Abstract
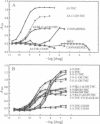
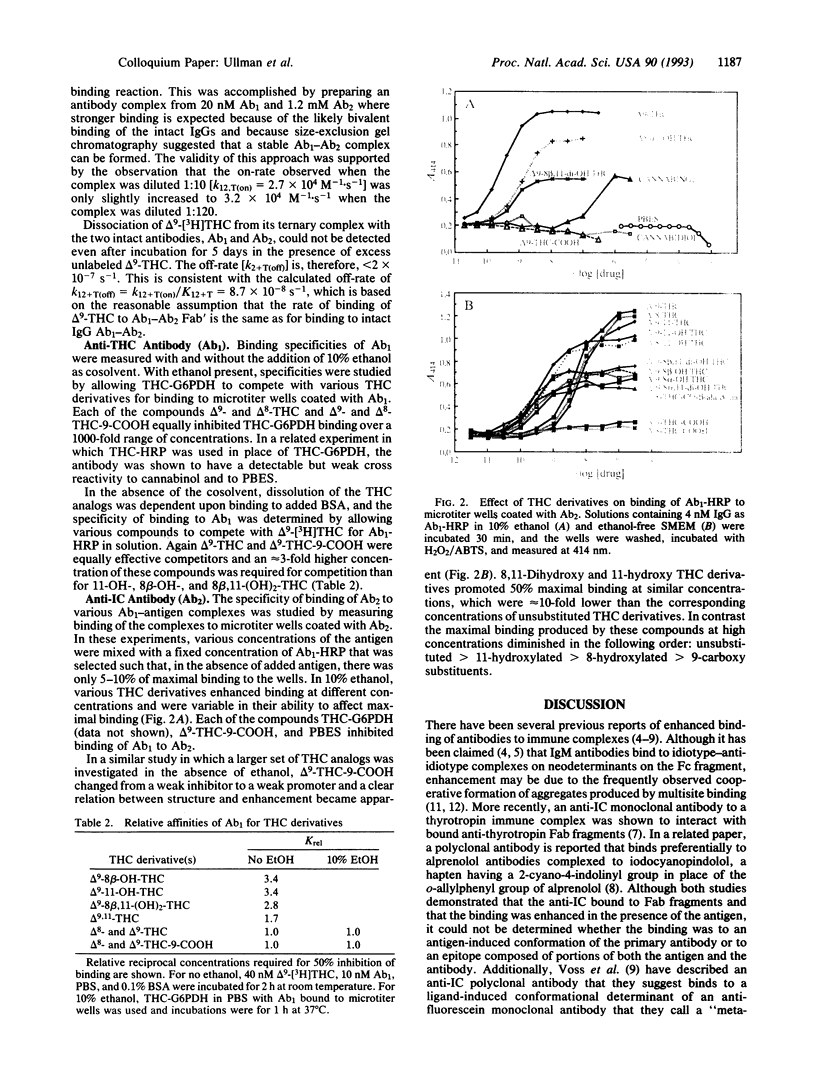
Antibodies have previously been described that enhance the binding of a second antibody to its antigen. The origin of this effect has been variously ascribed to binding to a neodeterminant on the Fc region, to a combined determinant representing portions of the second antibody and the immunogen, and to a ligand-induced conformation of the Fab fragment. This paper describes an antibody that recognizes an immune complex of an antibody to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The antibody binds the anti-THC antibody at an epitope recognized by an anti-idiotype antibody that is capable of blocking THC binding. The ability of various THC derivatives to enhance or inhibit binding taken together with equilibria and kinetic data support a model in which the anti-immune complex antibody interacts through adventitious binding to pendant groups on the THC derivatives. This type of interaction offers the opportunity to increase the sensitivity and specificity of immunoassays beyond the limits imposed by normal antibody binding. The implications of these findings with regard to earlier observations of anti-immune complex antibodies are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekisz J., Brown E. J. A mouse monoclonal antibody that reacts specifically with immune-complexed human IgG. Mol Immunol. 1985 Oct;22(10):1225–1230. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benkirane M. M., Bon D., Cordeil M., Delori P., Delaage M. A. Immunization with immune complexes: characterization of monoclonal antibodies against a TSH-antibody complex. Mol Immunol. 1987 Dec;24(12):1309–1315. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamat S., Hoebeke J., Emorine L., Guillet J. G., Strosberg A. D. The immune response towards beta-adrenergic ligands and their receptors. VI. Idiotypy of monoclonal anti-alprenolol antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3805–3811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich P. H., Moyle W. R., Moustafa Z. A., Canfield R. E. Mixing two monoclonal antibodies yields enhanced affinity for antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2709–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. C., Butcher G. W., Galfrè G., Milstein C., Milstein C. P. Monoclonal antibodies as tools to analyze the serological and genetic complexities of major transplantation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:139–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Sato V. L. Enhancing antibody: a novel component of the immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3828–3832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawutz D. G., Koury R., Homcy C. J. Enhanced antigen-antibody binding affinity mediated by an anti-idiotypic antibody. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5275–5282. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss E. W., Jr, Miklasz S. D., Petrossian A., Dombrink-Kurtzman M. A. Polyclonal antibodies specific for liganded active site (metatype) of a high affinity anti-hapten monoclonal antibody. Mol Immunol. 1988 Aug;25(8):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner K. M., Denzin L. K., Voss E. W., Jr Molecular stabilization effects of interactions between anti-metatype antibodies and liganded antibody. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10281–10288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner K. M., Voss E. W., Jr Characterization of interactions involving anti-metatype antibodies and immune complexes. Mol Immunol. 1992 Mar;29(3):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90016-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]