Abstract
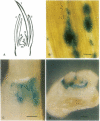
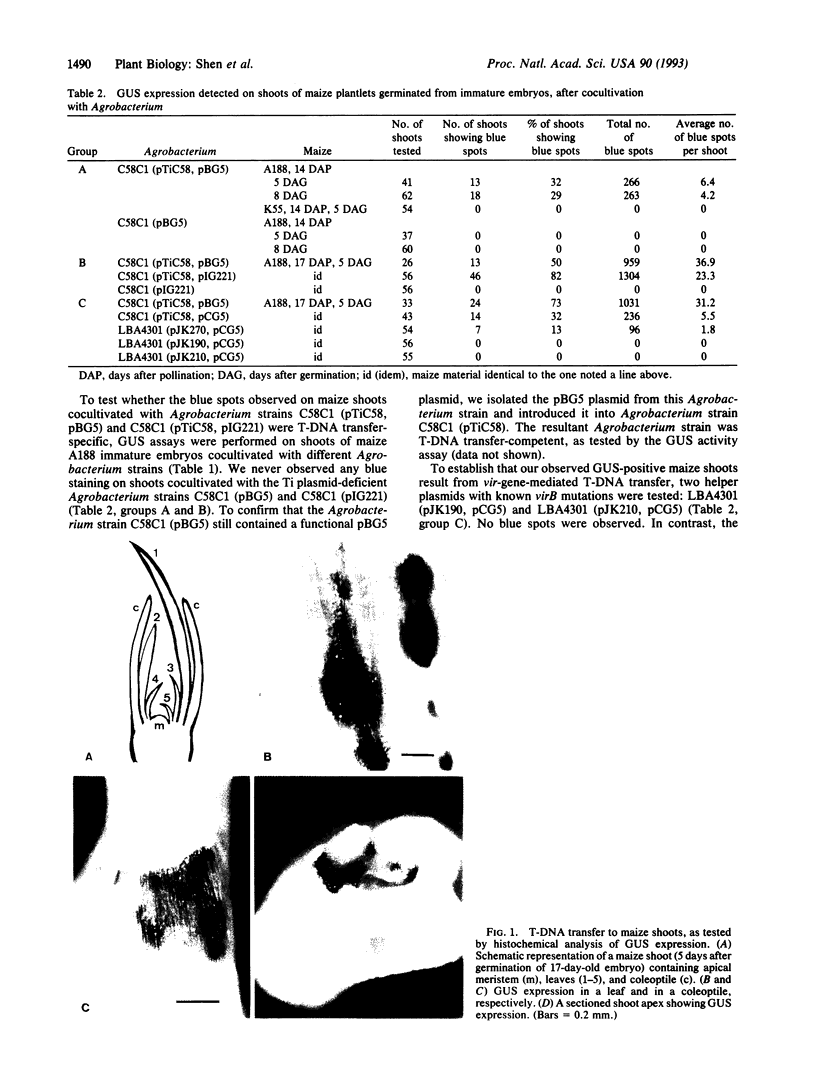
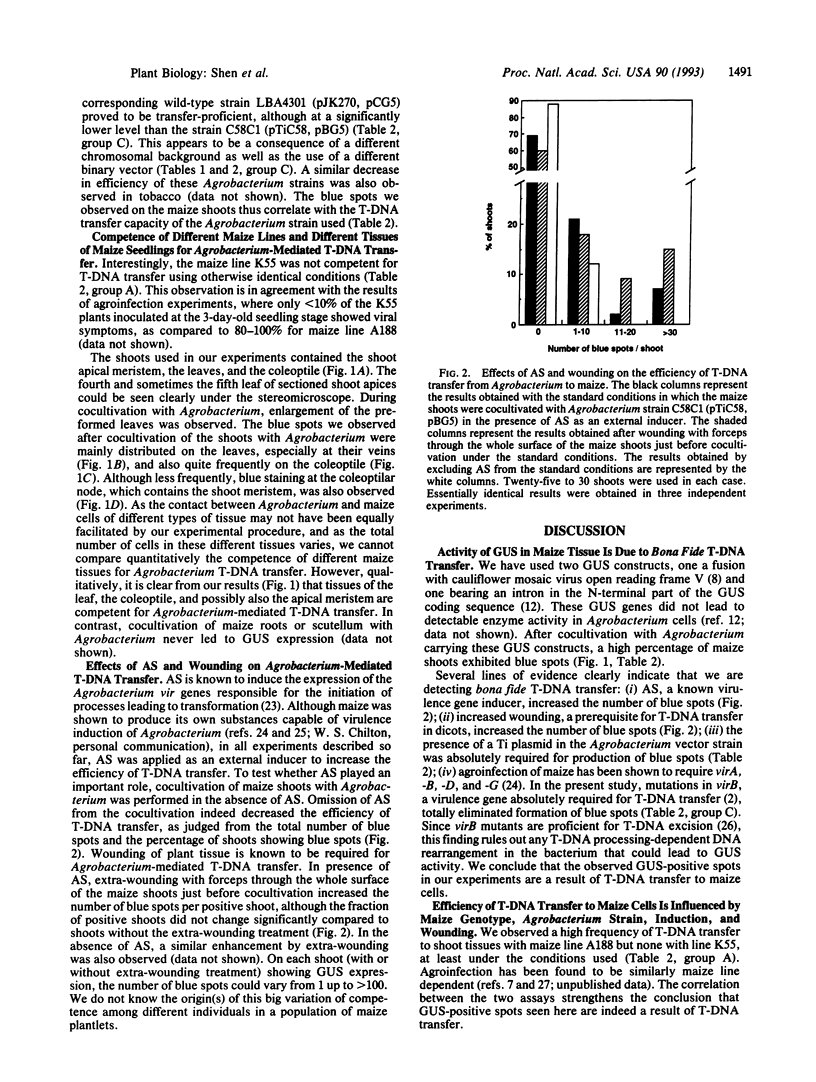
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is routinely used to engineer desirable genes into dicotyledonous plants. However, the economically important graminaceous plant maize is refractory to tumor induction by inoculation with virulent strains of A. tumefaciens. Currently, the only clearcut evidence for transferred DNA (T-DNA) transport from Agrobacterium to maize comes from agroinfection. To study T-DNA transfer from Agrobacterium to maize cells in a virus-free system, we used here the beta-glucuronidase (GUS; EC 3.2.1.31) gene as a marker. GUS expression was observed with high efficiency on shoots of young maize seedlings after cocultivation with Agrobacterium carrying the GUS gene. Agrobacterium virulence mutants, incapable of transferring T-DNA to dicot tissue, were shown to be deficient in eliciting GUS expression in maize. Hence, expression of the T-DNA-located GUS gene in maize cells is strictly dependent on Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer. Histochemical staining of maize shoots revealed GUS expression located mainly in the leaves and the coleoptile.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8711–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsley N., Hohn B., Hohn T., Walden R. "Agroinfection," an alternative route for viral infection of plants by using the Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3282–3286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsley N., Hohn B., Ramos C., Kado C., Rogowsky P. DNA transfer from Agrobacterium to Zea mays or Brassica by agroinfection is dependent on bacterial virulence functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):309–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02464898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsters M., Silva B., Van Vliet F., Genetello C., De Block M., Dhaese P., Depicker A., Inzé D., Engler G., Villarroel R. The functional organization of the nopaline A. tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):212–230. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapwijk P. M., van Beelen P., Schilperoort R. A. Isolation of a recombination deficient Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jun 7;173(2):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00330307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren G., Lau A., Klein J., Golas C., Bologa-Campeanu M., Soldin S., MacLeod S. M., Prober C. Pharmacokinetics and adverse effects of amphotericin B in infants and children. J Pediatr. 