Abstract
Over the last few years, we have identified an orally active, novel neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing molecule, the flavonoid fisetin. Fisetin not only has direct antioxidant activity but it can also increase the intracellular levels of glutathione, the major intracellular antioxidant. Fisetin can also activate key neurotrophic factor signaling pathways. In addition, it has anti-inflammatory activity against microglia and astrocytes and inhibits the activity of lipoxygenases, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids and their byproducts. However, key questions about its targets and brain penetration remain. In this study, we used label-free two-photon microscopy of intrinsic fisetin fluorescence to examine the localization of fisetin in living nerve cells and the brains of living mice. In cells, fisetin but not structurally related flavonols with different numbers of hydroxyl groups, localized to the nucleoli suggesting that key targets of fisetin may reside in this organelle. In the mouse brain, following intraperitoneal injection and oral administration, fisetin rapidly distributed to the blood vessels of the brain followed by a slower dispersion into the brain parenchyma. Thus, these results provide further support for the effects of fisetin on brain function. In addition, they suggest that label-free two-photon microscopy may prove useful for studying the intracellular and tissue distribution of other intrinsically-fluorescent flavonoids.
Keywords: flavonoid, microscopy, fluorescence, nucleolus, brain, nerve cells
1. Introduction
The flavonoid fisetin (3,7,3′,4′-tetrahydroxyflavone) is an orally active, novel neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing molecule (Maher, 2009). Fisetin protects nerve cells from multiple toxic insults including amyloid toxicity, ischemia and hyperglycemia. It has both direct antioxidant activity and maintains glutathione, the major intracellular antioxidant, under conditions of stress by inducing the transcription factors, Nrf2 and ATF4 (Ehren and Maher, 2013). Fisetin is also able to maintain ATP levels under ischemic conditions (Maher et al., 2007). In addition, fisetin possesses neurotrophic activity and can induce neurite outgrowth (Sagara et al., 2004). Further studies have shown that fisetin facilitates long-term potentiation (LTP) in hippocampal slices via modulation of ERK and CREB phosphorylation and that oral administration promotes learning and memory in mice using the object recognition test (Maher et al., 2006). Using three different models of Huntington’s disease (mutant huntingtin-expressing PC12 cells, mutant huntingtin-expressing Drosophila and the R6/2 mouse) we found that fisetin was able to reduce the impact of mutant huntingtin in each of these disease models (Maher et al., 2011a). Fisetin is also effective in two different models of stroke (Gelderblom et al., 2012; Maher et al., 2007). Moreover, fisetin reduces markers of CNS inflammation and prevents learning and memory deficits in AD transgenic mice (Currais et al., 2014).
Despite these clear effects of fisetin on the CNS, there is an ongoing debate about whether flavonoids such as fisetin actually get into the brain (Faria et al., 2012; Schaffer and Halliwell, 2012). Although pharmacokinetic studies have provided some evidence for brain penetration, more direct evidence is needed especially as it is possible that many of the effects of fisetin could be mediated by its actions on the microvasculature. A promising approach to address this question is in vivo two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) imaging.
Fisetin is an efficient fluorophore due to its conjugated ring structure and its fluorescence emission spectrum can be distinguished from endogenous tissue fluorophores such as NADH and FAD+ based on both intensity and spectral features. In this study, we report on the detection of fisetin both in nerve cells in culture and in the brain following both intraperitoneal and oral administration using label-free TPEF microscopy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study with any flavonoid that provides direct evidence for the entrance of the molecule into the brain parenchyma.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Cell culture experiments
Mouse hippocampal HT22 nerve cells were plated at a density of 7.5 × 103 to 1 × 104 cells per 35 mm glass culture dish coated with 50 μg/mL polyornithine. The cells were grown for ~48 hours in phenol-free DMEM (Gibco 31053) containing 4 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 1 mM pyruvate and 10% FCS. The cells were treated with 10 μM of the compounds dissolved in DMSO (for a total addition of 10 μL) or 10 μL of DMSO as a control.
