Abstract
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine malignancy with increasing incidence. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is an important downstream mediator of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K/Akt) signaling and regulates cell growth, apoptosis and metabolism. The mTOR gene is frequently mutated in human cancers. Although PI3K/Akt pathway and its component genes were extensively studied in thyroid cancer, it is not known whether mTOR gene is somatically mutated and play a role in differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). To determine the status of mTOR mutations in 53 DTC, we extensively examined 19 selected exons of mTOR gene which were reported to be frequently mutated in other human cancers. Unlike in other human cancers, we did not find common somatic mutations in the mTOR gene in differentiated thyroid cancer, except for some synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms. Our results suggest that mTOR mutation is very rare and may not play a significant role in DTC.
Keywords: mTOR Mutation, Oncogene, Thyroid, PI3K/Akt signaling, MTOR
1. Introduction
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine malignancy with increasing incidence in many parts of the world. The follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer is histologically classified into differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), poorly differentiated thyroid cancer (PDTC) and anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC). DTC is further classified to papillary (PTC) and follicular thyroid cancer (FTC). Genes of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling (EGFR, Ras, BRAF, RET/PTC, etc.) and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt (PI3K/Akt) signaling (ALK, PIK3CA, PTEN, AKT1, etc.) pathways are the most frequently mutated genes in thyroid cancer (Xing, 2013; Murugan et al., 2011). Aberrant activation of these major signaling pathway genes results in uncontrolled cell division, proliferation, invasion and metastasis. (Liu et al., 2008; Murugan & Xing, 2011). mTOR is a serine/threonine kinase that is an important downstream mediator of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. The mTOR is a key regulator of protein synthesis, cell size and growth, apoptosis, and metabolism in response to nutrients, growth factors and cellular energy. It is frequently deregulated in many types of human cancers (Cornu et al., 2013). Recently, whole exome sequencing of ATC showed 9% (2/22) of somatic point mutations (R164Q and M2327I) in mTOR gene (Kunstman et al., 2015). An mTOR mutation (F2108L) has also recently been found in a whole exome sequencing of a patient with ATC (Wagle et al., 2014). However, to our knowledge, systematic search for mTOR mutations in DTC in a large sample using conventional methods has not been undertaken despite the importance of the PI3K/Akt pathway and its component genes which were extensively studied in thyroid cancer (Liu et al., 2008). We therefore, analyzed the mTOR mutations both in benign and follicular cell-derived DTC in a series of patients including a sample with highly aggressive histopathological features from Saudi Arabia.
2. Materials and methods
We initially analyzed 63 thyroid neoplasms that include 10 benign multi nodular goiters and 53 DTC (41 classical papillary thyroid cancer (CPTC), 7 follicular variant (FVPTC), 1 tall cell variant, 1 hurthle cell cancer, 1 columnar cell variant PTC, and 2 PDTC). After obtaining an institutional review board (IRB) approval, the tumor samples were carefully examined by an endocrine pathologist and 10 μm tumor samples were dissected from formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue. Genomic DNA was extracted using the Gentra Puregene DNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to the manufacturer's instruction. The primers were designed to encompass the exon and the exon-intron boundaries (Table 1). Since the mTOR gene is large with 58 exons, we choose exons that were previously reported to be frequently mutated in other human cancers (exons 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 12, 16, 21, 25, 29, 38, 42, 46, 50, 51, 52, and 55) based on the COSMIC (Catalog of Somatic Mutations in Cancer) Database, UK. (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cancergenome/projects/cosmic/). The PCR conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 1 min, annealing at 59 °C for 45 s, and extension at 72 °C for 45 s. This was followed by a final extension step at 72 °C for 7 min. We amplified the selected exons by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and directly sequenced the PCR product using the Big Dye terminator v3.1 cycle sequencing ready reaction kit (Applied Biosystems). Identified genetic variants were confirmed in forward and reverse directions. After the completion of screening of the 63 samples for the exons mentioned above and in order to increase the chance of finding mutations, we then extended our search for mTOR mutations to 21 selected high grade tumors (large tumors with extra-thyroidal extension and lymph node metastases and/or distant metastases) and limited our search to the most frequently previously described mutated exons (1, 3, 21, 38, 42, 46, and 55). GenBank accession number of mTOR gene is NM_004958.3.
Table 1.
