Figure 7.
Presynaptic GABAB Receptors at BA IN-PN Synapses Mediate Depression of FFI
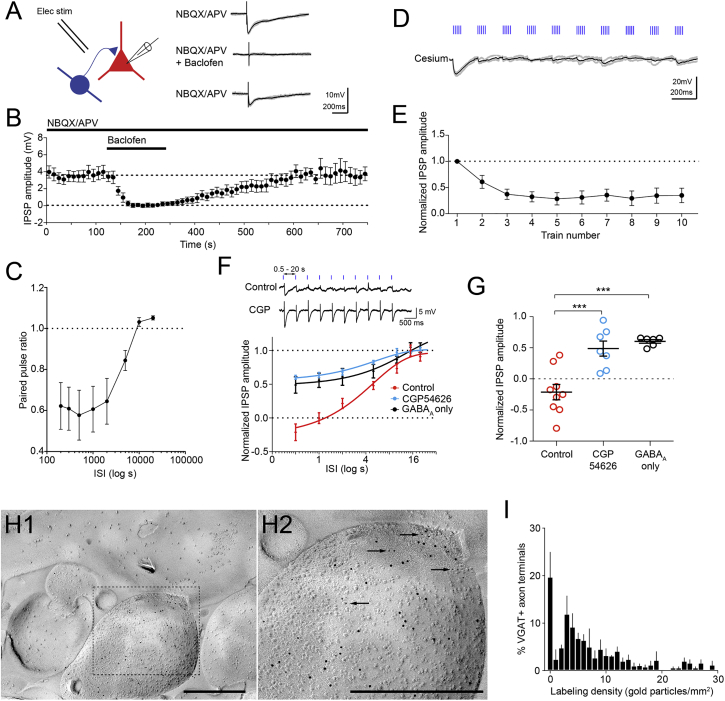
(A) Left, schematic of the experimental configuration. Local electrical stimulation is applied while recording from PNs. Right, representative current clamp recording (−65 mV) showing monosynaptic IPSP induced by local electrical stimulation in presence of NBQX/APV. The IPSP was abolished by the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen (10 μM). During baclofen application, neurons hyperpolarized but were held at −65 mV to avoid changes in driving force for Cl−.
(B) Pooled data, (n = 6).
(C) PPR of IPSCs recorded in PNs and evoked by local electrical stimulation. PPR reduced with shorter ISIs.
(D) The depression of IPSPs during TBS occurred in a PN recorded at 0 mV with cesium-containing intracellular solution.
(E) Pooled data (n = 7).
(F) Trains of ten single pulses were delivered with variable ISIs (0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 15, and 20 s) while recording from PNs. Top, representative trace during which light pulses were delivered at 0.5-s intervals. Depression of the IPSP was largely blocked by CGP54626. Bottom, average of the last three IPSPs evoked for each ISI normalized to the first IPSP. The IPSP amplitude became smaller with shorter ISIs. This depression was reduced when stimulation evoked only GABAA receptor IPSPs or in presence of CGP54626 (5 μM).
(G) Averaged amplitudes of last three IPSPs elicited with a train of ten single pulses delivered every 0.5 s: IPSP amplitude in control conditions (n = 9) was significantly lower than in presence of CGP54626 (p < 0.001 versus control, n = 7) or in PNs where only a GABAA IPSP was evoked (p < 0.001 versus control, n = 6).
(H1) Electron micrograph of a GABAergic terminal in the BA as obtained with the SDS-digested FRIL method. Scale bar: 500 nm.
(H2) Enlarged view of the area within the dashed lines in (H1). Larger gold particles (10 nm) reveal VGAT, whereas smaller gold particles (5 nm; arrowheads) identify GABAB receptors. Scale bar: 500 nm.
(I) Frequency distribution of VGAT+ axon terminals with different density of GABAB receptor labeling (n = 179 synapses obtained from three mice). Data are presented as means ± SEM.