Abstract
Diabetes is associated with a paucity of insulin-producing β-cells. With the goal of finding therapeutic routes to treat diabetes, we aim to find molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in β-cell neogenesis and regeneration. To facilitate discovery of such mechanisms, we use a vertebrate organism where pancreatic cells readily regenerate. The larval zebrafish pancreas contains Notch-responsive progenitors that during development give rise to adult ductal, endocrine, and centroacinar cells (CACs). Adult CACs are also Notch responsive and are morphologically similar to their larval predecessors. To test our hypothesis that adult CACs are also progenitors, we took two complementary approaches: 1) We established the transcriptome for adult CACs. Using gene ontology, transgenic lines, and in situ hybridization, we found that the CAC transcriptome is enriched for progenitor markers. 2) Using lineage tracing, we demonstrated that CACs do form new endocrine cells after β-cell ablation or partial pancreatectomy. We concluded that CACs and their larval predecessors are the same cell type and represent an opportune model to study both β-cell neogenesis and β-cell regeneration. Furthermore, we show that in cftr loss-of-function mutants, there is a deficiency of larval CACs, providing a possible explanation for pancreatic complications associated with cystic fibrosis.
Introduction
The zebrafish has a remarkable regenerative capacity, including an ability to regenerate pancreatic β-cells (1,2). The regenerative capacity of the fish has already revealed new avenues by which therapies may be developed to replace tissues in patients that otherwise would not normally heal (3). Humans and other mammals can also undergo somewhat limited β-cell regeneration (4–6), yet whether such regeneration includes β-cell neogenesis is still under debate (7–9). Investigation into whether β-cell neogenesis occurs in mammals has likely been hindered by the more limited regenerative capacity of those models. Knowledge of the mechanisms used in the adult zebrafish pancreas to regenerate endocrine tissue has the potential to reveal routes by which missing β-cells could be replaced in diabetic patients.
Pancreata from zebrafish and mammals share considerable similarity in terms of morphology and gene expression. The larval zebrafish pancreas contains a single principal islet and, starting at 5 days postfertilization, secondary islets that form throughout the pancreas parenchyma (10). The adult zebrafish pancreas consists of four lobes: gallbladder-spleen, middle, left, and ventral. β-Cells are arranged as isolated single cells and in islets along with other endocrine cells. The principal islet is normally located in the gallbladder-spleen lobe (11).
During zebrafish development, pancreatic Notch-responsive cells (PNCs) give rise to endocrine, ductal, and centroacinar (CACs) cells (10,12). CACs are defined as specialized ductal epithelial cells located at the ends of ducts within the acinar lumen. Both PNCs and CACs are ductal cells that share the following characteristics: 1) possession of long-cytoplasmic extensions (13), 2) distinctive ultrastructure (14), and 3) responsiveness to Notch signaling (10,15,16). CACs have been proposed to be adult multipotent progenitors in rodents (15–19). Although the progenitor status of mammalian CACs remains controversial (20–24), the idea is supported by the observation that mammalian CACs proliferate in response to different injuries, including streptozotocin-induced destruction of β-cells (25), partial pancreatectomy (26), and acute or chronic administration of caerulein (27).
To characterize CACs in more detail, we used RNA-Seq to define their transcriptome. Gene ontology analysis revealed that CACs are enriched for genes important in progenitor biology. To explore whether CACs are involved in β-cell regeneration, we have used two injury models in zebrafish: 1) a transgenic method to specifically ablate β-cells and 2) partial pancreatectomy (PPx), a surgical procedure that removes the left lobe of the pancreas. Using inducible genetic lineage tracing, we find that CACs do indeed contribute to β-cell regeneration. Our discovery that CACs act as endocrine progenitors in a rapidly regenerating, genetically tractable model can reveal mechanisms important in β-cell neogenesis that have been difficult to study in mammals and that may ultimately be applied to improve regenerative capacity in diabetic patients to restore β-cell mass.
Research Design and Methods
Transgenic Lines
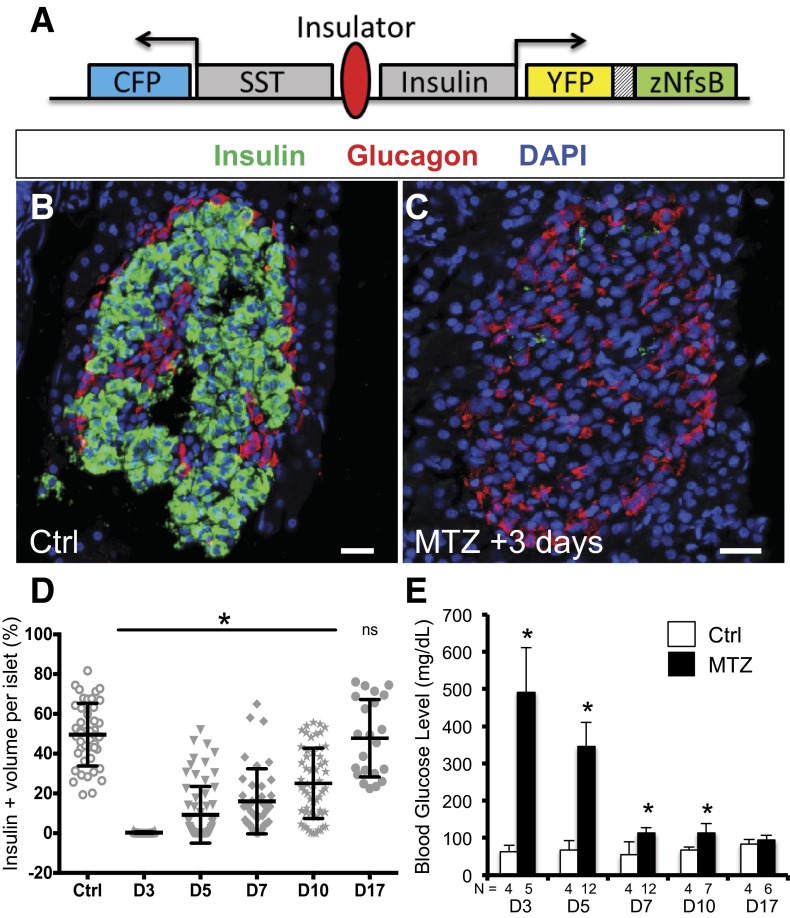
Tg(HS4-sst2:CFP;ins:PhiYFP-m-dest1-2TA-nfsB)lmc009 (abbreviated ins:NTR) carries a transgene containing 1) insulin promoter driving a zebrafish codon–optimized NTR-T2A–yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) open-reading frame and 2) somatostatin2 promoter/enhancer driving CFP transcription (Fig. 4A). Other lines are listed in Supplementary Table 2.
