Abstract
In recent years, a variety of low molecular weight antibiotics have been isolated from diverse animal species. These agents, which include peptides, lipids, and alkaloids, exhibit antibiotic activity against environmental microbes and are thought to play a role in innate immunity. We report here the discovery of a broad-spectrum steroidal antibiotic isolated from tissues of the dogfish shark Squalus acanthias. This water-soluble antibiotic, which we have named squalamine, exhibits potent bactericidal activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In addition, squalamine is fungicidal and induces osmotic lysis of protozoa. The chemical structure of the antibiotic 3 beta-N-1-(N-[3-(4-aminobutyl)]- 1,3-diaminopropane)-7 alpha,24 zeta-dihydroxy-5 alpha-cholestane 24-sulfate has been determined by fast atom bombardment mass spectroscopy and NMR. Squalamine is a cationic steroid characterized by a condensation of an anionic bile salt intermediate with spermidine. The discovery of squalamine in the shark implicates a steroid as a potential host-defense agent in vertebrates and provides insights into the chemical design of a family of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Full text
PDF
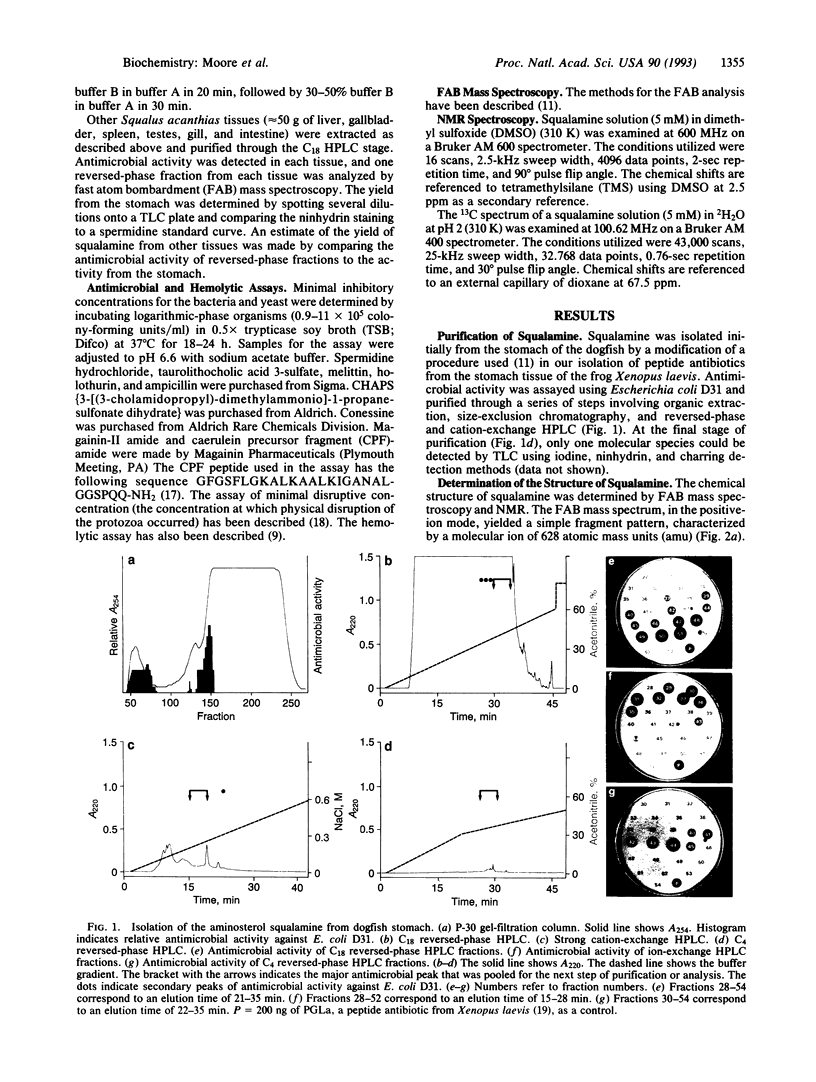
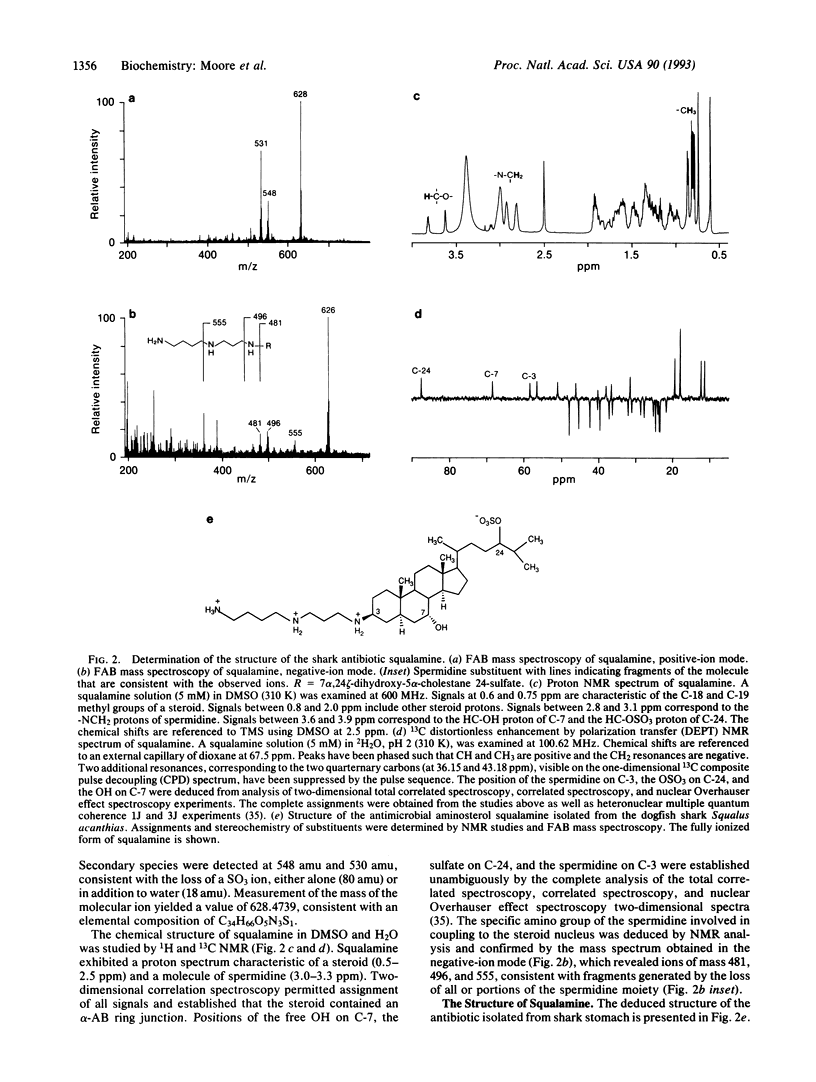
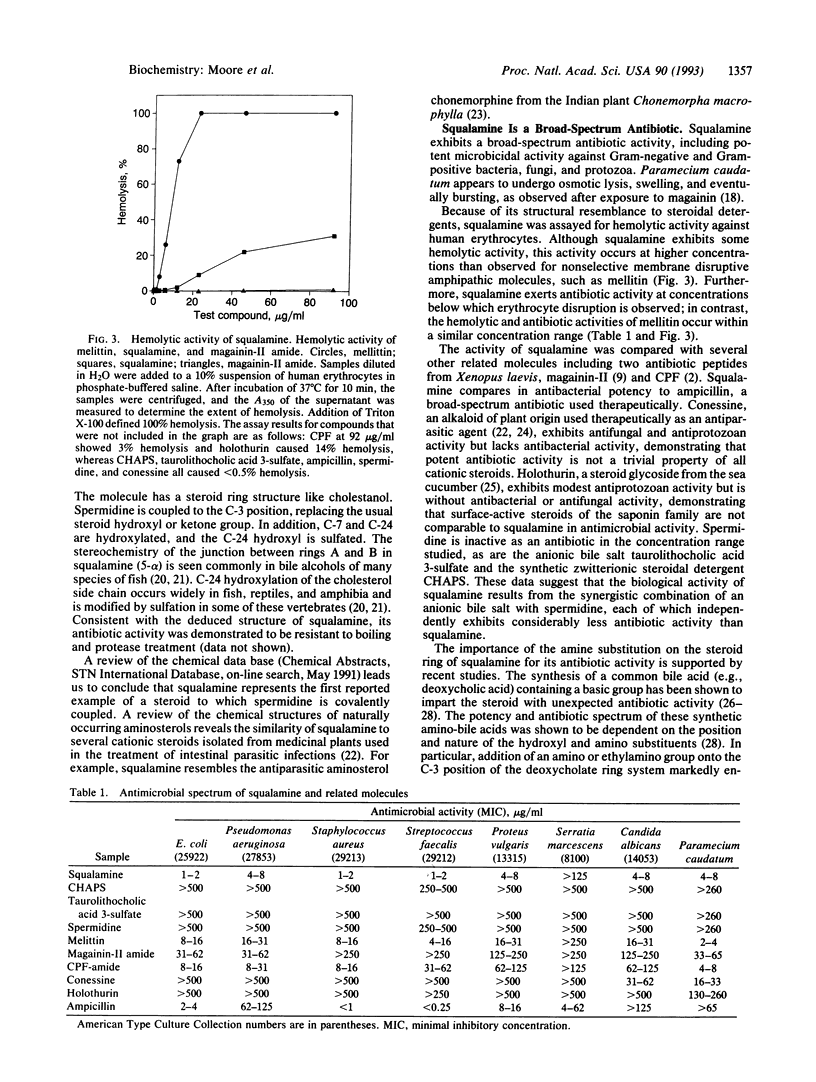

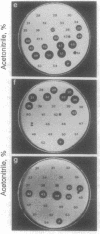
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agerberth B., Lee J. Y., Bergman T., Carlquist M., Boman H. G., Mutt V., Jörnvall H. Amino acid sequence of PR-39. Isolation from pig intestine of a new member of the family of proline-arginine-rich antibacterial peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):849–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreu D., Aschauer H., Kreil G., Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase synthesis of PYLa and isolation of its natural counterpart, PGLa [PYLa-(4-24)] from skin secretion of Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 18;149(3):531–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwer M. S., O'Maille E. R., Hofmann A. F., DiPietro R. A., Michelotti E. Influence of side-chain charge on hepatic transport of bile acids and bile acid analogues. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):G479–G488. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.4.G479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini A. M., Mencini E., Quaglio M. P., Guarneri M., Fini A. Antimicrobial activity of basic cholane derivatives. Part IX. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 1990 Apr;323(4):201–205. doi: 10.1002/ardp.19903230404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevins C. L., Zasloff M. Peptides from frog skin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:395–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibel D. J., Miller S. J., Brown B. E., Pandey B. B., Elias P. M., Shinefield H. R., Aly R. Antimicrobial activity of stratum corneum lipids from normal and essential fatty acid-deficient mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Apr;92(4):632–638. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12712202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides: key components needed in immunity. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90154-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissette J. L., Cabacungan E. A., Pieringer R. A. Studies on the antibacterial activity of dodecylglycerol. Its limited metabolism and inhibition of glycerolipid and lipoteichoic acid biosynthesis in Streptococcus mutans BHT. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6338–6345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Kabara J. J. Antimicrobial action of esters of polyhydric alcohols. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Nov;4(5):501–506. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.5.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Myers C. W., Whittaker N. Further classification of skin alkaloids from neotropical poison frogs (Dendrobatidae), with a general survey of toxic/noxious substances in the amphibia. Toxicon. 1987;25(10):1023–1095. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(87)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond G., Zasloff M., Eck H., Brasseur M., Maloy W. L., Bevins C. L. Tracheal antimicrobial peptide, a cysteine-rich peptide from mammalian tracheal mucosa: peptide isolation and cloning of a cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslewood G. A. Bile salt evolution. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):535–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Bevins C. L. Paneth cells of the human small intestine express an antimicrobial peptide gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23216–23225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabara J. J., Vrable R. Antimicrobial lipids: natural and synthetic fatty acids and monoglycerides. Lipids. 