Abstract
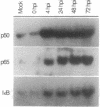
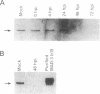
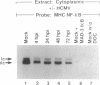
Infection-induced activation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early enhancer/promoter has been shown to be regulated primarily by transcription factor NF-kappa B cis elements. However, the mechanism(s) by which human cytomegalovirus induces NF-kappa B activity is unknown. A study was therefore undertaken to determine how this virus would affect normal NF-kappa B regulation. Viral infection of fibroblasts resulted in the specific stimulation of promoters containing major histocompatibility complex NF-kappa B cis elements fused upstream of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays of nuclear extracts derived from mock- and virus-infected cells showed dramatic and sustained increases in DNA-binding proteins specific for these NF-kappa B sequences. Experiments using MAD-3 I kappa B, a specific inhibitor of NF-kappa B, and antibodies directed against rel family members demonstrated that the induced binding activities contained p50 and p65 proteins but not c-rel. Northern analysis indicated maximal levels of p50 mRNA by 4 h postinfection, whereas p65 and MAD-3 I kappa B mRNA accumulation peaked at 48-72 h postinfection, suggesting different regulatory mechanisms for p50 and p65/I kappa B genes. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays with deoxycholate-treated cytoplasmic extracts demonstrated a 3- to 4-fold decrease in the cytosolic stores of NF-kappa B binding activity by 4 h postinfection. Western blots probed with antibodies directed against MAD-3 I kappa B or pp40 (a protein isolated from chicken with sequence and biochemical properties similar to those of MAD-3 I kappa B) indicated that a cross-reactive peptide of 39 kDa was no longer detectable after 24 h postinfection. These results demonstrate that the activation and maintenance of nuclear NF-kappa B DNA binding and enhancer activities upon human cytomegalovirus infection occurs by multiple mechanisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht T., Boldogh I., Fons M., Lee C. H., AbuBakar S., Russell J. M., Au W. W. Cell-activation responses to cytomegalovirus infection relationship to the phasing of CMV replication and to the induction of cellular damage. Subcell Biochem. 1989;15:157–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Azizkhan J. C., Jensen D. E., Beg A. A., Coodly L. R. Induction of NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4943–4951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegalke B. J., Geballe A. P. Sequence requirements for activation of the HIV-1 LTR by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90151-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Burd P. R., Brown K., Villalobos J., Park S., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. A novel mitogen-inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappa B participates in transactivation through a kappa B site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):685–695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Bargmann W., Lim M. Y., Bose H., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed lymphoid cells contain multiple pp59v-rel complexes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.584-591.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Ghosh S., Simmons D. L., Tempst P., Liou H. C., Baltimore D., Bose H. R., Jr Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the rel family of transcription factors. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.1891714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Generation of p50 subunit of NF-kappa B by processing of p105 through an ATP-dependent pathway. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):395–398. doi: 10.1038/354395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Hennighausen L. Multiple sequence-specific transcription factors modulate cytomegalovirus enhancer activity in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1809–1811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier C., Walker S., Caswell R., Kouzarides T., Sinclair J. The human cytomegalovirus 80-kilodalton but not the 72-kilodalton immediate-early protein transactivates heterologous promoters in a TATA box-dependent mechanism and interacts directly with TFIID. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4452–4456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4452-4456.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. III. Virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):298–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.298-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Kakizuka A., Verma I. M. I kappa B gamma, a 70 kd protein identical to the C-terminal half of p110 NF-kappa B: a new member of the I kappa B family. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90082-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Groudine M. Transcriptional regulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene is associated with induction of DNase I-hypersensitive sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):452–461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olashaw N. E., Kowalik T. F., Huang E. S., Pledger W. J. Induction of NF-kappa B-like activity by platelet-derived growth factor in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1131–1139. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivière Y., Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Processing of the precursor of NF-kappa B by the HIV-1 protease during acute infection. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):625–626. doi: 10.1038/350625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Cherrington J. M., Wilkinson G. W., Mocarski E. S. NF-kappa B activation of the cytomegalovirus enhancer is mediated by a viral transactivator and by T cell stimulation. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4251–4258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn S. A., Eierman D. F., Johnson C. E., Morris J., Martin G., Ladner M., Haskill S. Monocyte adherence results in selective induction of novel genes sharing homology with mediators of inflammation and tissue repair. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4434–4441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten R. M., Paya C. V., Israël N., Le Bail O., Mattei M. G., Virelizier J. L., Kourilsky P., Israël A. The characterization of the promoter of the gene encoding the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B indicates that it participates in its own regulation. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):195–203. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dobrzanski P., Mohn K. L., Cressman D. E., Hsu J. C., Bravo R., Taub R. Rapid induction in regenerating liver of RL/IF-1 (an I kappa B that inhibits NF-kappa B, RelB-p50, and c-Rel-p50) and PHF, a novel kappa B site-binding complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2898–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade M., Kowalik T. F., Mudryj M., Huang E. S., Azizkhan J. C. E2F mediates dihydrofolate reductase promoter activation and multiprotein complex formation in human cytomegalovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S., Hagemeier C., Sissons J. G., Sinclair J. H. A 10-base-pair element of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat (LTR) is an absolute requirement for transactivation by the human cytomegalovirus 72-kilodalton IE1 protein but can be compensated for by other LTR regions in transactivation by the 80-kilodalton IE2 protein. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1543–1550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1543-1550.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Baeuerle P. A. Purified human I kappa B can rapidly dissociate the complex of the NF-kappa B transcription factor with its cognate DNA. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90806-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]