Abstract
The patterns of prehistoric migrations across the Bering Land Bridge are far from being completely understood: there still exists a significant gap in our knowledge of the population history of former Beringia. Here, through comprehensive survey of mitochondrial DNA genomes retained in ‘relic' populations, the Maritime Chukchi, Siberian Eskimos, and Commander Aleuts, we explore genetic contribution of prehistoric Siberians/Asians to northwestern Native Americans. Overall, 201 complete mitochondrial sequences (52 new and 149 published) were selected in the reconstruction of trees encompassing mtDNA lineages that are restricted to Coastal Chukotka and Alaska, the Canadian Arctic, Greenland, and the Aleutian chain. Phylogeography of the resulting mtDNA genomes (mitogenomes) considerably extends the range and intrinsic diversity of haplogroups (eg, A2a, A2b, D2a, and D4b1a2a1) that emerged and diversified in postglacial central Beringia, defining independent origins of Neo-Eskimos versus Paleo-Eskimos, Aleuts, and Tlingit (Na-Dene). Specifically, Neo-Eskimos, ancestral to modern Inuit, not only appear to be of the High Arctic origin but also to harbor Altai/Sayan-related ancestry. The occurrence of the haplogroup D2a1b haplotypes in Chukotka (Sireniki) introduces the possibility that the traces of Paleo-Eskimos have not been fully erased by spread of the Neo-Eskimos or their descendants. Our findings are consistent with the recurrent gene flow model of multiple streams of expansions to northern North America from northeastern Eurasia in late Pleistocene–early Holocene.
Introduction
During the last glacial maximum (28–18 thousand years ago, kya), the Siberian Arctic and Subarctic were either completely abandoned1 or sparsely populated.2 A significant environmental shift was driven by the warming, which occurred in the High Arctic ~17–15 kya.3 It appears that some Siberian groups may have reached western Alaska ~14.5 kya, whereas others were stuck in the lowlands of central Beringia (the Bering Isthmus proper) until the last flooding of the Bering Strait, ~11.5 kya.4 The northern rim of the Pacific, offering a wealth of resources, may have led coastal migrants deep into the interior from marine and estuarine habitats to riverine, lake, and marsh ecosystems all the way down the Pacific Coast of North America.5
Initial settlement of the New World was followed by a period of extensive gene flow between Asian and American populations, inhabiting the Arctic landscapes. Recently, owing to an exhaustive nuclear DNA study taken from 17 Siberian and 52 Native American groups, it has been shown that the initial settlement of the Western Hemisphere was followed by at least two separate population movements from northeastern Eurasia, with the contribution from the first arrival accounting for the majority of total Paleo-Indian ancestry, and with decreasing contributions from the subsequent movements, which mainly affected Na-Dene and Eskimo-Aleut groups.6 However, this model has not been fully evaluated, in part, because researchers were unable to date their arrival, which instead could be inferred from entire mitochondrial genomes.7
The last inhabitants of former Beringia, reflected genetically in the Yukaghir, Chukchi, Eskimo-Aleuts, Na-Dene, and Northwestern North American Indians, have been a focus of extensive comparisons between complete mtDNA sequences from Siberia and from North America. As a result, the Siberian affinities of major Native American mtDNA haploclusters (A–D), initially detected by comparing a few single-nucleotide polymorphisms of similar haplotypes from Eurasia and the Americas,7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 have been revised and extended. It has become evident that the range of distinct lineages confined to the entire Eskimo Arctic is a subset of haplogroups A2a, A2b, D2a, and D4b1a2a1, though each of their evolutionary histories is far from being explicitly clear. The high variance of molecular dates, owing to insufficient sampling from living native groups with small effective population sizes, could have considerably influenced coalescence estimates for trans-Beringian mtDNA lineages.10, 13, 15
In the present study, newly obtained entire mtDNA sequences were integrated with those previously published, and updated genealogies and age estimates were generated to shed additional light on source populations from which ancestors of modern Chukchi, Eskimos, Aleuts, and even some Na-Dene groups originated.
