Abstract
Endotracheal intubation is frequently complicated by laryngeal edema, which may present as postextubation stridor or respiratory difficulty or both. Ultimately, postextubation laryngeal edema may result in respiratory failure with subsequent reintubation. Risk factors for postextubation laryngeal edema include female gender, large tube size, and prolonged intubation. Although patients at low risk for postextubation respiratory insufficiency due to laryngeal edema can be identified by the cuff leak test or laryngeal ultrasound, no reliable test for the identification of high-risk patients is currently available. If applied in a timely manner, intravenous or nebulized corticosteroids can prevent postextubation laryngeal edema; however, the inability to identify high-risk patients prevents the targeted pretreatment of these patients. Therefore, the decision to start corticosteroids should be made on an individual basis and on the basis of the outcome of the cuff leak test and additional risk factors. The preferential treatment of postextubation laryngeal edema consists of intravenous or nebulized corticosteroids combined with nebulized epinephrine, although no data on the optimal treatment algorithm are available. In the presence of respiratory failure, reintubation should be performed without delay. Application of noninvasive ventilation or inhalation of a helium/oxygen mixture is not indicated since it does not improve outcome and increases the delay to intubation.
Introduction
Laryngeal edema (LE) is a frequent complication of intubation and is caused by trauma to the larynx [1, 2]. The edema results in a decreased size of the laryngeal lumen, which may present as stridor or respiratory distress (or both) following extubation. Ultimately, postextubation laryngeal edema (PLE) may lead to respiratory failure with subsequent need for reintubation. Since reintubation is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, it is important to prevent reintubation if possible [3]. Recent studies have focused on several methods to assess airway patency before extubation, aiming to identify patients at risk for PLE. This may enable timely and targeted treatment of patients at risk for postextubation respiratory failure (PRF). This review provides an update on this topic, focusing on these recent developments [4].
Etiology
PRF may result from liberation failure (i.e., the inability to ventilate spontaneously without ventilator support) or extubation failure (i.e., the inability to tolerate removal of the endotracheal tube) or both [5]. Liberation failure may result from primary respiratory failure, congestive heart failure, or neurological impairment. Causes of extubation failure include upper airway obstruction and inadequate clearance of airway secretions [5, 6].
Endotracheal intubation causes damage to the airway in most patients, leading to LE, ulcerations, and damage to the vocal cords [1, 7–9]. Although these injuries are generally reversible, they may cause a decrease of the available airway lumen and lead to respiratory difficulty directly after extubation [1, 7, 9]. The decreased airway lumen results in an increase of air flow velocity, leading to postextubation stridor (PES), which is a clinical marker of relevant PLE. Although the exact quantitative relationship between lumen narrowing and clinical symptoms is unclear, the presence of respiratory distress and PES is thought to reflect a narrowing of the airway lumen of more than 50 % [10].
Incidence of postextubation laryngeal edema, stridor, and respiratory failure
Postextubation laryngeal edema and stridor
Earlier studies have reported an incidence of PLE ranging from 5.0 % to 54.4 % (Table 1) [2, 11–15]. The large variation may be explained by the lack of a standardized method to identify LE, resulting in the use of different definitions of PLE in various studies. Similarly, the reported incidence of PES varies widely; estimated incidence ranges from 1.5 % to 26.3 % [1, 14–29].
Table 1.
Incidence of postextubation stridor, postextubation laryngeal edema, and reintubation
| Author | Year | Participants, number | Cases, number | Percentage | Reintubation due to PES/PLE, number | Percentage of participants | Percentage of cases | Reintubation total, number | Percentage of participants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postextubation stridor | |||||||||
| Colice et al. [1] | 1989 | 82 | 5 | 6.1 % | N/A | N/A | N/A | 9 | 11 % |
| Ho et al. [17]a | 1996 | 38 | 10 | 26.3 % | 1 | 2.6 % | 10 % | N/A | N/A |
| Miller and Cole [22] | 1996 | 100 | 6 | 6.0 % | 3 | 3.0 % | 50 % | 17 | 17.0 % |
| Epstein and Ciubotaru [3] | 1998 | 745 | N/A | N/A | 11 | 1.5 % | N/A | 74 | 9.9 % |
| Sandhu et al. [21] | 2000 | 110 | 13 | 11.8 % | 6 | 5.5 % | 46.2 % | N/A | N/A |
| De Bast et al. [2] | 2002 | 76 | 10 | 13.2 % | 8 | 10.5 % | 80 % | 14 | 18.4 % |
| Jaber et al. [25]b | 2003 | 112 | 13 | 11.6 % | 9 | 8.0 % | 69.2 % | 11 | 9.8 % |
| Maury et al. [20]b | 2004 | 99 | 4 | 4.0 % | 1 | 1.0 % | 25.0 % | 18 | 18.2 % |
| Kriner et al. [18] | 2005 | 462 | 20 | 4.3 % | 7 | 1.5 % | 35 % | N/A | N/A |