2.2 Animal studies
The fisetin solution for intraperitoneal injection was prepared in PEG200:DMSO (Sigma) (7:3), filtered through a 0.45 μm filter and then sonicated in a water bath sonicator. For administration by gavage, the fisetin solution was prepared in 10% ethanol: 40% Solutol HS15:50% PBS and administered at 25 mg/kg as described (Maher et al., 2006). The preparation of the mice was as described (Lin et al., 2014) except that the mice were anesthesized using ketamine (10 mg/ml)-xylazine (1.49 mg/ml). Briefly, C57Bl6 mice were placed on a heating pad in a stereotactic frame. The scalp was removed to create a field of view and the skull was thinned. Vaseline was used to create a saline well and covered by a glass cover slip to aid in two-photon imaging. All procedures were performed in accordance with the regulations of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of California, Irvine.
2.3 In vitro two-photon excited fluorescence imaging
Label-free two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) emission spectra were obtained using the 32-channel Meta detector of the Zeiss LSM 510 Meta NLO microscopy system equipped with a Zeiss EC Plan-Neofluar (100 x, Ph3, n.a.1.3) oil immersion objective. Detector (Hamamatsu PMTs) settings were chosen to keep the signal intensity on a linear part of the response curve. TPEF excitation at 780 nm was generated using a Chameleon-Ultra femtosecond pulsed tunable laser (Coherent Inc.). This particular wavelength was chosen to be close to the maximum according to the known one-photon excitation spectrum of fisetin (Sengupta et al., 2005). Two channels were acquired in imaging mode: the blue channel (390–465 nm) detected free fisetin emission in an aqueous environment (λmax = 460 nm) while the green channel (500–550 nm range) detected the emission of protein-bound fisetin (λmax = 540 nm) (Sengupta et al., 2005). The detector settings of both channels were chosen to minimize the fluorescence signal of cellular NAD(P)H and FAD so detector sensitivity was set by imaging control cells. These settings were established and used in all experiments. Laser scanning did not induce any visible damage to the cells or noticeable bleaching of the sample.
2.4 In vivo two-photon excited fluorescence imaging
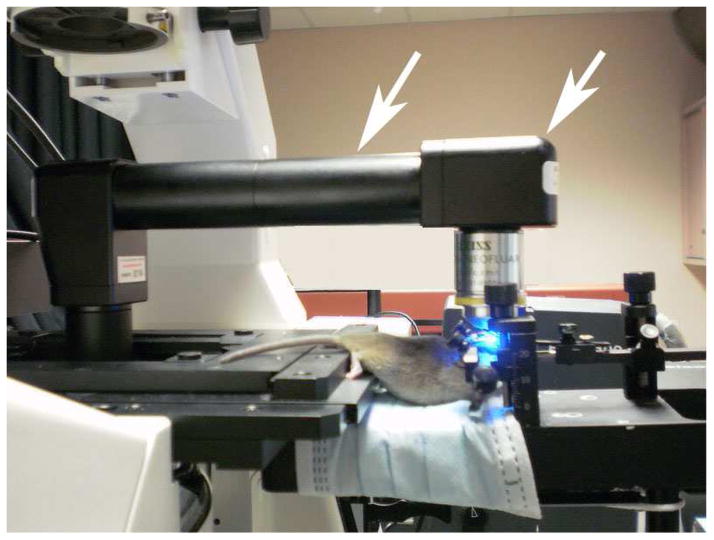
Microscopy imaging and measurements of fisetin fluorescence emission spectra in mouse brain in vivo were performed on a Zeiss LSM NL META microscope equipped with an objective inverter (LSM Tech. Inc, Stewartstown, Pennsylvania). The inverter converts any inverted microscope into an upright configuration by simultaneously changing the orientation of the objective and moving the sample off of the stage. This allows maximum flexibility in sample positioning and handling while still retaining the ability to automatically acquire z-stacks. A mouse was positioned by a stereotactic device, which was placed on a small platform next to the microscope stage; a round coverslip with a ring glued to its surface was placed on the skull opening and a drop of water added on top of it to provide a matching refractive index media for a chosen objective (Fig. 1). The objective lens for the in vivo experiments was a long working distance Zeiss 40x 0.8 na water immersion objective. The maximum depth for imaging was up to 80 μm from the brain surface using an excitation wavelength of 780 nm (Chameleon-Ultra Titanium:Sapphire laser, Coherent, Inc.). Spectral acquisition was obtained using a META polychromatic 32-channel detector.