Materials and methods
Populations
Siberian Eskimos
By the turn of the 20th century, the territory inhabited by Siberian (Yupik) Eskimos had been reduced to small enclaves on the northeastern and southern coasts of the Chukchi Peninsula: Naukan, Ungaziq (Chaplin), Plover (Provideniya) Bay, and Sireniki.16 The Naukan community of ~330 members, including part of the Eskimo group from Big Diomede Island (Ostrov Ratmanova), went through a process of displacement of native villages beginning in the early 1950's. In recent centuries, Inupiaq replaced Yupik on Seward Peninsula, thus breaking the American-Siberian Yupik chain and creating a major language barrier between Big Diomede and Naukan. The Sireniki language (now extinct), a relic of probably the earliest wave of Yupik in Chukotka, occupied most of the south shore of the Chukchi Peninsula two centuries ago.17 From the present-day genetic standpoint, Sireniki, Plover, and Chaplin Eskimos appear to be an amalgamation of previously highly endogamous distinct populations.10, 18
Chukchi
The Chukchi, especially Maritime Chukchi, are thought to have emerged as small group of fishing and sea-mammal hunting populations during the period of Neolithic marine-hunter culture or even earlier. Whereas present-day Chukchi, both coastal and inland, speak a dialect of the Chukchi-Kamchatkan language family, a North Alaskan Inupiaq language was spoken along the Arctic Coast of Chukotka from Uelen to as far as Shelagski Cape since at least 1791 and into the 19th century.17, 19 Fusing the Yupik coastal people and reindeer Chukchi camps into one village was a common practice while of administrative relocations and resettlements of indigenous communities in Russia's Northeast in 1940–1950's.18
Commander Aleuts
Modern archeology in the Aleut region (Alaska) has generated a series of radiocarbon dates from across the Aleutians to confirm and refine the widely held view that the initial peopling of the archipelago took place from east to west; the earliest human occupation in the eastern Aleutians is dated to ~9.0 kya (reviewed in Veltre D and Smith M, 200820). In contrast to all of the larger Aleutian Islands, which had considerably longer histories of permanent inhabitation, the Commander Islands were initially peopled only in 1825–1826. Subsequently, new settlers from the eastern Aleutians and Alaska were brought by the Russian-American Company in 1840.9, 21, 22 As a result, the Aleut community extensively admixed with Russians were established on the Commander Islands, the village of Nikolskoye, Bering Island, and the village of Preobrazhenskoye on the Copper (Medniy) Island, the latter no longer exists.
Samples
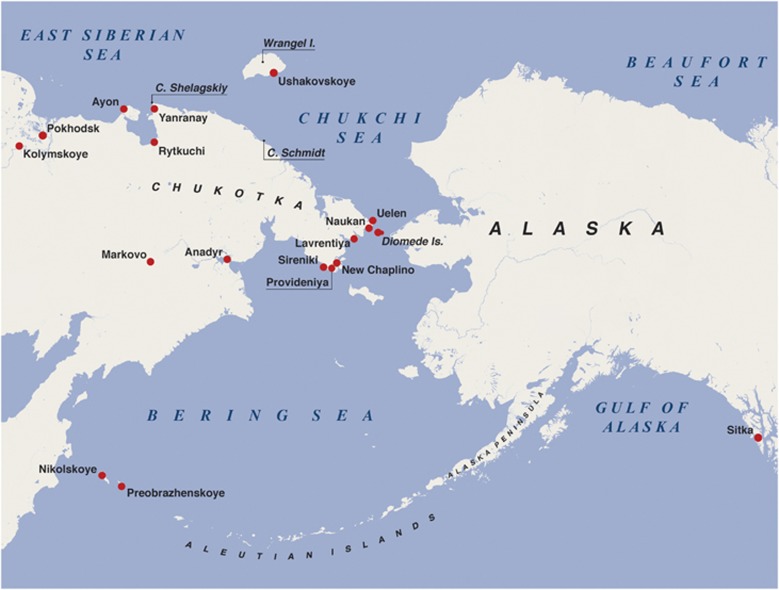
The Chukchi and Siberian Eskimo samples (n=47) come from individuals who were largely born in or derived from coastal villages scattered around the perimeter of the Chukchi Peninsula (Figure 1). With respect to the Commander Aleut samples, 31 of 36 mtDNAs were completely sequenced previously, whereas the remaining five individuals of presumably Tlingit maternal origin were assessed only at the SNP-level.10 To discern their ancestral status in full, these five mtDNA samples were entirely sequenced, and a phylogenetic tree encompassing all 36 complete mtDNA genomes was built.
Figure 1.
Map of northeastern end of Siberia adjoining to Alaska and Aleutian Islands, showing mtDNA sampling locations.
mtDNA analysis
The complete sequencing procedure entailed PCR amplification of the 22 overlapping mtDNA templates, which were sequenced in both directions with BigDye terminator chemistry (PE Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and the ABI Prism 3130 DNA Analyzer. Trace files were analyzed with Sequencher (version 4.5 GeneCode Corporation) software. We used facilities of the ‘Genomics' Sequencing Center, SBRAS, Novosibirsk, Russian Federation. Variants were scored relative to the revised Cambridge Reference Sequence, rCRS (GenBank accession number NC_012920.1).23 Entire mtDNA sequences revealing shared lineages or sublineages within and among related Siberian/American sources were assembled into phylogenetic trees by using the median-joining algorithm of Network 4.5.1.024 and mtPhyl v4.015 software.