| Ding et al. [23] | 2006 | 51 | 4 | 7.8 % | 2 | 3.9 % | 50 % | N/A | N/A |
| Cheng et al. [16]c | 2006 | 236 | 18 | 7.6 % | 10 | 4.2 % | 55.6 % | 14 | 5.9 % |
| Lee et al. [30]d | 2007 | 325 | 25 | 7.7 % | 6 | 1.8 % | 24.0 % | 6 | 1.8 % |
| Tadié et al. [14] | 2010 | 136 | 18 | 13.2 % | 4 | 2.9 % | 22.2 % | 17 | 12.5 % |
| Cheng et al. [26]c | 2011 | 113 | 16 | 14.2 % | 11 | 9.7 % | 68.8 % | 14 | 12.4 % |
| Gros et al. [27] | 2012 | 104 | 7 | 6.7 % | 6 | 5.8 % | 85.7 % | 29 | 27.9 % |
| Sutherasan et al. [15] | 2013 | 101 | 16 | 15.8 % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Mikaeili et al. [28] | 2014 | 41 | 4 | 9.8 % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Abbasi et al. [29]a | 2014 | 35 | 7 | 20 % | N/A | N/A | N/A | 11 | 31.4 % |
| Laryngeal edema | |||||||||
| Darmon et al. [12]a | 1992 | 337 | 17 | 5.0 % | 5 | 1.5 % | 29.4 % | N/A | N/A |
| De Bast et al. [2] | 2002 | 76 | 8 | 10.5 % | 8 | 10.5 % | 100 % | 14 | 18.4 % |
| Chung et al. [13] | 2006 | 95 | 35 | 36.8 % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| François et al. [11]a | 2007 | 343 | 76 | 22.2 % | 11 | 3.2 % | 14.5 % | 26 | 7.6 % |
| Tadié et al. [14] | 2010 | 136 | 74 | 54.4 % | 13 | 9.6 % | 17.6 % | N/A | N/A |
| Sutherasan et al. [15] | 2013 | 101 | 17 | 16.8 % | 2 | 2.0 % | 11.8 % | N/A | N/A |
Adapted from Wittekamp et al. [4]
PES/PLE postextubation stridor/postextubation laryngeal edema, N/A data not available
aPlacebo group
bOnly reintubation after first extubation attempt was included in analysis
cNonintervention group (cuff leak volume (CLV) ≥24 %) and placebo group combined
dNonintervention group (CLV >110 ml) and placebo group combined
Postextubation respiratory failure
As mentioned earlier, PRF may result from liberation failure or extubation failure [5]. The reported overall incidence of PRF leading to reintubation ranges from 1.8 % to 31.4 % (Table 1) [1–3, 11–14, 16–18, 20–23, 25–30]. The reported incidence of reintubation due to PLE or PES (or both) is 1.1–10.5 %, whereas reintubation is necessary in 10.0–100 % of patients with PES or PLE or both. Given the available data, it is unclear what percentage of PRF is caused by PLE, although from the available evidence PLE and PES seem to be important contributors to the overall incidence of PRF.
Risk factors
Several studies have aimed to identify risk factors for PLE and PES (Table 2) [1, 3, 7, 11, 12, 16–21, 25, 31–33]. Important risk factors include female gender, longer duration of intubation, use of large tube size and high cuff pressure, and difficult intubation. Unfortunately, none of these risk factors is sufficiently reliable to identify patients at risk for PLE and this prevents targeted treatment of high-risk patients.
Table 2.
Risk factors for complications following extubation
| Outcome measure | Study | Year | Risk factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laryngeal injury | Colice et al. [1] | 1989 | Persistent laryngeal neuromotor activity, tracheostomy |
| Kastanos et al. [7] | 1983 | Severe respiratory failure, high cuff pressure, duration of endotracheal intubation, secretion infection | |
| Esteller-Moré et al. [31] | 2005 | Longer duration of intubation, tracheostomy, number of days in the intensive care unit | |
| Laryngeal edema | Darmon et al. [12] | 1992 | Duration of intubation (>36 hours, female gender) |
| François et al. [11] | 2007 | Trauma at admission, gender (female), short duration of intubation (<7 days), smaller height-to-tube diameter ratio, absence of methylprednisolone pretreatment | |
| Postextubation stridor | Cheng et al. [16] | 2006 | Gender (female), lower Glasgow Coma Scale score, non-sedation treatment |
| Sandhu et al. [21] | 2000 | Duration of intubation (>3 days) | |
| Daley et al. [32] | 1996 | Tracheostomy, time to reintubation | |
| Ho et al. [17] | 1996 | Gender (female) | |
| Jaber et al. [25] | 2003 | High SAPS II, medical patients, difficult intubation, history of self-extubation, prolonged intubation, high cuff pressure | |
| Kriner et al. [18] | 2005 | Gender (female), duration on intubation (>6 days), ration tube size to laryngeal size >45 % | |
| Wang et al. [19] | 2007 | Gender (female) | |
| Maury et al. [20] | 2004 | Gender (female) | |
| Erginel et al. [33] | 2005 | Duration of ventilation (>5 days), body mass index (>26.5) | |
| Reintubation | Daley et al. [32] | 1996 | Tracheostomy, postextubation stidor |
| Jaber et al. [25] | 2003 | Postextubation stridor | |
| Epstein and Ciubotaru [3] | 1998 | APACHE II score, age, cardiopulmonary cause for reintubation | |
| Sandhu et al. [21] | 2000 | Duration of previous intubation (>3 days) |
Adapted from Wittekamp et al. [4]
SAPS II Simplified Acute Physiology Score II, APACHE II Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II
Assessment of airway patency before extubation
In an effort to allow identification of patients at risk for PLE, several tests have been evaluated for the assessment of airway patency before extubation, including the cuff leak test (CLT), ultrasonography, and video laryngoscopy.
