Abstract
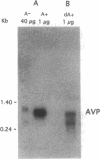
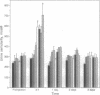
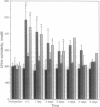
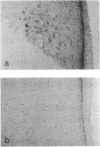
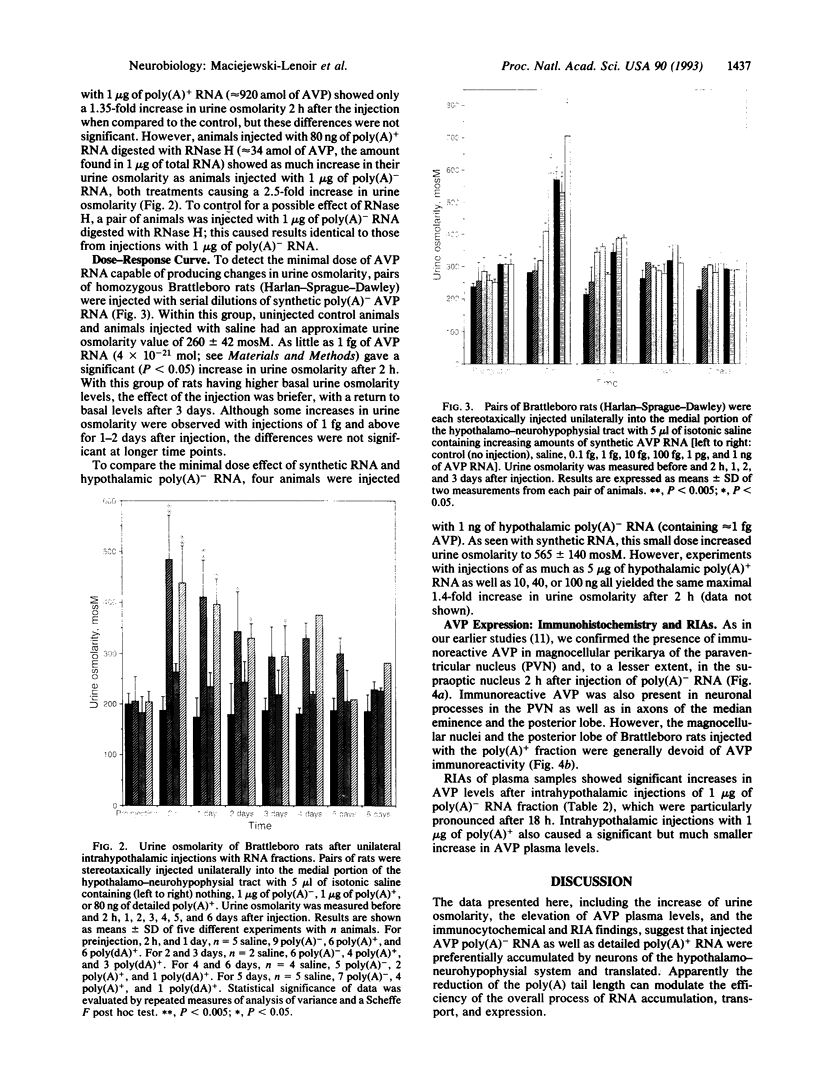
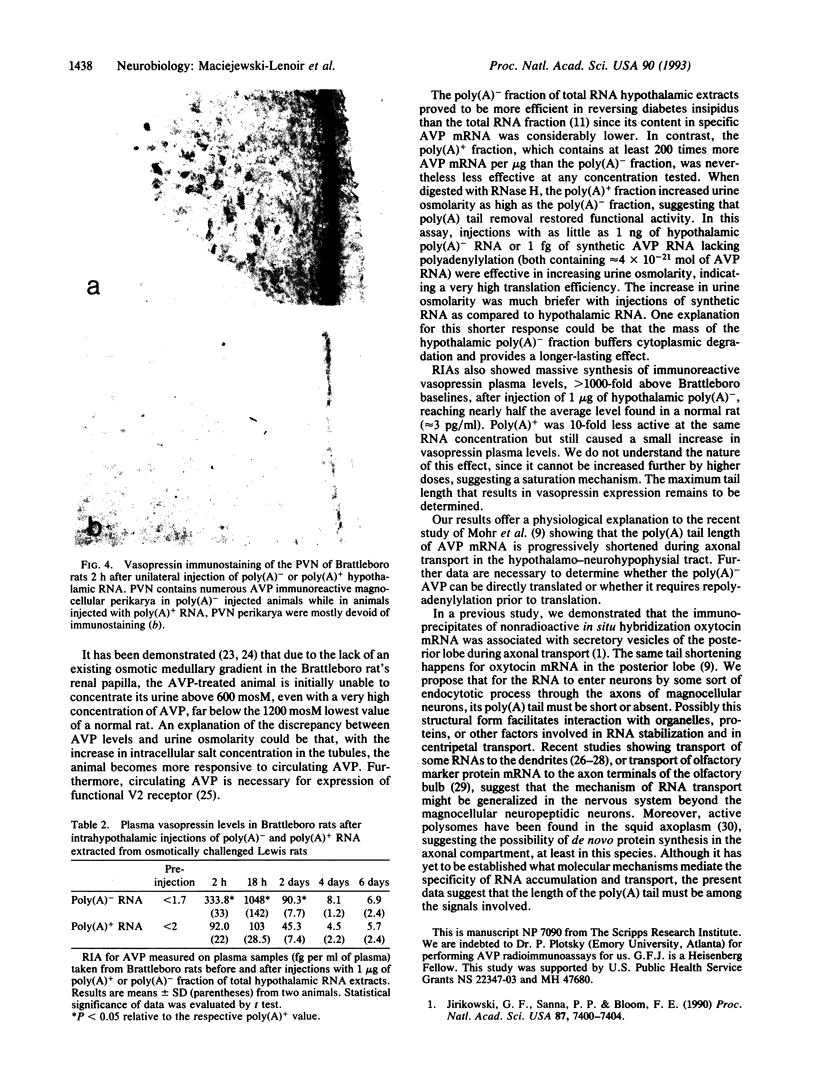
Magnocellular hypothalamic neurons in Brattleboro rats can accumulate, transport, and translate exogenous [Arg8]vasopressin (AVP) mRNA after injection in the hypothalamo-hypophysial tract in amounts sufficient to reverse transiently the animals' characteristic diabetes insipidus. In the present study, different preparations of hypothalamic RNA extracted from normal rats or synthetic AVP RNA were injected into the lateral hypothalamus of Brattleboro rats. Poly(A)- RNA and poly(A)+ RNA from which tails were removed by RNase H digestion were much more effective than poly(A)+ RNA in expressing AVP in the magnocellular hypothalamic neurons and in raising urine osmolarity. Synthetic AVP RNA lacking a poly(A) tail also produced a very potent dose-dependent diabetes insipidus reversal. Our results suggest that a short or absent poly(A) tail may facilitate the accumulation, transport, or expression of exogenous AVP mRNA by magnocellular neurons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch B., Guitteny A. F., Normand E., Chouham S. Presence of neuropeptide messenger RNAs in neuronal processes. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Feb 16;109(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90004-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckenstein D. A., Lein P. J., Higgins D., Fremeau R. T., Jr Distinct spatial localization of specific mRNAs in cultured sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):809–819. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90340-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrazana E. J., Pasieka K. B., Majzoub J. A. The vasopressin mRNA poly(A) tract is unusually long and increases during stimulation of vasopressin gene expression in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2267–2274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett L. E., Breckinridge S. M., Koike T. I. Induction of V2 receptors in renal medulla of homozygous Brattleboro rats by arginine vasopressin. Peptides. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):985–991. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlouhá H., Krecek J., Zicha J. Postnatal development and diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;394:10–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb37406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuditta A., Menichini E., Perrone Capano C., Langella M., Martin R., Castigli E., Kaplan B. B. Active polysomes in the axoplasm of the squid giant axon. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Jan;28(1):18–28. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490280103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington A. R., Valtin H. Impaired urinary concentration after vasopressin and its gradual correction in hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):502–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI105746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussler H. U., Jirikowski G. F., Caldwell J. D. Sex differences among oxytocin-immunoreactive neuronal systems in the mouse hypothalamus. J Chem Neuroanat. 1990 Jul-Aug;3(4):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivell R., Richter D. Structure and comparison of the oxytocin and vasopressin genes from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2006–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirikowski G. F. A non-surgical technique for accurate intracerebral injections in rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1992 Apr;42(1-2):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(92)90141-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirikowski G. F., Ramalho-Ortigao F. J., Caldwell J. D. Transitory coexistence of oxytocin and vasopressin in the hypothalamo neurohypophysial system of parturient rats. Horm Metab Res. 1991 Oct;23(10):476–480. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirikowski G. F., Sanna P. P., Bloom F. E. mRNA coding for oxytocin is present in axons of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7400–7404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirikowski G. F., Sanna P. P., Maciejewski-Lenoir D., Bloom F. E. Reversal of diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro rats: intrahypothalamic injection of vasopressin mRNA. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):996–998. doi: 10.1126/science.1546298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman R., Banker G., Steward O. Differential subcellular localization of particular mRNAs in hippocampal neurons in culture. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):821–830. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90341-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann E., Hänze J., Pauschinger M., Ganten D., Lang R. E. Vasopressin mRNA in the neurolobe of the rat pituitary. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 26;111(1-2):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90363-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig G., Hänze J., Lehmann E., Lang R. E., Burbach J. H., Ganten D. Measurement of mRNA by solution hybridization with 32P-labelled single stranded cRNA probe ("SP6 test"). Comparison with a 32P-labelled single stranded cDNA as hybridization probe ("S1 test") for measurement of AVP mRNA. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1988;10(3):467–483. doi: 10.3109/10641968809033904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr E., Fehr S., Richter D. Axonal transport of neuropeptide encoding mRNAs within the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract of rats. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2419–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr E., Zhou A., Thorn N. A., Richter D. Rats with physically disconnected hypothalamo-pituitary tracts no longer contain vasopressin-oxytocin gene transcripts in the posterior pituitary lobe. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81407-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Carter D. Vasopressin gene expression in the rodent hypothalamus: transcriptional and posttranscriptional responses to physiological stimulation. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1051–1059. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-7-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Levy A., Lightman S., Carter D. Vasopressin RNA in the neural lobe of the pituitary: dramatic accumulation in response to salt loading. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9002–9005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Tosi M., Pittet A. C., Fabiani L., Wellauer P. K. Tissue-specific expression of mouse alpha-amylase genes. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Richter D. Single base deletion in the vasopressin gene is the cause of diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro rats. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):705–709. doi: 10.1038/308705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh-Trang-Tan M. M., Bouby N., Kriz W., Bankir L. Functional adaptation of thick ascending limb and internephron heterogeneity to urine concentration. Kidney Int. 1987 Feb;31(2):549–555. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]