For the phylogeny reconstruction, preliminary-reduced median network analyses led to a suggested branching order for the trees, which we then constructed most parsimoniously by hand.
Estimates of coalescence and expansion times
The coalescence dates were estimated with the ρ statistics.25 Standard error (σ) was calculated according to Saillard et al.26 Mutational distances were converted into years using the substitution rate for the entire molecule of 2.67 × 10−8 substitutions per site per year.27 BEAST 1.8.1 was used to calculate maximum likelihood (ML) estimates and to obtain Bayesian skyline plots (BSPs) for complete A2a, A2b, D2a, and D4b1a2 sequences with a log-normal relaxed molecular clock (uncorrelated). The general time-reversible sequence substitution model with a fixed fraction of invariable sites and gamma-distributed rates (GTR+I+G) was used because this model has the best fit to our data according to jModelTest 2.1.4.28 These calculations were performed on entire mtDNA sequences (excluding the mutations at np m.16182A>C, m.16183A>C, m.16194A>C, and m.16519T>N because of the high instability of these nucleotide positions). The KC417443.1 sequence from an ancient modern human securely dated at 39.5 kya was used as an outgroup and provided a consistent internal calibration point in our analyses.27 Using the MCMC approach, 40 000 000 iterations were performed, with samples taken every 1000 steps. The initial 10% of iterations were considered burn-in and discarded. Inspection of posterior samples ensured sufficient sampling and was used as a check for convergence to the stationary distribution. Tracer v1.6 was used to visualize BSPs. In order to generate a tree structure that would be directly comparable between analyses, larger subhaplogroups were forced to be monophyletic.
Results
The 52 samples (25 Chukchi, 22 Siberian Eskimos, and 5 Aleut) were chosen from a much larger collection of our previously collected samples9, 10, 18 not yet examined at the entire mtDNA genome level, and were completely sequenced. These were merged with 66 complete mitogenomes, we generated for the same and related Siberian groups previously, and then combined with 83 publicly available complete sequences. The total data set (n=201) was assigned mainly to lineages A2a, A2b, D2a, and D4b1a2. To focus phylogenetic analyses, we removed C5a2, C4b2, and D3 sequences (n=8), a likely admixture between expanding Chukchi and adjoining Yukaghir and/or Even.10, 13 The complete mtDNA genomes from Alaska, NW Canada, and Greenland were downloaded for comparative purposes from GenBank (Supplementary Table S1). The coalescence time and variance computed from the roots of A2a, A2b, D2a, and D4b1a lineages (haplogroups) and their younger nodes are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Age estimates (maximum likelihood and ρ statistics) for haplogroups A2a, A2b, D2a, and D4b1a2 and their major subhaplogroups.
| Lineage | n | ML age (95% CI) | ρ age (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2a | 66 | 3.94 (1.80; 6.10) | 3.86 (2.11; 5.64) |
| >A2a1 | 2 | 0.60 (0; 2.02) | 0.80 (0; 2.40) |
| >A2a2 | 7 | 1.96 (0.48; 3.92) | 2.08 (0; 4.74) |
| >A2a3 | 8 | 1.44 (0.14; 3.41) | 1.00 (0; 2.06) |
| >A2a4 | 7 | 0.57 (0.10; 1.22) | 0.23 (0; 0.68) |
| >A2a5 | 13 | 1.49 (0.54; 2.66) | 1.86 (0.12; 3.64) |
| A2b | 42 | 2.57 (0.93; 4.37) | 3.13 (0.10; 6.27) |
| >A2b1 | 39 | 2.07 (0.54; 3.79) | 1.70 (0.97; 2.43) |
| D2a | 63 | 4.43 (3.23; 5.89) | 4.26 (1.28; 7.32) |