Cuff leak test
The CLT is an easy-to-perform, non-invasive test which provides information on the available laryngeal lumen and has been evaluated in several studies (Tables 3 and 4) [2, 13, 16, 18–22, 25, 27, 28, 34, 35]. The difference between the inspiratory tidal volume and the averaged expiratory tidal volume with the balloon deflated is defined as the cuff leak volume (CLV). The CLV is then compared with a predefined cutoff value, yielding a negative (CLV ≥ cutoff value) or positive (CLV < cutoff value) result. Whereas the positive predictive value for PES strongly differs according to the used cutoff value, the negative predictive value is consistently above 90 % in the studies addressing this test. In a recent study, the results of a CLT before extubation were compared with the results of a CLT performed directly after intubation [27]. Given that no LE is present at intubation, the difference (ΔCLT) reflects the decrease of available airway lumen caused by LE [27]. With a cutoff value of 0 ml, indicating an absence of LE, sensitivity (86 %), specificity (48 %), positive predictive value (11 %), and negative predictive value (99 %) were calculated and they were not superior to those of conventional CLT. Therefore, the CLT is mainly effective in identifying patients not at risk for PLE or PES.
Table 3.
Measurement of the cuff leak volume in mechanically ventilated patients
| Before performing the cuff leak test, first suction endotracheal and oral secretions and set the ventilator in the assist control mode. |
| With the cuff inflated, record displayed inspiratory and expiratory tidal volumes to see whether these are similar. Record cuff pressure. |
| Deflate the cuff. |
| Directly record the expiratory tidal volume over the next six breathing cycles as the expiratory tidal volume will reach a plateau value after a few cycles. |
| Average the three lowest values. |
| The difference between the inspiratory tidal volume (measured before the cuff was deflated) and the averaged expiratory tidal volume is the cuff leak volume. |
Table 4.
Predictive value of the cuff leak test and laryngeal ultrasonography for postextubation stridor, laryngeal edema, and reintubation
| Author | Year | Predefined cutoff value | Outcome | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuff leak test | Volume, ml | Percentage of tidal volume | ||||||
| Miller and Cole [22] | 1996 | 110 | Stridor | 0.67 (0.51–0.82) | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0.98 | |
| Jaber et al. [25] | 2003 | 130 | 12 | Stridor | 0.85 (0.65–0.99) | 0.95 (0.91–0.99) | 0.69 | 0.98 |
| De Bast et al. [2] | 2002 | 15.5 | Reintubation | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.25 | 0.96 | |
| Sandhu et al. [21] | 2000 | 10.0 | Stridor or reintubation | 0.54 | 0.96 | 0.64 | 0.94 | |
| Wang et al. [19] | 2007 | 88 | Stridor | 0.60 | 0.89 | 0.55 | 0.91 | |
| Maury et al. [20] | 2004 | 0 | Stridor | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 1.00 | |
| Chung et al. [13] | 2006 | 140 | Laryngeal edema | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.93 | |
| Engoren [34] | 1999 | 110 | Stridor | 0.00 | 0.96 | 0.00 | 0.99 | |
| Kriner et al. [18] | 2005 | 110 | Stridor | 0.50 | 0.84 | 0.12 | 0.97 | |
| Cheng et al. [16] | 2006 | 18.0 | Stridor | 0.85 | 0.72 | 0.21 | 0.98 | |
| Mikaeili et al. [28] | 2014 | 110 | Stridor | 0.25 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 0.91 | |
| 130 | 0.25 | 0.81 | 0.13 | 0.91 | ||||
| 249 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.96 | ||||
| Gros et al. [27] | 2012 | 130 | Stridor | 0.86 (0.42–1.00) | 0.76 (0.67–0.84) | 0.21 (0.08–0.40) | 0.99 (0.93–1.00) | |
| Sutherasan et al. [15] | 2013 | 110 | Laryngeal edema | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.46 | 0.96 | |
| Ultrasonography | ACWD, mm | |||||||
| Sutherasan et al. [15] | 2013 | 1.6 | Laryngeal edema | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.32 | 0.92 | |
| Mikaeili et al. [28] | 2014 | 0.85 | Stridor | 0.50 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.91 | |
95 % confidence intervals are provided if available
Adapted from Wittekamp et al. [4]
PPV positive predictive value, NPV negative predictive value, ACWD air column width difference
The poor performance of the CLT in the identification of high-risk patients might be explained in part by the relatively low prevalence of PLE and PES in most studies on the predictive value of the CLT. However, the low positive predictive value of the CLT for PLE and PES might be explained by the characteristics of the test as well and this has been shown in a physiological study [36]. For an optimal positive predictive value of the CLT, the cross-sectional area around the deflated cuff should be the only determinant of the CLV. However, this study indicated that the outcome of the CLT is significantly affected by the inspiratory leak volume since the expiratory leak volume is only 30 % of the total leak volume. This inspiratory leak volume is significantly affected by the respiratory system compliance and inspiratory flow, which are therefore additional determinants of the CLV. Therefore, the timing of cuff deflation is important, and ideally the cuff should be deflated immediately prior to expiration to eliminate the inspiratory leak volume. However, to the best of our knowledge, no published studies have compared the conventional CLT with an adapted version of the CLT, in which the cuff is deflated only during expiration.
