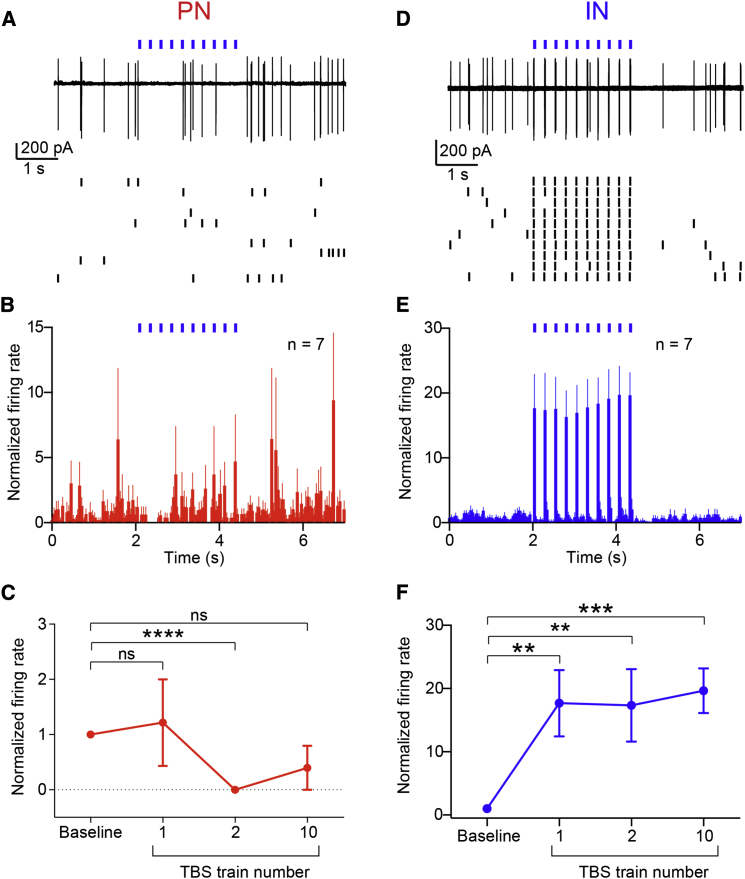
Figure 4.
Optical TBS of Hippocampal Axons Transiently Inhibits PNs and Triggers Firing in INs Ex vivo
(A) Ex vivo cell-attached recording from a representative BA PN inhibited by TBS of vCA1 axons (ten superimposed sweeps, top; singularly represented in raster plot, bottom).
(B) Pooled data showing PNs firing rates over time during TBS (bin = 50 ms, n = 7).
(C) Firing rates of PNs compared between baseline, first, second, and tenth trains of the TBS. Firing is significantly reduced during the second train and partially recovers at tenth train.
(D) Ex vivo cell-attached recording from a representative BA IN. TBS of vCA1 axons triggers action potentials (ten superimposed sweeps, top; singularly represented in raster plot, bottom).
(E) Pooled data showing INs firing rates over time during TBS (bin = 50 ms, n = 7).
(F) Firing rates of INs compared between baseline, first, second, and tenth trains of the TBS. Firing is significantly increased during TBS trains. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data are presented as means ± SEM.