| >D2a1 | 44 | 3.96 (3.01; 5.12) | 3.59 (1.02; 6.24) |
| >>D2a1a | 31 | 1.35 (0.07; 2.62) | 0.98 (0.19; 1.79) |
| >>D2a1b | 9 | 1.15 (0.04; 2.33) | 1.43 (0; 3.03) |
| >D2a2 | 13 | 2.23 (0.47; 4.21) | 0.74 (0; 1.51) |
| D4b1a2 | 22 | 8.73 (4.15; 13.16) | 10.08 (4.52; 15.91) |
| >D4b1a2a | 21 | 6.95 (3.56; 10.72) | 8.17 (3.50; 13.04) |
| >>D4b1a2a1 | 18 | 5.39 (2.25; 8.72) | 7.00 (2.81; 11.35) |
| >>>D4b1a2a1-16093 | 13 | 4.34 (1.81; 7.18) | 6.22 (1.89; 10.73) |
| >>>>D4b1a2a1-11383-14122C-16093 | 11 | 1.92 (0.05; 3.81) | 2.80 (0.99; 4.65) |
Haplogroups A2a and A2b
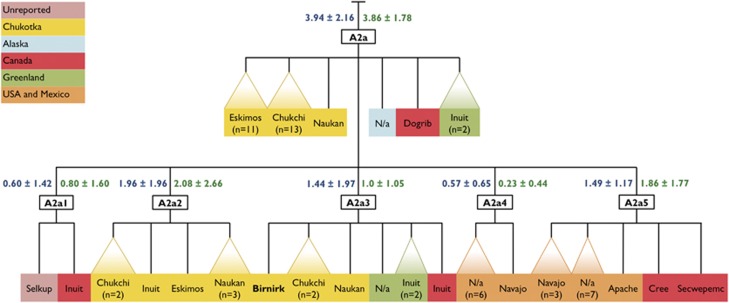
Of 201 mtDNA genomes scattered on both sides of the Bering Strait, 108 samples (53.7%) fall into different sublineages of A2a and A2b haplogroups (Supplementary Table S1). The phylogeny of A2a is structured into five major subbranches, assigned as A2a1, A2a2, A2a3, A2a4, and A2a5, in accord with the latest release of PhyloTree-Build29 (Figures 2 and 3, Supplementary Figure S1). In addition, there is a large number of independent basal branches and haplotypes. Contrary to A2a1, A2a2, and A2a3, which are confined to the Chukchi and Eskimos (Yupik and Inuit-Inupiaq), A2a4 and A2a5 are associated with various Na-Dene-speaking tribes, as well as Apache and Navajo in areas where Athapaskan populations expanded (eg, US Southwest). The estimated age of the A2a cluster encompassing 66 sequences is ~3.9 kya. The A2b root appears to emerge somewhere within the Bering Sea/Bering Strait region relatively recently (ML: 2.6 kya; rho: 3.1 kya), shortly before the split and subsequent spread of Inupiaq-speakers into northern Alaska and the Canadian Arctic.
Figure 2.
Schematic phylogeny of mtDNA hg A2a complete sequences at the Chukchi-Bering Sea area and beyond. Ancient samples are in bold.
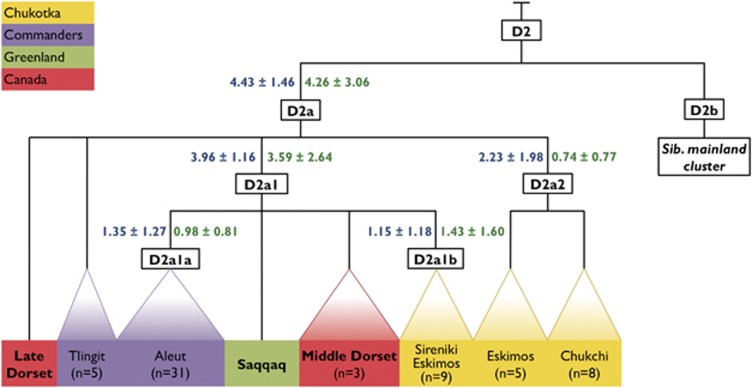
Figure 3.
Schematic phylogeny of mtDNA hg D2a complete sequences revealed in the Commanders, Greenland, and Chukotka. Ancient samples are in bold.
Haplogroup D2a
Among the 63 haplogroup D2a complete mtDNA sequences generated and publicly available to date, 36 are from the Commanders, 22 from Chukotka, with the remaining 5 sequences derived from the Canadian Arctic and Greenland (Figure 3, Supplementary Table S1). The D2a1 defined by m.9667A>G is particularly widespread. It is well separated from the major branch (D2a), and encompassing Paleo-Eskimo (Saqqaq), dated to ~3600–4170 14C years,30 Aleut D2a1a, Sireniki D2a1b, and Middle Dorset D2a1-m.11176G>A (Supplementary Figure S3).
Interestingly, D2a2 defined by m.4991G>A is associated at most with mtDNA samples from the Plover and Chaplin Eskimos, as well as the Chukchi from the arctic coast. The occurrence of D2a2 on the East Siberian and Chukchi Sea coasts is intriguing. One possible explanation is the relocation of ~50 Yupik from the Plover (Provideniya) Bay area in 1926 by the Soviet Government, aiming to extend their sovereignty over Wrangel Island. A tiny colony in the village of Ushakovskoye persisted until the 1970s, when descendants of the original settlers started being repatriated to the mainland, largely to the Ayon Island and Cape Schmidt, the homeland of Maritime Chukchi.10, 16 The age of the entire D2a cluster is 4.4/4.3 kya. Remarkably, the age of the D2a1a subcluster, calculated on the basis of 31 mitogenomes uniquely marked by the m.8910C>A transversion, is only 1.4/1.0 kya, implying shallow historical depth for the Aleut-specific D2a1a.
