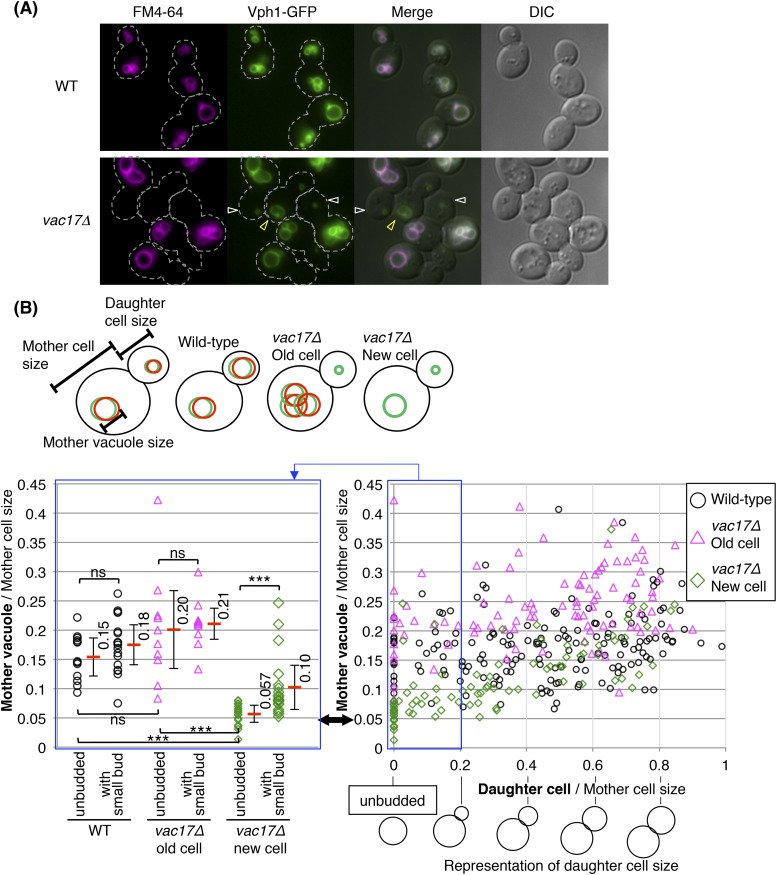
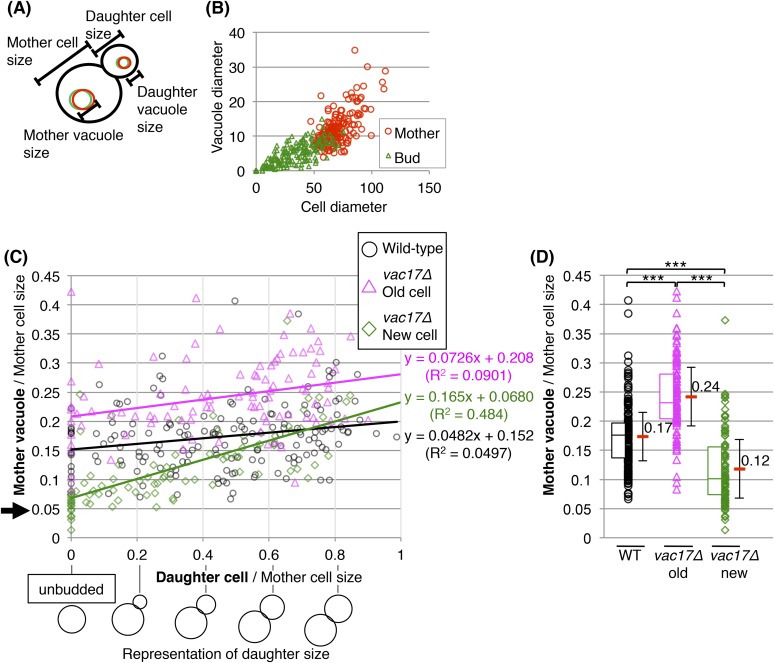
Figure 1. Yeast require vacuoles of a specific size prior to formation of a bud.
(A) Wild-type and vac17Δcells which express Vph1-GFP from its endogenous locus, were pulse labeled with the vacuole specific dye FM4-64. Wild-type cells have both FM4-64 and Vph1-GFP signals in both mother and daughter cells. vac17Δ cells have both Vph1-GFP and FM4-64 on the vacuole in old mother cells, however the daughter cells solely have a Vph1-GFP labeled vacuole. White arrowheads; new vacuoles in daughter cells. Yellow arrowheads; new vacuoles in new mother cells. Dashed line; outline of cells. (B) (Left panel) A new cell does not form a bud until its vacuole reaches a specific size. Graph indicates the vacuole diameter of wild-type, vac17Δ old cell and vac17Δ new cells with no bud and mother cells with a small bud (less than 20% of diameter of the mother cell). Cell/vacuole diameter was measured by ImageJ. Each cell/vacuole diameter was normalized to its mother cell diameter. Black arrow; minimum size of mother vacuoles in cells with a bud. Average in each category (red bar). Error bar; standard deviation (SD). Not a significant difference; ns, p-value > 0.10. A statistically significant difference; *** (p-value < 1 × 10−3). (Right panel) The vacuoles of the new mother cells of vac17Δ grow faster than vacuoles in either a wild-type or vac17Δ old mother cell. Scatter plots of bud sizes and mother vacuole sizes.