Abstract
Cleavage of mutant huntingtin (HTT) is an essential process in Huntington’s disease (HD), an inherited neurodegenerative disorder. Cleavage generates N-ter fragments that contain the polyQ stretch and whose nuclear toxicity is well established. However, the functional defects induced by cleavage of full-length HTT remain elusive. Moreover, the contribution of non-polyQ C-terminal fragments is unknown. Using time- and site-specific control of full-length HTT proteolysis, we show that specific cleavages are required to disrupt intramolecular interactions within HTT and to cause toxicity in cells and flies. Surprisingly, in addition to the canonical pathogenic N-ter fragments, the C-ter fragments generated, that do not contain the polyQ stretch, induced toxicity via dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and increased ER stress. C-ter HTT bound to dynamin 1 and subsequently impaired its activity at ER membranes. Our findings support a role for HTT on dynamin 1 function and ER homoeostasis. Proteolysis-induced alteration of this function may be relevant to disease.
Keywords: Drosophila, endoplasmic reticulum, ER dilation, Huntington’s disease, TEV proteolysis
See also: M Jimenez-Sanchez & DC Rubinsztein (September 2015)
Introduction
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a devastating autosomal dominant inherited neurodegenerative disorder characterised by personality changes, cognitive deterioration, involuntary choreiform movements and hypokinesia. HD neuropathology involves the preferential loss of neurons from the striatum and the cortex. There is currently no effective treatment to delay or prevent disease progression. HD is caused by an abnormal polyglutamine (polyQ) expansion at the extreme N-terminus (N-ter, amino acid 18) of the protein huntingtin (HTT), a large protein of 3,144 amino acids (aas). Although the mechanisms that lead to HD are not fully understood, a series of events that ultimately lead to the death of neurons in the brain have been described (Cattaneo et al, 2005; Borrell-Pages et al, 2006; Imarisio et al, 2008).
A crucial step in HD pathogenesis is the cleavage of full-length HTT releasing smaller N-ter fragments that contain the polyQ stretch and that are toxic to neurons. Such polyQ-containing fragments have been consistently observed in human HD brains and HD mouse models (Kim et al, 2001; Mende-Mueller et al, 2001; Wellington et al, 2002; Wang et al, 2008; Landles et al, 2010). Several proteases, including caspases, calpains, cathepsins and metalloproteinases, that cleave HTT have been reported (Goldberg et al, 1996; Kim et al, 2001, 2006; Gafni & Ellerby, 2002; Lunkes et al, 2002; Hermel et al, 2004; Ratovitski et al, 2009; Miller et al, 2010; Tebbenkamp et al, 2012), and inhibition of HTT cleavage reduces toxicity both in vitro and in vivo (Wellington et al, 2000; Gafni et al, 2004; Graham et al, 2006; Miller et al, 2010). PolyQ N-ter fragments can reproduce several aspects of the disease. For example, a fragment corresponding to Exon1, containing the polyQ stretch, is sufficient to induce a neurological phenotype in mouse (Mangiarini et al, 1996). Consequently, such N-ter fragments have been extensively used to study HD. Toxicity expressed by N-ter fragments requires their nuclear translocation (Saudou et al, 1998); this causes transcriptional dysregulation detrimental to neuronal survival (Sugars & Rubinsztein, 2003; Landles & Bates, 2004). Mutant HD fragments also induce neuronal dysfunctions, including defects in signal transduction, autophagy and both calcium and mitochondrial homoeostasis (for reviews, see Borrell-Pages et al, 2006; Imarisio et al, 2008; Li & Li, 2010). Together, these studies have established that N-ter fragment(s) containing the polyQ stretch are the crucial factors responsible for HD pathogenesis.
However, the cascade of proteolytic events leading to the generation of these toxic fragments is unclear. Also, the precise consequences of full-length HTT proteolysis at the molecular and cellular levels are unknown. This could be partly due to the complexity to monitor HTT proteolysis. Also, the reasons why some N-ter fragments are more toxic than others are obscure. One consensus theory is that these mutant fragments are more toxic the shorter they are (Hackam et al, 1998; Landles et al, 2010), but this does not explain why some proteolytic cleavages are more toxic than others, independently of any major difference in the sizes of the resulting fragments (Graham et al, 2006). Also, HTT is cleaved by numerous proteases, some of which have not yet been identified (Lunkes et al, 2002; Gafni et al, 2012). Finally, activating a specific protease will induce the cleavage of many substrates besides HTT itself. This makes it difficult to determine the consequences of individual cleavages. Although N-ter fragments recapitulate features of HD in cells and in vivo, such models only incompletely reproduce what is observed in patients with HD. Indeed, in human HD, the full-length protein is present from early stages; consequently, any HTT cleavage generating short N-ter fragments (amino acid positions ranging from 1–105 to 1–586) will also generate corresponding C-ter fragments. Such C-ter fragments are observed in post-mortem HD brain samples (Mende-Mueller et al, 2001; Landles et al, 2010), but their contribution, if any, to the pathogenic process has not been studied.
Here, we report the development of a time- and site-specific controlled system for HTT proteolysis in vitro and in vivo. We used this system to investigate the consequences of proteolysis of full-length mutant HTT and the generation of both N-ter and C-ter fragments on neuronal survival in vitro and in vivo. We report that cleavage of HTT releases a C-terminal HTT that impairs dynamin 1 activity leading to endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell death.
Results
Time- and site-specific control of huntingtin proteolysis
Studies focusing on HTT cleavage and toxicity have used either protease inhibitors mutated the sites to become non-cleavable ones or expressed truncated fragments containing the polyQ stretch. To recapitulate the cleavage of full-length HTT occurring in cells, we took advantage of the ability of the tobacco etch virus (TEV) protease to specifically cleave engineered proteins that contain a seven amino acid sequence that is not present in the mammalian proteome but is recognised by the TEV protease. As a proof of concept for HTT-specific proteolysis, we generated full-length HTT constructs in which the putative caspase-6 site (position 586), caspase-3 site (513) and Cp2 site (167) are replaced by a TEV recognition cleavage site (TEVrcs) (Fig1A) as cleavage at these sites has been implicated in HD pathogenesis (Wellington et al, 2000; Graham et al, 2006; Ratovitski et al, 2011). We validated our system by expressing the various HTT-TEV constructs in HEK293T cells and incubating protein extracts with an excess of recombinant TEV protease. Whereas TEV protease was unable to cleave polyQ FL-HTT constructs that did not contain the TEVrcs (referred to as “no TEV”), it efficiently cleaved all of polyQ FL-HTT586TEV, FL-HTT513TEV, FL-HTT167TEV (Fig EV1A). HTT proteolysis in patient brains is the result of a combination of various cleavage events, so we also generated constructs containing two TEVrcs (Fig1A). Incubation of these constructs with recombinant TEV generated proteolytic fragments of the expected sizes including intermediate fragments that are those which are cleaved at only one site (Fig EV1A). We next assessed whether inserting the TEV sequences in HTT influenced protein toxicity and function. First, we found that the presence of the TEV sequence (without proteolysis induction) at positions 586, or 167 and 586 had no major effect on the toxicity of the polyQ FL-HTT constructs (FigEV1B). We next focused on HTT function in Golgi maintenance as this function is (i) well described (Caviston et al, 2007; Pardo et al, 2010) and (ii) depends on HTT interaction with dynein/dynactin complex in the N-terminal region of HTT (regions 171–230 and 536–698 that are close to or contain the TEV sites). We therefore silenced endogenous HTT in HeLa cells and tested whether re-expressing siRNA-insensitive HTT constructs containing two TEV sites were able to reassemble Golgi ribbons. The wild-type HTT containing two TEV sites reformed intact Golgi apparatus after nocodazole wash out to the same extent as the FL-HTTQ23 without TEV sites. And similarly to the polyQ-HTT inability to reassemble the Golgi apparatus (Pardo et al, 2010), the polyQ-HTT containing two TEV sites was unable to do so. We conclude that HTT with two TEV sites remains functional on its dynein/dynactin scaffolding function (FigEV1C).
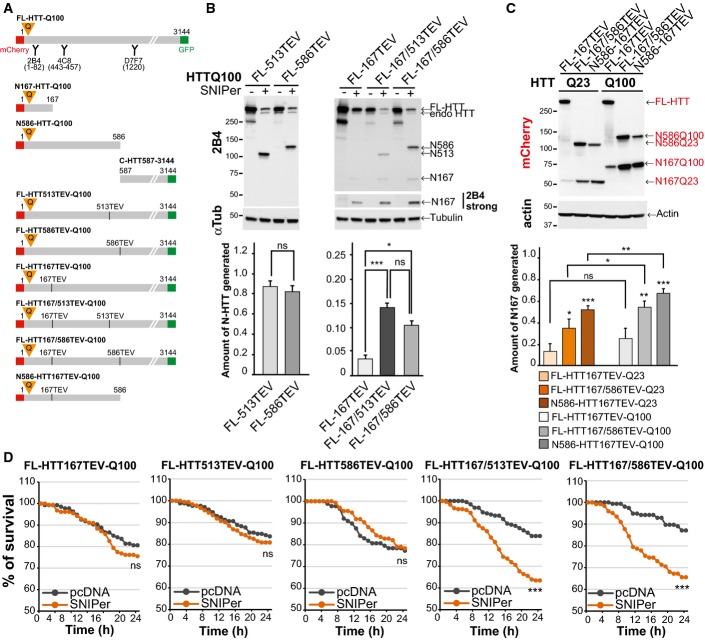
Figure 1.
Sequential proteolysis of huntingtin reveals toxic events
- Schematic representations of N-ter, C-ter or full-length polyQ-HTT constructs used and location of antibody epitopes and tags.
- Analyses of HTT N-ter fragments generated after cleavage of the indicated HTT-TEV-Q100 constructs by the SNIPer-TEV in HEK293T cells at 24 h.
- Analyses of HTT N167 fragments generated upon cleavage of wild-type and mutant HTT (24 h) in striatal cells.
- Survival of striatal cells upon SNIPer-TEV-induced cleavage of FL-HTT-TEV-Q100.
Data information: The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from four (B) or five (C) independent experiments. For (D), the total numbers of cells and number of independent experiments are as follows: FL-HTT167TEV+pcDNA: 134 or +SNIPer: 155 (n = 3), FL-HTT513TEV+pcDNA: 171 or +SNIPer: 183 (n = 4), FL-HTT586TEV+pcDNA: 88 or +SNIPer: 134 (n = 3), FL-HTT167/513TEV+pcDNA: 155 or +SNIPer: 122 (n = 3), FL-HTT167/586TEV+pcDNA: 192 or +SNIPer: 238 (n = 4). Statistics were done by unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction P = 0.5730 (B, left panel), one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison (B, right panel), one-way ANOVA with Fisher LSD test and one-way ANOVA with paired t-test (C), Kaplan–Meier, log-rank test (D). ns: non-significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See also FigEV1.
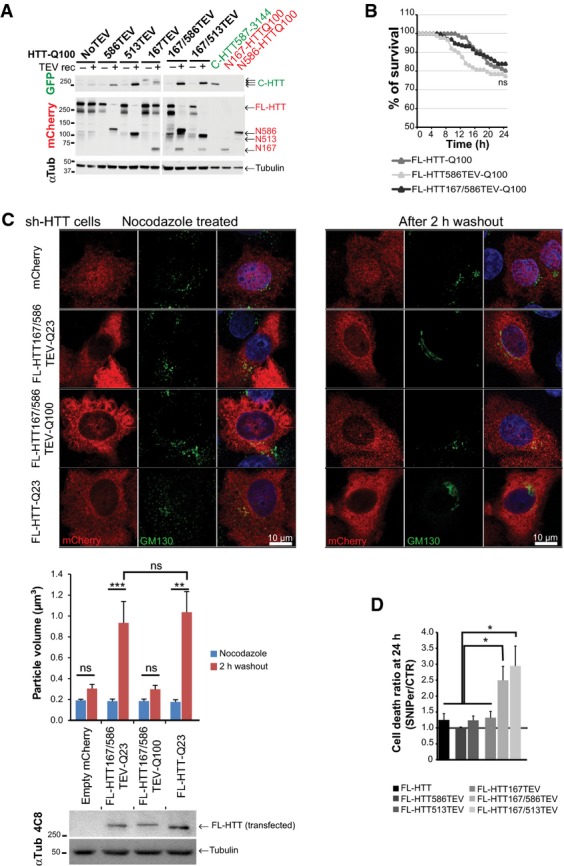
Time- and site-specific control of huntingtin proteolysis
- Immunoblotting analyses of HTT N-ter and C-ter fragments generated after cleavage of the indicated constructs expressed in HEK293T cells and using recombinant TEV system. “no TEV” referred to FL-HTT-Q100 constructs, without TEVrcs.