Haplogroup D4b1a2
A portion of the eastern Asian D4b1 phylogeny is given in Supplementary Figure S3. Apart from a relic haplotype (EU482305.1) stemming directly from the basic D4b1a2, there are two major subbranches (D4b1a2a1 and D4b1a2a2) that share a prominent node, m.13720C>T. The geographic distribution of the complete D4b1a2 mtDNAs and its time-depth (8.7/10.1 kya) may be attributed to those Siberians who underwent pronounced differentiation in the Altai-Sayan refugium, followed by far-reaching dispersals toward the northeastern edge of Siberia and subsequent isolation between ancestral and descendant groups. This conjecture is supported by the overlap of the Yukaghir, Tubalar, Altai-kizhi, Buryat, Tuvan, Chukchi, Naukan, and Canadian Eskimo (Inuit) mtDNA sequences within the D4b2a phylogeny.10, 13, 31
The coalescence date of the D4b1a2a1-m.16093T>C subhaplogroup distinguished by m.14305G>A, m.15448C>A, m.16172T>C, and m.16215A>G unequivocally links a portion of the Tubalar maternal gene pool from northeastern Altai to that harbored by the Neo-Eskimos. An updated time estimate of the D4b1a2a1-m.11383T>C-m.14122A>C-m.16093T>C, based on 11 complete sequences is 1.9/2.8 kya, being much younger D4b1a2a1-m.16093T>C aged 4.4/6.2 kya. Because the founding haplotype marked by m.11383T>C-m.14122A>C appear to derive from Arctic Canada, it is likely that the D4b1a2a1-m.11383T>C-m.14122A>C-m.16093T>C (D3a2 in Volodko et al10) would define original Inuit territory as the geographic origin of the D4b1a2a1-m.11383T>C-m.14122A>C-m.16093T>C range expansion.
Discussion
New findings and interpretation
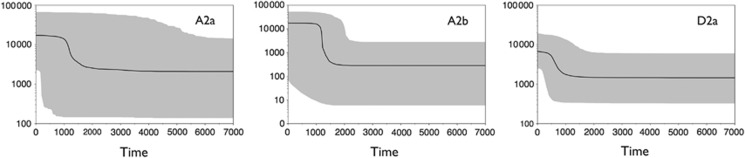
The above results appear to reflect the origins and expansion history of Beringian-specific mtDNA lineages. To reconstruct their migratory trajectories during population expansion, we used BSPs for major haplogroups. Thus, the BSP for A2a and A2b points to demographic growth events dated at ~2.0 and ∼1.5 kya, respectively, whereas the steepest D2a expansion took place less than ∼1 kya (Figure 4). The phylogeographic profiles support the scenario that central Beringia was the ancestral homeland for A2 as a whole originating in situ around 15.0 kya, but only much later were its particular derivatives (A2a and A2b) involved in the Chukotka-Alaska coastal expansion. Unlike basal A2a and A2b sequences, the A2 root have scarcely ever been encountered, with only three mitogenomes reported to date.10, 29 Lack of the A2 root on both sides of the Bering Strait may indicate that a basal population, being restricted in an isolated glacial refugium, have gone extinct during the time of postglacial submergence of the Bering Isthmus. Surprisingly, the first evidence for human presence in Alaska (Swan Point), the most likely region for entry into the New World, has a similar date of ~14.5 kya,4 thus eliminating discordance between inferences based on paleoecological, genetic, and archeological records regarding the timing of settlement in central Beringia.
Figure 4.
Bayesian Skyline Plots for A2a, A2b, D2a mtDNAs. The y axis indicates the effective number of females. The solid line is the median estimate and the colored shading shows the 95% highest posterior density limits.
Of particular note, A2 mtDNAs are virtually absent from the Siberian interior.10, 13, 31, 32, 33 In this connection, we consider challenging the assertion by Tamm et al.34: ‘A novel demographic scenario of relatively recent gene flow from Beringia to deep into western Siberia (Samoyed-speaking Selkups) is the most likely explanation for the phylogeography of haplogroup A2a, which is nested within an otherwise exclusively Native American A2 phylogeny'. The single Selkup mitogenome, attributed to A2a by Tamm et al,34 indeed belongs to A2a1 (Supplementary Figure S1). Aside from an almost identical A2a1 complete sequence harbored by an Inuit gleaned from GenBank (Supplementary Table S1), the HVS-I database also indicates a major presence of A2a1 among the Chukchi10 and in the Aleut.35 Hence, our reevaluation of the claimed Selkup record of A2 casts doubts on its validity and makes it clear that western-central Siberia is essentially bereft of the A2 lineage.