Figure 4.
β-Cell ablation and regeneration. A: ins:NTR transgene (see research design and methods). SST, somatostatin2. B and C: Three days following treatment, control transgenic fish (B) compared with MTZ-treated fish (C). Insulin-expressing β-cells (green) were nearly absent from islets. Anti-insulin (green), anti-glucagon (red), DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. D: The percentage of β-cells per islet returns to control levels by MTZ +17 days. E: Blood glucose levels in MTZ- and vehicle-treated fish. β-Cell ablation results in hyperglycemia, which returns to control levels by MTZ +17 days. Ctrl, control; D, day; N, number of fish analyzed. *P < 0.05; ns, not significant, t test compared with control.
CAC Isolation
Three-month postfertilization adult Tp1:GFP (method 1) and Tp1:gfp; fli1:DsRed (method 2) fish were killed and pancreata dissected in 1× Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS) without Ca2+ or Mg2+. Pancreata were dissociated in 0.7 mg/mL Collagenase P (Roche) (37°C, 20 min), followed by addition of FBS (Gibco) to a 5% final concentration on ice. Cells were collected by 3 × 5 min centrifugation (700g, 4°C) with resuspension in 1× HBSS with 5% FBS. Cells were then resuspended in 1× HBSS, 0.01% Trypsin (Gibco) (37°C, 5 min), followed by 3 × 5 min centrifugation (700g, 4°C) with resuspension in 1× HBSS and 5% FBS and filtration through 70 μmol/L and 40 μmol/L nylon filters (BD Falcon). For method 1, allophycocyanin-conjugated anti–CD-105 (60039AD; STEMCELL Technologies) was used to label endothelial cells. Cells were sorted on a BD Biosciences FACSAria III cell sorter.
RNA Sequencing
Total RNA was isolated (RNeasy Mini, Qiagen) and RNA-Seq libraries were prepared (version 2; TruSeq RNA Sample Preparation kit, Illumina). Fifty-cycle single-end reads were collected (Genome Analyzer II, Illumina). Reads were processed and mapped to Zv9/danRer7 using RSEM (28). EBSeq (29) was used to determine differential expression and significance values. Data files have been submitted to GEO (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/).
Quantitative PCR
cDNAs were made (SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis kit, Invitrogen). Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed on a Bio-Rad C1000 Bio-Rad thermal cycler and analyzed using the CFX Manager software (Bio-Rad). qPCR primers are listed in Supplementary Table 3.
Drug Treatments
For ablation of β-cells, 30 mmol/L metronidazole (MTZ) (M3761; Sigma) in PBS was intracoelomically (i.c.) injected into ins:NTR fish at a dose of 0.25 g/kg body wt. Control fish were injected with PBS. For activation of CreERT2, 20 μL of 2 μmol/L 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OHT) (T176; Sigma) (12) was i.c. injected daily for 3 days. For induction of 2° islets, 50 μmol/L N-[N-(3,5-Difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester (DAPT) in E3 medium (30) was applied to larvae from 3–5 dpf (10).
Partial Pancreatectomy
Fish were anesthetized in 0.168 mg/mL tricane (Sigma) (30). An incision was made on the left flank, and most of the left pancreatic lobe was removed. Sham surgeries were performed as controls. Fish were kept in still water (28°C) that was changed after daily feeding. For the first 3 days after surgery, EdU was added to the water (2.5 μmol/L). After PPx plus 3 days, EdU was delivered by i.c. injection of 20 μL of 25 μmol/L 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU).
Immunohistochemistry, In Situ Hybridization, and Microscopy
Five dpf larvae were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (4°C overnight). Antibody staining and in situ hybridization were performed as previously described (12,31). Primers for making riboprobes are listed in Supplementary Table 3. For adult pancreata, 3-month postfertilization zebrafish were fixed overnight in 10% formalin at 4°C. Viscera were then dissected, embedded in paraffin blocks, and processed using standard procedures (Abcam). Antibodies are listed in Supplementary Table 4. Images were collected using a Nikon AZ100 microscope or a Nikon A1-si Laser Scanning Confocal microscope. For adult quantification, at least five sections of each individual islet >1,000 μm were counted per fish.
Glucose Assays
Adult fish were fasted (24 h) and killed, and blood glucose was measured using a OneTouch Ultra (LifeScan) glucose meter (32). Larval glucose levels were determined in 5 dpf larvae using a glucose assay kit (BioVision). The cftrpd1049 mutant larvae were genotyped by observing Kupffer vesicle in 10-somite stage embryos (33). As a positive control, ins:nfsb-mCherryjh4 larvae were treated with 10 mmol/L MTZ (Sigma) or vehicle from 3 to 5 dpf (2).
Results
Transcriptome Analysis of CACs
During development, endocrine cells, ductal cells, and CACs originate from ductal PNCs, which are the only Notch-responsive cells in the larval pancreas (Fig. 1A) (10,12). CACs are the only PNC-derived cells that remain Notch-responsive in adults (12) (Fig. 1B); hence, we hypothesized that CACs may function as adult progenitors. To explore this possibility, we sought to characterize the CAC transcriptome using RNA-seq. To flow sort adult CACs, we dissociated pancreata from Tp1:GFP adult fish and used two methods to remove contaminating Notch-responsive endothelial cells: a CD105 allophycocyanin-conjugated antibody to label endothelial cells red (method 1) and a second transgene, fli:dsRed, which drives red fluorescent protein expression in endothelial cells (method 2) (Supplementary Fig. 1A). Using either red fluorescent blood vessel marker (bv), we collected four populations from dissociated adult pancreata: green fluorescent protein (GFP)+/bv−, GFP+/bv+, GFP−/bv+, and GFP−/bv− (Supplementary Fig. 1B). As expected, qPCR revealed high expression of the CAC marker sox9b in GFP+ populations and of the vascular marker cdh5 in bv+ populations (Supplementary Fig. 1C).