- Survival curves of striatal cells expressing FL-HTT constructs containing no TEV, one or two TEVrcs. Toxicity is expressed as the percentage of survival over time.
- FL-HTT constructs with TEV sequence insertions at positions 167 and 586 are as functional as FL-HTT on the dynein-dependent Golgi reassembly assay. Upper panels show representative HeLa cells stably silenced for endogenous HTT and that re-express FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q23, HTT167/586TEV-Q100 or FL-HTT-Q23 and treated with nocodazole for 2 h (left panels) and after 2-h washout (right panels). Western blotting shows the expression level of transfected FL-HTT in sh-HTT cell line.
- Graph summarising cell death ratio at 24 h of FL-HTTTEV-Q100 analysed in Fig1D. HTT proteolysis-induced toxicity is shown as a ratio of the percentage of cell death obtained in SNIPer-TEV condition over pcDNA condition.
Data information: The graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from three to four independent experiments (B), from two independent experiments performed in duplicates (C) or from three to four independent experiments (D). In (B), total number of cells and number of independent experiments are as follows: FL-HTT-Q100 + pcDNA: 96 (n = 3) and FL-HTT586TEV-Q100 + pcDNA: 88 (n = 3) and FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q100 + pcDNA: 192 (n = 4). In (C), total number of cells is as follows: nocodazole treated: 6, washout condition: 8. In (D), total number of cells is as in Fig1D with 140 cells for FL-HTT. Statistics were done by Kaplan–Meier, log-rank test (B), one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests (C) and ordinary one-way ANOVA with Fisher LSD test (D). ns: non-significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
We next analysed the proteolysis of these HTT constructs in cells using the inducible SNIPer-TEV system. This system involves two vectors encoding the N and C parts of the TEV fused to FRB and FKBP fragments, respectively. Addition of 10 or 20 nM of rapamycin induces a rapid heterodimerisation of the fragments and thereby expression of the TEV protease activity (Gray et al, 2010). We treated HEK293T cells expressing the HTT-TEV and the SNIPer-TEV constructs with 20 nM rapamycin and analysed proteolysis at 24 h. Rapamycin at this concentration had no effect on proteolysis of endogenous HTT or on its toxicity. Whereas 80–95% of FL-HTT constructs were cleaved at positions 513 or 586 (Fig1B), proteolysis at position 167 did not occur efficiently unless if HTT was also cleaved at positions 513 or 586, suggesting that the proteolytic cleavage sites in HTT are not all equally accessible.
We next compared the proteolysis of WT versus polyQ-HTT at position 167 in the striatal STHdh cell line referred after as striatal cells (Trettel et al, 2000). We confirmed that for both WT and polyQ constructs, cleavage at position 586 enhanced cleavage at position 167 (Fig1C). Also, the presence of a polyQ stretch in HTT slightly favoured the production by proteolysis of the N167 fragment, suggesting that polyQ expansion may render the 167 site more accessible. Our findings validate the use of the TEV approach to study intrinsic proteolytic properties of HTT. It also suggests that HTT is subject to a proteolytic cascade that may be more efficient when HTT contains a pathogenic expanded polyQ stretch.
Sequential proteolysis accelerates huntingtin toxicity
We used the striatal cells to analyse the toxicity associated with HTT proteolysis at particular positions. We transfected the cells with the various HTT-TEV constructs and the two SNIPer-TEV plasmids or an empty pcDNA vector as a control; 20 h later, 10 nM of rapamycin was added to transfected cells, identified by the presence of the mCherry tag on HTT constructs. The fate of individual cells containing HTT was then followed for 24 h by robotic automated videomicroscopy. Expression of the SNIPer-TEV or rapamycin treatment had no significant effect on non-cleavable HTT constructs (FigEV1D). We next analysed the toxicity of the various constructs upon cleavage (Fig1D). The FL-HTT167TEV-Q100 construct displayed no obvious toxicity (Figs1D and EV1D); this is consistent with the poor efficiency of cleavage at position 167 by TEV. Surprisingly, cleavage of the constructs with TEVrcs at positions 513 and 586 had no evident effect on cell survival (Figs1D and EV1D) although proteolysis of these HTT constructs was very efficient (Fig1B and C). In contrast, double cleavage at sites 586/167 or 513/167 led to a significant increase in polyQ-HTT-induced toxicity compared to each site alone (Figs1D and EV1D and Movie EV1). These results suggest that cleavage at 513 or 586 sites has no immediate consequences on polyQ-mediated toxicity. Rather, the sequential proteolysis promotes mutant HTT-induced toxicity.
Huntingtin intramolecular interaction is lost upon specific proteolysis
N-terminal regions of HTT interact with more C-terminal regions (Palidwor et al, 2009). Since cleavage at 513 and 586 gave similar results, we focused on 586 site and tested whether N586 fragment and the C-HTT587-3144 fragment interacted. Using brain extracts from heterozygous HdhQ7/Q111 mice treated in vitro with recombinant caspase-6, we found that the C-HTT587-3144 fragment interacted with the N586 fragment and that this interaction was not affected by the polyQ expansion (Fig2A). We next expressed simple or double FL-HTT-TEV constructs with the SNIPer-TEV system in HEK293T cells and treated cells for 24 h with 20 nM rapamycin to induce HTT proteolysis. C-ter fragments produced by cleavage at position 586 co-immunoprecipitated the corresponding wild-type and polyQ N586 fragments. However, there was no interaction between the C-HTT587-3144 fragments and the N167 fragments (Figs2B and EV2A). We conclude that polyQ N586 fragments interact with their corresponding C-ter fragments, but that further proteolysis of the N-ter fragment abolishes the interaction.
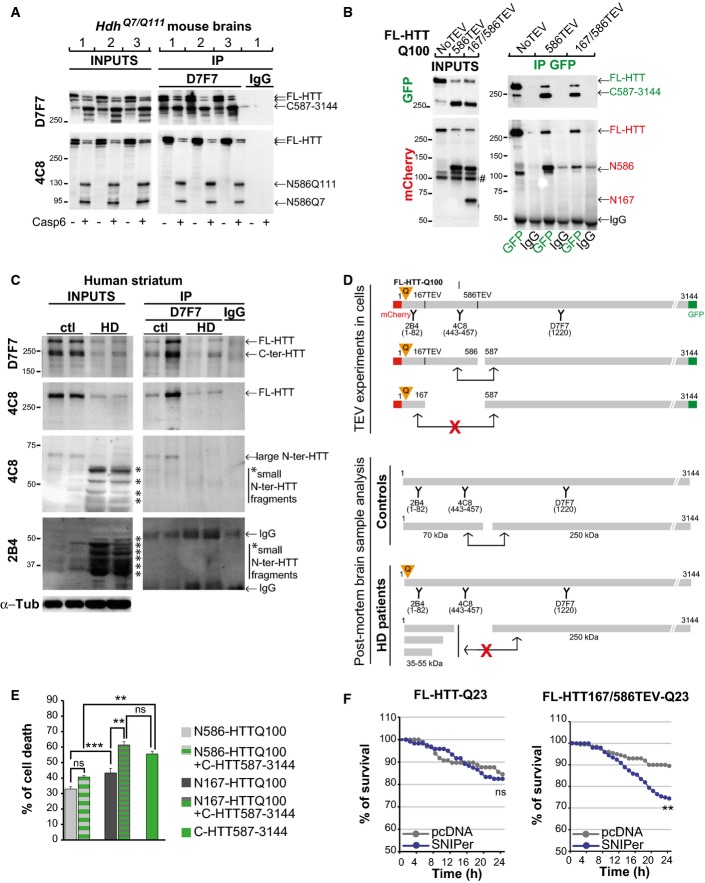
Figure 2.
Intramolecular interactions between proteolytic huntingtin fragments
- Protein lysates from HdhQ7/Q111 mouse brains were cleaved with recombinant caspase-6, and generated N-ter and C-ter fragments were subjected to immunoprecipitation.
- Immunoprecipitation performed in HeLa cells upon cleavage of FL-HTT-TEV-Q100. # indicates a non-specific band.
- Immunoblotting analysis of HTT proteolysis and co-immunoprecipitation of HTT C-ter and N-ter fragments in post-mortem control and HD human striatum samples. Asterisks indicate the position of small N-ter fragments.
- Schematic representation of antibody epitope locations and interactions between various HTT fragments generated in cells and in human brain samples.
- Cell death induced by the indicated HTT constructs in transfected striatal cells.
- Survival curves of striatal cells upon cleavage of FL-HTT-TEV-Q23.
Data information: The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from 3 independent experiments in triplicates (E). For (F), the total numbers of cells and number of independent experiments are as follows: FL-HTT-Q23 + pcDNA: 97 + SNIPer: 120 (n = 2), FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q23 + pcDNA: 200 + SNIPer: 199 (n = 4). Statistics were done by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests (E) and Kaplan–Meier, log-rank test (F). ns: non-significant, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See also FigEV2.
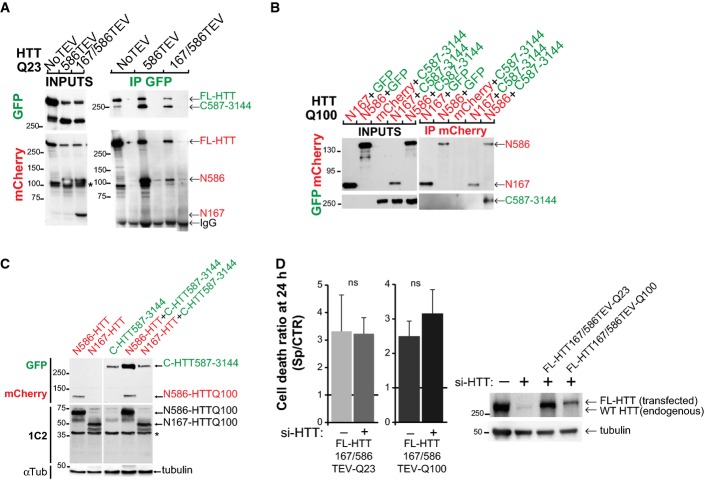
Intramolecular interactions between proteolytic huntingtin fragments
- Immunoprecipitations upon cleavage of FL-HTT-TEV-Q23 by the SNIPer-TEV performed in HEK293T cell. * indicates a non-specific band.
- Immunoprecipitations of HeLa cell extracts expressing mCherry-N-HTTQ100 constructs or mCherry and C-HTT587-3144-GFP or GFP using anti-mCherry antibody.
- Immunoblotting analysis of the expression level of N- and C-HTT alone or in combination with striatal cells. * indicates a non-specific band.
- Toxicity in striatal cells transfected with FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q23 and FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q100 and siRNA targeted against endogenous HTT (si-HTT). Graph summarising cell death ratio at 24 h of proteolysis-induced toxicity is shown as a ratio of the percentage of cell death obtained in SNIPer-TEV condition over pcDNA condition. Downregulation of HTT expression was assessed by immunoblotting (right). The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from two to four independent experiments. Total number of cells is as follows: FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q23 without si-HTT: 399 cells; with si-HTT: 230 cells; FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q100 without si-HTT: 430 cells; with si-HTT: 199 cells. Statistics were done by unpaired t-test. ns: non-significant.