Interaction between Tlingit and Aleut
Analysis of mtDNA variation in Commander Islands inhabitants has disclosed five D2a mtDNA genomes (13.9%) of non-Aleut origin, lacking the m.8910C>A variant. Their Native American – rather than Aleut – identity is based on self-reported family ancestry and genealogies (field notes compiled by Rem Sukernik in 2001 and 2007, unpublished). It appears that the mtDNA data are consistent with historical records indicating that some Tlingit women were among the Alaskan natives and Russian sea otter hunters relocated by the Russian-American Company from New Archangel in 1840, the Russian outpost (present-day Sitka) in southeastern Alaska.21 This finding is congruent with the identification of D2a HVS-I markers (m.16092T>C, m.16129G>A, and m.16271T>C) in a few of the mtDNA samples retrieved from pre-Columbian remains on or near the Alaska Peninsula.35 It is likely that the D2a root defined by m.11959A>G and its derivative (D2a-m.16092T>C) traces its origin to populations initially established in southeastern Alaska. Likewise, one modern Aleut in the sample of Rubizc et al36 and one Apache (Na-Dene) in the sample of Torroni et al37 exhibit D2a-m.16092T>C. The fact that D2a is virtually absent in the present-day Tlingit38 may imply that a severe bottleneck played a critical role in Russian Alaska and Tlingit demographic history.39 Notably, the Tlingit are most closely related to Alaskan Athapaskan as revealed by HLA-DRB1 allele frequencies.22 Taken together, the archeological, linguistic, and genetic evidence support a single origin for Athapaskan Indians and Northwest Coastal inhabitants, the Tlingit included, prior to their spread to the interior of Alaska.40
Neo-Eskimos versus Paleo-Eskimos
The first human colonization of the North American Arctic was accomplished by Paleo-Eskimos who ~5000 years ago lived in small groups, widely distributed at very low density across the vast Arctic coastline, separating the eastern tip of Siberia from the southern tip of Greenland. The far-reaching Paleo-Eskimo migrations have occurred during a particularly warm postglacial period, and may have been partly motivated by the movements of their primary food source: herds of caribou and muskox. Around 1000 years ago, almost all of the Paleo-Eskimo groups had been replaced throughout their territories by the Alaskan Thule culture (sometimes called Neo-Eskimos), the direct ancestors of the Inuit. Their settlement patterns have changed to that of large coastal communities that reflect an increased reliance on sea mammals hunting, especially whaling, for subsistence. Although Neo-Eskimos are found to be mainly of in situ origin from Arctic Coast, it is not explicitly clear whether the Inuit people and the Paleo-Eskimo cultures that preceded them were genetically the same people or independent groups.41, 42, 43, 44
Previous studies of mtDNA variation in Neo-Eskimos demonstrated a close similarity between mtDNA pools of the Bering Sea Eskimos and Canadian and Greenlandic Inuit.10, 18, 26, 45 Most recently, the genetic prehistory of the North American Arctic was the focus of considerable research that led to a number of new insights into human migration patterns in the New World Arctic.46 The study has been conducted using nuclear and mitochondrial DNA data. The authors concluded that despite cultural differences, Paleo-Eskimos display a substantial level of genetic continuity. However, the sampling problem is an important issue: of large data set comprising 169 ancient samples from the sites in the High Arctic, mostly in Canada, Greenland and Alaska, only seven ancient mtDNAs were successfully retrieved and entirely sequenced.46 To have a richer picture of mitochondrial diversity in Beringia, we incorporated these particular mitogenomes into the trees allowing for inferences pertaining to the genetic origins and relationships of the various cultures to each other (Supplementary Figures S1–S3). Of the three Siberian Eskimo tribes – Sireniki, Chaplin, and Naukan – only Naukan is genetically similar to Canadian and Greenlandic Inuit, primarily because they share subhaplogroup D4b1a2a1-m.16093T>C harboring m.11383T>C-m.14122A>C motif, whereas Neo-Eskimos, the Naukan included, do not exhibit D2a10, 15, 46 (also refer this study). In contrast, the occurrence of D2a1b in the Sireniki mtDNA gene pool implies that traces of the Paleo-Eskimo cultures have not been fully erased by the subsequent spread of Neo-Eskimos. This conjecture is congruent with the fundamental genetic position of the Sireniki language that led Krauss to conclude that Siberian Eskimoan was never a dialect continuum, but rather a result of distinctive coastal dispersals.17
Conclusion
The initial split between eastern and western Beringian haplogroups is likely located in the southern extent of Siberia and the Russian Far East, the territory of the presumptive origin of founding haplotypes for major Native American mtDNA haplogroups at or near the last glacial maximum. Current analysis, based on the largest and most diverse set of complete mtDNA sequences, generated to date on both sides of the Bering Strait has revealed a palimpsest of different migrations. The direct ancestors of Paleo-Eskimos are primarily drawn from Chukotka, whereas Neo-Eskimos are found to be mainly of the northern Alaska/Arctic Canada origin but also to harbor Altai-Sayan-related ancestry. Co-representation of A2a and D2a, as well as our phylogeographical and BSP analyses of these haplogroups, point to a common origin of Paleo-Eskimos, Aleuts, and Tlingit (and probably other Na-Dene groups), whose direct ancestors must have lived along the southern coastline of the former Bering Land Bridge in the early Holocene.
