Abstract
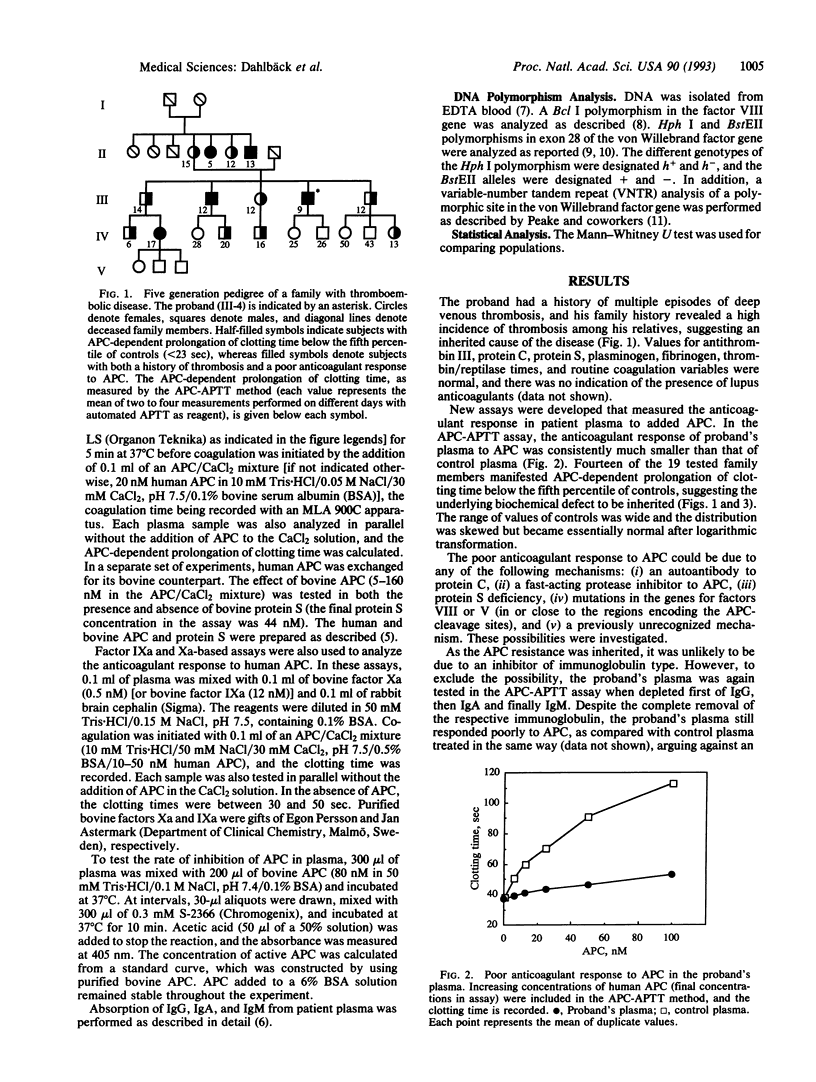
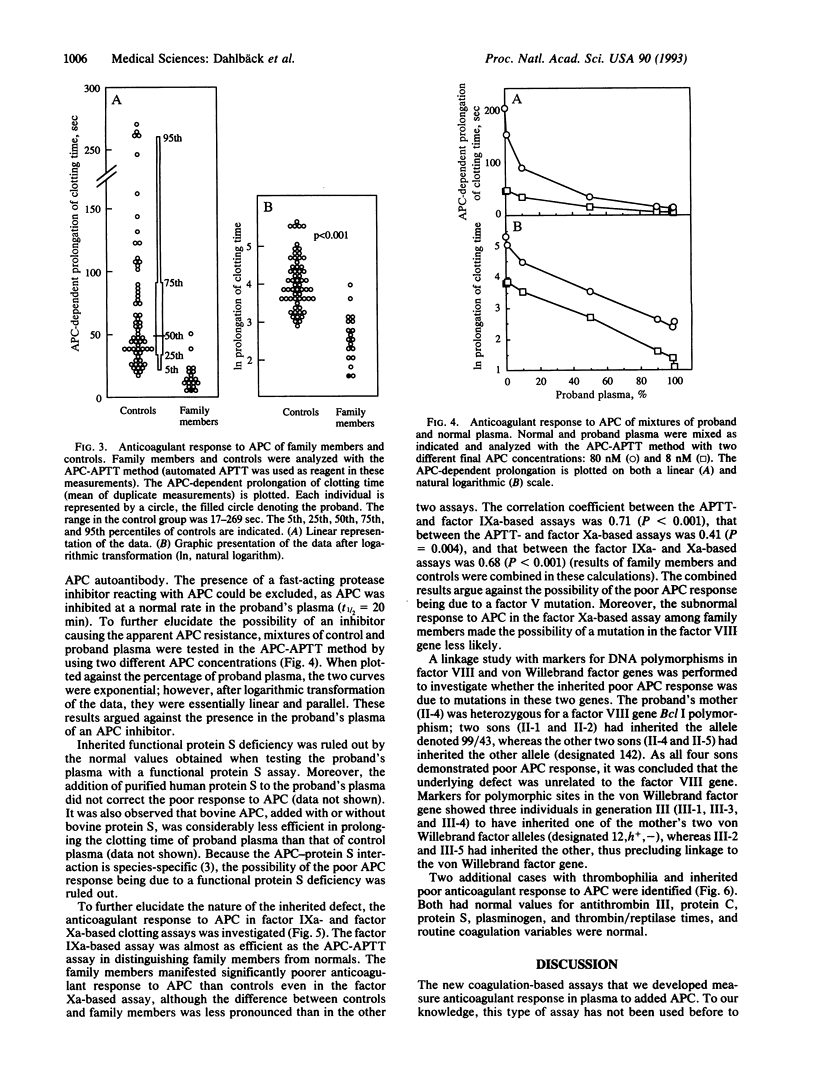
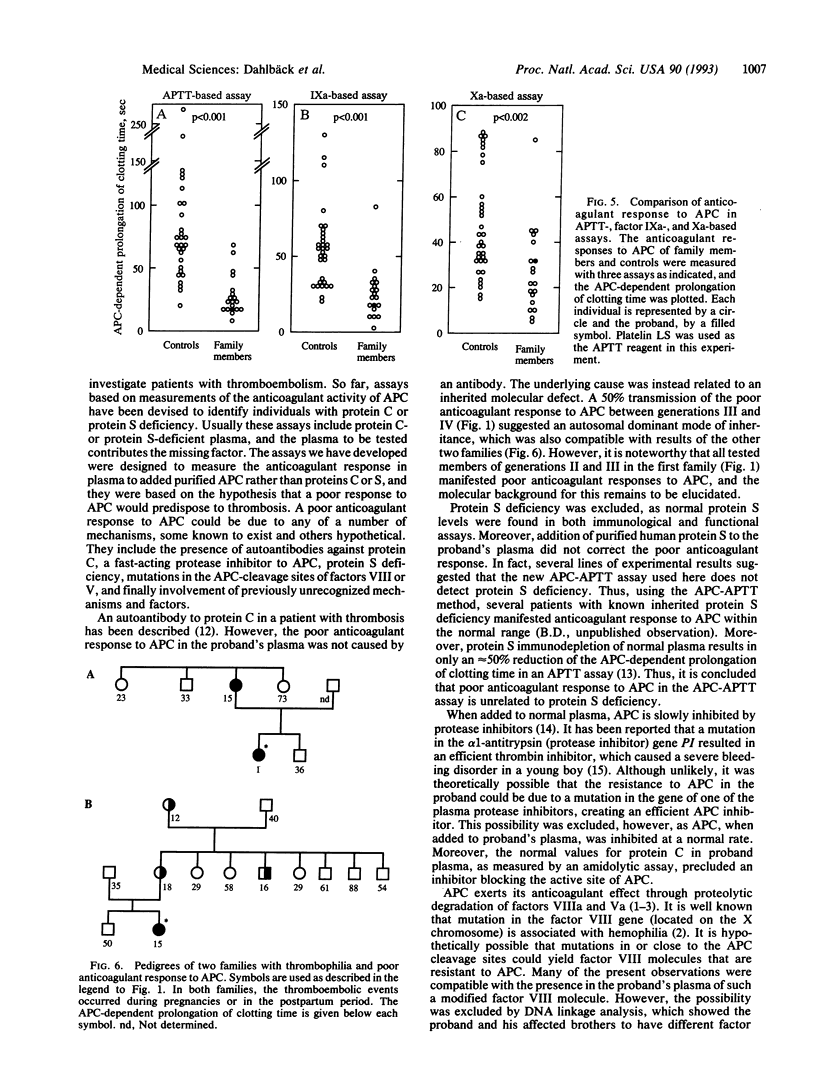
Although patients with thromboembolic disease frequently have family histories of thrombosis, well-defined defects such as inherited deficiencies of anticoagulant proteins are found only in a minority of cases. Based on the hypothesis that a poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C (APC) would predispose to thrombosis, a set of new coagulation assays was developed that measure the anticoagulant response in plasma to APC. A middle-aged man with a history of multiple thrombotic events was identified. The addition of APC to his plasma did not result in a normal anticoagulant response as measured by prolongation of clotting time in an activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) assay. Four of the proband's relatives had medical histories of multiple thrombotic events, and they and several other family members responded poorly to APC in the APTT-based assay. Subnormal anticoagulant responses to APC were also found in factor IXa- and Xa-based assays. Several possible mechanisms for the observed phenomenon were ruled out, such as functional protein S deficiency, a protein C-inhibitory antibody, or a fast-acting protease inhibitor against APC. Moreover, restriction fragment-length polymorphism analysis excluded possible linkage of the underlying molecular defect to factor VIII and von Willebrand factor genes. We now describe a previously unrecognized mechanism for familial thromboembolic disease that is characterized by poor anticoagulant response to APC. This would appear to be explained best by a hypothesized inherited deficiency of a previously unrecognized cofactor