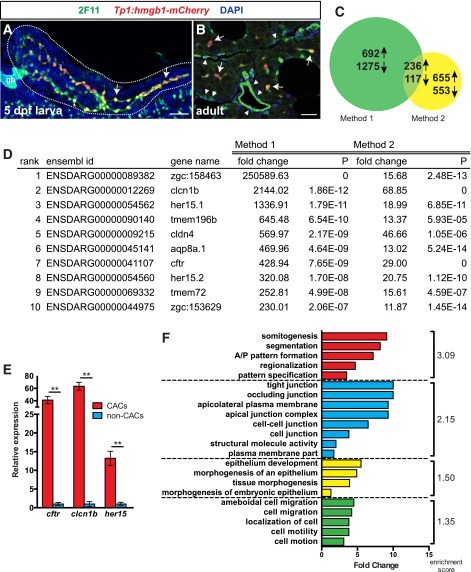
Figure 1.
RNA-Seq of the CAC transcriptome. A: PNCs (arrows) form the entire pancreatic duct (green) in 5 dpf larvae. gb, gallbladder. Scale bar = 50 μm. B: In the adult pancreas, CACs (arrows) represent a subset of the ductal epithelium (green), which contains mostly non-Notch-responsive cells (arrowheads). CACs are the only epithelial pancreas cells that remain Notch responsive. Scale bar = 20 μm. Anti-2F11 (green), Tp1:hmgb1-mCherry (red), DAPI (blue). C: Differential gene expression (fold change >1.5) between CACs and non-CACs from two separate preparations. Expression of 236 genes was enriched in CACs in both preparations. D: Genes most highly enriched in CACs vs. non-CACs. P, probability of a gene being equally expressed in CAC and non-CAC samples. E: qPCR for cftr, clcn1b, and her15 from an independent cell preparation confirms their enrichment in CACs (**P ≤ 0.005, t test). F: Functional annotation clustering of genes upregulated in CACs. DAVID analysis of biological process, cellular component, and molecular function gene ontology terms reveals significant enrichment (enrichment score >1.3) of four clusters of terms associated with the identified 236 CAC markers.
Using each method, we sequenced RNA from GFP+/bv− (CAC) populations and GFP−/bv− (non-CAC) populations. Considering the intersection of both sequencing experiments, we identified 353 genes that were differentially expressed with >1.5-fold change difference in CACs versus non-CACs, including 236 upregulated genes (Fig. 1C and D and Supplementary Table 1). As expected for an epithelial cell type, these genes included a number of ion channels (clcn1b, cftr) but also transcription factors important in regulating pancreas progenitors such as the Notch-downstream targets her15.1/her15.2 (34). Using method 2, we generated another independent preparation of RNA and quantified expression of cftr, clcn1b, and her15 by qPCR. These genes were significantly upregulated in CACs versus non-CACs (Fig. 1E), confirming that our catalog is enriched for CAC markers.
Using the functional annotation-clustering algorithm in DAVID (35), we investigated whether our 236 CAC markers were enriched for particular gene ontology terms. This analysis identified four biological clusters with a statistically significant enrichment score >1.3 (Fig. 1F): 1) developmental programming, 2) epithelial cell biology, 3) epithelial development, and 4) cell motility/cytoskeletal organization (Supplementary Fig. 2). This analysis confirms that CACs express a genetic program consistent with an epithelial progenitor cell population, supporting our hypothesis that CACs function as an adult progenitor cell pool.
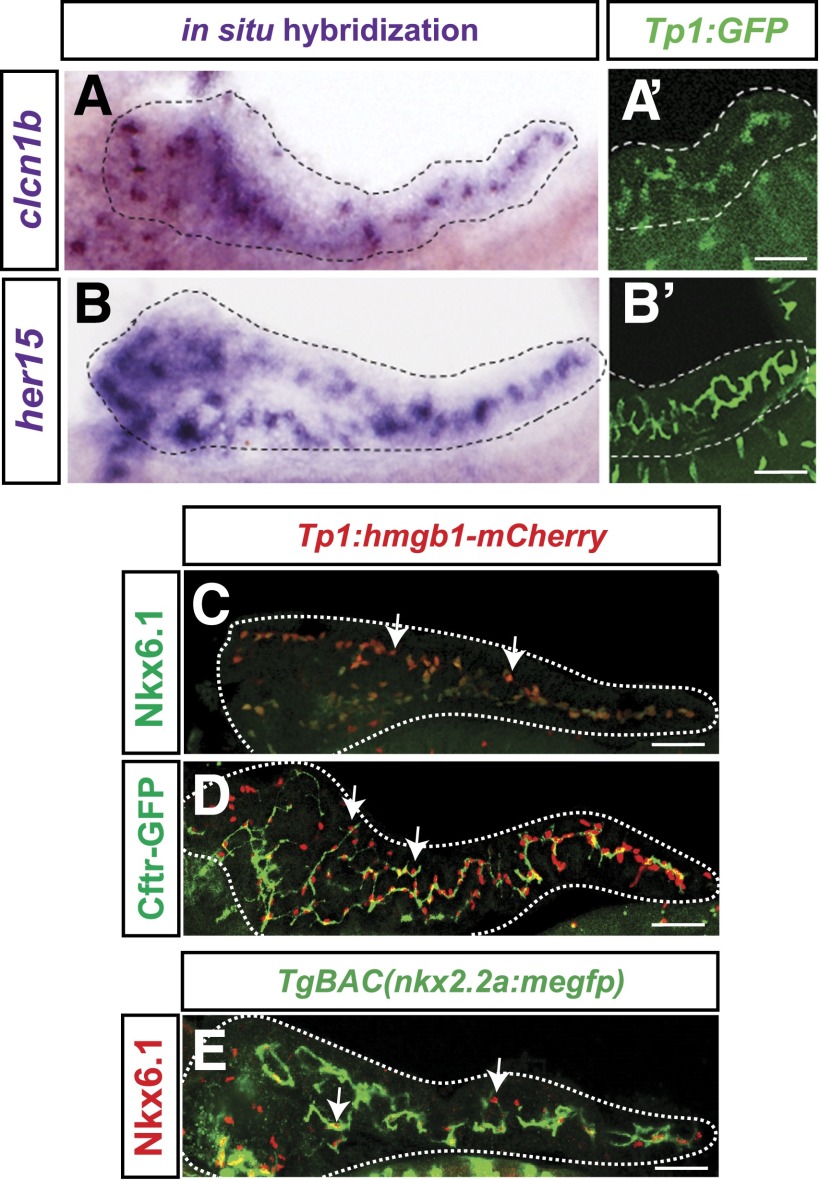
We next investigated the expression pattern of three CAC markers in adult pancreas: Nkx6.1, Cftr, and Nkx2.2a. Nkx6.1 is important for endocrine differentiation and is a known marker of PNCs (36). Using the Tp1:hmgb1-mCherry reporter line, in which all Notch-responsive cells express nuclear mCherry, we observed Nkx6.1 expression in all CACs (Fig. 2A). Using TgBAC(cftr-gfp) fish, we observed the endogenous expression pattern of a Cftr-GFP fusion protein (33), which was localized to the thin cellular extensions of Nkx6.1-expressing cells (Fig. 2B). Without the advantage of using CAC or cell polarity markers, others have concluded that Cftr marks the apical surface of ductal cells (37). In fact, the protein is restricted to the thin extensions of CACs that cover the inner lumen of the pancreatic duct. (See also Fig. 3D.) Lastly, we used TgBAC(nkx2.2a:meGFP [membrane GFP]) fish to examine the endogenous expression pattern of nkx2.2a, a transcription factor important in endocrine differentiation (38). In these fish, Nkx6.1-expressing CACs expressed meGFP (Fig. 2C). Overall, our analysis establishes a new set of markers that are consistent with the predicted role of CACs as progenitor cells.