Figure 1. Zeiss LSM 510 microscopy system equipped with objective inverter for the in vivo study.
Shown is the general layout of the experimental set-up and, in particular, the one unusual optical element in it, an objective inverter, which is indicated by the white arrows.
3. Results
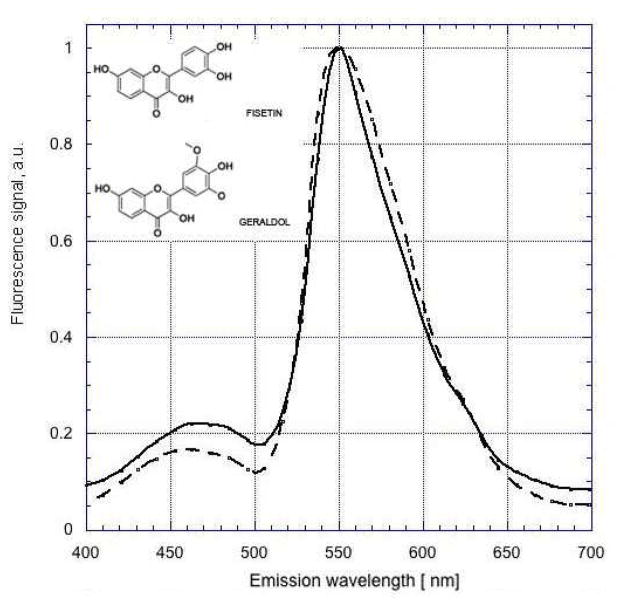
Emission spectra for fisetin in DMSO were obtained using two-photon excitation at 780 nm (Fig. 2). This wavelength was chosen based on the reported one-photon excitation spectrum of fisetin (Sengupta et al., 2005). A distinct emission peak at ~550 nm as well as an expected blue-shifted peak at 460 nm were observed. These results were similar to those reported using conventional one-photon excitation (Sengupta et al., 2005).
Figure 2. Two-photon excited fluorescence emission spectra of fisetin and geraldol.
Solutions of fisetin (solid line) or geraldol, a major in vivo metabolite of fisetin (dashed line), in DMSO were excited at 780 nm Spectra were normalized to unity at 550 nm.
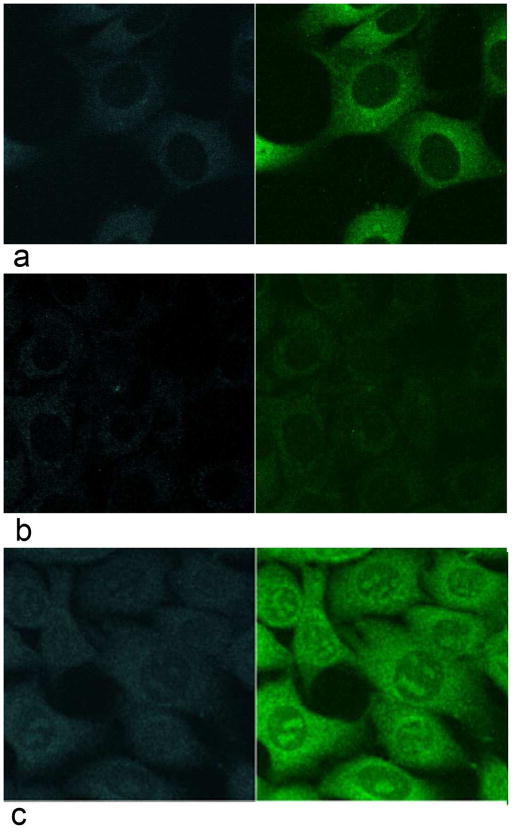
Fisetin was solubilized in DMSO and added to the medium of HT22 mouse hippocampal nerve cells (10 μM) in order to determine its detectability in cultured cells. The cells were examined by TPEF microscopy both before the addition of fisetin and at increasing times after the addition of the flavonoid. To distinguish the fluorescence emission of fisetin from endogenous NADH (blue channel) and FAD+ (green channel) signals, cells were treated with an equal amount of DMSO and imaged 30 min after treatment (Fig. 3a). The exact same parameters (scanner, detector, laser power) were used in the imaging of fisetin-treated cells. As shown in Figure 3, after 30 min of treatment the characteristic fluorescence emission of fisetin (Fig. 3b, c) was clearly visible inside cells. Closer examination showed that fisetin was concentrated in both the cytoplasm and the nucleolus (Fig. 3b).