Ultrasonography
Several studies on the assessment of airway patency using ultrasonography have been published in recent years [15, 23, 28]. Using ultrasonography, the air column width (ACW), which is defined as the width of the acoustic shadow present at the level of the vocal cords, can be measured. If the ACW is measured before and after endotracheal cuff deflation, the air column width difference (ACWD) can be calculated. Results from the study by Ding et al. showed a significantly lower ACWD (0.35 versus 1.5 mm; P < 0.01) and lower ACW during cuff deflation (4.5 versus 6.4 mm; P = 0.01) in patients who developed a stridor compared with patients who did not [23]. Owing to the small sample size (n = 51), including only four patients with PES, results from this study should be interpreted with caution. In the study by Sutherasan et al., similar results were found with decreased ACW after cuff deflation (5.97 versus 6.87 mm; P < 0.05) and ACWD (1.08 versus 1.99 mm; P < 0.001) in patients who developed PLE [15]. Unfortunately, these results could not be replicated in the study by Mikaeili et al. [28]. They reported no significant difference regarding ACW before deflation (12 versus 11.5 mm; P = 0.48) or ACWD (0.1 versus 1.0 mm; P = 0.59) between patients with and without PES. This might be explained by the small sample size (n = 41) and the subsequent small number of patients developing PES (n = 4). Further statistical analysis of available evidence indicates that ultrasonography has a low positive predictive value, sensitivity, and specificity for predicting PES or PLE or both (Table 4). However, these findings should be interpreted with caution since available evidence is limited to small-scale studies with only small numbers of patients with PES or PLE or both.
Video laryngoscopy
Results on the use of video laryngoscopy for the assessment of airway patency have been published in one case series, including only three patients [37]. The case series included two patients with PES and one patient with LE secondary to extensive airway manipulation due to an unanticipated difficult airway of unknown cause. In these patients, it was shown that video laryngoscopy enables visualization of periglottic structures and pathology. Whereas the CLT cannot differentiate PLE from structural laryngeal lesions or laryngeal spasm, video laryngoscopy or flexible endoscopy might potentially enable identification of the cause of the laryngeal narrowing and thus guide treatment. However, further studies on the added value of video laryngoscopy or flexible endoscopy (or both) in the prediction of PLE and PES as well as the diagnostic approach of laryngeal narrowing are needed before they can be implemented in clinical practice.
Prevention
Elimination of possible risk factors might prevent PLE and thus decrease the incidence of PLE. Firstly, an adequate-size endotracheal tube should be selected. Generally accepted maximum endotracheal tube sizes are 7.0 mm for women and 8.0 mm for men. However, smaller endotracheal tubes may interfere with endoscopic endotracheal procedures and increase the work of breathing and this should be taken into account during the weaning process. Secondly, the duration of intubation should be minimized since the duration of intubation in patients with PES is consistently increased compared with patients without PES. No data on a potential cutoff length of intubation increasing the risk for PES are available; however, in general, extubation should not be postponed in order to prevent unnecessary prolongation of intubation. The application of noninvasive ventilation (NIV) might facilitate early detubation, although no data on the effect of early detubation combined with NIV on PES have been published. Thirdly, cuff pressures should be measured regularly to prevent formation of pressure ulcers due to high cuff pressure. Although no evidence on the maximum acceptable cuff pressure is available, 25 cm H2O is a widely accepted upper limit [38]. Since the use of continuous cuff pressure monitoring is also associated with a decreased incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia, the use of continuous cuff pressure monitoring should be strongly advised [39].
Several studies have investigated the use of intravenously administered corticosteroids in the prevention of LE (Table 5), and initial studies failed to show a beneficial effect of corticosteroids on PLE [12, 17]. However, in more recent studies, corticosteroids were shown to decrease the incidence of PLE by more than 50 % (Table 5) [11, 16, 26, 30]. This difference is probably caused by the implementation of different treatment algorithms. Whereas in the initial studies extubation was performed 1 hour after the administration of the corticosteroids, later studies implemented different treatment algorithms with at least 4–48 hours between administration of corticosteroids and extubation. Furthermore, in later studies, low-risk patients were identified by the CLT and excluded from the study, resulting in a study group with a higher risk for PLE. In a recent trial, corticosteroids (budesonide) were nebulized following extubation and compared with nebulized saline, showing more than 50 % reduction in the incidence of respiratory distress and need for reintubation [29]. However, it should be noted that, although a CLT was performed, low-risk patients were not excluded on the basis of the outcome of the CLT.
Table 5.