Primers used for PCR amplification of the mTOR gene.
| Exons | Sense | (5′→ 3′) | Antisense |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GTGACCAGGGCCATAAGTAAAT | GACAGGTTGGGTGCCTTTAT | |
| 2 | CCACCACCACAGTTAGAGAATTA | CAGGGCTGCTGCTAGAATTA | |
| 3 | CCTCCCAAAGTGCTAGGATTAC | CCACCACACCATGCTAGATT | |
| 4 | TCCTGGTGTGTATGGCTCTAA | TTTGCTAGTGGTGGGAATGG | |
| 5 | TAGATGGGATGGGCCTGTAT | CTTGCCTCGCTCACAGAAT | |
| 6 | TAGTTGCGTTTCGGGATTAGG | ACACCTGAGAGAGGAAGGATAA | |
| 8 | CCTAACCCTGACCTGGAGC | TGGGCGTAAGCTCCGTGGA | |
| 12 | AATCTTCCCACTACGCTGATG | CAGGGAAACATTTGGACCTTTG | |
| 16 | TCTCGTACTGGCTCATTGAATC | CCATCGTCCCAGCAAAGT | |
| 21 | GCTGCGTGTCCTTAGATACTT | GAAAGATGGCCTGGGAACTTA | |
| 25 | AATTGGCCCTTGAAACTGATTG | AGATGCTACAGTATGAGCTTGTT | |
| 29 | AGCAGCACATTAGGAAAGAGAG | CTGAAGTGAGAACTCCGTGTG | |
| 38 | CCATTTCTGAGTGTCTCCTTGA | GCAGTGCTGGATGGTAGATAG | |
| 42 | CTGGTAGTCTCAAGCAGATGTT | TGGAGACACAGGAGGTACTATT | |
| 46 | GAGCTGAGGACCTCTGATGTA | CATGCCTGGCTCCCTAATTT | |
| 50 | AGATAGCACCACTGCCTTC | GACCTTACATATACAATAC | |
| 51 | ATCGTTTGCCAACTCCTAG | TTAACTACAGCCTTGGTAG | |
| 52 | TTGCTTTGGGTGGAGAGTTAG | CCAGTCTCAGGCAGTTCTTTAT | |
| 55 | CCTGTTGTATTGCTCCCATTCT | GTGCCAAAGCTCGTCACTAA |
3. Results
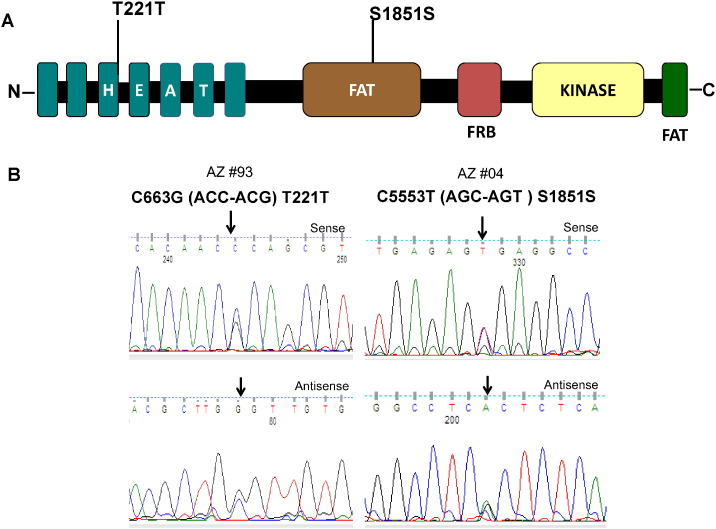
Irrespective of our approach, neither the initial screening of 63 randomly selected thyroid tumors (exons 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 12, 16, 21, 25, 29, 38, 42, 46, 50, 51, 52, and 55) nor the further search in the 21 high grade thyroid cancer revealed mTOR mutations (exons 1, 3, 21, 38, 42, 46, 50, 51, 52 and 55). Nonetheless, as illustrated in Fig. 1, we found a rare synonymous genetic variant resulting in C > G transversion (C663G) in 1 out 63 samples (1.6%) and a frequent synonymous variant resulting in C > T transition (C5333T) in 14 out of 84 samples, (16%). Both of these single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been reported (C663G, rs112439072; C5553T, rs2275527) in the SNP databases (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP/) and (http://asia.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Transcript/Variation_Transcript/).
Fig. 1.
Identification of mTOR genetic variants. A) Schematic diagram of domains of mTOR protein showing single nucleotide polymorphisms (T221T and S1851S) identified in thyroid cancer. B) The sequencing results were shown with a representative sense and antisense sequence chromatogram of single nucleotide polymorphisms found in exons 4 and 38, respectively.