To further investigate the physiological relevance of increased proteolysis and loss of HTT intramolecular interaction, we analysed the presence of N-ter and C-ter fragments in post-mortem striatal brain samples from patients with HD and control individuals (Fig2C). In control samples, we detected full-length HTT as well as C-ter and N-ter fragments of approximate sizes of 250 and 70 kDa, respectively. These fragments may correspond to HTT proteolysis in the 500- to 600-amino acid region of HTT, and they have been previously reported in control samples (Kim et al, 2001; Mende-Mueller et al, 2001; Gafni & Ellerby, 2002; Lunkes et al, 2002; Wellington et al, 2002; Hermel et al, 2004; Landles et al, 2010). Interestingly, the 250 and 70 kDa fragments may correspond to the C-HTT587-3144 and N586-HTT fragments generated after single TEV proteolysis (Figs2A and B and EV2A). In HD post-mortem striatal brain samples, we found a lower level of full-length HTT compared to control individuals. We also detected the C-ter fragment of 250 kDa as well as large amounts of N-ter fragments that are smaller than the 70 kDa fragment observed in control samples. This increased level of very small N-ter fragments recognised only by the 2B4 antibody and the loss of the 70 kDa N-ter fragment suggest an increased proteolysis of the 70 kDa fragment. However, we cannot exclude that part of these fragments might be generated by repeat length-dependent alternative splicing (Sathasivam et al, 2013). Because we observed in cells that the C-HTT587-3144 fragment interacted with the N586 but not shorter ones, we investigated whether increased proteolysis in HD samples leads to loss of intramolecular interaction and perform immunoprecipitation experiments of brain samples using anti C-ter HTT antibody (D7F7) (Fig2C, right panel). Whereas the C-ter antibody co-immunoprecipitated the large 70 kDa N-ter fragment in striatal brain samples from control individuals, no shorter fragments were detected in the striatal brain samples from HD individuals. We conclude that in HD situation, the C-ter fragment, although less abundant than in control situation, is potentially free from its intramolecular interaction with N-ter fragments (Fig2D).
Both N- and C-terminal huntingtin fragments induce toxicity that depends on the size of N-terminal fragments
To further study the relation between intramolecular interaction and toxicity, we generated constructs that mimic the different fragments generated after HTT cleavage at 586 and expressed them in HeLa or striatal cells (Fig EV2B and C). As shown by immunoprecipitation, the N586 fragment but not the short N167 one interacts with the C-HTT587-3144 fragment (FigEV2B). As expected (Hackam et al, 1998), N167-HTTQ100 is more toxic than N586-HTTQ100 (Fig2E). Interestingly, co-expression of C-HTT587-3144 construct potentiated the toxicity induced by the N167-HTTQ100 fragment but had no effect on that of the N586-HTTQ100 fragment (Figs2E and EV2C). We also measured the toxicity of the C-HTT587-3144 fragment alone in striatal cells. Surprisingly, it was highly toxic and even more toxic than the N167-HTTQ100 fragment (Fig2E). As such fragments are also generated upon wild-type FL-HTT cleavage, inducing artificially the cleavage of wild-type FL-HTT should also lead to toxicity. Indeed, whereas TEV activation had no effect on FL-HTT-Q23, it significantly increased toxicity of WT-FL-HTT with TEV sites at positions 167 and 586 (Fig2F). Since the C-ter fragment when expressed alone induced some toxicity, we tested the possibility that this could occur through a dominant-negative effect on full-length endogenous HTT that is present in cells. We therefore expressed FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q23 and FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q100 constructs in cells silenced or not for endogenous HTT and induced cleavage by SNIPer-TEV activation (Fig EV2D). We found no difference in the toxicity upon HTT double proteolysis whether endogenous HTT was present or downregulated. We conclude that in addition to mutant N-ter fragments, C-ter fragments generated from either wild-type or mutant HTT cleavage are toxic. The interaction of N-ter and C-ter fragments prevents them from being toxic.
C-terminal huntingtin fragment causes endoplasmic reticulum-derived vacuolation, stress and toxicity
To study the consequences of the loss of N–C interactions as N-ter fragments become shorter (as this is the case in post-mortem HD samples), we determined the localisation of C-HTT587-3144 with N586-HTTQ100 or N167-HTTQ100 in striatal cells. In agreement with biochemical findings (Fig2), C-HTT587-3144 (GFP) co-localised with N586-HTTQ100 (mCherry) but less with N167-HTTQ100 (Fig3A). As the interaction between the C-HTT587-3144 fragment and the short N-terminal fragments weakened, the proportion of the N-ter fragments in the nucleus increased; the C-ter fragment remained in the cytoplasm in all cases (Fig3A). These findings are in agreement with previous reports showing an inverse correlation between nuclear localisation and the size of the N-ter fragments (Hackam et al, 1998; Saudou et al, 1998). When analysing cells at longer time points (24 h), large cytoplasmic vacuoles developed in cells producing both the C-HTT587-3144 fragment and the short non-interacting fragments (N167-HTTQ100) or producing the C-ter fragment alone (Fig3B). These vacuoles were less frequent in cells producing the C-HTT587-3144 fragment and the N586-HTTQ100 fragment. No such vacuolar phenotype was observed in cells producing one of the polyQ N-ter HTT fragments alone (Fig3B). Vacuoles formed around 36 h post-transfection and death occurred rapidly after the vacuoles started to emerge (11 h ± 0.8; n = 26 cells) (Movie EV2), suggesting a fast and dynamic process consistent with the kinetics of death observed following HTT-induced proteolysis (Fig1).
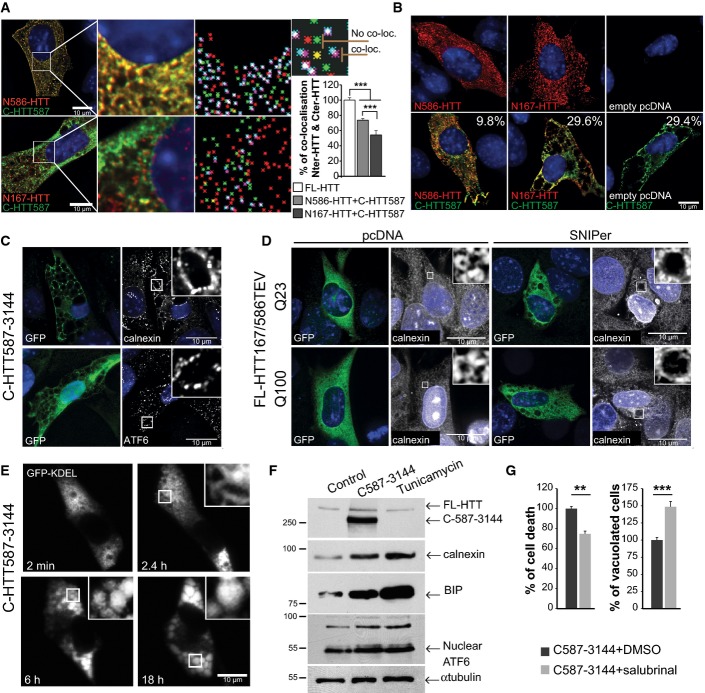
Figure 3.
Released C-terminal huntingtin fragment elicits endoplasmic reticulum dilation, stress and cell death
- Immunostaining of striatal cells transfected with C-HTT587-3144 (GFP) and N-HTTQ100 constructs (mCherry). Co-localisation was measured using the JACoP plugin (ImageJ, see Appendix Supplementary Materials and Methods). Maps illustrating the mass centre of particles from the two fluorophores are shown in the right column. Loc stands for localisation. Graph indicates the mean percentage of co-localisation between fragments. mCherry- and GFP-tagged FL-HTT are used as reference (100%).
- Immunostaining of striatal cells expressing the indicated constructs. Values indicate the percentage of cells undergoing cytoplasmic vacuolation.
- C-HTT587-3144-expressing striatal cells immunostained with anti-calnexin and anti-ATF6 antibodies.
- Immunostaining of calnexin shows ER dilation upon cleavage of HTT167/586TEV-Q100 or Q23 (anti-GFP) in striatal cells.
- Time-lapse imaging of luminal ER marker (GFP-KDEL) in a C-HTT587-3114-expressing striatal cells.
- ER stress chaperones are upregulated in C-HTT587-3144-GFP striatal cells. Tunicamycin was used as a control for ER stress.
- Cell death and vacuolation after treatment with salubrinal, an ER stress inhibitor in striatal cells.
Data information: The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from two to four (A) or three (G) independent experiments. Total number of cells analysed in (A) are as follows: FL-HTT: n = 51; N586HTT+C-HTT587: n = 109; N167HTT+C-HTT587: n = 95. Statistics were done by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests (A) and one-way ANOVA with unpaired t-test (G). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See also FigEV3.
We investigated the nature of the C-HTT587-3144 fragment-induced vacuoles. They were immuno-negative for GM130, CTR 433, TGN38, Rab5 and EEA1 (FigEV3A) and are therefore unlikely to be derived from the Golgi apparatus, the trans-Golgi network or early endosomes. In addition, the vacuoles did not localise with LC3-GFP and LAMP2, suggesting they are not linked to autophagosomes or lysosomes (FigEV3A). However, the C-terminal HTT-induced vacuoles were stained by antibodies for calnexin and ATF6, both chaperone proteins found in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes (Fig3C). To confirm the role of the C-ter fragment in the formation of these ER-derived vacuoles, we SNIPer-TEV-induced proteolysis of the FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q100 and Q23 constructs. As in cells expressing the C-HTT587-3144 construct, double proteolysis of both WT and mutant HTT was associated with dilation of the ER (in more than half the cells) and the emergence of cytoplasmic vacuoles (Fig3D). We also co-expressed the C-HTT587-3144 fragment with a vector encoding GFP fused to the KDEL motif, a luminal marker of the ER: the vacuoles progressively filled with GFP-KDEL (Fig3E and Movie EV3). Finally, C-HTT587-3144 fragment increased calnexin and BIP protein levels; it also led to an upregulation of full-length and truncated nuclear ATF6 (Fig3F). Our data thus support that the C-HTT587-3144 fragment of HTT causes ER dilation and the formation of cytoplasmic vacuoles.
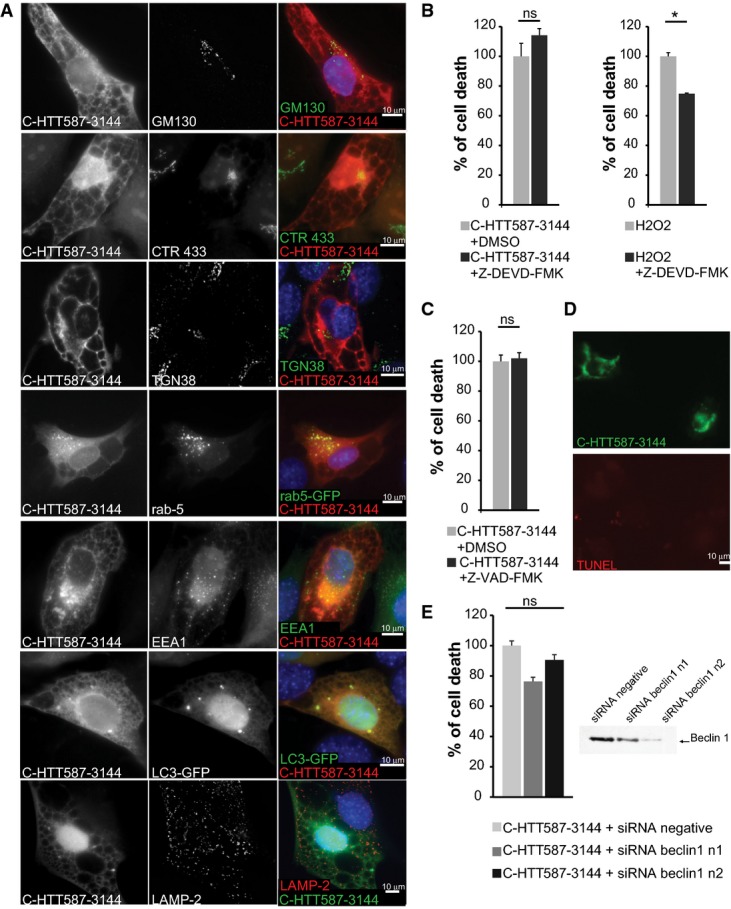
Released C-terminal HTT fragment elicits endoplasmic reticulum dilation, stress and cell death
- Immunostainings of striatal cells transfected with mCherry-tagged C-HTT587-3144 fragment. Golgi apparatus compartments were immunostained with anti-GM130 (cis-Golgi), anti-CTR433 (medial-Golgi) and anti-TGN38 (trans-Golgi) antibodies. Early endosomes were either stained with anti-EEA1 or labelled with Rab5-GFP-expressing constructs. LC3-GFP-labelled autophagosomes and lysosomes were immunostained with anti-LAMP2.