Figure 2.
CAC-enriched gene expression in adult pancreas. A: Nkx6.1 (green) is expressed in CACs visualized using the Notch reporter Tp1:hmgb1-mCherry (red). B: Endogenous expression pattern and subcellular location of a Cftr in TgBAC(cftr-GFP) fish. Cftr-GFP fusion protein (green) is expressed in cell extensions of Nkx6.1-expressing cells (red). C: Endogenous expression pattern of nkx2.2a in TgBAC(nkx2.2a:meGFP) fish; membrane GFP (green) is expressed in Nkx6.1-expressing cells (red). Membrane GFP expression is occasionally observed in non-CACs cells within islets (yellow asterisk). CACs (arrows), scale bars = 20 μm.
Figure 3.
PNCs express CAC markers. A and B: Whole mount in situ hybridization for clcn1b and her15 mRNA (purple) in Tp1:GFP (green) pancreata at 5 dpf. C and D: Nkx6.1 and TgBAC(cftr-GFP) expression (green) in whole mount Tp1:hmgb1-mCherry (red nuclei) pancreata at 5 dpf. E: TgBAC(nkx2.2a:meGFP) expression in Nkx6.1-expressing cells in 5 dpf pancreas. Scale bars = 50 μm.
Larval Notch-Responsive Progenitors Express CAC Markers
Our transcriptome analysis suggested that CACs are adult progenitors, so we next hypothesized that CACs and PNCs may represent a single cell type. Thus, we used in situ hybridization and the above-mentioned transgenic lines to examine the expression pattern of several of our new CAC markers in larval pancreata. To visualize PNCs, we used our Notch-responsive reporter lines, Tp1:GFP or Tp1:hmgb1-mCherry. In 5 dpf fish, we observed clcn1b, her15, Nkx6.1, Cftr-GFP, and nkx2.2a:meGFP expression in PNCs (5 of 5 genes examined) (Fig. 3A–E). As PNCs are progenitors for adult CACs (12) and share marker gene expression, cell morphology, and ultrastructure with them (10), we conclude that PNCs are in fact an early population of CACs. Henceforth, we will refer to PNCs as larval CACs.
CACs Proliferate and Are More Proximal to Islets During β-Cell Regeneration
Larval CACs contribute to endocrine and ductal cell populations during development (12). Thus, we next set out to discover whether adult CACs play a role in β-cell regeneration. To ablate β-cells, we used HS4-sst2:CFP;ins:PhiYFP-m-dest1-2TA-nfsBlmc009 zebrafish (abbreviated ins:NTR). In these animals, β-cells express destabilized YFP and nitroreductase, which converts MTZ to a cytotoxin (Fig. 4A). Fish were initially injected with MTZ (MTZ +0 days) or vehicle and then were killed at MTZ +3, +5, +7, +10, and +17 days. We then analyzed blood glucose levels and pancreas morphology. At MTZ +3 days, we observed near total β-cell ablation (99.7%) and an unaffected α-cell population (Fig. 4B–D and Supplementary Fig. 3A and B). These fish were severely hyperglycemic but returned to euglycemia after 2 weeks of recovery (Fig. 4E), confirming previous studies (1). By MTZ +5 to +7 days, the number of single β-cells and β-cell clusters (small groups of β-cells not containing α-cells) initially increased and then resolved between MTZ +10 and +17 days (Supplementary Fig. 3C and D). This observation is consistent with a model of β-cell neogenesis, where single cells differentiate, proliferate, and form islets (25).
To visualize CACs after β-cell ablation, we used the Notch reporter Tp1:GFP. Single β-cells were often seen proximal to or in contact with CACs in controls (Fig. 5A). By measuring the distance between single β-cell nuclei and the nuclei of the two nearest GFP-positive cells, we determined that at MTZ +5 and +7 days, CACs were significantly closer to single β-cells (14.35 ± 0.6 µm and 14.74 ± 0.7 µm, respectively) than in controls (22.81 ± 1.56 µm, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 5A–D). Additionally, adjacent to CACs we occasionally saw single insulin-expressing cells that were GFP positive and lacked extensions (6 of 19 fish at MTZ +5 and +7 days) (Fig. 5C). These results are consistent with a cell-fate transition from CAC to single β-cell via a double-positive stage.
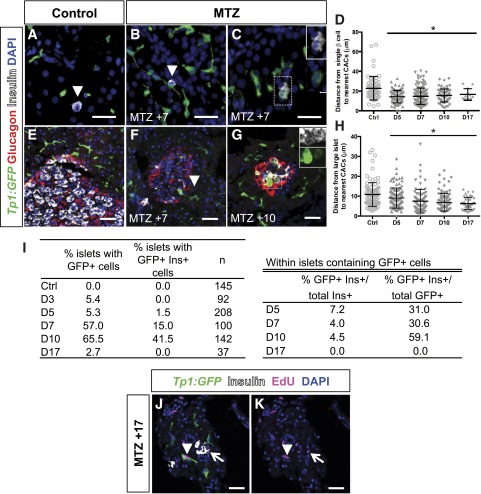
Figure 5.