The effect of corticosteroids on postextubation laryngeal edema, stridor, respiratory distress, and reintubation
| Author | Year | Intervention | Time before extubation | Intervention group | Control group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome parameter | Number | Percentage | Outcome parameter | Number | Percentage | P value | ||||
| Darmon et al. [12] | 1992 | Dexamethasone 8 mg i.v. | 1 hour | Laryngeal edema | 11/327 | 3.4 % | Laryngeal edema | 17/337 | 5.0 % | ns |
| Ho et al. [17] | 1996 | Hydrocortisone 100 mg i.v. | 1 hour | Laryngeal edema | 7/39 | 17.9 % | Laryngeal edema | 10/38 | 26.3 % | ns |
| Cheng et al. [16] | 2006 | Methylprednisolone 40 mg i.v. | 24 hours | Stridor | 5/43 | 11.6 % | Stridor | 13/43 | 30.2 % | 0.15 |
| Reintubation | 3/43 | 6.9 % | Reintubation | 11/43 | 25.6 % | NA | ||||
| Methylprednisolone 4 × 40 mg i.v. | 24 hours | Stridor | 3/42 | 7.1 % | Stridor | 13/43 | 30.2 % | 0.005 | ||
| Reintubation | 7/42 | 16.7 % | Reintubation | 11/43 | 25.6 % | NA | ||||
| François et al. [11] | 2007 | Methylprednisolone 3 × 20 mg i.v. | 12 hours | Laryngeal edema | 11/355 | 3.1 % | Laryngeal edema | 76/343 | 22. % | <0.01 |
| Reintubation | 13/355 | 3.7 % | Reintubation | 36/343 | 10.5 % | 0.02 | ||||
| Lee et al. [30]a | 2007 | Dexamethasone 4 × 5 mg i.v. | 48 hours | Stridor | 4/40 | 10 % | Stridor | 11/40 | 27.5 % | 0.037 |
| Reintubation | 1/40 | 2.5 % | Reintubation | 2/40 | 5.0 % | 0.56 | ||||
| Cheng et al. [26]b | 2011 | Methylprednisolone 40 mg i.v. | 4 hours | Stridor | 6/38 | 15.8 % | Stridor | 13/33 | 39.4 % | 0.025 |
| Reintubation | 3/38 | 7.9 % | Reintubation | 10/33 | 30.3 % | NA | ||||
| Abbasi et al. [29] | 2014 | Budesonide 4 × 1 mg nebulized | 48 hours | Respiratory distress | 3/35 | 8.6 % | Respiratory distress | 11/35 | 31.4 % | 0.017 |
| Stridor | 3/35 | 8.6 % | Stridor | 7/35 | 20 % | 0.17 | ||||
| Reintubation | 3/35 | 8.6 % | Reintubation | 11/35 | 31.4 % | 0.017 | ||||
i.v. intravenous, ns not significant, NA not applicable
aOnly patients with cuff leak volume (CLV) <110 ml were included. In patients with CLV ≥110 ml, stridor was found in 4.9 % of patients, and 1.4 % of patients were reintubated
bOnly patients with cuff leak percentage (CLP) <24 % were included. In patients with CLP ≥24 %, stridor was found in 3.8 % of patients, and intubation was performed in 5 % of patients
From these studies, it can be concluded that intravenously administered corticosteroids are effective in the prevention of PLE if started several hours before extubation. This conclusion was supported by two meta-analyses, stating that data from the latest well-designed studies suggest that the incidence of PLE and associated PRF is reduced if intravenously administered corticosteroids are started 12–24 hours before extubation and if multiple doses are administered [40, 41]. However, it should be noted that in the most recent trial corticosteroids were started only 4 hours before extubation and a similar reduction of PLE and reintubation rate was observed [26]. Furthermore, recent data suggest that administration of nebulized corticosteroids following extubation might well be as effective as intravenously administered corticosteroids [29]. Therefore, further research is needed to identify the optimal route of administration and treatment algorithm. Perhaps more importantly, future research should focus on the identification of patients at risk for PLE and associated PRF, enabling targeted treatment of these patients and prevention of unnecessary treatment of low-risk patients.
Treatment
Reintubation should be performed without delay in the presence of respiratory insufficiency due to PLE. Although NIV has been shown to be effective in the prevention of intubation in respiratory insufficiency in general, it was shown to be ineffective in the treatment of respiratory insufficiency following extubation [42]. More than that, NIV for PRF has been associated with increased mortality, probably due to the increased delay to intubation [43]. Therefore, the use of NIV for PRF failure cannot be recommended.
The use of airway exchange catheters (AECs), which has been included in the Difficult Airway Society extubation guidelines for patients at risk for PRF, provides important advantages [44]. Firstly, the AEC may facilitate over-the-wire insertion of an endotracheal tube in the instance of difficult visualization of the glottis and this is not uncommon in the presence of LE [45]. Secondly, the development of the Ventrain® (Ventinova Medical B.V., Eindhoven) device has made emergency ventilation through a narrow-bore catheter possible [46]. Unfortunately, identification of patients at risk for PRF is difficult since no reliable test is available.