1977 Sep;12(9):753–759. doi: 10.1007/BF02570908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Boman A., Sun C. X., Andersson M., Jörnvall H., Mutt V., Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides from pig intestine: isolation of a mammalian cecropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9159–9162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Defensins: endogenous antibiotic peptides of animal cells. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. S., Bevins C. L., Brasseur M. M., Tomassini N., Turner K., Eck H., Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides in the stomach of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19851–19857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Greco R. M., James M., Frederick D., Naftilan J., Fallon J. T. Developmental regulation of cryptdin, a corticostatin/defensin precursor mRNA in mouse small intestinal crypt epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1687–1695. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preusser H. J., Habermehl G., Sablofski M., Schmall-Haury D. Antimicrobial activity of alkaloids from amphibian venoms and effects on the ultrastructure of yeast cells. Toxicon. 1975 Aug;13(4):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(75)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter K., Egger R., Kreil G. Sequence of preprocaerulein cDNAs cloned from skin of Xenopus laevis. A small family of precursors containing one, three, or four copies of the final product. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3676–3680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D. S., Choppin P. W. Biochemical studies on cell fusion. I. Lipid composition of fusion-resistant cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1578–1590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Djerassi C. Phospholipid studies of marine organisms: 14. Ether lipids of the sponge Tethya aurantia. Lipids. 1987 Apr;22(4):236–240. doi: 10.1007/BF02533985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Antibiotic peptides as mediators of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(1):3–7. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90115-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Martin B., Chen H. C. Antimicrobial activity of synthetic magainin peptides and several analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):910–913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]