Abstract
Lessons Learned
Addition of cetuximab may affect tolerability and, in turn, affect eventual outcomes.
The incidence of prior human papillomavirus infection has emerged as an important variable that can confound trials enrolling patients with oropharyngeal cancer.
Background.
We investigated the efficacy of cetuximab when added to induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Methods.
Patients were randomized to receive three cycles of docetaxel and cisplatin (TP regimen) with or without cetuximab (TP plus cetuximab [CTP] vs. TP) as induction chemotherapy. Patients in the CTP arm received CCRT with cetuximab and cisplatin, whereas patients in the TP arm received cisplatin alone. The primary endpoint was the objective response rate (ORR) after induction chemotherapy.
Results.
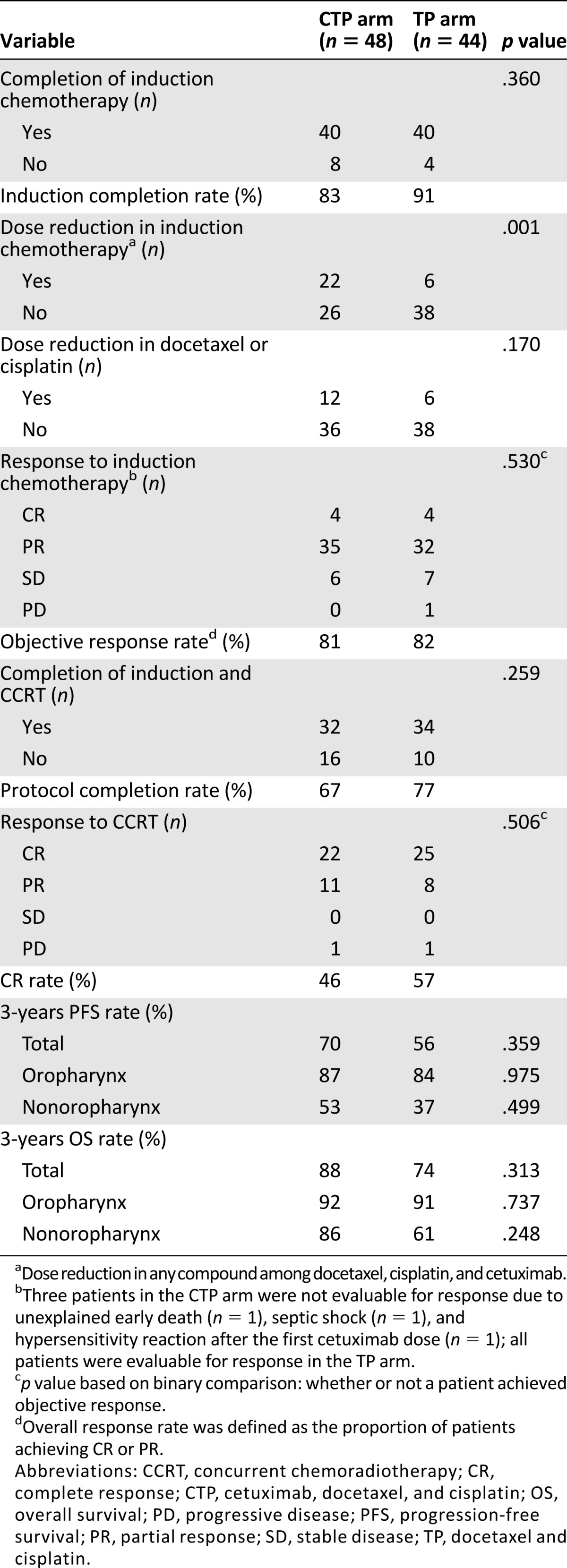
Overall, 92 patients were enrolled. The ORRs for induction chemotherapy in the CTP and TP arms were not different (81% vs. 82%). Adding cetuximab lowered the completion rate of induction chemotherapy and CCRT and resulted in more frequent dose reductions of the induction chemotherapy, although this did not reach statistical significance. In the CTP and TP arms, respectively, the 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% and 56% (p = .359), and the overall survival (OS) rates were 88% and 74% (p = .313). When limited to patients who completed induction chemotherapy, 3-year PFS rates of 78% and 59% (p = .085) and OS rates of 94% and 73% (p = .045) were observed in the CTP and TP arms, respectively.
Conclusion.
Adding cetuximab to sequential treatment did not increase the treatment efficacy and resulted in greater toxicity. In the intent-to-treat population, neither PFS nor OS was improved by the addition of cetuximab to sequential treatment; however, a suggestion of improved survival outcomes was observed in patients completing cetuximab-containing induction chemotherapy.