- Left: Striatal cells transfected with C-HTT587-3144 were treated with Z-DEVD-FMK, a caspase-3 inhibitor and analysed for cell death. Right: Non-transfected cells were treated for 2 h with 1 mM of H2O2 and Z-DEVD-FMK.
- Toxicity in striatal cells transfected with C-HTT587-3144 and treated with Z-VAD-FMK.
- Assessment of DNA fragmentation in C-HTT587-3144-expressing striatal cells using a TUNEL assay.
- Toxicity in striatal cells transfected with C-HTT587-3144 fragment and siRNA targeted against Beclin-1 (two independent siRNA n1 & n2). Downregulation of Beclin-1 expression was assessed by immunoblotting.
Data information: The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from three to five independent experiments in triplicates. For the quantification of cell death after H2O2 treatment (B), one experiment was performed in duplicate and more than 1,000 cells were analysed. Statistics were done by unpaired t-test (B, C) or one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. ns: Non-significant, *P < 0.05.
What is the death pathway elicited by C-ter HTT? Caspase inhibitors did not block cell death and C-ter-expressing cells were TUNEL negative (FigEV3B–D). Also, Beclin-1 silencing failed to reduce cellular toxicity (FigEV3E). Together, these data suggest that apoptosis and autophagy are unlikely to be directly involved. In contrast, treatment with the ER stress inhibitor salubrinal significantly decreased cell death among C-HTT587-3144-containing cells; it also resulted in an increase in the percentage of cells containing vacuoles (Fig3G). Therefore, ER-derived vacuoles in C-HTT587-3144-containing cells induce ER stress and toxicity.
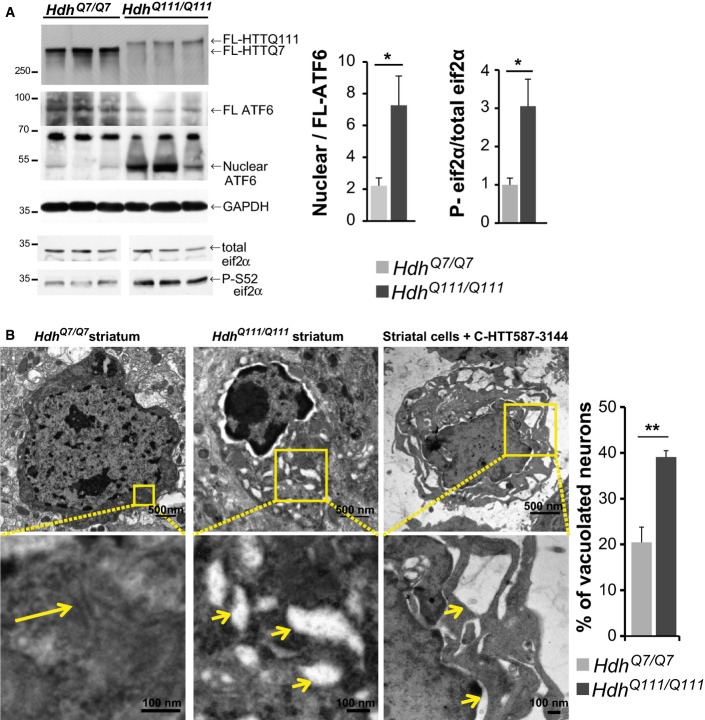
ER stress and vacuolation are observed in Huntington’s disease knock-in mice
FL-HTT is proteolysed to give C-ter and N-ter fragments in brains of patients with HD and HD knock-in mouse models (Mende-Mueller et al, 2001)(Fig2A and C). Therefore, the consequences of the putative C-ter fragment-associated toxicity we describe, such as ER stress activation and dilated ER, should also present in the brains of HD knock-in mice, in which mutant huntingtin is expressed at endogenous levels. We analysed ER stress signalling in the striata from 20-month-old HdhQ111/Q111 mice: nuclear ATF6 abundance and eif2α phosphorylation were significantly higher in mutant HdhQ111/Q111 than control wild-type HdhQ7/Q7 mice (Fig4A). Next, we used electron microscopy to study the striatum of 20-month-old HdhQ111/Q111 mice. We found a significantly higher number of neurons showing swollen ER tubules in the striatum of HdhQ111/Q111 mice as compared to HdhQ7/Q7 mice (Fig4B). Such dilation is reminiscent of ER dilation and vacuolation observed in striatal cells expressing the C-HTT587-3144 fragment (Figs3 and 4B). These various findings suggest a possible toxic effect of C-ter fragments inducing ER stress and vacuolation in vivo.
Figure 4.
ER stress and vacuolation in HD mouse model
- Activation of ER stress in HdhQ111/Q111 knock-in HD mouse model compared to wild-type HdhQ7/Q7 mice.
- Electron microscopy analysis of striatal sections from 20-month-old HdhQ7/Q7 (left), HdhQ111/Q111 mice (middle) and striatal cells expressing the C-HTT587-3144 construct (right). The long arrow indicates ER, and the small ones depict vacuolated ER.
Data information: The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from 6 to 8 mice of 20 months of age of each genotype (A) and from three mice (B). In (B), total number of neurons analysed are as follows: HdhQ7/Q7 mice: 225; HdhQ111/Q111: 233. Statistics were done by one-way ANOVA with unpaired t-test (B, P = 0.0068). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
HTT proteolysis and the presence of C-ter huntingtin lead to neurodegeneration in flies
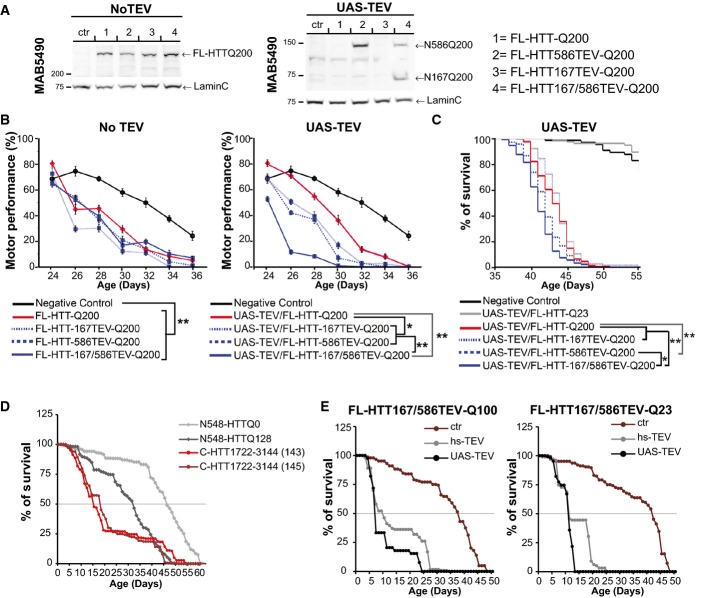
We used Drosophila as a model to assess the relevance of our findings in vivo as expression of TEV has been successfully used in flies for proteolysis of proteins in vivo and showed no long-term effects (Harder et al, 2008; Pauli et al, 2008). Also, full-length transgenic models of HD have been previously reported (Romero et al, 2008), and HTT functions are conserved between flies and mammals (Godin et al, 2010; Zala et al, 2013). We generated a set of fly strains by site-directed insertion of FL-HTT constructs with 200Q; thus, all transgenic strains showed similar expression of the construct (Fig5A, left panel). Crossing these flies with UAS-TEV flies led to selective cleavage of HTT in vivo (Fig5A, right panel). Flies expressing the various FL-HTTQ200 constructs without TEV showed similar deficits in their climbing activity (Fig5B, left graph). Upon TEV induction, only double proteolysis of HTT significantly decreased the climbing activity of the flies (Fig5B, right graph). Similarly, and as observed in cells, double HTT proteolysis was significantly more toxic to flies than any other combinations (Fig5C).
Figure 5.
Sequential proteolysis of huntingtin causes toxicity in vivo
- A Expression analysis of FL-HTT-TEV-Q200 in Drosophila.
- B Charts showing motor performance in climbing tests as a function of age.
- C–E Kaplan–Meier chart depicts survivorship in flies. Expression of the TEV was under an UAS or heat-shock (hs) promoter.
Data information: The graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from two replicates of 30 female virgins for each genotype (B, C), from three independent crosses (D, E). Total number of flies are as follows: N548-HTTQ0: 440, N548-HTTQ128: 478, C-HTT1722–3144 (143): 223, C-HTT1722–3144 (145)=223 (D) and FL-HTT167/586TEVQ100: ctr: 144, hs-TEV=119, UAS-TEV: 39; FL-HTT167/586TEVQ23: ctr: 124, hs-TEV: 99, UAS-TEV: 106 (E). Statistics were done by Z-test, P-values comparing the slope of decline in motor performance, **P < 0.00001, *P = 0.006756 (B), or were done by Kaplan–Meier, log-rank significance test (C–E). (C) FL-HTT-Q200 vs FL-HTT167TEV-Q200: ns, FL-HTT-Q200 vs FL-HTT586TEV-Q200: **P < 0.0001, FL-HTT-Q200 vs FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q200: **P < 0.0001, FL-HTT586TEV-Q200 vs FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q200: *P < 0.0069. (D) N548-HTTQ0 vs N548-HTTQ128: P < 0.001, C-HTT1722–3144 (143) & (145) vs N548-HTTQ128: P < 0.01. (E) pcDNA vs TEV: P < 0.001. See also FigEV4.
We investigated whether the C-ter fragment alone was sufficient to alter fly survival in vivo. We failed to generate transgenic flies expressing the C-HTT587-3144 fragment, so we used a shorter C-terminal fragment: C-HTT1722–3144. This fragment interacts with the N586 fragment but not with the N167 fragment and, when expressed in cells, leads to vacuolation and death (FigEV4A). N548-HTTQ128 flies showed a decreased survival rate compared to flies expressing wild-type N548-HTTQ0 (Lee et al, 2004). C-HTT1722–3144 flies had even a shorter lifespan (Fig5D) as shown in two independent lines (143 & 145). It is unlikely that the toxicity was due to overexpression as the C-HTT1722–3144 fragment was detected only by immunoprecipitation, whereas the N548-HTT fragments were readily detected directly in whole fly brain extracts (Fig EV4B and C).
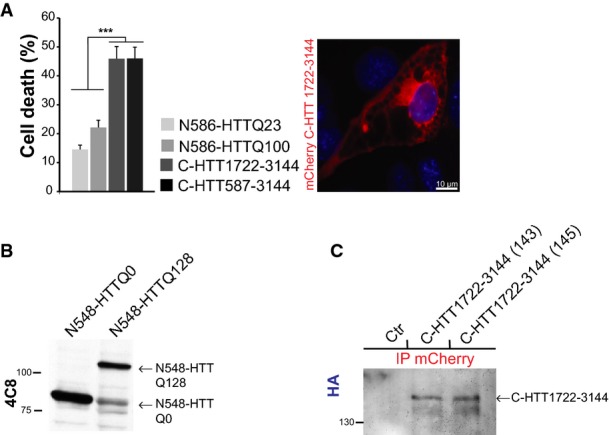
C-ter huntingtin causes toxicity in fly
- Analysis of C-HTT1722–3144 toxicity in striatal cells (left) and representative image of vacuolation in C-HTT1722–3144-expressing cells (right). The graph (mean ± SEM) displays pooled data from three independent experiments in duplicate. Total number of cells is as follows: N586-HTTQ23: 2285, N586-HTTQ100: 1698, C-HTT1722–3144: 483, C-HTT587-3144: 708. Statistics were done by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, ***P < 0.001.
- Assessment of N548-HTT transgene expression on total brain lysates of adult flies (4 days of age) by immunoblotting.
- Detection of C-HTT1722–3144 transgenes in two independent fly strains (143, 145) by immunoprecipitation. Control flies (ctr) are W1118 flies.
Thus, both N-ter and C-ter products of polyQ FL-HTT proteolysis are toxic in vivo. Finally, we generated transgenic flies expressing the TEV protease constructs and FL-HTT containing two TEV sites and with either 100Q or 23Q with expression driven by Elav-Gal4. TEV expression led to a dramatic reduction in fly survival both for the polyQ-containing ones and for wild-type flies. Similar results were obtained in experiments with TEV expression under the control of the heat-shock promoter, hs-TEV (Pauli et al, 2008), or of the UAS-TEV (Fig5E).
