degenerated NMJs based on post-synaptic morphology. (D) Percentage distribution of NMJs based on number of post-synaptic myonuclei. Scale bar = 10 μm. N = 4 mice, 20 NMJs/mouse. *p < 0.05 compared to Ctrl and P7DTA sham, **p < 0.05 compared to Ctrl-sham, P7DTA-sham and Ctrl-SNT, ANOVA/Bonferroni multiple comparisons test.