Abstract
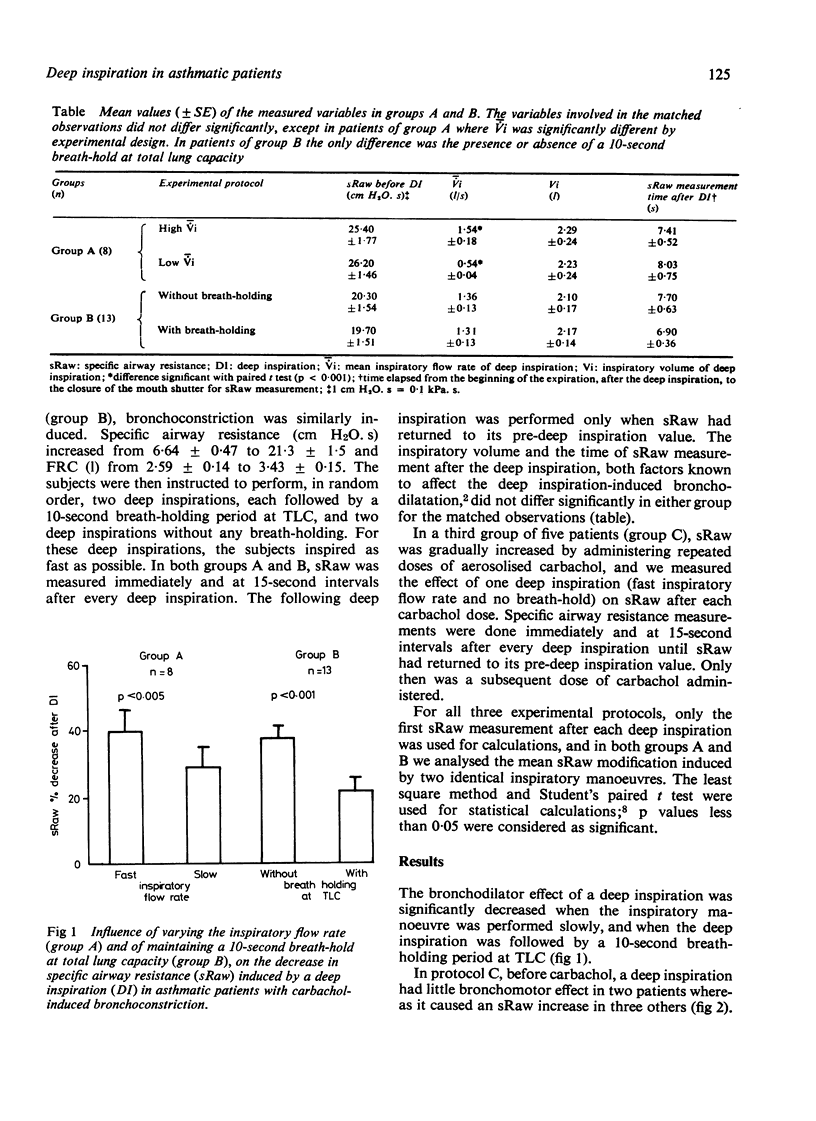
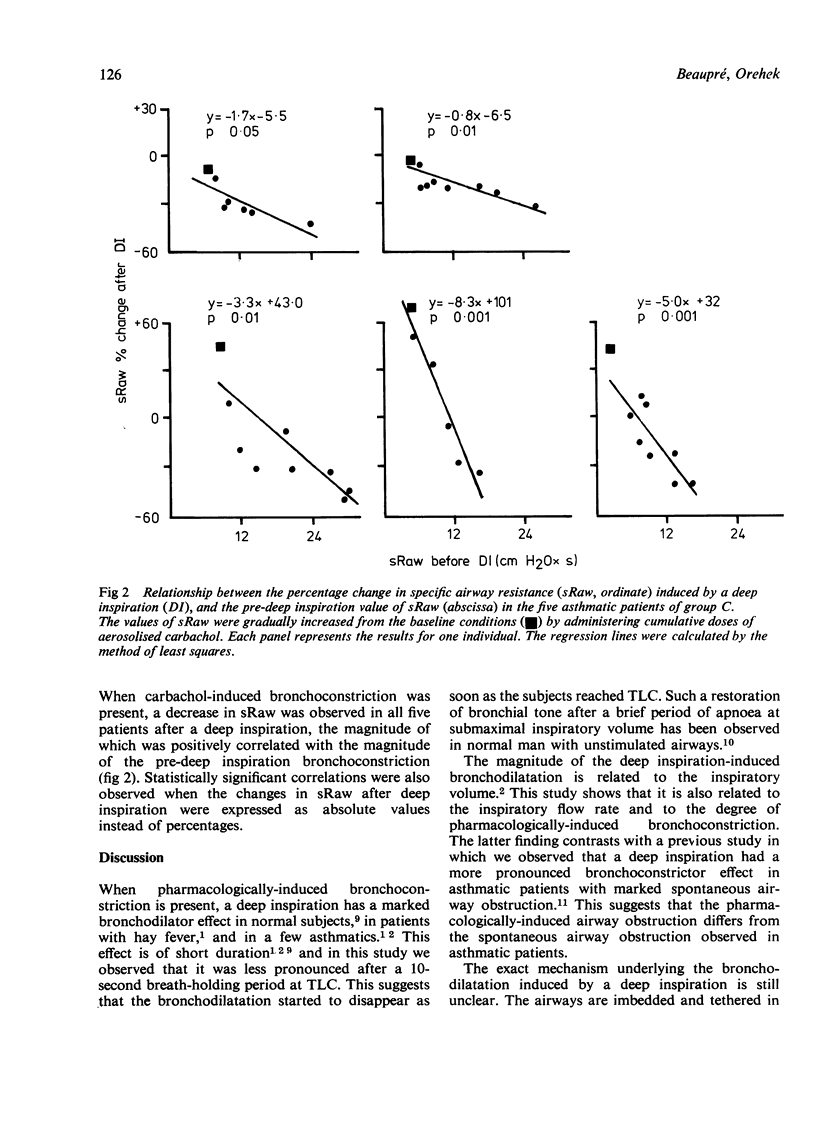
We have studied 26 asthmatic patients in whom deep inspiration induced a transient but marked bronchodilatation when carbachol-induced bronchoconstriction was present. Changes in bronchial tone were assessed by specific airway resistance measurements. Bronchodilatation after a slow inspiration (eight subjects) or a 10-second breath-hold at total lung capacity (13 subjects) was significantly less than that observed after either a fast inspiration or no breath-holding period. The magnitude of the bronchodilatation induced by a fast inspiration without breath-holding was directly and significantly related to the magnitude of the carbachol-induced bronchoconstriction in five subjects.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry E. M., Edmonds J. F., Wyllie H. Release of prostaglandin E2 and unidentified factors from ventilated lungs. Br J Surg. 1971 Mar;58(3):189–192. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H. L., FOWLER W. S., LAMBERT E. H. Effect of volume and rate of inflation and deflation on transpulmonary pressure and response of pulmonary stretch receptors. Am J Physiol. 1956 Dec;187(3):558–566. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.3.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish J. E., Peterman V. I., Cugell D. W. Effect of deep inspiration on airway conductance in subjects with allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Jul;60(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froeb H. F., Mead J. Relative hysteresis of the dead space and lung in vivo. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Sep;25(3):244–248. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.3.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayrard P., Orehek J., Grimaud C., CHarpin J. Bronchoconstrictor effects of a deep inspiration in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):433–439. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Mead J. Time dependence of flow-volume curves. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Dec;37(6):793–797. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. L., Watson A., Wilson A. G., Pride N. B. Influence of bronchomotor tone on airway dimensions and resistance in excised dog lungs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Aug;49(2):270–278. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.2.