Figure 4. Inhibition of PPM1D increases RBM38 phosphorylation at ser195.
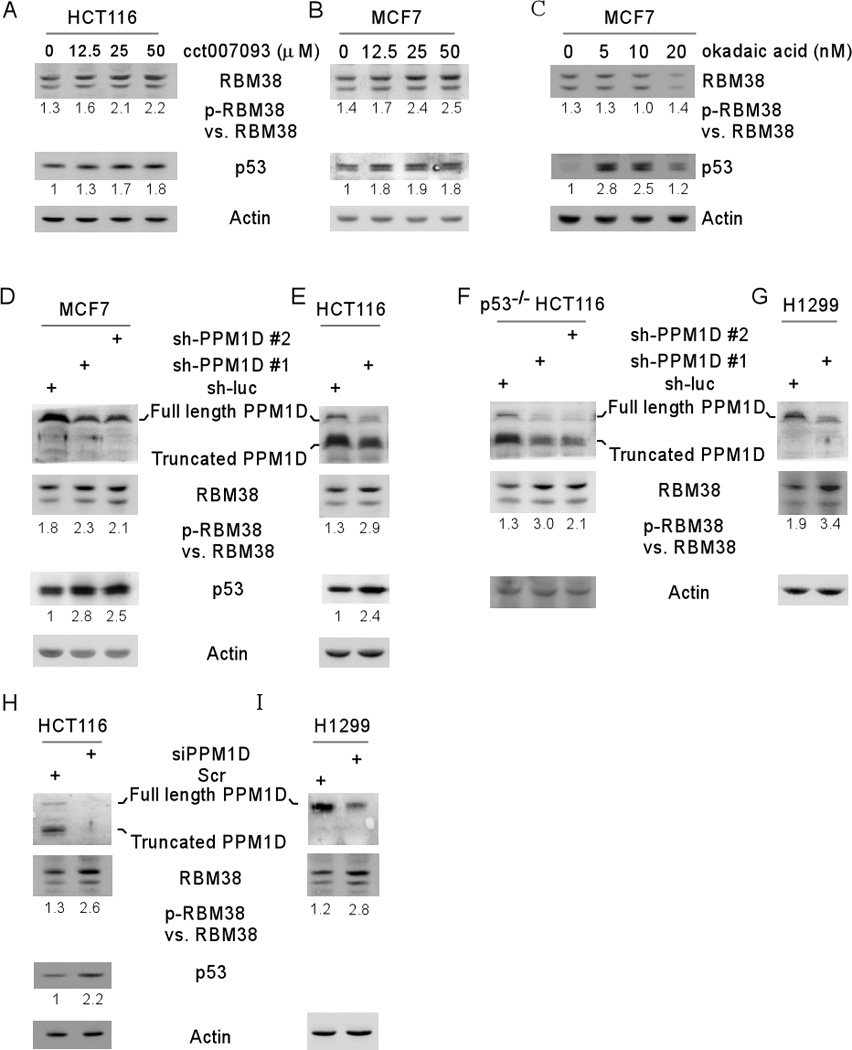
(A–B) The ratio of p-RBM38 vs. RBM38 is increased by a PPM1D inhibitor in a dose-dependent manner. The levels of RBM38, p53, and actin proteins were measured in HCT116 (A) and MCF7 (B) cells mock-treated or treated with PPM1D inhibitor CCT007093 (0–50 µM) for 12 h. (C) Okadaic acid has no effect on RBM38 phosphorylation. The levels of RBM38, p53, and actin proteins were measured in MCF7 cells mock-treated or treated with okadaic acid (0–20 nM) for 12 h. (D–I) Knockdown of PPM1D increases the ratio of p-RBM38 vs. RBM38. The levels of RBM38, p53, and actin proteins were measured in MCF7 (D), HCT116 (E), p53−/− HCT116 (F) and H1299 (G) cells transduced with lentivirus particles expressing a control shRNA, shRNA #1 shRNA #2 against PPM1D for 72 h, or in HCT116 (H) and H1299 (I) cells transduced with siRNA against PPM1D for 72 h. The ratio of p-RBM38 vs. RBM38 was calculated and showed below each lane.