CACs respond dynamically and proliferate during β-cell regeneration. A–C: ins:NTR fish contain single β-cells (arrowheads) (A), which become more closely associated with CACs by MTZ +7 days (B). GFP/insulin double-positive single cells are seen at this time (C). D: Quantification of the distance between single β-cells and the nearest two CACs. E: Large islets are also associated with CACs. F: By MTZ +7 days, CACs (arrowhead) are also found within islets. G: GFP/insulin double-positive cells are observed in islets at MTZ +10 days (inset). H: Quantification of the distance between islets and the nearest two CACs. I: Quantification of the percentage of islets containing Notch-responsive cells and the percentage of islets containing GFP/insulin (Ins) double-positive cells. Within those islets containing GFP+ cells, quantification of GFP+ β-cells and insulin+ CACs. J and K: At MTZ +17 days, β-cells (open arrow) and CACs (arrowhead) have incorporated EdU. Tp1:GFP (green), anti-glucagon (red), anti-insulin (white), anti-EdU (magenta), DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. Ctrl, control; D, day. *P < 0.05, t test compared with control.
Large islets were associated with CACs in regenerating and control pancreata (Fig. 5E). During regeneration, the distance between large islets and CACs significantly decreased (10.84 ± 0.6 μm in controls vs. 6.27 +/− 0.4 μm at MTZ +17, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 5H). GFP-positive cells, many of which coexpressed insulin (59.1% at MTZ +10 days, 7 of 7 fish), could even be found inside regenerating islets (Fig. 5F, G, and I). Together, these results are consistent with CAC migration during regeneration—a hypothesis supported by similar observations in rodents (39).
We also observed cell proliferation during β-cell regeneration using EdU incorporation (40). Fish were coinjected with EdU on MTZ +0 days and every other day thereafter until sacrifice. In contrast to controls, by MTZ +17 days many β-cells were labeled with EdU (4% vs. 50%, n = 4 and 6 fish, respectively), and CACs peripheral to islets were also EdU labeled (6% vs. 30%, respectively) (Fig. 5J and K). Thus, proliferation of both β-cells and CACs had occurred during regeneration after cell-specific ablation. Altogether, our observations led us to hypothesize that CACs play an active role in β-cell regeneration.
CACs Directly Contribute to β-Cell Regeneration
To directly test whether CACs are a bona fide adult progenitor population, we used our cre-based strategy to lineage trace Notch-responsive cells (12,41). This system uses two transgenes: 1) a Notch-responsive cre driver, Tp1:CreERT2, and 2) the cre responder, βactin:lox-stop-lox-hmgb1-mCherry. Zebrafish carrying both transgenes are called lineage-tracing fish (LT). Addition of 4OHT to LT fish indelibly labels Notch-responsive cells with nuclear-mCherry (nuc-mCherry). To quantify the efficiency of 4OHT-dependent labeling in adults, we used LT fish that also carried the Notch-responsive reporter, Tp1:GFP. After injection of adult LT; Tp1:GFP fish with 4OHT daily for 3 days, 75% of GFP-positive cells were labeled with nuc-mCherry (n = 5) (Fig. 6A–C).
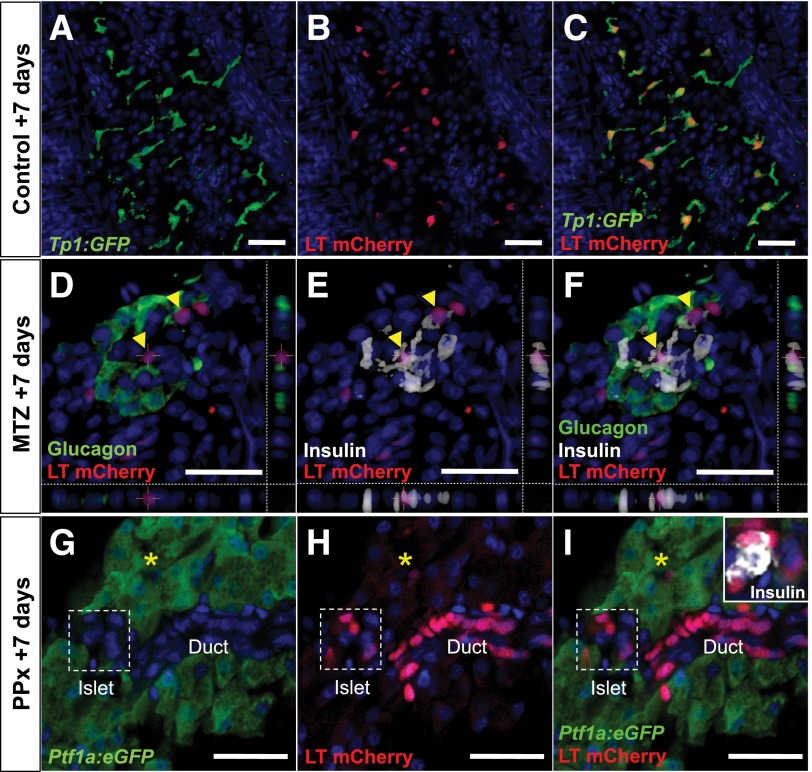
Figure 6.
CACs are progenitors of endocrine and ductal cell types. A–C: 4OHT injection labels 75% of Notch-responsive cells (green) with nuc-mCherry (red nuclei) in LT; Tp1:GFP fish. D–F: LT; ins:NTR regenerating islets at MTZ +7 days. nuc-mCherry labels insulin-expressing CAC progeny (yellow arrowheads). G–I: LT; Ptf1a:gfp fish at PPx +7 days. nuc-mCherry (red nuclei) labels regenerating duct, CACs (yellow asterisks), and insulin-expressing islet cells (white) but not eGFP-positive acinar cells (green). Anti-insulin (white), anti-glucagon (green in B), anti-mCherry (red), DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 25 μm.
LT; ins:NTR triple-transgenic zebrafish were injected daily for 3 days with 4OHT to label CACs and on the next day were injected with MTZ to induce β-cell ablation. Control fish received identical 4OHT injections followed by vehicle injection. In control pancreata, nuc-mCherry label was seen in CACs but never in insulin-expressing cells (n = 1,191 cells from 5 fish). During early regeneration at MTZ +3 days, β-cells were ablated and only CACs were nuc-mCherry labeled, as in controls. However, by MTZ +7 days, in addition to CACs, cells within recovering islets were also labeled. At MTZ +10 days, 43% of insulin-expressing cells were nuc-mCherry labeled (n = 320 cells from 4 fish) (Fig. 6D–F). Hence, we concluded that CACs are progenitors that contribute to β-cell neogenesis.