The current treatment of choice for PLE consists of intravenous corticosteroids and nebulized epinephrine. Corticosteroids decrease LE by diminishing the inflammatory response and decreasing capillary vessel dilation and permeability. However, the efficacy of corticosteroids in the treatment of PLE has not been investigated and thus no data on the most effective dose are available. Based on the dosages used in the prevention of PLE, a dosage of methylprednisolone 20–40 mg or dexamethasone 5 mg could be suggested and therapy might be continued for 24–48 hours after extubation [11, 16, 26, 30].
Nebulized epinephrine is thought to decrease LE through vasoconstriction, although high-quality evidence on the efficacy is lacking. In pediatric upper airway obstruction caused by severe viral croup, it has been shown to decrease upper airway obstruction scores, and a beneficial effect has been suggested in upper airway obstruction of other etiologies [47–49]. The optimal dosage is currently unknown, although 1 mg in 5 ml has been suggested [49].
The efficacy of combined intravenous corticosteroids and nebulized epinephrine on PLE has been investigated in pediatric patients, although administration of corticosteroids was started before extubation and treatment was not limited to symptomatic patients [50]. In this overall well-designed study, dexamethasone and nebulized epinephrine did not prevent clinical progression of airway obstruction due to PLE. Therefore, the efficacy of both intravenous corticosteroids and nebulized epinephrine as well as the combination of both treatments has not been established.
The inhalation of a helium-oxygen mixture (heliox) decreases airway resistance and thus work of breathing. Although no evidence on the efficacy of heliox administration in adult PLE is available, a 38 % reduction in respiratory distress score was reported in children with PES, although no change in outcome was found [51]. Therefore, heliox does not lead to a reduction of LE but may decrease work of breathing and buy time to establish a definitive solution for the upper airway obstruction and this may be useful in circumstances in which it is difficult to intubate patients. However, in the context of PLE, it should (similar to NIV) not lead to a delay to intubation since that may potentially lead to a worse outcome.
Based on the best available evidence, a practical extubation algorithm, including prevention and treatment of PLE and PRF, may be proposed (Fig. 1). However, it should be emphasized that the CLT effectively identifies low-risk patients only. Treatment of all patients with a positive CLT would result in overtreatment. Therefore, one could decide to perform a CLT in all patients and start pretreatment with corticosteroids in the presence of additional risk factors only, as suggested in the algorithm. Alternatively, a CLT could be performed in patients with risk factors only.
Fig. 1.
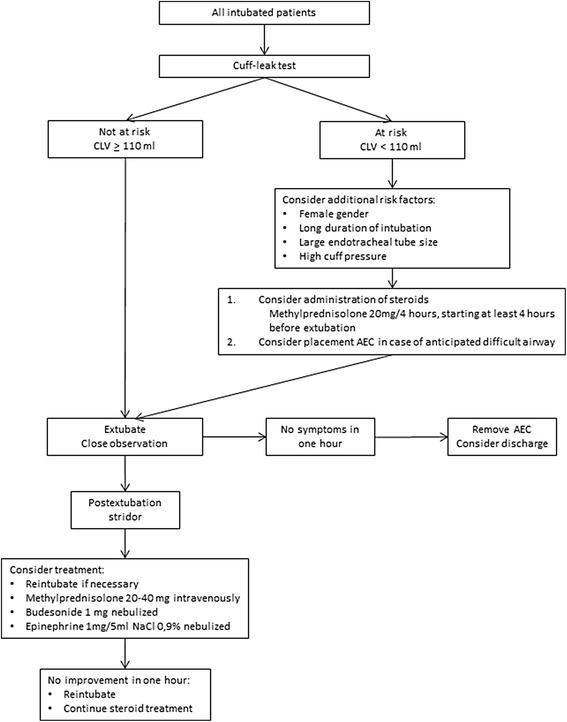
Proposed extubation algorithm. AEC airway exchange catheter, CLV cuff leak volume. Adapted from Wittekamp et al. [4]
Conclusions
PLE is a frequent complication of intubation and leads to reintubation in up to 10 % of all extubated patients. Pretreatment with intravenous corticosteroids or administration of nebulized corticosteroids following extubation seems fairly effective in the prevention of PLE, decreasing the need for reintubation by more than 50 %. However, the lack of reliable predictors prevents identification of patients at high risk for PLE and PRF. Patients with a low risk of PLE and PRF can be identified by using the CLT, which is therefore advisable. In patients with a positive CLT, the decision to start pretreatment with corticosteroids should be made on an individual basis and on the basis of the presence of additional risk factors. If corticosteroid therapy is considered to be indicated, treatment should be started at least 4 hours before extubation and multiple doses should be administered. If PES or PLE is present, the treatment of choice should be corticosteroids combined with nebulized epinephrine. However, if PLE or PES leads to respiratory insufficiency, reintubation is the only definitive resolution and should not be postponed.