to APC. As we have identified two additional, unrelated cases with thrombosis and inherited poor anticoagulant response to APC, this may constitute an important cause for familial thrombophilia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney K. A., Nichols W. C., Bruck M. E., Bahou W. F., Shapiro A. D., Bowie E. J., Gralnick H. R., Ginsburg D. The molecular defect in type IIB von Willebrand disease. Identification of four potential missense mutations within the putative GpIb binding domain. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1227–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI115123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B., Malm J. Characterization of functionally important domains in human vitamin K-dependent protein S using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8127–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Inhibition of protein Ca cofactor function of human and bovine protein S by C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12022–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Nilsson I. M., Frohm B. Inhibition of platelet prothrombinase activity by a lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Protein S and C4b-binding protein: components involved in the regulation of the protein C anticoagulant system. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):49–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnér M., Holmberg L., Kristoffersson A. C., Nilsson I. M. An HphI-polymorphism in exon 28 of the von Willebrand factor gene, and its frequency among patients with various forms of von Willebrand's disease. Br J Haematol. 1991 Jul;78(3):403–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Davie E. W. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):539–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm J., Laurell M., Nilsson I. M., Dahlbäck B. Thromboembolic disease--critical evaluation of laboratory investigation. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. A., Rowell J. A., Hau L., Young J. P., Salem H. H. A fatal thrombotic disorder associated with an acquired inhibitor of protein C. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 24;317(26):1638–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712243172606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. C., Brennan S. O., Lewis J. H., Carrell R. W. Mutation of antitrypsin to antithrombin. alpha 1-antitrypsin Pittsburgh (358 Met leads to Arg), a fatal bleeding disorder. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 22;309(12):694–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309223091203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake I. R., Bowen D., Bignell P., Liddell M. B., Sadler J. E., Standen G., Bloom A. L. Family studies and prenatal diagnosis in severe von Willebrand disease by polymerase chain reaction amplification of a variable number tandem repeat region of the von Willebrand factor gene. Blood. 1990 Aug 1;76(3):555–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Deyashiki Y., Nishioka J., Toma K. Protein C inhibitor: structure and function. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Jun 30;61(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Identification of a new protein involved in the regulation of the anticoagulant activity of activated protein C. Protein S-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10941–10944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