Figure 3. Spectral signature of fisetin in HT22 nerve cells.
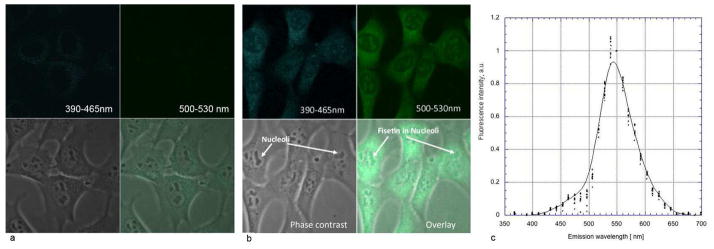
Cells were treated with 10 μM fisetin for 30 min and then examined by two-photon microscopy using excitation at 780 nm (b). Control cells were treated with DMSO and imaged 30 min after treatment (a). The emission spectra were measured for 10 individual cells and normalized to unity at 550 nm (c). In other words, the signal intensity measured at 550 nm was assigned a value of 1 and all other points were scaled according to this ratio. Imaging panels: blue fluorescence channel (390–466 nm), top left; green fluorescence channel (500–530 nm), top right; conventional phase contrast image, bottom left and an overlay of all three, bottom right panel. Field of view (FOV) was 90 μm × 90 μm.
It was then asked if the localization of fisetin to nucleoli was unique to this flavonol or if other flavonols with similar structures also localized to this intracellular site. Accordingly, the intracellular distribution of fisetin (3,7,3′4′-tetrahydroxyflavone) was compared to that of 3,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone and quercetin (3,5,7,3′,4′-pentahydroxyflavone). As shown in Figure 4, the addition (Fig. 4b; quercetin) or removal (Fig. 4a; 3,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone) of even a single hydroxyl group eliminated the localization of the flavonol to the nucleolus.
Figure 4. Structurally related flavonols do not localize to the nucleoli while the fisetin metabolite geraldol does.
Two-photon microscopy of cells treated with 10 μM 3,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone (a) or quercetin (b) for 30 min show a localization pattern for these flavonols distinct from that of fisetin. Cells treated with 10 μM geraldol for 30 min show a nucleolar localization pattern identical to that of fisetin (c). Excitation wavelength was 780 nm. FOV 90μm × 90μm
Geraldol (3,7,4′-trihydroxy-3′-methoxyflavone) is an in vivo metabolite of fisetin (Touil et al., 2011) and so it was asked if geraldol is also localized to the nucleolus of cultured cells. As shown in Figure 4c, similar to fisetin, treatment of the HT22 cells with 10 μM geraldol resulted in a high concentration of the flavonol in the nucleolus. Together, these results indicated that fisetin and its metabolite could be readily detected in living cultured nerve cells by TPEF microscopy. We then asked if they could be detected in vivo as well.
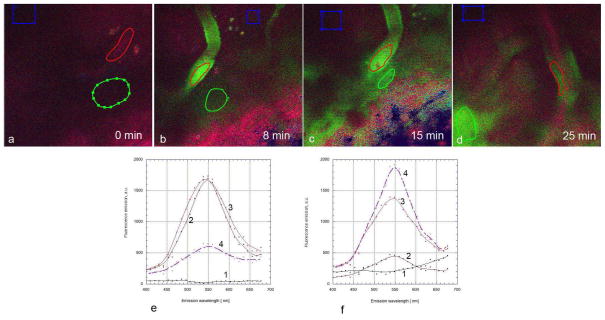
In the first set of in vivo studies, fisetin was solubilized in PEG200:DMSO (7:3) and then injected intraperitoneally at 74 mg/kg. Mouse brains were imaged before fisetin injection as well as 8, 15 and 25 minutes after fisetin injection. As shown in Figure 5a, using excitation at 780 nm, no emission at 550 nm was seen prior to fisetin injection. However, within 8 min of fisetin injection, clear emission at 550 nm was seen within the blood vessels of the brain which were identified by visual recognition as they have a very distinctive morphology (Fig. 5b). Importantly, when the brain was imaged 15 min after injection not only did the emission at 550 nm continue to be seen within the blood vessels but emission outside the vessels was also readily apparent (Fig. 5c, e, f). With further time progression, fisetin fluorescence intensity in the blood vessels diminished, while the diffuse signal from adjacent parenchyma clearly increased. (Fig. 5d, e, f)
Figure 5. Time course of fisetin accumulation in the brains of living mice following intraperitoneal injection.