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NADEL J. A., TIERNEY D. F. Effect of a previous deep inspiration on airway resistance in man. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Jul;16:717–719. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.4.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Charpin D., Velardocchio J. M., Grimaud C. Bronchomotor effect of bronchoconstriction-induced deep inspirations in asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):297–305. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Massari J. P., Gayrard P., Grimaud C., Charpin J. Effect of short-term, low-level nitrogen dioxide exposure on bronchial sensitivity of asthmatic patients. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):301–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI108281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Nicoli M. M., Delpierre S., Beaupre A. Influence of the previous deep inspiration on the spirometric measurement of provoked bronchoconstriction in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Mar;123(3):269–272. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. Vagal sensory receptors and their reflex effects. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):159–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Kitamura S., Yoshida T., Preskitt J., Holden L. D. Humoral control of airways. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;221:103–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb28205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hoppin F. G., Jr Hysteresis of contracted airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Dec;47(6):1251–1262. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.6.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Johnson F. N., Goldberg N. B., Van Lith P. Hysteresis and stress adaptation in the human respiratory system. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Oct;23(4):487–497. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. F., Widdicombe J. G. The interaction of chemo- and mechanoreceptor signals in the control of airway calibre. Respir Physiol. 1975 Dec;25(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(75)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. The activity of pulmonary stretch receptors during bronchoconstriction, pulmonary oedema, atelectasis and breathing against a resistance. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:436–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



