Abstract
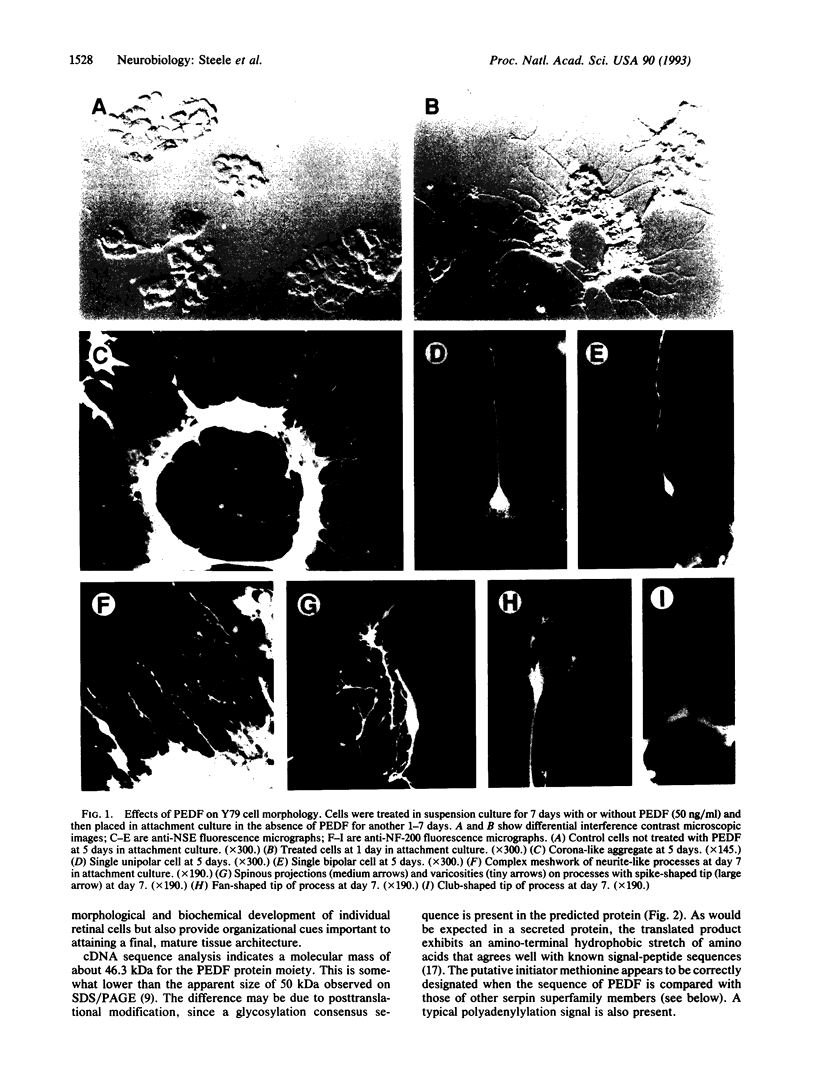
Cultured pigment epithelial cells of the fetal human retina secrete a protein, pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), that induces a neuronal phenotype in cultured human retinoblastoma cells. Morphological changes include the induction of an extensive neurite meshwork and the establishment of corona-like cellular aggregates surrounding a central lumen. The differentiated cells also show increases in the expression of neuron-specific enolase and the 200-kDa neurofilament subunit. Amino acid and DNA sequence data demonstrate that PEDF belongs to the serine protease inhibitor (serpin) family. The PEDF gene contains a typical signal-peptide sequence, initiator methionine codon, and polyadenylylation signal and matches the size of other members of the serpin superfamily (e.g., alpha 1-antitrypsin). It lacks homology, however, at the putative serpin reactive center. Thus, PEDF could exert a paracrine effect in the embryonic retina, influencing neuronal differentiation by a mechanism that does not involve classic inhibition of serine protease activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrell R. W., Pemberton P. A., Boswell D. R. The serpins: evolution and adaptation in a family of protease inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:527–535. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt A. T., Lindsey J. D., Carbott D., Adler R. Photoreceptor survival-promoting activity in interphotoreceptor matrix preparations: characterization and partial purification. Exp Eye Res. 1990 Jan;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(90)90013-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. A surprising new protein superfamily containing ovalbumin, antithrombin-III, and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):864–871. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. T., Kretzer F. L., Hittner H. M., Glazebrook P. A., Bridges C. D., Lam D. M. Development of the subretinal space in the preterm human eye: ultrastructural and immunocytochemical studies. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 22;233(4):497–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyritsis A. P., Tsokos M., Triche T. J., Chader G. J. Retinoblastoma--origin from a primitive neuroectodermal cell? Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):471–473. doi: 10.1038/307471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Strandberg L., Ericson J., Ny T. Structure-function studies of the SERPIN plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. Analysis of chimeric strained loop mutants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20293–20301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D. Cell-derived proteases and protease inhibitors as regulators of neurite outgrowth. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Niday E., Limat A., Solomon F. Inhibition of protease activity can lead to neurite extension in neuroblastoma cells. Prog Brain Res. 1983;58:359–364. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi Y. The histogenesis of retinoblastoma. An electron-microscopic analysis of rosette. Ophthalmologica. 1977;174(3):129–136. doi: 10.1159/000308590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield J. B., Graff D. Extracellular proteases in developing chick neural retina. Exp Eye Res. 1991 Jun;52(6):733–741. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90025-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone R. A., McGlinn A. M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive nerves in human and rhesus monkey eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Feb;29(2):305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombran-Tink J., Chader G. G., Johnson L. V. PEDF: a pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal differentiative activity. Exp Eye Res. 1991 Sep;53(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90248-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombran-Tink J., Johnson L. V. Neuronal differentiation of retinoblastoma cells induced by medium conditioned by human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Aug;30(8):1700–1707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombran-Tink J., Li A., Johnson M. A., Johnson L. V., Chader G. J. Neurotrophic activity of interphotoreceptor matrix on human Y79 retinoblastoma cells. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Mar 8;317(2):175–186. doi: 10.1002/cne.903170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tone M., Kikuno R., Kume-Iwaki A., Hashimoto-Gotoh T. Structure of human alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor deduced from the cDNA sequence. J Biochem. 1987 Nov;102(5):1033–1041. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]