Fisetin (74 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally and the characteristic green fluorescence of fisetin (max at 550 nm) was detected in the blood vessels within 8 min after injection (b) and in both the blood vessels and brain parenchyma 15 min and 25 min after injection (c, d). No detectable levels of green emission were seen in prior to fisetin injection (a). Fisetin progressively moves out of the blood vessels into the parenchyma following intraperitoneal injection (e, f). Spectra were acquired from regions of interest (ROI) covering blood vessels (red), adjacent areas of parenchyma (green) and more distant areas (blue, used for background correction). Spectra were acquired before (1) and at 8 min (2), 15 min (3) and 25 min (4) after intraperitoneal injection on ROIs covering blood vessels (e) and adjacent parenchyma (f). FOV was 225 μm × 225 μm in all experiments.
Many of the animal studies which showed physiological effects of fisetin have used oral administration (Currais et al., 2014; Maher et al., 2006; Maher et al., 2011a; Maher et al., 2011b). Thus, it was important to determine if a similar pattern of fisetin distribution in the brain could be seen if fisetin was administered orally. Again, using excitation at 780 nm, no emission at 550 nm was visible prior to gavage of fisetin (Fig. 6a). Following gavage at 25 mg/kg, the same dose used in one of previous animal studies (Maher et al., 2006), fisetin was readily detectable within the blood vessels of the brain after 40 min (Fig. 6b). Some fisetin signal was also detectable outside the blood vessels at this time. At 2 hours post-gavage, signal from fisetin was still detectable from both blood vessels and parenchyma along with more localized areas suggestive of individual neuronal cell uptake (Fig. 6d).
Figure 6. Fisetin can be detected in the brains of living mice following oral administration.
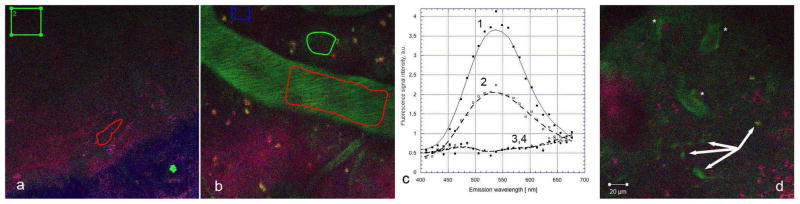
Fisetin (25 mg/kg) was given by gavage and the characteristic emission peak of fisetin was detected strongly in the blood vessels and more weakly in the brain parenchyma within 40 min after administration (b, c). Within 120 min (d), fisetin fluorescence was detectable in blood vessels (asterisks), the adjacent brain parenchyma and also in individual neuronal cells (arrows). No emission at 550 nm was seen in prior to fisetin administration (a, c). Spectral measurements were taken before (3, 4) and 40 min after (1, 2) oral administration at the blood vessel (1, 3) and adjacent parenchymal area (2, 4) on ROIs. FOV was 225 μm × 225 μm in all experiments.
4. Discussion
The major conclusion from this study is that physiologically relevant concentrations of fisetin, as well as closely related flavonols, can be readily imaged both in cultured cells and in the brains of living animals using label-free two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) microscopy. In cells, this allowed the determination of fisetin’s intracellular localization without the need for fixation or other forms of preparation that might lead to artifacts. In the mouse brain, this led to the observation of the rapid distribution of fisetin to blood vessels followed by its dispersion into the brain parenchyma. These results are consistent with the reported effects of fisetin on brain function (Maher, 2009) and suggest that its sites of action within the brain include not only the vasculature but the cells of the parenchyma as well. As far as we know, this is the first demonstration of the use of label-free TPEF microscopy to detect exogenous flavonoids in both living cells and the brains of living animals.