1988 Sep;113(3):559–563. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80653-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattanovich D., Rüker F., Machado A. C., Laimer M., Regner F., Steinkellner H., Himmler G., Katinger H. Efficient transformation of Agrobacterium spp. by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6747–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride K. E., Summerfelt K. R. Improved binary vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;14(2):269–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00018567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchta H., Hohn B. A transient assay in plant cells reveals a positive correlation between extrachromosomal recombination rates and length of homologous overlap. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2693–2700. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P. M., Close T. J., Chimera J. A., Shaw J. J., Kado C. I. Regulation of the vir genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5101–5112. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5101-5112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlappi M., Hohn B. Competence of Immature Maize Embryos for Agrobacterium-Mediated Gene Transfer. Plant Cell. 1992 Jan;4(1):7–16. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze M., Hohn T., Jiricny J. The reverse transcriptase gene of cauliflower mosaic virus is translated separately from the capsid gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1177–1185. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W. H., Hohn B. Excision of a transposable element from a viral vector introduced into maize plants by agroinfection. Plant J. 1992 Jan;2(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W. H., Hohn B. Mutational analysis of the small intergenic region of maize streak virus. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):721–730. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91001-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. R., Close T. J., Kado C. I. High levels of double-stranded transferred DNA (T-DNA) processing from an intact nopaline Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Mita S., Ohta S., Kyozuka J., Shimamoto K., Nakamura K. Enhancement of foreign gene expression by a dicot intron in rice but not in tobacco is correlated with an increased level of mRNA and an efficient splicing of the intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6767–6770. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]