Abstract
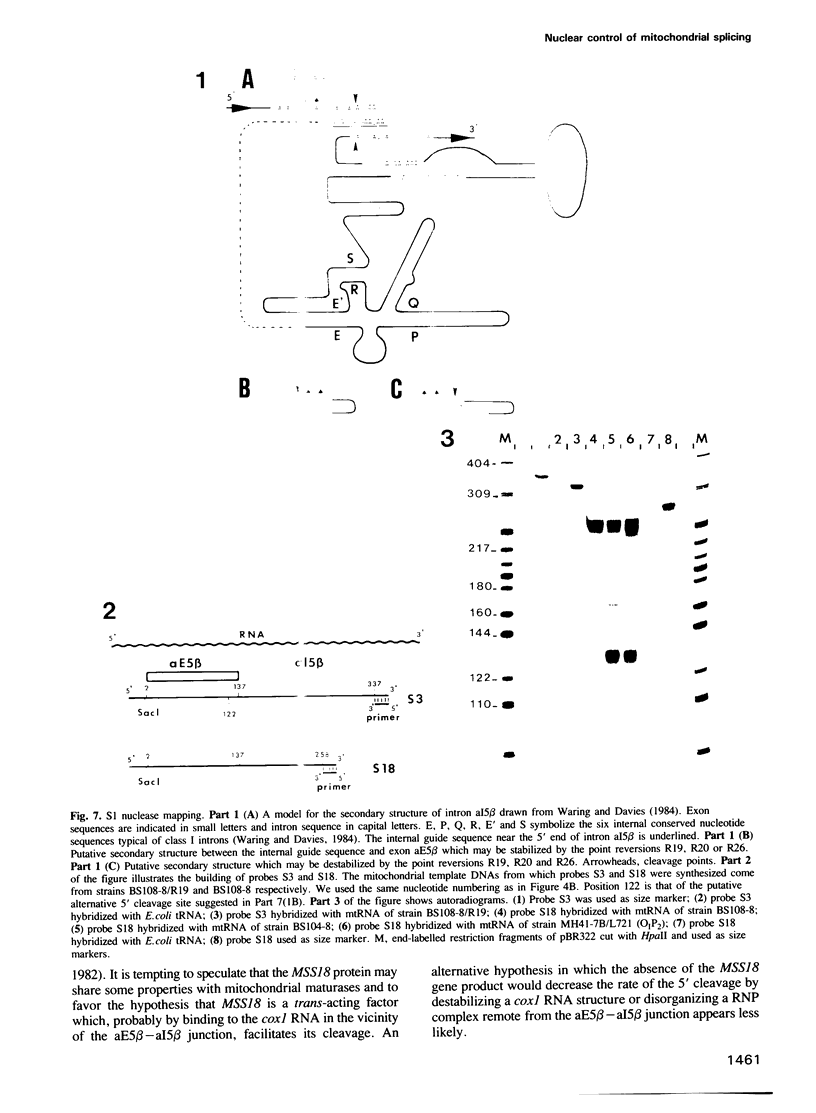
We have isolated and characterized a nuclear gene, MSS18, which is implicated in the splicing of intron aI5 beta of the mitochondrial cox1 transcript (subunit 1 of the cytochrome c oxidase). Northern blotting and S1 nuclease protection experiments as well as the analysis of mitochondrial point revertants suggest that mss18 mutations block (perhaps indirectly) the cleavage of the 5' exon-intron junction of aI5 beta. Mitochondrial point revertants also indicate that up to 13 bases of the aI5 beta exon sequence, upstream of the 5' splice site of aI5 beta, are involved in vivo in the splicing of this intron. The implications of this result on the splicing of group I introns are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C., Cesareni G. Plasmids pEMBLY: new single-stranded shuttle vectors for the recovery and analysis of yeast DNA sequences. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Fay G., Fukuhara H. Temperature-sensitive respiratory-deficient mitochondrial mutations: isolation and genetic mapping. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):295–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00693083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonitz S. G., Coruzzi G., Thalenfeld B. E., Tzagoloff A., Macino G. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for subunit 1 of yeast cytochrme oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11927–11941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Thomas M., Cameron J., St John T. P., Scherer S., Padgett R. A. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Salle H., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Critical sequences within mitochondrial introns: pleiotropic mRNA maturase and cis-dominant signals of the box intron controlling reductase and oxidase. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Daves R. S., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A short nucleotide sequence required for regulation of HIS4 by the general control system of yeast. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M., Finkelstein D., Butow R. A. Analysis of products of mitochondrial protein synthesis in yeast: genetic and biochemical aspects. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:58–66. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Simon M. Analysis of a yeast nuclear gene involved in the maturation of mitochondrial pre-messenger RNA of the cytochrome oxidase subunit I. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Arnberg A. C., Roosendaal E., van der Horst G., van der Veen R., van Ommen G. J., Grivell L. A. Variation, transcription and circular RNAs of the mitochondrial gene for subunit I of cytochrome c oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):35–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Bonen L., de Haan M., van der Horst G., Grivell L. A. Two intron sequences in yeast mitochondrial COX1 gene: homology among URF-containing introns and strain-dependent variation in flanking exons. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J., McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. A mutation in yeast mitochondrial DNA results in a precise excision of the terminal intron of the cytochrome b gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3235–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreike J., Schulze M., Pillar T., Körte A., Rödel G. Cloning of a nuclear gene MRS1 involved in the excision of a single group I intron (bI3) from the mitochondrial COB transcript in S. cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1986;11(3):185–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00420605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The yeast nuclear gene NAM2 is essential for mitochondrial DNA integrity and can cure a mitochondrial RNA-maturase deficiency. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancashire W. E., Mattoon J. R. Cytoduction: a tool for mitochondrial genetic studies in yeast. Utilization of the nuclear-fusion mutation kar 1-1 for transfer of drug r and mit genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 5;170(3):333–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00267067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. F. The mitochondrial genome of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: highly homologous introns are inserted at the same position of the otherwise less conserved cox1 genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Aspergillus nidulans. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2129–2136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Lei S. P., Wilcox G. An improved DNA sequencing strategy. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee E. E., McEwen J. E., Poyton R. O. Mitochondrial gene expression in saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Fidelity of translation in isolated mitochondria from wild type and respiratory-deficient mutant cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9332–9338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Lang B. F. Mitochondrial class II introns encode proteins related to the reverse transcriptases of retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):641–643. doi: 10.1038/316641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene (MST1) coding for the mitochondrial threonyl-tRNA1 synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15362–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Faye G. Steps in processing of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I pre-mRNA affected by a nuclear mutation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):8–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Seraphin B., Faye G. KIN28, a yeast split gene coding for a putative protein kinase homologous to CDC28. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2697–2701. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Boulet A., Simon M., Faye G. Construction of a yeast strain devoid of mitochondrial introns and its use to screen nuclear genes involved in mitochondrial splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6810–6814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Faye G. A mitochondrial reading frame which may code for a maturase-like protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):3005–3014. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Van der Horst G., Kamps A. M., Arnberg A. C. Interlocked RNA circle formation by a self-splicing yeast mitochondrial group I intron. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W., Scazzocchio C., Brown T. A. Internal structure of a mitochondrial intron of Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Horst G., Tabak H. F. Self-splicing of yeast mitochondrial ribosomal and messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90335-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]