CACs Contribute to Ductal Cells and Endocrine Cells After Partial Pancreatectomy
We predicted that adult CACs represent a progenitor source for other pancreatic cell types. To test this capacity of CACs during regeneration, we next used PPx in LT; Ptf1a:eGFP double-transgenic fish, which express enhanced GFP (eGFP) in all acinar cells. We injected fish with 4OHT and EdU as previously before surgically removing the left pancreatic lobe and treating with EdU for the following 7 days. By PPx +7 days, the operated pancreata appeared indistinguishable from sham controls and 27.6% of the cells in the regenerating lobe had incorporated EdU (vs. 1% in sham controls, n = 5 and 5, respectively), demonstrating that proliferation had occurred (Supplementary Fig. 4). We detected nuc-mCherry–labeled endocrine cells, ductal cells, and CACs in the regenerated lobe but did not observe nuc-mCherry label in eGFP-expressing acinar cells (Fig. 6G–I). Accordingly, we concluded that CACs represent a progenitor pool for both endocrine and ductal cells during regeneration, as do larval CACs during development (12).
cftr Is Necessary for Pancreas Development
Having established that CACs are endocrine and ductal progenitors during development and regeneration, we next became interested in whether any of the CAC markers that we identified were important for pancreas development. The expression of cftr in CACs is of particular interest, as loss of function of this gene in humans leads to cystic fibrosis (CF), a debilitating disorder associated in 90% of cases with pancreatic insufficiency, pancreatic ductal blockage, and CF-related diabetes (CFRD) (42). Analysis of the pancreata from cftr mutant larvae showed that by 5 dpf, there was a small but significant deficit in pancreas size and fewer Nkx6.1-expressing larval CACs (Fig. 7A–C, G, and H). Consequently, the potential of cftr−/− larvae to produce secondary islets was also significantly reduced (Fig. 7D–F and I), although this reduction did not affect glycemia (Supplementary Fig. 5). Taken together, our results suggest that Cftr plays a role in zebrafish CAC development and function. Ultimately, cftr mutant fish may serve as a critically important CFRD disease model.
Figure 7.
Cftr plays an important role in the pancreas. A–F: Five dpf cftr−/− pancreata have fewer CACs (anti-Nkx6.1, green) (A–C), and secondary islet cells induced by DAPT treatment (anti-insulin plus anti-glucagon plus anti-somatostatin, arrows, red) (D–F) compared with cftr+/− and wild-type pancreata. Scale bar = 100 μm. G–I: Quantification of the number (#) of CACs (G), surface area (H), and number of induced secondary islet cells (I) in wild-type, cftr+/−, and cftr−/− 5 dpf pancreata. N, number of pancreata quantified. **P < 0.05. ***P < 0.001, t test.
Discussion
Previously, we described a pancreatic Notch-responsive population that resides in the larval ducts. These progenitor cells differentiate and give rise to at least three kinds of cells in the adult: endocrine cells, ductal cells, and CACs. Two pieces of data suggested that CACs may also be progenitors: 1) as shown previously by us and others, CACs closely resemble their larval precursors in terms of morphology and ultrastructure (10,13,39), and 2) as reported here, our newly discovered markers for adult CACs are also expressed in the larval progenitors. As we are interested in the cellular origins of β-cell regeneration, we decided that CACs were a promising candidate and set out to see whether these cells were involved in pancreas recovery after tissue damage.
Using a Notch-responsive reporter, we observed CACs physically responding to the regeneration process, even appearing to infiltrate damaged islets. However, the formal possibility existed that non-CAC cells of unknown origin became Notch responsive during the regenerative response. Therefore, we used genetic lineage tracing of Notch-responsive cells in our LT fish to label CACs and their progeny before tissue damage. The presence of labeled cells near the periphery of islets suggests that lineage-traced CACs migrate from their centroacinar position toward damaged islets. Interestingly, our functional annotation analysis revealed that the CAC transcriptome is significantly enriched for genes important for cell migration in other contexts (e.g., cxcl12, npr2a). Investigation into the role these genes play during β-cell regeneration may reveal the mechanism behind this remarkable movement.
Clearly, β-cells can regenerate via neogenesis from CACs in the adult zebrafish pancreas in a manner analogous to endocrine formation during development. However, the precise extent to which CACs contribute to β-cell neogenesis cannot be reliably quantified using our methods. For reasons discussed below, our data (and those of other lineage tracing experiments) should not be overinterpreted. Additionally, we appreciate that other cell types also contribute to pancreas regeneration, such as α- and δ-cells that have been shown to transdifferentiate in murine and zebrafish models of β-cell loss (43–45).
Hepatocytes in the liver of zebrafish can regenerate from biliary epithelial cells (BECs) in larvae and adults (41). Like CACs, BECs are Notch-responsive ductal cells. Hepatocyte regeneration is dependent on the function of the transcription factor Sox9b, which is upregulated as biliary epithelial cells dedifferentiate (41). Sox9b function is also required for the differentiation of pancreas progenitors toward an endocrine fate (31). In contrast to BECs, we observe that CACs maintain developmental programs, as evidenced by their continued expression of sox9b and nkx6.1. Indeed, the master regulators of β-cell differentiation nxk6.1 and nkx2.2a are expressed in fish CACs but not in mammalian CACs (34,38). This difference may underlie the enhanced ability of the zebrafish pancreas to regenerate after β-cell loss, as maintenance of developmental programs in fish CACs may allow them to be continually available for differentiation once the need for new β-cells arises.
The notion that CACs and/or ductal cell types contribute to adult β-cell neogenesis in mammals has been the focus of intense scrutiny. A number of studies have used various loci to lineage trace CACs/ductal cells during murine pancreas development and regeneration including CAII (20), Hnf1β (21), Muc1 (22), Hes1 (23), and Sox9 (24). While all of the labeled cell populations contributed to the endocrine compartment during embryogenesis, most of these studies were unable to demonstrate that adult pancreatic ductal cells contribute to β-cell neogenesis after either pancreatic ductal ligation or β-cell–specific ablation in adults (21–24). However, the results of these studies come with several caveats. If genes important in maintaining progenitor status (thus blocking differentiation) are used to drive lineage tracing, the highest creER activity will likely occur in cells that are the least expected to differentiate. As such, unless 100% of a particular cell population can be reliably labeled, one cannot definitively rule out the contribution of ductal cells to β-cell regeneration in mammals. Therefore, the contribution of zebrafish CACs to β-cell regeneration presents an intriguing and potentially critical model of β-cell neogenesis from endogenous progenitors.