Dynamin 1 interacts with the C-terminal part of huntingtin
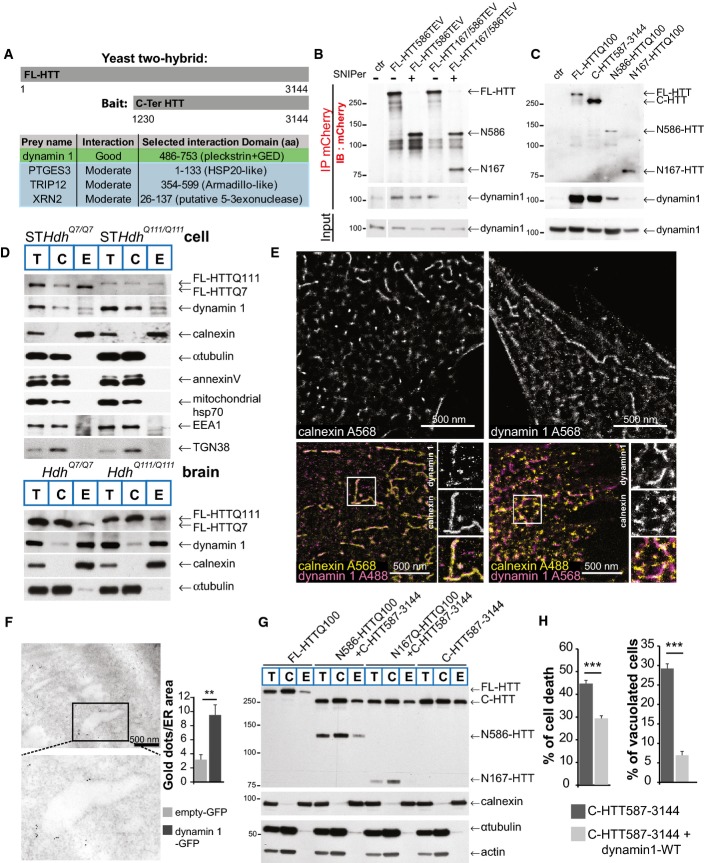
To decipher the mechanism by which the C-HTT587-3144 fragment leads to ER vacuolation, we searched for proteins interacting with the C-terminal domain of HTT. However, most reported yeast two-hybrid screens have been performed using N-terminal fragments of HTT, and the ones performed with C-terminal fragments as baits did not identify any specific interactors (Faber et al, 1998; Kaltenbach et al, 2007).
To optimise the strategy for identifying potential C-terminal HTT interactors, we searched the primary sequences of HTT orthologues for highly conserved regions. We found a fragment from position 1230 to position 3144 that shows a substantial similarity between the various species (FigEV5A and B) and used it as bait for a yeast two-hybrid screen using an adult human brain library. We obtained four interactors with high confidence (Fig6A) including dynamin 1. Dynamin 1 is involved in membrane fission reactions during several cellular processes (Ferguson & De Camilli, 2012) and has been identified as an interactor with the HTT N-terminal region (Kaltenbach et al, 2007) and full-length HTT (Moreira Sousa et al, 2013). Therefore, dynamin 1 may interact with both the N-ter and C-ter domains of full-length HTT, and proteolysis may affect the interaction between dynamin 1 and HTT. To test this possibility, we SNIPer-TEV-cleaved HTT at position 586 or at both positions 167 and 586 and immunoprecipitated HTT N-ter. FL-HTT and the N586 fragment interacted with dynamin 1, but the N167 fragment produced after the double cleavage did not (Fig6B). We also found that FL-HTT, C-HTT587-3144 and N586-HTTQ100, but not the shorter N167-HTTQ100 fragment, interacted with dynamin 1 (Fig6C). We conclude that the interaction between HTT and dynamin 1 may be affected by sequential proteolysis of N-ter fragments.
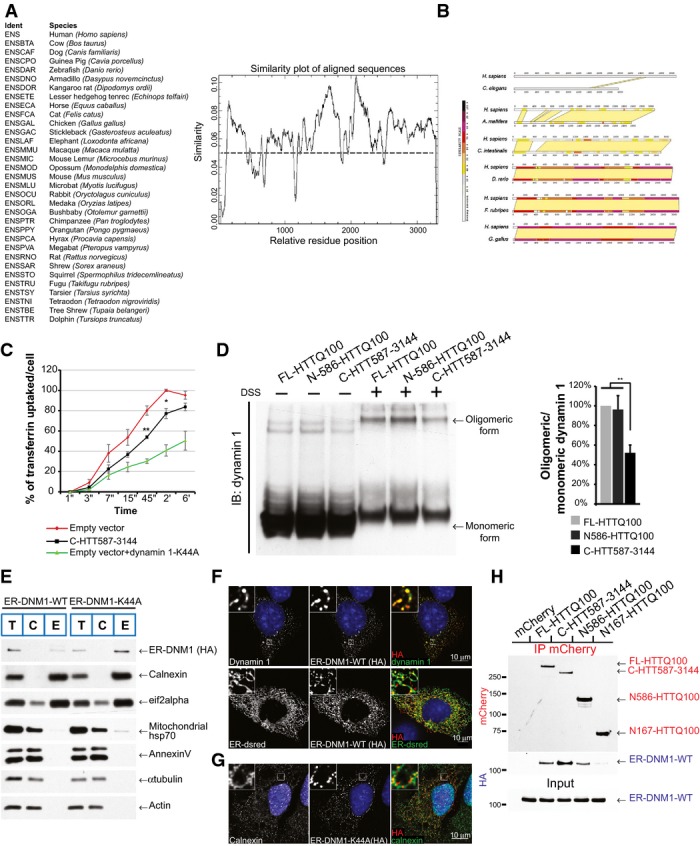
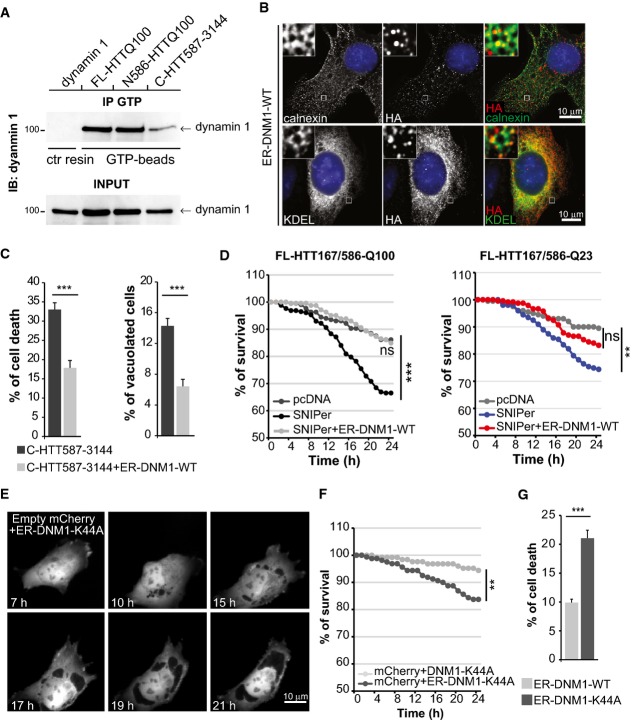
C-terminal HTT impairs the activity of ER-localised dynamin 1 that induces ER dilation and death
- A Identification of conserved regions in huntingtin. Search of primary sequence of HTT orthologues for highly conserved regions. Analysis of 32 orthologous sequences and generation of a residue conservation plot using the EMBOSS package tool “plocon”. Smoothing was applied to the results revealing regions with higher degrees of identity.
- B Pairwise comparison of human HTT versus C. elegans, A. mellifera, C. intestinalis, D. rerio, F. rubripes or G. gallus Htt. Very N-ter part of HTT (residues 170–400) and regions starting from 1200 to 3144 showed high similarity between the different species.
- C Assessment of dynamin 1 activity by transferrin uptake in striatal cells. GFP-tagged dynamin 1-K44A construct was used as a positive control for endocytosis inhibition. The curves indicate the percentage of transferrin uptake over time in s (‘‘) and min (‘).
- D Dynamin 1 oligomeric profile in HTT-expressing cells treated or not with DSS, a non-cleavable cross-linker. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated HTT fragments and dynamin 1. Endogenous HTT was downregulated using siRNA which do not target the HTT constructs.
- E Localisation of engineered ER-targeted dynamin 1 (ER-DNM1-WT or ER-DNM1-K44A) constructs at ER by cellular fractionation in striatal cells. Total (T), cytosolic (C) and ER membrane (E) fractions. ER-DNM1 was detected using anti-HA.
- F, G Analysis of localisation of engineered ER-targeted dynamin 1 (ER-DNM1-WT or ER-DNM1-K44A) using anti-HA immunostaining in striatal cells. Note the artificial high co-localisation on ER network as shown by immunostaining with ER-dsRed and calnexin.
- H Striatal cells expressing the indicated mCherry-tagged HTT fragments and ER-DNM1-WT were subjected to immunoprecipitation and analysed by immunoblotting.
Data information: The graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from three independent experiments in triplicate. In (C), total number of cells is 10,000 cells per experiment. Statistics were done by unpaired t-test (C) or one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Figure 6.
Dynamin 1 interacts with C-terminal huntingtin and both associate to ER membranes
- A Schematic representation of the bait used in the yeast two-hybrid screen and list of the four confident interactors with their HTT-interacting domains.
- B, C HeLa cells expressing HTT-TEV (B) or HTT fragments (C) with dynamin 1 were subjected to immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses.
- D Cellular fractionation analysis of striatal cells or Hdh mice model. Total (T), cytosolic (C) and ER membrane (E) fractions.
- E Localisation of dynamin 1 at ER membranes (calnexin immunostaining) using dSTORM method in striatal cells.
- F Immuno-electron microscopy analyses of dynamin 1 at ER in striatal cells. Enlargement indicates an ER tubule.
- G Cellular fractionation and ER localisation of HTT fragments expressed in striatal cells.
- H Cell death (left) and vacuolation (right) analysis in C-HTT587-3144 cells co-expressing WT-dynamin 1 in striatal cells.
Data information: The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from 80 isolated ER tubules in empty GFP-expressing cells and 140 in dynamin 1-GFP-expressing cells (F) or from 6 independent experiments in triplicate (H). Statistics were done by one-way ANOVA, unpaired t-test, **P = 0.0015 (F) and by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, ***P < 0.001 (H). See also FigEV5.
Dynamin 1 and huntingtin localise at ER membranes
Although dynamin 1 has not been described at the ER, dynamin-like proteins, including atlastin/Sey1p and Lnp1p, are enriched at the ER where they mediate its fusion/fission (Hu et al, 2009; Orso et al, 2009; Chen et al, 2013). Fractionation of both wild-type (STHdhQ7/Q7)- and mutant (STHdhQ111/Q111)-immortalised striatal cell line samples and of mouse brains revealed the presence of dynamin 1 in the enriched ER membrane fractions (Fig6D). ER-enriched fractions did not show the presence of cytosolic proteins such as tubulin, plasma membrane proteins such as annexin V, nor mitochondrial proteins such as the mitochondrial protein hsp70. ER fraction was slightly contaminated with the endosomal marker EEA1 and TGN138. However, it exhibited a large enrichment in the ER membrane protein calnexin (Fig6D). We next used direct STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (dSTORM) to localise endogenous dynamin 1 and calnexin in cells: Alexa 568 was used as the photoswitchable fluorophore and revealed that both proteins had a tubulo-membranous organisation (Fig6E, top panels). Co-immunostaining revealed dynamin 1 on ER structures identified by calnexin staining (Fig6E, lower panels). Finally, we transfected striatal cells with a construct encoding dynamin 1-GFP and performed immuno-electron microscopy. There were significantly more gold particles at ER membranes in cells transfected with the dynamin 1-GFP construct than those transfected with the GFP vector (Fig6F). These various analyses demonstrate that dynamin 1 can be found at ER membranes.