Near-infrared (NIR) two-photon excitation helps facilitate more effective deep tissue in-vivo imaging. This is due to diminished tissue light scattering in the NIR compared to the UV/blue excitation required for conventional fluorescence. Because the conjugated ring structure of fisetin makes it an effective fluorophore, TPEF is an ideal method for visualizing fisetin in thick tissues in vivo. If significant changes to the ring structure occurred in vivo, this would alter the fisetin fluorescence emission spectrum and be readily detectable using TPEF. Since fisetin’s fluorescence was clearly observed in both cells and brain, we expect that the fisetin ring structure remains fully intact in vivo.
Alterations to the fisetin ring, such as the addition of hydroxyl groups, can potentially change the emission characteristics and subcellular localization. Interestingly, we show that in cells the number of hydroxyl groups on the rings dramatically affects intracellular localization such that flavonols having one more (quercetin) or one fewer (3, 3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone) hydroxyl group show a very different intracellular localization as compared with fisetin. In contrast, modification of a hydroxyl such as is seen in geraldol where the 3′ hydroxyl is a methoxy group, does not appear to alter the intracellular localization pattern. Since geraldol is an active in vivo metabolite of fisetin (Touil et al., 2011), its similar nucleolar distribution suggests that in vivo it may target the same structures as fisetin. Other in vivo metabolites involve glucuronidation or sulfation (Shia et al., 2009; Touil et al., 2011) of one or more hydroxyls.
Our observation that fisetin and its active metabolite geraldol both localize to the nucleoli in living cells is unlikely to be due to an artifact. The cells are not fixed or otherwise treated before examination by two-photon microscopy and this localization is not seen with closely related flavonols with different numbers of hydroxyl groups. Although the primary function of the nucleolus has long been considered to be ribosome subunit biogenesis, over the last 10 years over 6000 nucleolar proteins have been identified and only 30% of those have a function obviously related to the production of ribosome subunits (Boisvert et al., 2007). It is now known that the nucleolus helps to manage the cell cycle, stimulate DNA repair and modulate cellular stress responses (Leslie, 2014). Moreover, nucleolar stress is emerging as a common component of multiple neurodegenerative disorders (Parlato and Liss, 2014). Thus, the localization of fisetin to the nucleolus in combination with its known neuroprotective effects suggests that some of these processes may be mediated by a reduction of nucleolar stress. In addition, PARP, a known binding target of fisetin (Geraets et al., 2007) localizes to the nucleolus (Meder et al., 2005). Further studies are needed to directly address the question of fisetin and metabolite sub-cellular distribution and molecular targeting pathways.
There is an ongoing debate about whether flavonoids such as fisetin can reach levels in the brain that are sufficient to affect brain function (Schaffer and Halliwell, 2012). The results presented here show that fisetin rapidly distributes to the brain vasculature and parenchyma at levels that are readily detectable by two-photon microscopy. Although this does not provide a quantitative estimate of fisetin levels, it does provide direct visual evidence for brain penetration. While fisetin and geraldol cannot be distinguished in vivo by this approach, the observation that the levels of geraldol are 5–20% of those of fisetin in multiple tissues following intraperitoneal injection (Touil et al., 2011) strongly suggest that the majority of the compound visualized is fisetin. Furthermore, this approach might prove useful for studying the potential brain distribution of other flavonoids and related polyphenols that can be imaged by TPEF microscopy.
In summary, we show for the first time that an exogenously added flavonoid can be readily visualized in cells and the brain in vivo using label-free TPEF microscopy. Since this approach allows the distribution of the flavonoid to be examined directly in living cells and tissues in the absence of fixation, it has the potential to provide new insight into both the intracellular and tissue distribution of fluorescent flavonoids. Future studies that combine both endogenous and exogenous fluorescent probes could lead to a deeper understanding of fisetin’s distribution and targeting. In addition, the role of fisetin’s structural congeners and metabolites could be further elucidated by employing more sophisticated two-photon excited fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM) methods that provide powerful approaches for separating and identifying the origins of multiple, complex fluorescence signals.
Highlights.