Despite conflicting evidence for CAC contribution to mammalian pancreas regeneration, injury does seem to reactivate developmental pathways in the adult pancreas. After pancreatic ductal ligation, Sox9-expressing ductal cells give rise to a few cells expressing Ngn3 (24), a gene that encodes a master regulator of embryonic endocrine differentiation. In another study, lineage tracing of Ngn3-expressing cells demonstrated that some of these cells do indeed complete differentiation and become β-cells (46). Although this latter result clearly demonstrates that neogenesis can occur in the mammalian pancreas, this form of regeneration is very limited and dependent on the severity of the injury. Interestingly, isolated aldehyde dehydrogenase isoform 1 (ALDH1)+ murine CACs/terminal ductal cells can produce endocrine cells in both pancreatosphere and dorsal bud explant cultures (47). However, whether these ALDH1+ cells are in fact CACs is unclear, as they do not highly express Hes1, a downstream target of canonical Notch signaling and a hallmark of CACs (10,15,16). In the fish, Aldh1-expressing cells have recently been described in association with, but separate from, larval and juvenile CACs (48). Whether CACs represent a genetically uniform or heterogeneous population in either fish or mammals remains to be determined. Regardless, all together these observations suggest that it may be possible to manipulate developmental pathways in the adult in order to improve the regenerative capacity of the mammalian pancreas.
Knowing that CACs are adult progenitors in the pancreas will facilitate future studies into other human diseases. As an example, we decided to study the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (cftr), transcripts for which are highly enriched in zebrafish CACs. Abnormal CFTR channel function causes CF, a debilitating disease often associated with CFRD. CFRD is characterized by diminished β-cell mass and insulin dependence (42). Our examination of cftr mutant larvae (5 dpf) revealed that these fish had a small but significant reduction in pancreas size. Such early pancreatic phenotypic consequences of Cftr loss of function were not observed by Navis and Bagnat (37). There are numerous reasons for this apparent discrepancy between studies: 1) the well-documented occurrence of phenotypic variation in CF due to modifiers in the genetic background (49), 2) confocal microscopy on microdissected pancreata providing better resolution, and 3) potential differences in animal husbandry, which is known to affect phenotype in other CF animal models (50). Using our Notch-responsive reporters and microdissection to facilitate careful observation, we detect fewer CAC progenitors in cftr mutant larvae. Possibly due to having fewer progenitors, these fish develop fewer secondary islets. As patients with CFRD have a diminished β-cell mass, these observations in mutant fish are intriguing and warrant further investigation.
In summary, regeneration occurs readily in the adult zebrafish pancreas, and we believe that studies with this model organism will continue to shed light on mechanisms that can be exploited to improve regeneration in diabetic patients. Furthermore, our new insights into the importance of cftr in pancreas development suggest that the role of CFTR in the human pancreas should be reevaluated.
Supplementary Material
Article Information
Acknowledgments. The authors thank Dr. Garry Cutting and Dr. David Hackam of Johns Hopkins University for critical reading of the manuscript and Dr. Sarah Kucenas of Vanderbilt University and Dr. Michel Bagnat of Duke University for fish. The authors also thank Frazer Matthews for his invaluable fish facility management and laboratory support.
Funding. This work was supported by Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation International grant 17-2012-408; National Institutes of Health grants R01DK080730, 5P30DK079637, and 1F32DK101289; and the Maryland Stem Cell Research Fund 2013 Postdoctoral Fellowship.
Duality of Interest. No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author Contributions. F.D. and R.L.B. researched data and wrote the manuscript. M.R. researched data and reviewed the manuscript. W.H., G.W., S.G., and M.d.C.V. researched data. S.J.W. analyzed data and contributed to discussion. M.J.P. wrote and edited the manuscript and contributed to discussion. M.J.P. is the guarantor of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Footnotes
This article contains Supplementary Data online at http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.2337/db15-0153/-/DC1.
References
- 1.Moss JB, Koustubhan P, Greenman M, Parsons MJ, Walter I, Moss LG. Regeneration of the pancreas in adult zebrafish. Diabetes 2009;58:1844–1851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pisharath H, Rhee JM, Swanson MA, Leach SD, Parsons MJ. Targeted ablation of beta cells in the embryonic zebrafish pancreas using E. coli nitroreductase. Mech Dev 2007;124:218–229 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Poss KD. Advances in understanding tissue regenerative capacity and mechanisms in animals. Nat Rev Genet 2010;11:710–722 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Faustman DL, Tran SD, Kodama S, et al. Comment on papers by Chong et al., Nishio et al., and Suri et al. on diabetes reversal in NOD mice. Science 2006;314:1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meier JJ, Bhushan A, Butler AE, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Sustained beta cell apoptosis in patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes: indirect evidence for islet regeneration? Diabetologia 2005;48:2221–2228 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Suri A, Calderon B, Esparza TJ, Frederick K, Bittner P, Unanue ER. Immunological reversal of autoimmune diabetes without hematopoietic replacement of beta cells. Science 2006;311:1778–1780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bonner-Weir S, Li WC, Ouziel-Yahalom L, Guo L, Weir GC, Sharma A. Beta-cell growth and regeneration: replication is only part of the story. Diabetes 2010;59:2340–2348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kopp JL, Dubois CL, Hao E, Thorel F, Herrera PL, Sander M. Progenitor cell domains in the developing and adult pancreas. Cell Cycle 2011;10:1921–1927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xiao X, Chen Z, Shiota C, et al. No evidence for β cell neogenesis in murine adult pancreas. J Clin Invest 2013;123:2207–2217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Parsons MJ, Pisharath H, Yusuff S, et al. Notch-responsive cells initiate the secondary transition in larval zebrafish pancreas. Mech Dev 2009;126:898–912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen S, Li C, Yuan G, Xie F. Anatomical and histological observation on the pancreas in adult zebrafish. Pancreas 2007;34:120–125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang Y, Rovira M, Yusuff S, Parsons MJ. Genetic inducible fate mapping in larval zebrafish reveals origins of adult insulin-producing β-cells. Development 2011;138:609–617 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Leeson TS, Leeson R. Close association of centroacinar/ductular and insular cells in the rat pancreas. Histol Histopathol 1986;1:33–42 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ekholm R, Zelander T, Edlund Y. The ultrastructural organization of the rat exocrine pancreas. II. Centroacinar cells, intercalary and intralobular ducts. J Ultrastruct Res 1962;7:73–83 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Miyamoto Y, Maitra A, Ghosh B, et al. Notch mediates TGF alpha-induced changes in epithelial differentiation during pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2003;3:565–576 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stanger BZ, Stiles B, Lauwers GY, et al. Pten constrains centroacinar cell expansion and malignant transformation in the pancreas. Cancer Cell 2005;8:185–195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gasslander T, Ihse I, Smeds S. The importance of the centroacinar region in cerulein-induced mouse pancreatic growth. Scand J Gastroenterol 1992;27:564–570 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hayashi K, Takahashi T, Kakita A, Yamashina S. Regional differences in the cellular proliferation activity of the regenerating rat pancreas after partial pancreatectomy. Arch Histol Cytol 1999;62:337–346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Seymour PA, Freude KK, Tran MN, et al. SOX9 is required for maintenance of the pancreatic progenitor cell pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:1865–1870 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Inada A, Nienaber C, Katsuta H, et al. Carbonic anhydrase II-positive pancreatic cells are progenitors for both endocrine and exocrine pancreas after birth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:19915–19919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Solar M, Cardalda C, Houbracken I, et al. Pancreatic exocrine duct cells give rise to insulin-producing beta cells during embryogenesis but not after birth. Dev Cell 2009;17:849–860 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kopinke D, Murtaugh LC. Exocrine-to-endocrine differentiation is detectable only prior to birth in the uninjured mouse pancreas. BMC Dev Biol 2010;10:38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kopinke D, Brailsford M, Shea JE, Leavitt R, Scaife CL, Murtaugh LC. Lineage tracing reveals the dynamic contribution of Hes1+ cells to the developing and adult pancreas. Development 2011;138:431–441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kopp JL, Dubois CL, Schaffer AE, et al. Sox9+ ductal cells are multipotent progenitors throughout development but do not produce new endocrine cells in the normal or injured adult pancreas. Development 2011;138:653–665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nagasao J, Yoshioka K, Amasaki H, et al. Morphological changes in the rat endocrine pancreas within 12 h of intravenous streptozotocin administration. Anat Histol Embryol 2005;34:42–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hayashi KY, Tamaki H, Handa K, Takahashi T, Kakita A, Yamashina S. Differentiation and proliferation of endocrine cells in the regenerating rat pancreas after 90% pancreatectomy. Arch Histol Cytol 2003;66:163–174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gasslander T, Smeds S, Blomqvist L, Ihse I. Proliferative response of different exocrine pancreatic cell types to hormonal stimuli. I. Effects of long-term cerulein administration. Scand J Gastroenterol 1990;25:1103–1110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011;12:323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Leng N, Dawson JA, Thomson JA, et al. EBSeq: an empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2013;29:1035–1043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Westerfield M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Eugene, OR, University of Oregon Press, 2000 [Google Scholar]
- 31.Manfroid I, Ghaye A, Naye F, et al. Zebrafish sox9b is crucial for hepatopancreatic duct development and pancreatic endocrine cell regeneration. Dev Biol 2012;366:268–278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Eames SC, Philipson LH, Prince VE, Kinkel MD. Blood sugar measurement in zebrafish reveals dynamics of glucose homeostasis. Zebrafish 2010;7:205–213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Navis A, Marjoram L, Bagnat M. Cftr controls lumen expansion and function of Kupffer’s vesicle in zebrafish. Development 2013;140:1703–1712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schaffer AE, Taylor BL, Benthuysen JR, et al. Nkx6.1 controls a gene regulatory network required for establishing and maintaining pancreatic Beta cell identity. PLoS Genet 2013;9:e1003274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, et al. The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: a novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol 2007;8:R183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huang W, Wang G, Delaspre F, Vitery MdelC, Beer RL, Parsons MJ. Retinoic acid plays an evolutionarily conserved and biphasic role in pancreas development. Dev Biol 2014;394:83–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Navis A, Bagnat M. Loss of cftr function leads to pancreatic destruction in larval zebrafish. Dev Biol 2015;399:237–248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sussel L, Kalamaras J, Hartigan-O’Connor DJ, et al. Mice lacking the homeodomain transcription factor Nkx2.2 have diabetes due to arrested differentiation of pancreatic beta cells. Development 1998;125:2213–2221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pour PM. Pancreatic centroacinar cells. The regulator of both exocrine and endocrine function. Int J Pancreatol 1994;15:51–64 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chehrehasa F, Meedeniya AC, Dwyer P, Abrahamsen G, Mackay-Sim A. EdU, a new thymidine analogue for labelling proliferating cells in the nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 2009;177:122–130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.He J, Lu H, Zou Q, Luo L. Regeneration of liver after extreme hepatocyte loss occurs mainly via biliary transdifferentiation in zebrafish. Gastroenterology 2014;146:789–800.e8 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Hameed S, Jaffé A, Verge CF. Cystic fibrosis related diabetes (CFRD)--the end stage of progressive insulin deficiency. Pediatr Pulmonol 2011;46:747–760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Thorel F, Népote V, Avril I, et al. Conversion of adult pancreatic alpha-cells to beta-cells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature 2010;464:1149–1154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chera S, Baronnier D, Ghila L, et al. Diabetes recovery by age-dependent conversion of pancreatic δ-cells into insulin producers. Nature 2014;514:503–507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ye L, Robertson MA, Hesselson D, Stainier DY, Anderson RM. Glucagon is essential for alpha cell transdifferentiation and beta cell neogenesis. Development 2015;142:1407–1417 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Van de Casteele M, Leuckx G, Cai Y, et al. Partial duct ligation: β-cell proliferation and beyond. Diabetes 2014;63:2567–2577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rovira M, Scott SG, Liss AS, Jensen J, Thayer SP, Leach SD. Isolation and characterization of centroacinar/terminal ductal progenitor cells in adult mouse pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:75–80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Matsuda H, Parsons MJ, Leach SD. Aldh1-expressing endocrine progenitor cells regulate secondary islet formation in larval zebrafish pancreas. PLoS One 2013;8:e74350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Blackman SM, Commander CW, Watson C, et al. Genetic modifiers of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. Diabetes 2013;62:3627–3635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wilke M, Buijs-Offerman RM, Aarbiou J, et al. Mouse models of cystic fibrosis: phenotypic analysis and research applications. J Cyst Fibros 2011;10(Suppl. 2):S152–S171 [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.