Acknowledgments
The authors have greatly benefited from conversations with Anatoly P Derevianko. The help of Andre M Sukernik and Alexander Kim in editing the final draft of the manuscript is gratefully acknowledged. This work received support from Russian Foundation for Basic Research (#12-04-01851), the Ministry of Education and Science, Russian Federation, and was partly funded by the Russian Academy of Science Program on Molecular and Cellular Biology.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Supplementary Material
References
- 1Kuzmin Y: Siberia at the Last Glacial Maximum: environment and archaeology. J Archaeol Res 2008; 16: 163–221. [Google Scholar]
- 2Graf KE: “The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly”: evaluating the radiocarbon chronology of the middle and late Upper Paleolithic in the Enisei River valley, south-central Siberia. J Archaeol Sci 2009; 36: 694–707. [Google Scholar]
- 3Meiri M, Lister AM, Collins MJ et al: Faunal record identifies Bering isthmus conditions as constraint to end-Pleistocene migration to the New World. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 2014; 281: 2013–2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4Hoffecker JF, Elias SA: Human Ecology of Beringia. New York: Columbia University Press, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 5Erlandson J, Braje T: Foundations for the Far West: Paleoindian Cultures on the Western Fringe of North America. The Oxford Handbook of North American Archaeology. New York: Oxford University Press, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 6Reich D, Patterson N, Campbell D et al: Reconstructing Native American population history. Nature 2012; 488: 370–374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7Achilli A, Perego UA, Lancioni H et al: Reconciling migration models to the Americas with the variation of North American native mitogenomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 14308–14313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8Torroni A, Sukernik RI, Schurr TG et al: mtDNA variation of aboriginal Siberians reveals distinct genetic affinities with Native Americans. Am J Hum Genet 1993; 53: 591–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9Derbeneva OA, Sukernik RI, Volodko NV, Hosseini SH, Lott MT, Wallace DC: Analysis of mitochondrial DNA diversity in the Aleuts of the Commander Islands and its implications for the genetic history of Beringia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 415–421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10Volodko NV, Starikovskaya EB, Mazunin IO et al: Mitochondrial genome diversity in arctic Siberians, with particular reference to the evolutionary history of Beringia and Pleistocenic peopling of the Americas. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 1084–1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11Fagundes NJ, Kanitz R, Ecker R et al: Mitochondrial population genomics supports a single pre-Clovis origin with a coastal route for the peopling of the Americas. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 583–592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12Perego UA, Angerhofer N, Pala M et al: The initial peopling of the Americas: a growing number of founding mitochondrial genomes from Beringia. Genome Res 2010; 20: 1174–1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13Sukernik RI, Volodko NV, Mazunin IO, Eltsov NP, Dryomov SV, Starikovskaya EB: Mitochondrial genome diversity in the Tubalar, Even, and Ulchi: Contribution to the prehistory of Native Siberians and their affinities to Native Americans. Am J Phys Antropol 2012; 148: 123–138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14Kumar S, Bellis C, Zlojutro M, Melton PE, Blangero J, Curran JE: Large scale mitochondrial sequencing in Mexican Americans suggests a reappraisal of Native American origins. BMC Evol Biol 2011; 11: 293–310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15Gilbert MT, Kivisild T, Grønnow B et al: Paleo-Eskimo mtDNA genome reveals matrilineal discontinuity in Greenland. Science 2008; 320: 1787–1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16Krupnik I, Chlenov M: Yupik Transitions: Change and Survival at Bering Strait, 1900–1960. Fairbanks: University of Alaska Press, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 17Krauss M: Eskimo languages in Asia, 1791 on, and the Wrangel Island-Point Hope connection. Études/Inuit/Studies 2005; 29: 163–185. [Google Scholar]
- 18Starikovskaya YB, Sukernik RI, Schurr TG, Kogelnik AM, Wallace DC: Mitochondrial DNA diversity in Chukchi and Siberian Eskimos: Implications for the genetic history of ancient Beringia and the peopling of the New World. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63: 1473–1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19Bogoras W: The Chukchee. Publications of the Jesup North Pacific Expedition 1910; 8 (pt. 1). [Google Scholar]
