Abstract
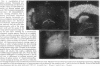
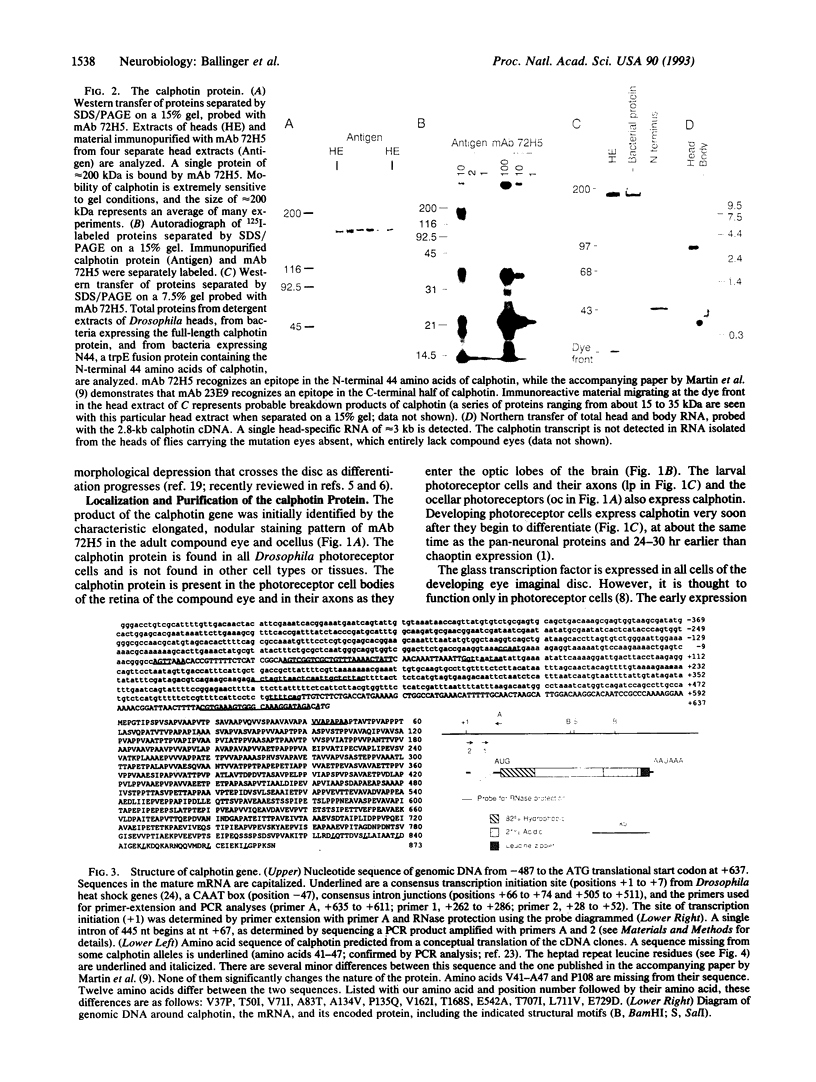
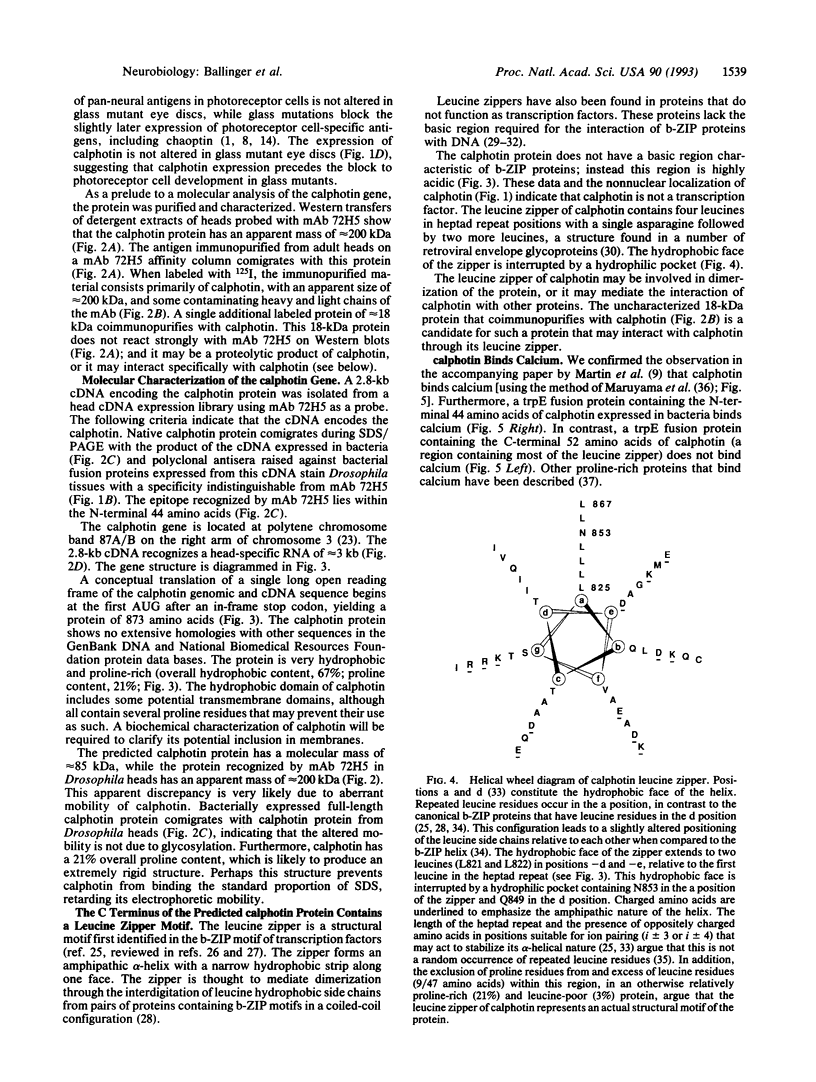
The calphotin protein, encoded by the calphotin (cap) gene, is expressed in the soma and axons of all Drosophila photoreceptor cells. It is expressed early in photo-receptor cell development, at the time when cell-type decisions are being made. Expression of calphotin is not altered by the glass mutation, which blocks photoreceptor cell development. The calphotin protein binds calcium and contains a long C-terminal leucine zipper. Potential implications of these properties are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballinger D. G., Benzer S. Targeted gene mutations in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9402–9406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee U., Zipursky S. L. The role of cell-cell interaction in the development of the Drosophila visual system. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90093-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. The binding of calcium to a salivary phosphoprotein, protein A, common to human parotid and submandibular secretions. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1550163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braitenberg V. Patterns of projection in the visual system of the fly. I. Retina-lamina projections. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(3):271–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00235589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Karlin S. Too many leucine zippers? Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):574–575. doi: 10.1038/341574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland R., Wild F. Leucine zipper motif extends. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):547–547. doi: 10.1038/338547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Dimers, leucine zippers and DNA-binding domains. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwart E. L., Mosialos G., Gilmore T. Retroviral envelope glycoproteins contain a "leucine zipper"-like repeat. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):703–706. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. C., Zipursky S. L., Benzer S., Ferrús A., Shotwell S. L. Monoclonal antibodies against the Drosophila nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7929–7933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I., Rubin G. M. Making a difference: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90470-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz D. E., Zipursky S. L. Drosophila chaoptin, a member of the leucine-rich repeat family, is a photoreceptor cell-specific adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1969–1977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leucine-zipper motif update. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):103–104. doi: 10.1038/340103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Benzer S., Rudnicka M., Miller C. A. Calphotin: a Drosophila photoreceptor cell calcium-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1531–1535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack K., Tanouye M. A., Iverson L. E., Lin J. W., Ramaswami M., McCormack T., Campanelli J. T., Mathew M. K., Rudy B. A role for hydrophobic residues in the voltage-dependent gating of Shaker K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Ngai J., Wold B. J., Lazarides E. Tissue-specific expression of distinct spectrin and ankyrin transcripts in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):152–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses K., Ellis M. C., Rubin G. M. The glass gene encodes a zinc-finger protein required by Drosophila photoreceptor cells. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):531–536. doi: 10.1038/340531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses K., Rubin G. M. Glass encodes a site-specific DNA-binding protein that is regulated in response to positional signals in the developing Drosophila eye. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):583–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready D. F., Hanson T. E., Benzer S. Development of the Drosophila retina, a neurocrystalline lattice. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):217–240. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renfranz P. J., Benzer S. Monoclonal antibody probes discriminate early and late mutant defects in development of the Drosophila retina. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):411–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. Signal transduction in the visual system of Drosophila. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:161–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. S., Sapp R., Carlson S. D. Ultrastructure of the ocellar visual system in normal and mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurogenet. 1989 May;5(2):127–153. doi: 10.3109/01677068909066203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Neuronal differentiation in Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):366–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription factors: a new family gathers at the cAMP response site. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90081-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky S. L., Venkatesh T. R., Teplow D. B., Benzer S. Neuronal development in the Drosophila retina: monoclonal antibodies as molecular probes. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]