4. Discussion
The mTOR and its canonical signaling pathway has been shown to be frequently deregulated in human cancer and has become a major therapeutic target. Point mutations of the mTOR gene are expected to play an important role in tumorigenesis and tumor invasion as it has been recently demonstrated that artificially induced mutations of conserved amino acids in mTOR exhibit gain-of-function and oncogenic potential both in vitro and in vivo (Murugan et al., 2013). Furthermore, natural somatic mTOR mutations identified in other types of human cancer have also been shown to be activating mutations leading to increased rapamycin sensitivity (Grabiner et al., 2014). mTOR mutations have rarely been investigated in thyroid cancer. However, in a patient with ATC, an mTOR mutation was identified and shown to confer resistance to allosteric mTOR inhibition, although this mTOR mutation has been shown to be sensitive to mTOR kinase inhibitors (Wagle et al., 2014). Therefore, finding mTOR mutations in a patient not only becomes an important factor in the selection of cancer treatment but might be a valuable and promising prognostic marker.
In this report, we found two previously reported SNPs but no other genetic variants. These results suggest that somatic mutations of the mTOR gene are rare in DTC and genetic alterations of mTOR gene may not play a significant role in the pathogenesis of this cancer. Genetic mutations in other genes in the PIK3/AKT pathway including PIK3CA, PTEN, and AKT have been described in thyroid cancer, mostly in PDTC. It has also been reported that other genetic deregulation of the genes of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is common in PDTC (Liu et al., 2008) but not DTC wherein the majority of the MAPK pathway genes are commonly mutated (Xing, 2013). Furthermore, as the previously reported mTOR mutations were from patients with ATC, we considered the possibility that mTOR mutations might be limited to high grade PTC. However, our search for mTOR mutations in 21 such samples in the most frequently mutated exons yielded no mutations. We have analyzed a large number of previously reportedly mutated mTOR exons. However, it is also possible that mTOR mutations occur in the other non-analyzed exons of mTOR and may also occur in other ethnic groups. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that systematically analyzed a large number of mTOR exons for mutations in a relatively large sample of thyroid cancer using standard methods of PCR and Sanger sequencing.
Despite the low yield of mutations in this study, further studies from other ethnic backgrounds are warranted focusing on more advanced thyroid cancer types and analyzing all exons of mTOR in order to make definitive conclusions on the role of the mTOR mutations in thyroid cancer and its sub-types.
Declaration of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (12-BIO2952-20).
References
- Cornu M., Albert V., Hall M.N. mTOR in aging, metabolism, and cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013;23:53–62. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabiner B.C., Nardi V., Birsoy K., Possemato R., Shen K., Sinha S., Jordan A., Beck A.H., Sabatini D.M. A diverse array of cancer-associated mTOR mutations are hyperactivating and can predict rapamycin sensitivity. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:554–563. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunstman J.W., Juhlin C.C., Goh G., Brown T.C., Stenman A., Healy J.M., Rubinstein J.C., Choi M., Kiss N., Nelson-Williams C., Mane S., Rimm D.L., Prasad M.L., Höög A., Zedenius J., Larsson C., Korah R., Lifton R.P., Carling T. Characterization of the mutational landscape of anaplastic thyroid cancer via whole-exome sequencing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015;24:2318–2329. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Hou P., Ji M., Guan H., Studeman K., Jensen K., Vasko V., El-Naggar A.K., Xing M. Highly prevalent genetic alterations in receptor tyrosine kinases and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in anaplastic and follicular thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008;93:3106–3116. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-0273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murugan A.K., Xing M. Anaplastic thyroid cancers harbor novel oncogenic mutations of the ALK gene. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4403–4411. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murugan A.K., Alzahrani A., Xing M. Mutations in critical domains confer the human mTOR gene strong tumorigenicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:6511–6521. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.399485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murugan A.K., Dong J., Xie J., Xing M. Uncommon GNAQ, MMP8, AKT3, EGFR, and PIK3R1 mutations in thyroid cancers. Endocr. Pathol. 2011;22:97–102. doi: 10.1007/s12022-011-9155-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagle N., Grabiner B.C., Van Allen E.M., Amin-Mansour A., Taylor-Weiner A., Rosenberg M., Gray N., Barletta J.A., Guo Y., Swanson S.J., Ruan D.T., Hanna G.J., Haddad R.I., Getz G., Kwiatkowski D.J., Carter S.L., Sabatini D.M., Jänne P.A., Garraway L.A., Lorch J.H. Response and acquired resistance to everolimus in anaplastic thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:1426–1433. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1403352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing M. Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2013;12:245–262. doi: 10.1038/nrc3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]