Abstract
经验
• 西妥昔单抗联合治疗可能会影响耐受性, 继而影响患者最终转归。
• 既往人类乳头状瘤病毒感染已成为能够影响那些纳入口咽癌患者的研究中的重要变量。
摘要
背景. 我们对在局部晚期头颈部鳞状细胞癌患者的诱导化疗继以同步放化疗 (CCRT) 方案中添加西妥昔单抗的有效性进行了调查。
方法. 患者随机接受 3 个周期多西他赛和顺铂(TP方案) 联合或不联合西妥昔单抗 [TP+西妥昔单抗 (CTP) vs. TP] 诱导化疗。随后 CCRT 时 CTP 组患者接受西妥昔单抗和顺铂, 而 TP 组患者只接受顺铂。主要终点为诱导化疗后的客观缓解率 (ORR)。
结果. 共纳入 92 例患者。CTP 组和 TP 组诱导化疗的 ORR 无差异 (81% vs. 82%)。联合西妥昔单抗降低了诱导化疗和 CCRT 的完成率, 而且导致了更高频率的诱导化疗剂量下调, 但这一差异尚未达到统计学意义。CTP 组和 TP 组的 3 年无进展生存 (PFS) 率分别为 70% 和 56% (P = 0.359), 总生存 (OS) 率分别为 88% 和 74% (P = 0.313)。将分析范围缩小到完成诱导化疗的患者后, CTP 组和 TP 组观察到的 3 年 PFS 率分别为 78% 和 59% (P = 0.085), OS率分别为 94% 和 73% (P = 0.045)。
结论. 续贯治疗方案中联合西妥昔单抗并未提高治疗有效性, 并且导致了较多毒性事件。在意向性治疗人群中, 续贯治疗联合西妥昔单抗未能改善 PFS 和 OS, 但在完成含西妥昔单抗的诱导化疗的患者中观察到的数据提示生存转归得到改善。The Oncologist 2015;20:1119–1120
Author Summary
Discussion
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is highly overexpressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (SCCHN). The addition of the EGFR inhibitor cetuximab to radiotherapy has been found to improve survival outcomes in locally advanced SCCHN (LA-SCCHN), and combining cetuximab with cytotoxic agents prolongs survival in metastatic SCCHN. Based on these additive effects of cetuximab for both radiotherapy and chemotherapy, we hypothesized that the addition of cetuximab to both induction chemotherapy and concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) phases would improve treatment outcomes. The current study represents the first randomized trial to test the effect of cetuximab integration into both the induction and CCRT phases in LA-SCCHN.
In our study, although not statistically significant, cetuximab addition to sequential treatment seemed to decrease a patient’s ability to tolerate treatment. Adding cetuximab lowered the completion rate of induction chemotherapy (docetaxel plus cisplatin) and CCRT and caused more frequent dose reductions of induction chemotherapy (Table 1). Although there was no significant difference in the frequency of severe (grade ≥3) adverse events, overall adverse events occurred more frequently in the CTP arm. The objective response rate (the primary endpoint), progression-free survival, and overall survival were not improved by cetuximab addition in the intent-to-treat population (Table 1). Nonetheless, we found that the addition of cetuximab seemed to more favorably affect patients who completed the planned 3 cycles of induction chemotherapy (3-year PFS 78% vs. 59% [p = .085] and 3-year OS 94% vs. 73% [p = .045] in the CTP vs. TP arms).
Table 1.
Treatment compliance and outcomes
The shortcomings of our study are as follows. Because the importance of human papillomavirus tests in oropharyngeal cancer was little known when this study was initiated and the planned sample size was small, stratification according to primary tumor site or other additional clinical variables could not be performed in the randomization process. Instead, considering possible differences in clinical practice patterns at the various participating institutions, we stratified patients only according to institution; therefore, the sex distribution was unequal between the arms (p = .044), and the proportion of oropharyngeal disease was slightly higher in the CTP arm than in the TP arm, although this was not statistically significant. Consequently, we cannot exclude the possibility that these unexpectedly uneven patient distributions contributed to the favorable survival outcomes in patients who completed cetuximab-containing induction chemotherapy.
In conclusion, although the addition of cetuximab to sequential treatment of LA-SCCHN may somewhat decrease patient compliance, it was tolerable overall. The primary endpoint of this study was not met, but the survival data observed in patients who completed the planned cetuximab-containing induction chemotherapy suggest that further investigation of cetuximab addition in this setting is warranted.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Access the full results at: Lee-15-208.theoncologist.com
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00623558
Sponsor(s): None (investigator-initiated trial)
Principal Investigator: Dae Seog Heo
IRB Approved: Yes
Author disclosures available online.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