Abbreviations
- ACW
Air column width
- ACWD
Air column width difference
- AEC
Airway exchange catheter
- CLT
Cuff leak test
- CLV
Cuff leak volume
- LE
Laryngeal edema
- NIV
Noninvasive ventilation
- PES
Postextubation stridor
- PLE
Postextubation laryngeal edema
- PRF
Postextubation respiratory failure
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
The manuscript was prepared and edited by WAP. All authors helped to revise and improve the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- 1.Colice GL, Stukel TA, Dain B. Laryngeal complications of prolonged intubation. Chest. 1989;96:877–884. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.De Bast Y, De Backer D, Moraine JJ, Lemaire M, Vandenborght C, Vincent JL. The cuff leak test to predict failure of tracheal extubation for laryngeal edema. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28:1267–1272. doi: 10.1007/s00134-002-1422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Epstein SK, Ciubotaru RL. Independent effects of etiology of failure and time to reintubation on outcome for patients failing extubation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158:489–493. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.2.9711045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wittekamp BH, van Mook WN, Tjan DH, Zwaveling JH, Bergmans DC. Clinical review: post-extubation laryngeal edema and extubation failure in critically ill adult patients. Crit Care. 2009;13:233. doi: 10.1186/cc8142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Epstein SK. Decision to extubate. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28:535–546. doi: 10.1007/s00134-002-1268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Thille AW, Richard JC, Brochard L. The decision to extubate in the intensive care unit. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:1294–1302. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201208-1523CI. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kastanos N, Estopa Miro R, Marin Perez A, Xaubet Mir A, Agusti-Vidal A. Laryngotracheal injury due to endotracheal intubation: incidence, evolution, and predisposing factors. A prospective long-term study. Crit Care Med. 1983;11:362–367. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198305000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thomas R, Kumar EV, Kameswaran M, Shamim A, Al Ghamdi S, Mummigatty AP. Post intubation laryngeal sequelae in an intensive care unit. J Laryngol Otol. 1995;109:313–316. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100130002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Whited RE. A prospective study of laryngotracheal sequelae in long-term intubation. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:367–377. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198403000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mackle T, Meaney J, Timon C. Tracheoesophageal compression associated with substernal goitre. Correlation of symptoms with cross-sectional imaging findings. J Laryngol Otol. 2007;121:358–361. doi: 10.1017/S0022215106004142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.François B, Bellissant E, Gissot V, Desachy A, Normand S, Boulain T, et al. 12-h pretreatment with methylprednisolone versus placebo for prevention of postextubation laryngeal oedema: a randomised double-blind trial. Lancet. 2007;369:1083–1089. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60526-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Darmon JY, Rauss A, Dreyfuss D, Bleichner G, Elkharrat D, Schlemmer B, et al. Evaluation of risk factors for laryngeal edema after tracheal extubation in adults and its prevention by dexamethasone. A placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter study. Anesthesiology. 1992;77:245–251. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199208000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chung YH, Chao TY, Chiu CT, Lin MC. The cuff-leak test is a simple tool to verify severe laryngeal edema in patients undergoing long-term mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:409–414. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000198105.65413.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tadié JM, Behm E, Lecuyer L, Benhmamed R, Hans S, Brasnu D, et al. Post-intubation laryngeal injuries and extubation failure: a fiberoptic endoscopic study. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:991–998. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1847-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sutherasan Y, Theerawit P, Hongphanut T, Kiatboonsri C, Kiatboonsri S. Predicting laryngeal edema in intubated patients by portable intensive care unit ultrasound. J Crit Care. 2013;28:675–680. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cheng KC, Hou CC, Huang HC, Lin SC, Zhang H. Intravenous injection of methylprednisolone reduces the incidence of postextubation stridor in intensive care unit patients. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:1345–1350. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000214678.92134.BD. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ho LI, Harn HJ, Lien TC, Hu PY, Wang JH. Postextubation laryngeal edema in adults. Risk factor evaluation and prevention by hydrocortisone. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:933–936. doi: 10.1007/BF02044118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kriner EJ, Shafazand S, Colice GL. The endotracheal tube cuff-leak test as a predictor for postextubation stridor. Respir Care. 2005;50:1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang CL, Tsai YH, Huang CC, Wu YK, Ye MZ, Chou HM, et al. The role of the cuff leak test in predicting the effects of corticosteroid treatment on postextubation stridor. Chang Gung Med J. 2007;30:53–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maury E, Guglielminotti J, Alzieu M, Qureshi T, Guidet B, Offenstadt G. How to identify patients with no risk for postextubation stridor? J Crit Care. 2004;19:23–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2004.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sandhu RS, Pasquale MD, Miller K, Wasser TE. Measurement of endotracheal tube cuff leak to predict postextubation stridor and need for reintubation. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;190:682–687. doi: 10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Miller RL, Cole RP. Association between reduced cuff leak volume and postextubation stridor. Chest. 1996;110:1035–1040. doi: 10.1378/chest.110.4.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ding LW, Wang HC, Wu HD, Chang CJ, Yang PC. Laryngeal ultrasound: a useful method in predicting post-extubation stridor. A pilot study. Eur Respir J. 2006;27:384–389. doi: 10.1183/09031936.06.00029605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Efferen LS, Elsakr A. Post-extubation stridor: risk factors and outcome. J Assoc Acad Minor Phys. 1998;9:65–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jaber S, Chanques G, Matecki S, Ramonatxo M, Vergne C, Souche B, et al. Post-extubation stridor in intensive care unit patients. Risk factors evaluation and importance of the cuff-leak test. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29:69–74. doi: 10.1007/s00134-002-1563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cheng KC, Chen CM, Tan CK, Chen HM, Lu CL, Zhang H. Methylprednisolone reduces the rates of postextubation stridor and reintubation associated with attenuated cytokine responses in critically ill patients. Minerva Anestesiol. 2011;77:503–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gros A, Holzapfel L, Marque S, Perard L, Demingeon G, Piralla B, et al. Intra-individual variation of the cuff-leak test as a predictor of post-extubation stridor. Respir Care. 2012;57:2026–2031. doi: 10.4187/respcare.01527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mikaeili H, Yazdchi M, Tarzamni MK, Ansarin K, Ghasemzadeh M. Laryngeal ultrasonography versus cuff leak test in predicting postextubation stridor. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2014;6:25–28. doi: 10.5681/jcvtr.2014.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Abbasi S, Moradi S, Talakoub R, Kashefi P, Koushki AM. Effect of nebulized budesonide in preventing postextubation complications in critically patients: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Adv Biomed Res. 2014;3:182. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.139543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee CH, Peng MJ, Wu CL. Dexamethasone to prevent postextubation airway obstruction in adults: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Crit Care. 2007;11:R72. doi: 10.1186/cc5957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Esteller-Moré E, Ibañez J, Matiñó E, Ademà JM, Nolla M, Quer IM. Prognostic factors in laryngotracheal injury following intubation and/or tracheotomy in ICU patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;262:880–883. doi: 10.1007/s00405-005-0929-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Daley BJ, Garcia-Perez F, Ross SE. Reintubation as an outcome predictor in trauma patients. Chest. 1996;110:1577–1580. doi: 10.1378/chest.110.6.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Erginel S, Ucgun I, Yildirim H, Metintas M, Parspour S. High body mass index and long duration of intubation increase post-extubation stridor in patients with mechanical ventilation. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2005;207:125–132. doi: 10.1620/tjem.207.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Engoren M. Evaluation of the cuff-leak test in a cardiac surgery population. Chest. 1999;116:1029–1031. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Antonaglia V, Vergolini A, Pascotto S, Bonini P, Renco M, Peratoner A, et al. Cuff-leak test predicts the severity of postextubation acute laryngeal lesions: a preliminary study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010;27:534–541. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328333a0f0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Prinianakis G, Alexopoulou C, Mamidakis E, Kondili E, Georgopoulos D. Determinants of the cuff-leak test: a physiological study. Crit Care. 2005;9:R24–R31. doi: 10.1186/cc3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Newmark JL, Ahn YK, Adams MC, Bittner EA, Wilcox SR. Use of video laryngoscopy and camera phones to communicate progression of laryngeal edema in assessing for extubation: a case series. J Intensive Care Med. 2013;28:67–71. doi: 10.1177/0885066612437528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rose L, Redl L. Survey of cuff management practices in intensive care units in Australia and New Zealand. Am J Crit Care. 2008;17:428–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lorente L, Lecuona M, Jimenez A, Lorenzo L, Roca I, Cabrera J, et al. Continuous endotracheal tube cuff pressure control system protects against ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit Care. 2014;18:R77. doi: 10.1186/cc13837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Roberts RJ, Welch SM, Devlin JW. Corticosteroids for prevention of postextubation laryngeal edema in adults. Ann Pharmacother. 2008;42:686–691. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Khemani RG, Randolph A, Markovitz B. Corticosteroids for the prevention and treatment of post-extubation stridor in neonates, children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;8 doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001000.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lin C, Yu H, Fan H, Li Z. The efficacy of noninvasive ventilation in managing postextubation respiratory failure: a meta-analysis. Heart Lung. 2014;43:99–104. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2014.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Esteban A, Frutos-Vivar F, Ferguson ND, Arabi Y, Apezteguia C, Gonzalez M, et al. Noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation for respiratory failure after extubation. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2452–2460. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Group DASEG, Popat M, Mitchell V, Dravid R, Patel A, Swampillai C, Higgs A. Difficult Airway Society Guidelines for the management of tracheal extubation. Anaesthesia. 2012;67:318–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2012.07075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dark A, Armstrong T. Severe postoperative laryngeal oedema causing total airway obstruction immediately on extubation. Br J Anaesth. 1999;82:644–646. doi: 10.1093/bja/82.4.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hamaekers AE, Borg PA, Enk D. Ventrain: an ejector ventilator for emergency use. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108:1017–1021. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Argent AC, Hatherill M, Newth CJ, Klein M. The effect of epinephrine by nebulization on measures of airway obstruction in patients with acute severe croup. Intensive Care Med. 2008;34:138–147. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0855-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bjornson C, Russell K, Vandermeer B, Klassen TP, Johnson DW. Nebulized epinephrine for croup in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;10 doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006619.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.MacDonnell SP, Timmins AC, Watson JD. Adrenaline administered via a nebulizer in adult patients with upper airway obstruction. Anaesthesia. 1995;50:35–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1995.tb04510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cesar RG, de Carvalho WB. L-epinephrine and dexamethasone in postextubation airway obstruction: a prospective, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;73:1639–1643. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kemper KJ, Ritz RH, Benson MS, Bishop MS. Helium-oxygen mixture in the treatment of postextubation stridor in pediatric trauma patients. Critical Care Med. 1991;19:356–359. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