We also analysed the localisation of various HTT fragments. Subcellular fractionation identified FL-HTT and all the various HTT fragments in the ER-enriched fraction and, possibly, accumulation of the C-HTT587-3144 fragment in this fraction (Fig6G). This confirms previous reports that full-length HTT localises at the ER (Atwal et al, 2007) and shows that the C-HTT587-3144 fragment resulting from HTT sequential N-terminal proteolysis remains at the ER co-localising with dynamin 1.
Dynamin 1 impairment at the ER mediates the effect of C-ter huntingtin on vacuolation and death
We next investigated whether dynamin 1 influenced C-HTT587-3144 fragment-associated vacuolation and death. The toxicity associated with the presence of the C-HTT587-3144 fragment was significantly reduced by the co-expression of WT-dynamin 1 (Fig6H); similarly, the percentage of vacuolated cells was significantly reduced. These findings suggest that C-HTT587-3144 fragment-induced vacuolation and death involve deregulation of dynamin 1 activity.
The role of dynamin 1 in endocytosis has been clearly established. We measured transferrin uptake in striatal cells containing the C-HTT587-3144 fragment and found a lower endocytic rate than control values (FigEV5C); this effect was abolished by the expression of WT-dynamin 1. Oligomerisation of dynamin 1 is required for GTPase activity (Zhang et al, 2012); using a crosslinking approach, we found that dynamin 1 oligomerisation was reduced by the presence of the C-HTT587-3144 fragment (FigEV5D). To measure dynamin 1 activity selectively at the ER, we quantified the GTP-bound form of dynamin 1 at ER membranes purified from HEK293T cells expressing dynamin 1 and various HTT constructs. An anti-GTP immunoprecipitation (Sugiura et al, 2013) revealed that GTP-bound dynamin 1 was reduced by 55% (± 22%) in cells containing the C-HTT587-3144 fragment compared to those containing the FL-HTTQ100 or N586-HTTQ100 fragment (Fig7A). These experiments indicate that the C-ter fragment of HTT decreases dynamin 1 activity at both the plasma and ER membranes.
Figure 7.
C-terminal huntingtin impairs the activity of ER-localised dynamin 1 that subsequently induces ER dilation and death
- GTP-bound dynamin 1 levels were analysed in ER-enriched membranes from HEK293T cells expressing the indicated HTT constructs.
- Immunostaining of engineered artificially ER-targeted DNM1-WT (anti-HA) and ER network (calnexin and GFP-KDEL markers) expressed in striatal cells.
- Analysis of toxicity and vacuolation of striatal cells expressing C-HTT587-3144 fragment and ER-DNM1-WT.
- Survival curves upon cleavage of FL-HTT167/586TEV co-expressing ER-DNM1-WT in striatal cells.
- Time-lapse analysis by fluorescence live microscopy of striatal cells co-expressing an empty mCherry vector with ER-DNM1-K44A vector.
- Survival curves of striatal cells expressing empty mCherry vector and DNM1-K44A or ER-DNM1-K44A.
- Quantification of cell death induced by ER-targeted wild-type and mutant dynamin 1 in striatal cells
Data information: The graphs (mean ± SEM) display pooled data from three independent experiments. The total number of cells assessed are as follows: (D) FL-HTT167/586TEV+pcDNA: 192 or +SNIPer: 238; FL-HTT167/586-Q100 + ER-DNM1-WT: pcDNA: 272 or + SNIPer: 245; FL-HTT167/586TEV+pcDNA: 200 or + SNIPer: 199; FL-HTT167/586-Q23 + ER-DNM1-WT: pcDNA: 270 or + SNIPer: 239 and (F) DNM1-DN: 125, ER-DNM1-DN: 160. Statistics were done by unpaired t-test (C), log-rank test (D, F) or one-way ANOVA with unpaired t-test (G). ns: non-significant, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See also FigEV5.
We next tested whether the ER vacuolation associated with HTT proteolysis was due to a defect in the activity of the dynamin 1 localised at the ER. We generated constructs encoding WT or dominant-negative K44A dynamin 1 tagged with an HA sequence at its N-terminus and fused to the transmembrane domain of atlastin 1 at its C-terminus. These fusion proteins, termed ER-DNM1-WT and ER-DNM1-K44A, respectively, were artificially targeted to the ER, as evidenced both by cellular fractionation experiments (FigEV5E) and co-localisation with calnexin, KDEL-GFP and ER-dsRed markers in striatal cells (Figs7B and EV5F and G). We then co-expressed ER-DNM1 and various HTT constructs in striatal cells. Consistent with the findings for dynamin 1, a significant fraction of FL-HTTQ100, C-HTT587-3144 and N586-HTTQ100 interacted with ER-DNM1, whereas the shorter N167-HTTQ100 fragment did not (FigEV5H). These results indicate that both FL-HTT and the proteolytic products generated by cleavage at position 586 interact with dynamin 1 at the ER. However, sequential proteolysis generating small N-ter fragments results in only the C-ter HTT product remaining associated with the ER-localised dynamin 1.
We assessed the consequences of ER-targeted dynamin 1 expression on ER vacuolation and death associated with the C-HTT587-3144 fragment. The percentages of dead cells and vacuolated cells were significantly lower in the presence than absence of ER-DNM1-WT (Fig7C). We next co-expressed FL-HTT167/586TEV-Q100 and ER-DNM1-WT constructs in the presence of SNIPer-TEV system and treated the cells with 20 nM rapamycin. The toxicity induced by the double proteolysis of HTT was significantly reduced by the expression of the ER-DNM1-WT construct (Fig7D). Thus, re-establishing dynamin 1 activity at the ER membranes was sufficient to prevent the cell death caused by double cleavage of HTT.
These findings suggest that specifically targeting inactive dynamin 1 to the ER should be sufficient to cause vacuolation and death. Indeed, we found that targeting the DNM1-K44A mutant to the ER caused ER dilation and vacuolation in about 11% of the transfected cells (n = 160 cells), whereas no vacuolated cells were observed in cells transfected with the DNM1-K44A mutant not targeted to the ER (n = 125 cells) (Figs7E and EV5G). Similarly, ER-targeted inactive dynamin 1, but not its cytoplasmic form, caused significant cell death (Fig7F). Also, the inactive ER-DNM1-K44A mutant but not the ER-DNM1-WT constructs were toxic, showing that this effect was specifically due to inactivation of dynamin 1 at ER membranes (Fig7G).
Overall, our results indicate that sequential N-terminal proteolysis of HTT generates a C-terminal fragment that inactivates dynamin 1 at plasma and ER membranes. In addition to inhibit endocytosis, HTT C-ter fragment inhibits dynamin 1 at ER membranes that leads to abnormal ER vacuolation and death (Fig8).
Figure 8.
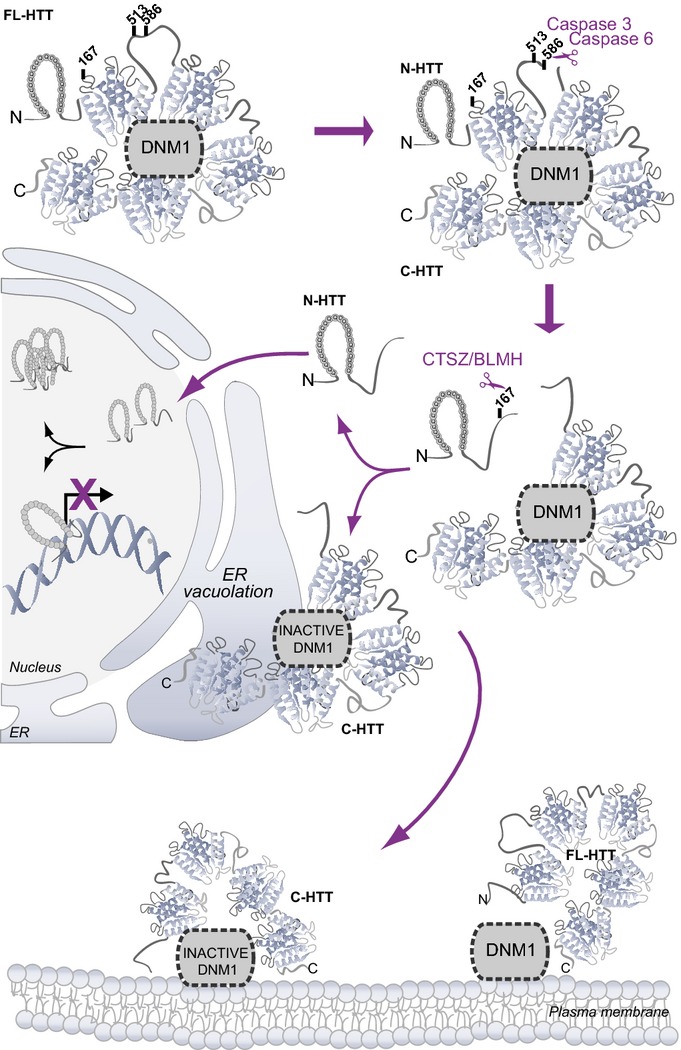
Canonical and non-canonical pathways induced after huntingtin proteolysis
Cartoon summarising the sequential proteolysis of full-length HTT (FL-HTT) leading to the generation of N-terminal-containing polyQ fragments (N-HTT) that translocate into the nucleus and C-terminal fragments (C-HTT) that localise at the ER and inactivate dynamin 1 (DNM1) leading to ER dilation, ER stress and toxicity. Toxicity may also involve dynamin 1 inhibition on endocytosis, at the plasma membrane.
Discussion
Studies that addressed the consequences of HTT proteolysis have either compared the relative toxicities of the various N-ter polyQ fragments generated by proteolysis (Hackam et al, 1998) or expressed point mutants for these sites and analysed the consequences of the absence of cleavage on polyQ-HTT-induced toxicity (Wellington et al, 2000; Gafni et al, 2004; Graham et al, 2006; Miller et al, 2010). Some studies have analysed the consequences of protease activation or inhibition on polyQ-mediated toxicity, although this approach has the disadvantage of inducing/inhibiting the cleavage of many substrates in addition to HTT. Moreover, the exact identity of the proteases that cleave major proteolytic sites on HTT remains to be established (Lunkes et al, 2002; Gafni et al, 2012). Here, we used mutant HTT variants in which TEV cleavage sites have been introduced at various known proteolytic sites to investigate the molecular and cellular consequences of selective HTT cleavage at the targeted sites in a controlled manner. Such strategy has been successfully used to investigate proteolysis by, and thus the role of, executioner caspases 3 and 7 (Gray et al, 2010). We show this approach to be particularly useful for the study of proteolysis in HD and possibly other neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease in which specific proteolytic events occur.
When assessing various proteolytic sites in HTT, we found that the site at position 167 was not as efficiently cleaved as the sites at positions 586 or 513. These differences may be due to differences in accessibility: positions 586 and 513 are in disordered and exposed regions of the protein, whereas position 167 is located in the first HEAT repeat of HTT which is composed of antiparallel α-helices and therefore may not be accessible to the TEV protease. The presence of a polyQ stretch in HTT favoured the appearance of the N-167 fragment, suggesting that polyQ expansion—in agreement with the polyQ-HTT conformation being different to the wild-type HTT conformation (Trottier et al, 1995)—may render the proteolytic site at position 167 more accessible. Cleavages at positions 586 or 513 also increased the accessibility of the site at position 167, consistent with a proteolytic cascade hypothesis. In addition, this approach allowed us to demonstrate that specific proteolytic events lead to the loss of intramolecular interaction between N-ter and C-ter fragments. Although the TEV strategy provides new approach to study HTT proteolysis and its consequences, further work will be necessary to investigate such cleavages on endogenous HTT. Nevertheless, by examining human post-mortem brain samples, we found that in disease, differential proteolysis of mutant HTT generating small N-ter fragments may release the C-ter HTT fragment from intramolecular interaction.