- 20Veltre D, Smith M: Historical overview of archaeological research in the Aleut region of Alaska. Hum Biol 2010; 82: 487–506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21Jochelson W: History, Ethnology, and Anthropology of Aleuts. Washington: Carnegie Inst. of Washington, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- 22Volodko NV, Derbeneva OA, Uinuk–ool TS, Sukernik RI: Genetic history of Aleuts of the Commander Islands as revealed by the analysis of the HLA class II gene variability. Genetika (Russian) 2003; 12: 1710–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23Andrews R, Kubacka I, Chinnery PF, Lightowlers RN, Turnbull DM, Howell N: Reanalysis and revision of the Cambridge reference sequence for human mitochondrial DNA. Nat Genet 1999; 23: 147–147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A: Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol and Evol 1999; 16: 37–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25Forster P, Harding R, Torroni A, Bandelt HJ: Origin and evolution of Native American mtDNA variation: a reappraisal. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: 935–935. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26Saillard J, Forster P, Lynnerup N, Bandelt H, Norby S: MtDNA variation among Greenland Eskimos: the edge of the Beringian expansion. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 718–726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27Fu Q, Mittnik A, Johnson PL et al: A revised timescale for human evolution based on ancient mitochondrial genomes. Curr Biol 2013; 23: 553–559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D: jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 2012; 9: 772–772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29van Oven M, Kayser M: Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: e386–e394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30Rasmussen M, Li Y, Lindgreen S et al: Ancient human genome sequence of an extinct Palaeo-Eskimo. Nature 2010; 463: 757–762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31Derenko M, Malyarchuk B, Grzybowski T et al: Phylogeographic analysis of mitochondrial DNA in northern Asian Populations. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 1025–1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32Starikovskaya EB, Sukernik RI, Derbeneva OA et al: Mitochondrial DNA diversity in indigenous populations of the southern extent of Siberia, and the origins of Native American haplogroups. Ann Hum Genet 2005; 69: 67–89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33Duggan AT, Whitten M, Wiebe V et al: Investigating the prehistory of Tungusic Peoples of Siberia and the Amur-Ussuri region with complete mtDNA genome sequences and Y-chromosomal markers. PloS One 2013; 8: e83570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34Tamm E, Kivisild T, Reidla M et al: Beringian standstill and spread of Native American founders. PLoS One 2007; 2: e829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35Raff J, Tackney J, O'Rurke DH: South from Alaska: a pilot aDNA study of genetic history on the Alaska Peninsula and the eastern Aleutians. Hum Biol 2010; 82: 677–693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36Rubicz R, Schurr T, Babb P, Crawford M: Mitochondrial DNA variation and the origins of the Aleuts. Hum Biol 2003; 75: 809–835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37Torroni A, Schurr TG, Cabell MF et al: Asian affinities and continental radiation of the four founding Native American mtDNAs. Am J Hum Genet 1993; 53: 563–590. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38Schurr TG, Dulik MC, Owings AC et al: Clan, language, and migration history has shaped genetic diversity in Haida and Tlingit populations from Southeast Alaska. Am J Phys Antropol 2012; 148: 422–435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39Dauenhauer N, Dauenhauer R, Black L: Russians in Tlingit America. The battles of Sitka, 1802 and 1804, in Anooshi Lingit, Aani Ka (eds) Seattle: University of Washington Press, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 40Ames KM, Maschner HDG: Peoples of the Northwest Coast: their Archaeology and Prehistory. London: Thames & Hudson, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 41McGhee R: Ancient People of the Arctic. Vancouver: UBC Press, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 42Rudenko SI: Ancient culture of the Bering Sea and Eskimo problem. Moscow-Leningrad: Izdatel'stvo Glavsevmorputi, 1947, in Russian. [Google Scholar]
- 43Harritt RK: Paleo-eskimo beginnings in North America: a new discovery at Kuzitrin Lake, Alaska. Etudes Inuit 1998; 22: 61–81. [Google Scholar]
- 44Savelle J, Dyke A: Paleoeskimo occupational history of Foxe Basin, Arctic Canada: implications for the Core Area model and Dorset origins. Am Antiquity 2014; 79: 249–276. [Google Scholar]
- 45Helgason A, Pálsson G, Pedersen HS et al: MtDNA variation in Inuit populations of Greenland and Canada: migration history and population structure. Am J Phys Anthropol 2006; 130: 123–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46Raghavan M, DeGiorgio M, Albrechtsen A et al: The genetic prehistory of the New World Arctic. Science 2014; 345: 1255832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.