Fisetin can be detected in the nucleoli of living cells by two photon microscopy
The fisetin metabolite geraldol also localizes to nucleoli
Other structurally related flavonols do not localize to nucleoli
Fisetin can be detected in the brains of living mice after oral and ip administration
Fisetin is found in both the blood vessels and parenchyma of the mouse brains
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from NIH (The Laser Microbeam and Medical Program (LAMMP) P41EB015890 to BJT and R41AI104034 to PM) and the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation (BJT).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- Boisvert FM, van Koningsbruggen S, Navascues J, Lamond AI. The multi-functional nucleolus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:574–585. doi: 10.1038/nrm2184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currais A, Prior M, Dargusch R, Armando A, Ehren J, Schubert D, Quehenberger O, Maher P. Modulation of p25 and inflammatory pathways by fisetin maintains cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Aging Cell. 2014;13:379–390. doi: 10.1111/acel.12185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehren JL, Maher P. Concurrent regulation of the transcription factors Nrf2 and ATF4 mediates the enhancement of glutathione levels by the flavonoid fisetin. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85:1816–1826. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faria A, Mateus N, Calhau C. Flavonoid transport across the blood-brain barrier: Implications for their direct neuroprotective actions. Nutr Aging. 2012;1:89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom M, Leypoldt F, Lewerenz J, Birkenmayer G, Orozco D, Ludewig P, Thundyil J, Arumugam TV, Gerloff C, Tolosa E, Maher P, Magnus T. The flavonoid fisetin attenuates postischemic immune cell infiltration, activation and infarct size after transient cerebral middle artery occlusion in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:835–843. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraets L, Moonen HJJ, Brauers K, Wouters EFM, Bast A, Hageman GJ. Dietary flavones and flavonols are inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 in pulmonary epithelial cells. J Nutr. 2007;137:2190–2195. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.10.2190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie M. Central command. Science. 2014;345:506–507. doi: 10.1126/science.345.6196.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin AJ, Castello NA, Lee G, Green KN, Durkin AJ, Choi B, LaFerla F, Tromberg BJ. In vivo optical signatures of neuronal death in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Lasers Surg Med. 2014;46:27–33. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. Modulation of multiple pathways involved in the maintenance of neuronal function during aging by fisetin. Genes Nutr. 2009;4:297–307. doi: 10.1007/s12263-009-0142-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P, Akaishi T, Abe K. Flavonoid fisetin promotes ERK-dependent long-term potentiation and enhances memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:16568–16573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607822103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P, Dargusch R, Bodai L, Gerard P, Purcell JM, Marsh JL. ERK activation by the polyphenols fisetin and resveratrol provides neuroprotection in multiple models of Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Gen. 2011a;20:261–270. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P, Dargusch R, Ehren JL, Okada S, Sharma K, Schubert D. Fisetin lowers methylglyoxal dependent protein glycation and limits the complications of diabetes. PLoS ONE. 2011b;6:e21226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P, Salgado KF, Zivin JA, Lapchak PA. A novel approach to screening for new neuroprotective compounds for the treatment of stroke. Brain Res. 2007;1173:117–125. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.07.061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meder VS, Boeglin M, de Murcia G, Schreiber V. PARP-1 and PARP-2 interact with nucleophosmin/B23 and accumulate in transcriptionally active nucleoli. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:211–222. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parlato R, Liss B. How Parkinson’s disease meets nucleolar stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:791–797. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara Y, Vahnnasy J, Maher P. Induction of PC12 cell differentiation by flavonoids is dependent upon extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. J Neurochem. 2004;90:1144–1155. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer S, Halliwell B. Do polyphenols enter the brain and does it matter? Some theoretical and practical considerations. Genes Nutr. 2012;7:99–109. doi: 10.1007/s12263-011-0255-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta B, Banerjee A, Sengupta PK. Interactions of the plant flavonoid fisetin with macromolecular targets: Insights from fluorescence spectroscopic studies. J Photochem Photobiol B:Biology. 2005;80:79–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2005.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shia C-S, Tsai S-Y, Kuo S-C, Hou Y-C, Chao P-DL. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of 3,3′,4′,7-tetrahydroxyflavone (fisetin), 5-hydroxyflavone and 7-hydroxyflavone and antihemolysis effects of fisetin and its serum metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:83–89. doi: 10.1021/jf802378q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touil YS, Auzeil N, Boulinguez F, Saighi H, Regazzetti A, Scherman D, Chabot GG. Fisetin deposition and metabolism in mice: Identification of geraldol as an active metabolite. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82:1731–1739. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.07.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]