To our knowledge, few studies have addressed the potential role and/or function of HTT C-ter fragments. One used a Drosophila HTT fragment that is more C-terminal than the fragment (positions 586–3144) used in our study (Takano & Gusella, 2002). As in our study, the authors found that this fragment was cytoplasmic. Cell death was not assessed, but it was found that this fragment could act as a regulator of the entry of NF-κB/dorsal into the nucleus. A more recent study investigated the potential function of the C-ter part of HTT and discovered that this region has similarity to yeast Atg11 and as such could play a role as a scaffold for selective autophagy. Interestingly, the described C-ter fragments used in this study were reported to be toxic in primary neurons (Ochaba et al, 2014). Although in this and our study some of the toxic effect of the C-ter fragment might be due to overexpression artefacts, we found that the selective proteolysis of full-length mutant polyQ-HTT dramatically increases its toxicity. Even, we found that when wild-type full-length HTT is proteolysed, this turns the non-toxic wild-type HTT into a highly toxic protein. This further supports our findings that C-ter fragments when released from full-length HTT might have some toxicity.
Here we showed that C-ter HTT is toxic in the cytoplasmic compartment by inactivating dynamin 1 at ER membranes leading to ER dilation, ER stress and cell death. We also observed that the C-ter fragment decreases endocytosis as shown by the reduction in transferrin uptake in cells expressing this fragment. The function of dynamin 1 is associated with endocytosis, and to our knowledge, no ER abnormalities in mice deleted for dynamin genes have been reported (Ferguson & De Camilli, 2012). In addition, dynamin inhibition either by dynasore or by the (non-targeted) expression of the dominant-negative dynamin 1 K44A shows no ER-derived phenomena. Nevertheless, using EM, high-resolution detection techniques and biochemical approaches, we reveal that a fraction of dynamin 1 interacts and co-localises with HTT at ER membranes. We also found that selective inactivation of dynamin 1 at the ER promotes ER dilation. Importantly, this functional defect was only observed when dominant-negative dynamin 1 was targeted to the ER or in the presence of the HTT C-ter fragment. Therefore, although we cannot exclude that part of C-ter HTT fragment-induced toxicity could be mediated by the inhibition of endocytosis, the inactivation of dynamin 1 on ER membranes may occur specifically in response to abnormal proteolysis of mutant HTT that is only observed during HD pathogenesis. In support, mutant HTT was shown to disrupt ER morphology leading to the accumulation of clear cytoplasmic vacuoles in striatal immortalised cell lines (Trettel et al, 2000), in the brain of knock-in mice (Fig4), in lymphoblasts from patients with HD (Nagata et al, 2004) and in iPSC from patients with HD (Juopperi et al, 2012). So it is plausible that a HTT–dynamin 1 complex regulates ER shaping/dynamics and that this complex, if altered in disease, could lead to the formation of cytoplasmic vacuoles. Our findings justify further studies to elucidate the role of this complex at the ER.
Other HTT interactors that bind through the C-ter part of HTT have been identified, but they are unlikely to be linked to the described mechanism since some of them are either co-repressor of transcription or regulate endosomal trafficking (Kegel et al, 2002; Pal et al, 2006). Recently, bioinformatic and functional analyses revealed that the C-ter fragment shares structural similarity to yeast Atg11. Atg11 is a receptor for the yeast dynamin 1 and promotes the fission of mitochondria and membranes of the ER (Cebollero et al, 2012; Mao et al, 2013). This further supports the possibility of a role for HTT in the regulation of ER membrane dynamics.
Huntingtin C-ter region may thus have several functions that have been underestimated. As stated previously, yeast two-hybrid screening experiments using HTT C-ter fragments as baits failed to identify any proteins interacting with HTT (Faber et al, 1998; Kaltenbach et al, 2007). Even by using a large region including HEAT repeats, we only found a small number of proteins interacting with the C-ter of HTT. Coherent with the intramolecular interaction observed (Li et al, 2006; Palidwor et al, 2009)(this study), HTT may adopt a closed conformation establishing only limited interactions between the C-ter region and other proteins. Nevertheless, our findings and the study by Ochaba and colleagues (Ochaba et al, 2014) provide evidence that the C-ter region of HTT has an important role in regulating HTT function and toxicity in health and disease.
Our study reveals that HTT proteolysis, in addition to generate small N-ter fragments that are toxic in the nucleus, releases non-polyQ C-ter fragments that may also be relevant to HD pathogenesis. Determining the physiological relevance of such fragments in disease may lead to new therapeutic strategies.
Materials and Methods
Mice
Mice are HdhQ111 HD knock-in mouse model (Wheeler et al, 1999). Experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the recommendations of the European Community (86/609/EEC) and the French National Committee (2010/63) for care and use of laboratory animals. See Appendix Supplementary Materials and Methods for further details.
Flies
FL-HTT-Q100 transgenic flies were generated by Bestgene, Inc. FL-HTT-Q200 flies were generated through subcloning of FL-HTT constructs into P[acman] and subsequent site-directed insertion using the PhiC31 integrase. Survival, climbing assay and brain structure analyses were performed on various HTT constructs expressing flies. Fly strains, crosses and analyses are described in Appendix Supplementary Materials and Methods.
Constructs
The FL-HTT-TEV constructs encode the human HTT protein containing a TEV recognition cleavage sites (TEVrcs) at specific positions. Amino acids corresponding to the endogenous cleavage sites of caspase-6 (D586), caspase-3 (D510SVDL514) and cathepsin Z/bleomycin hydrolase (R167) were replaced by the recognition cleavage site (rcs) of the TEV protease: ENLYFQS. ER-DNM1-WT and ER-DNM1-K44A constructs encode for dynamin 1-WT (DNM1-WT) or mutant K44A (DNM1-K44A), respectively, targeted to endoplasmic reticulum membranes by fusion to the endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane domain of atlastin 1. Further details on the generation of constructs are provided in Appendix Supplementary Materials and Methods.
Proteolysis of huntingtin-TEV constructs
For in vitro cleavage of HTT by recombinant TEV protease, cells were transfected with the FL-HTT-TEV and extracts were incubated with recombinant TEV protease. For intracellular HTT cleavage, cells were co-transfected with the FL-HTT-TEV constructs and the SNIPer-TEV plasmids or pcDNA for control conditions and treated with rapamycin.
Videomicroscopy, immunoelectron and super-resolution microscopies
For videomicroscopy, striatal cells were electroporated with fluorescent-tagged constructs and subsequently analysed by time-lapse multi-position videomicroscopy following individual transfected cells up to 24 h. Dynamics of individual cells were analysed to establish the kinetics of vacuolation and death upon various conditions and specific markers. For electron and light microscopy, cells or tissues were fixed and subjected to Epon embedding prior to sectioning. For immunoelectron microscopy, cells were fixed and stained with immunogold particles and uranyl acetate. For super-resolution microscopy, we used direct STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (dSTORM) on cells to analyse the localisation of dynamin 1 with the ER marker calnexin. Further details are provided in Appendix Supplementary Materials and Methods.
Endoplasmic reticulum isolation and dynamin 1 activity
ER membranes were purified through successive subcellular fractionation and sucrose gradient fractionation. Dynamin 1 activity was assessed by transferrin uptake measured on cell-sorted cells, measurement of the GTP binding of dynamin 1 on GTP-coupled beads and of the membrane-associated dynamin 1 through cross-linking of dynamin 1 using a non-cleavable and membrane permeable cross-linker DSS. Further details are provided in Appendix Supplementary Materials and Methods.
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Echard and members of the Saudou and Humbert laboratories for helpful comments and/or reading of the manuscript; N. Déglon, the IBISA Cell and Tissue Imaging Facility (F.P. Cordelières, D. Zaharia and M.N. Soler), the Cell Sorting facility (C. Lasgi), J. Souphron, C. Janke and C. Benstaali for help with experiments; and P. Chavrier, B. Goud, J.T. Littleton, J.R. Martin, R. Schuh, J.A. Wells for reagents and/or discussions. Human samples were provided by the Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center, which is supported in part by PHS grant number MH/NS 31862. This work was supported by grants from Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR-08-MNP-039, ANR-12-BLAN-SVSE2-HURIT, F.S.), DIM-NeRF Ile de France, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM, équipe labellisée, F.S.), CNRS, INSERM and the Institut Curie (F.S.) and NIH/NINDS (J.Bo.). We thank Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer for fellowship support (M.-T.E.-D.).
Author contributions
M-TE-D and EH conceived, designed and carried out experiments, analysed the data and wrote a draft of the manuscript. JB performed Golgi reassembly assays and the post-mortem brain analyses. RP did the first toxicity experiments with C-ter fragments and designed the Y2H. GP generated most of the constructs used in the study and helped throughout the study, IA-R generated and analysed the FL-HTT-Q23 and Q200 flies under JB supervision, NB, CM and SL-F developed and analysed dynamin 1 localisation by dSTORM, and SS and GPi performed the electronic microscopy. FS and SH conceived the project with M-TE-D, and EH helped interpret the data and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Expanded View Figures PDF
Appendix
Movie EV1
Movie EV2
Movie EV3
Movie Legends
Review Process File
References
- Atwal RS, Xia J, Pinchev D, Taylor J, Epand RM, Truant R. Huntingtin has a membrane association signal that can modulate huntingtin aggregation, nuclear entry and toxicity. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:2600–2615. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrell-Pages M, Zala D, Humbert S, Saudou F. Huntington’s disease: from huntingtin function and dysfunction to therapeutic strategies. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63:2642–2660. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6242-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo E, Zuccato C, Tartari M. Normal huntingtin function: an alternative approach to Huntington’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:919–930. doi: 10.1038/nrn1806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caviston JP, Ross JL, Antony SM, Tokito M, Holzbaur EL. Huntingtin facilitates dynein/dynactin-mediated vesicle transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:10045–10050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610628104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebollero E, Reggiori F, Kraft C. Reticulophagy and ribophagy: regulated degradation of protein production factories. Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:182834. doi: 10.1155/2012/182834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S, Novick P, Ferro-Novick S. ER structure and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013;25:428–433. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber PW, Barnes GT, Srinidhi J, Chen J, Gusella JF, MacDonald ME. Huntingtin interacts with a family of WW domain proteins. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1463–1474. doi: 10.1093/hmg/7.9.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson SM, De Camilli P. Dynamin, a membrane-remodelling GTPase. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:75–88. doi: 10.1038/nrm3266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafni J, Ellerby LM. Calpain activation in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci. 2002;22:4842–4849. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-12-04842.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafni J, Hermel E, Young JE, Wellington CL, Hayden MR, Ellerby LM. Inhibition of calpain cleavage of huntingtin reduces toxicity: accumulation of calpain/caspase fragments in the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:20211–20220. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401267200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafni J, Papanikolaou T, Degiacomo F, Holcomb J, Chen S, Menalled L, Kudwa A, Fitzpatrick J, Miller S, Ramboz S, Tuunanen PI, Lehtimaki KK, Yang XW, Park L, Kwak S, Howland D, Park H, Ellerby LM. Caspase-6 activity in a BACHD mouse modulates steady-state levels of mutant huntingtin protein but is not necessary for production of a 586 amino acid proteolytic fragment. J Neurosci. 2012;32:7454–7465. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6379-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin JD, Colombo K, Molina-Calavita M, Keryer G, Zala D, Charrin BC, Dietrich P, Volvert ML, Guillemot F, Dragatsis I, Bellaiche Y, Saudou F, Nguyen L, Humbert S. Huntingtin is required for mitotic spindle orientation and mammalian neurogenesis. Neuron. 2010;67:392–406. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg YP, Nicholson DW, Rasper DM, Kalchman MA, Koide HB, Graham RK, Bromm M, Kazemi-Esfarjani P, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Hayden MR. Cleavage of huntingtin by apopain, a proapoptotic cysteine protease, is modulated by the polyglutamine tract. Nat Genet. 1996;13:442–449. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham RK, Deng Y, Slow EJ, Haigh B, Bissada N, Lu G, Pearson J, Shehadeh J, Bertram L, Murphy Z, Warby SC, Doty CN, Roy S, Wellington CL, Leavitt BR, Raymond LA, Nicholson DW, Hayden MR. Cleavage at the caspase-6 site is required for neuronal dysfunction and degeneration due to mutant huntingtin. Cell. 2006;125:1179–1191. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray DC, Mahrus S, Wells JA. Activation of specific apoptotic caspases with an engineered small-molecule-activated protease. Cell. 2010;142:637–646. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackam AS, Singaraja R, Wellington CL, Metzler M, McCutcheon K, Zhang T, Kalchman M, Hayden MR. The influence of huntingtin protein size on nuclear localisation and cellular toxicity. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:1097–1105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder B, Schomburg A, Pflanz R, Kustner K, Gerlach N, Schuh R. TEV protease-mediated cleavage in Drosophila as a tool to analyse protein functions in living organisms. Biotechniques. 2008;44:765–772. doi: 10.2144/000112884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermel E, Gafni J, Propp SS, Leavitt BR, Wellington CL, Young JE, Hackam AS, Logvinova AV, Peel AL, Chen SF, Hook V, Singaraja R, Krajewski S, Goldsmith PC, Ellerby HM, Hayden MR, Bredesen DE, Ellerby LM. Specific caspase interactions and amplification are involved in selective neuronal vulnerability in Huntington’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:424–438. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J, Shibata Y, Zhu PP, Voss C, Rismanchi N, Prinz WA, Rapoport TA, Blackstone C. A class of dynamin-like GTPases involved in the generation of the tubular ER network. Cell. 2009;138:549–561. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imarisio S, Carmichael J, Korolchuk V, Chen CW, Saiki S, Rose C, Krishna G, Davies JE, Ttofi E, Underwood BR, Rubinsztein DC. Huntington’s disease: from pathology and genetics to potential therapies. Biochem J. 2008;412:191–209. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juopperi TA, Kim WR, Chiang CH, Yu H, Margolis RL, Ross CA, Ming GL, Song H. Astrocytes generated from patient induced pluripotent stem cells recapitulate features of Huntington’s disease patient cells. Mol Brain. 2012;5:17. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-5-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenbach LS, Romero E, Becklin RR, Chettier R, Bell R, Phansalkar A, Strand A, Torcassi C, Savage J, Hurlburt A, Cha GH, Ukani L, Chepanoske CL, Zhen Y, Sahasrabudhe S, Olson J, Kurschner C, Ellerby LM, Peltier JM, Botas J, et al. Huntingtin interacting proteins are genetic modifiers of neurodegeneration. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e82. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kegel KB, Meloni AR, Yi Y, Kim YJ, Doyle E, Cuiffo BG, Sapp E, Wang Y, Qin ZH, Chen JD, Nevins JR, Aronin N, DiFiglia M. Huntingtin is present in the nucleus, interacts with the transcriptional corepressor C-terminal binding protein, and represses transcription. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:7466–7476. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103946200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim YJ, Sapp E, Cuiffo BG, Sobin L, Yoder J, Kegel KB, Qin ZH, Detloff P, Aronin N, DiFiglia M. Lysosomal proteases are involved in generation of N-terminal huntingtin fragments. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;22:346–356. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim YJ, Yi Y, Sapp E, Wang Y, Cuiffo B, Kegel KB, Qin ZH, Aronin N, DiFiglia M. Caspase 3-cleaved N-terminal fragments of wild-type and mutant huntingtin are present in normal and Huntington’s disease brains, associate with membranes, and undergo calpain-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:12784–12789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.221451398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landles C, Bates GP. Huntingtin and the molecular pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. Fourth in molecular medicine review series. EMBO Rep. 2004;5:958–963. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landles C, Sathasivam K, Weiss A, Woodman B, Moffitt H, Finkbeiner S, Sun B, Gafni J, Ellerby LM, Trottier Y, Richards WG, Osmand A, Paganetti P, Bates GP. Proteolysis of mutant huntingtin produces an exon 1 fragment that accumulates as an aggregated protein in neuronal nuclei in Huntington disease. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:8808–8823. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.075028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee WC, Yoshihara M, Littleton JT. Cytoplasmic aggregates trap polyglutamine-containing proteins and block axonal transport in a Drosophila model of Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:3224–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400243101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W, Serpell LC, Carter WJ, Rubinsztein DC, Huntington JA. Expression and characterization of full-length human huntingtin, an elongated HEAT repeat protein. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:15916–15922. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511007200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li XJ, Li S. Proteasomal dysfunction in aging and Huntington disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;43:4–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.11.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunkes A, Lindenberg KS, Ben-Haiem L, Weber C, Devys D, Landwehrmeyer GB, Mandel JL, Trottier Y. Proteases acting on mutant huntingtin generate cleaved products that differentially build up cytoplasmic and nuclear inclusions. Mol Cell. 2002;10:259–269. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00602-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarini L, Sathasivam K, Seller M, Cozens B, Harper A, Hetherington C, Lawton M, Trottier Y, Lehrach H, Davies SW, Bates GP. Exon 1 of the HD gene with an expanded CAG repeat is sufficient to cause a progressive neurological phenotype in transgenic mice. Cell. 1996;87:493–506. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao K, Wang K, Liu X, Klionsky DJ. The scaffold protein Atg11 recruits fission machinery to drive selective mitochondria degradation by autophagy. Dev Cell. 2013;26:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mende-Mueller LM, Toneff T, Hwang SR, Chesselet MF, Hook VY. Tissue-specific proteolysis of Huntingtin (htt) in human brain: evidence of enhanced levels of N- and C-terminal htt fragments in Huntington’s disease striatum. J Neurosci. 2001;21:1830–1837. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-01830.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller JP, Holcomb J, Al-Ramahi I, de Haro M, Gafni J, Zhang N, Kim E, Sanhueza M, Torcassi C, Kwak S, Botas J, Hughes RE, Ellerby LM. Matrix metalloproteinases are modifiers of huntingtin proteolysis and toxicity in Huntington’s disease. Neuron. 2010;67:199–212. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreira Sousa C, McGuire JR, Thion MS, Gentien D, de la Grange P, Tezenas du Montcel S, Vincent-Salomon A, Durr A, Humbert S. The Huntington disease protein accelerates breast tumour development and metastasis through ErbB2/HER2 signalling. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5:309–325. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata E, Sawa A, Ross CA, Snyder SH. Autophagosome-like vacuole formation in Huntington’s disease lymphoblasts. NeuroReport. 2004;15:1325–1328. doi: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000127073.66692.8f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochaba J, Lukacsovich T, Csikos G, Zheng S, Margulis J, Salazar L, Mao K, Lau AL, Yeung SY, Humbert S, Saudou F, Klionsky DJ, Finkbeiner S, Zeitlin SO, Marsh JL, Housman DE, Thompson LM, Steffan JS. Potential function for the Huntingtin protein as a scaffold for selective autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:16889–16894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420103111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orso G, Pendin D, Liu S, Tosetto J, Moss TJ, Faust JE, Micaroni M, Egorova A, Martinuzzi A, McNew JA, Daga A. Homotypic fusion of ER membranes requires the dynamin-like GTPase atlastin. Nature. 2009;460:978–983. doi: 10.1038/nature08280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal A, Severin F, Lommer B, Shevchenko A, Zerial M. Huntingtin-HAP40 complex is a novel Rab5 effector that regulates early endosome motility and is up-regulated in Huntington’s disease. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:605–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200509091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palidwor GA, Shcherbinin S, Huska MR, Rasko T, Stelzl U, Arumughan A, Foulle R, Porras P, Sanchez-Pulido L, Wanker EE, Andrade-Navarro MA. Detection of alpha-rod protein repeats using a neural network and application to huntingtin. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo R, Molina-Calavita M, Poizat G, Keryer G, Humbert S, Saudou F. pARIS-htt: an optimised expression platform to study huntingtin reveals functional domains required for vesicular trafficking. Mol Brain. 2010;3:17. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-3-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli A, Althoff F, Oliveira RA, Heidmann S, Schuldiner O, Lehner CF, Dickson BJ, Nasmyth K. Cell-type-specific TEV protease cleavage reveals cohesin functions in Drosophila neurons. Dev Cell. 2008;14:239–251. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratovitski T, Chighladze E, Waldron E, Hirschhorn RR, Ross CA. Cysteine proteases bleomycin hydrolase and cathepsin Z mediate N-terminal proteolysis and toxicity of mutant huntingtin. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:12578–12589. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.185348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratovitski T, Gucek M, Jiang H, Chighladze E, Waldron E, D’Ambola J, Hou Z, Liang Y, Poirier MA, Hirschhorn RR, Graham R, Hayden MR, Cole RN, Ross CA. Mutant huntingtin N-terminal fragments of specific size mediate aggregation and toxicity in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:10855–10867. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804813200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero E, Cha GH, Verstreken P, Ly CV, Hughes RE, Bellen HJ, Botas J. Suppression of neurodegeneration and increased neurotransmission caused by expanded full-length huntingtin accumulating in the cytoplasm. Neuron. 2008;57:27–40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathasivam K, Neueder A, Gipson TA, Landles C, Benjamin AC, Bondulich MK, Smith DL, Faull RL, Roos RA, Howland D, Detloff PJ, Housman DE, Bates GP. Aberrant splicing of HTT generates the pathogenic exon 1 protein in Huntington disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:2366–2370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221891110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudou F, Finkbeiner S, Devys D, Greenberg ME. Huntingtin acts in the nucleus to induce apoptosis but death does not correlate with the formation of intranuclear inclusions. Cell. 1998;95:55–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81782-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugars KL, Rubinsztein DC. Transcriptional abnormalities in Huntington’s disease. Trends Genet. 2003;19:233–238. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(03)00074-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura A, Nagashima S, Tokuyama T, Amo T, Matsuki Y, Ishido S, Kudo Y, McBride HM, Fukuda T, Matsushita N, Inatome R, Yanagi S. MITOL regulates endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts via Mitofusin 2. Mol Cell. 2013;51:20–34. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano H, Gusella JF. The predominantly HEAT-like motif structure of huntingtin and its association and coincident nuclear entry with dorsal, an NF-kB/Rel/dorsal family transcription factor. BMC Neurosci. 2002;3:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-3-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebbenkamp AT, Crosby KW, Siemienski ZB, Brown HH, Golde TE, Borchelt DR. Analysis of Proteolytic Processes and Enzymatic Activities in the Generation of Huntingtin N-Terminal Fragments in an HEK293 Cell Model. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e50750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trettel F, Rigamonti D, Hilditch-Maguire P, Wheeler VC, Sharp AH, Persichetti F, Cattaneo E, MacDonald ME. Dominant phenotypes produced by the HD mutation in STHdh(Q111) striatal cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2799–2809. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.19.2799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trottier Y, Lutz Y, Stevanin G, Imbert G, Devys D, Cancel G, Saudou F, Weber C, David G, Tora L, Agid Y, Brice A, Mandel JL. Polyglutamine expansion as a pathological epitope in Huntington’s disease and four dominant cerebellar ataxias. Nature. 1995;378:403–406. doi: 10.1038/378403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang CE, Tydlacka S, Orr AL, Yang SH, Graham RK, Hayden MR, Li S, Chan AW, Li XJ. Accumulation of N-terminal mutant huntingtin in mouse and monkey models implicated as a pathogenic mechanism in Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:2738–2751. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellington CL, Ellerby LM, Gutekunst CA, Rogers D, Warby S, Graham RK, Loubser O, van Raamsdonk J, Singaraja R, Yang YZ, Gafni J, Bredesen D, Hersch SM, Leavitt BR, Roy S, Nicholson DW, Hayden MR. Caspase cleavage of mutant huntingtin precedes neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci. 2002;22:7862–7872. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-07862.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellington CL, Singaraja R, Ellerby L, Savill J, Roy S, Leavitt B, Cattaneo E, Hackam A, Sharp A, Thornberry N, Nicholson DW, Bredesen DE, Hayden MR. Inhibiting caspase cleavage of huntingtin reduces toxicity and aggregate formation in neuronal and nonneuronal cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:19831–19838. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001475200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler VC, Auerbach W, White JK, Srinidhi J, Auerbach A, Ryan A, Duyao MP, Vrbanac V, Weaver M, Gusella JF, Joyner AL, MacDonald ME. Length-dependent gametic CAG repeat instability in the Huntington’s disease knock-in mouse. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:115–122. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zala D, Hinckelmann MV, Saudou F. Huntingtin’s Function in Axonal Transport Is Conserved in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e60162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang YQ, Henderson MX, Colangelo CM, Ginsberg SD, Bruce C, Wu T, Chandra SS. Identification of CSPalpha clients reveals a role in dynamin 1 regulation. Neuron. 2012;74:136–150. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Expanded View Figures PDF
Appendix
Movie EV1
Movie EV2
Movie EV3
Movie Legends
Review Process File