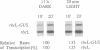Abstract
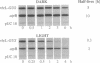
We have found that sequences in the 5' leader of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast rbcL gene, when fused 5' to foreign genes, destabilize transcripts of these chimeric genes in the chloroplast of transgenic Chlamydomonas but that 5' sequences of the rbcL structural gene prevent this destabilization. Transcripts of the chloroplast rbcL gene are about equally abundant at all times in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii growing on an alternating 12-h light/12-h dark cycle. However, Chlamydomonas chloroplast transformants, harboring chimeric genes containing the same rbcL promoter with 63 or 92 bp of the rbcL 5' leader sequence fused upstream of the Escherichia coli uidA (beta-glucuronidase, GUS) gene, accumulated GUS transcripts only in the dark. Transcripts disappeared rapidly upon illumination of the cells. The same phenomenon was exhibited by transcripts of chimeric genes in which the GUS gene coding sequence was replaced by other unrelated genes. The precipitous light-induced drop in GUS transcript abundance was found to be due to an approximately 16-fold increase in the rate of degradation of GUS transcripts in light rather than to a decrease in the rate of transcription of the GUS gene. Transcripts of a chimeric rbcL-GUS construct in which the leader sequence of the rbcL gene was replaced by 103 bp of the leader sequence of the atpB gene were stable in illuminated cells. The destabilizing effect of the rbcL 5' leader sequence was reversed by adding 257 bp of the 5' coding region of the rbcL gene. The results show that chloroplast transcript levels in illuminated Chlamydomonas cells--and perhaps in other cases--can be determined, at least to some extent, by sequences and interactions of sequences transcribed from the 5' ends of genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater J. A., Wisdom R., Verma I. M. Regulated mRNA stability. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:519–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. J., Schloss J. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Rapid changes in tubulin RNA synthesis and stability induced by deflagellation in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2074–2081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Bogorad L., Shark K. B., Sanford J. C. Studies on Chlamydomonas chloroplast transformation: foreign DNA can be stably maintained in the chromosome. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):123–132. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Ellmore G. S., Klein U., Bogorad L. Transcriptional analysis of endogenous and foreign genes in chloroplast transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1059–1070. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Harris E. H., Hosler J. P., Johnson A. M., Jones A. R., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Robertson D., Klein T. M., Shark K. B. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas with high velocity microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1534–1538. doi: 10.1126/science.2897716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. C., Stern D. B. Specific binding of chloroplast proteins in vitro to the 3' untranslated region of spinach chloroplast petD mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4380–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier D., Girard-Bascou J., Wollman F. A. Evidence for Nuclear Control of the Expression of the atpA and atpB Chloroplast Genes in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1992 Mar;4(3):283–295. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast DNA region of Chlamydomonas reinhardii containing the gene of the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase and parts of its flanking genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):775–793. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz C. C., Herget T., Wolter F. P., Schell J., Schreier P. H. Reduced steady-state levels of rbcS mRNA in plants kept in the dark are due to differential degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4458–4462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M. Transgenic expression of aminoglycoside adenine transferase in the chloroplast: a selectable marker of site-directed transformation of chlamydomonas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4083–4089. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a gene encoding a streptomycin/spectinomycin adenylyltransferase. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):17–30. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Burgess S. M., Hirsh D. beta-Glucuronidase from Escherichia coli as a gene-fusion marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8447–8451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaff P., Gruissem W. Changes in Chloroplast mRNA Stability during Leaf Development. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):517–529. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein U., De Camp J. D., Bogorad L. Two types of chloroplast gene promoters in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3453–3457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchka M. R., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., van Dillewijn J., Rochaix J. D. Mutation at the Chlamydomonas nuclear NAC2 locus specifically affects stability of the chloroplast psbD transcript encoding polypeptide D2 of PS II. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):869–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90939-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu S., White D., Michaels A. Cell cycle-dependent transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of chloroplast gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig S. R., Habera L. F., Dellaporta S. L., Wessler S. R. Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7092–7096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A., Jansson C. Photosynthetic electron transport controls degradation but not production of psbA transcripts in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):891–897. doi: 10.1007/BF00015080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod C., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rochaix J. D. Accumulation of chloroplast psbB RNA requires a nuclear factor in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):449–459. doi: 10.1007/BF00292715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., Link G. Interaction of a 3' RNA region of the mustard trnK gene with chloroplast proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9637–9648. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., Link G. RNA-protein interactions at transcript 3' ends and evidence for trnK-psbA cotranscription in mustard chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):89–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00282452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Kuchka M., Mayfield S., Schirmer-Rahire M., Girard-Bascou J., Bennoun P. Nuclear and chloroplast mutations affect the synthesis or stability of the chloroplast psbC gene product in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1013–1021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end processing requires a nuclear-encoded RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1493–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieburth L. E., Berry-Lowe S., Schmidt G. W. Chloroplast RNA Stability in Chlamydomonas: Rapid Degradation of psbB and psbC Transcripts in Two Nuclear Mutants. Plant Cell. 1991 Feb;3(2):175–189. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Jones H., Gruissem W. Function of plastid mRNA 3' inverted repeats. RNA stabilization and gene-specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18742–18750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]