Abstract
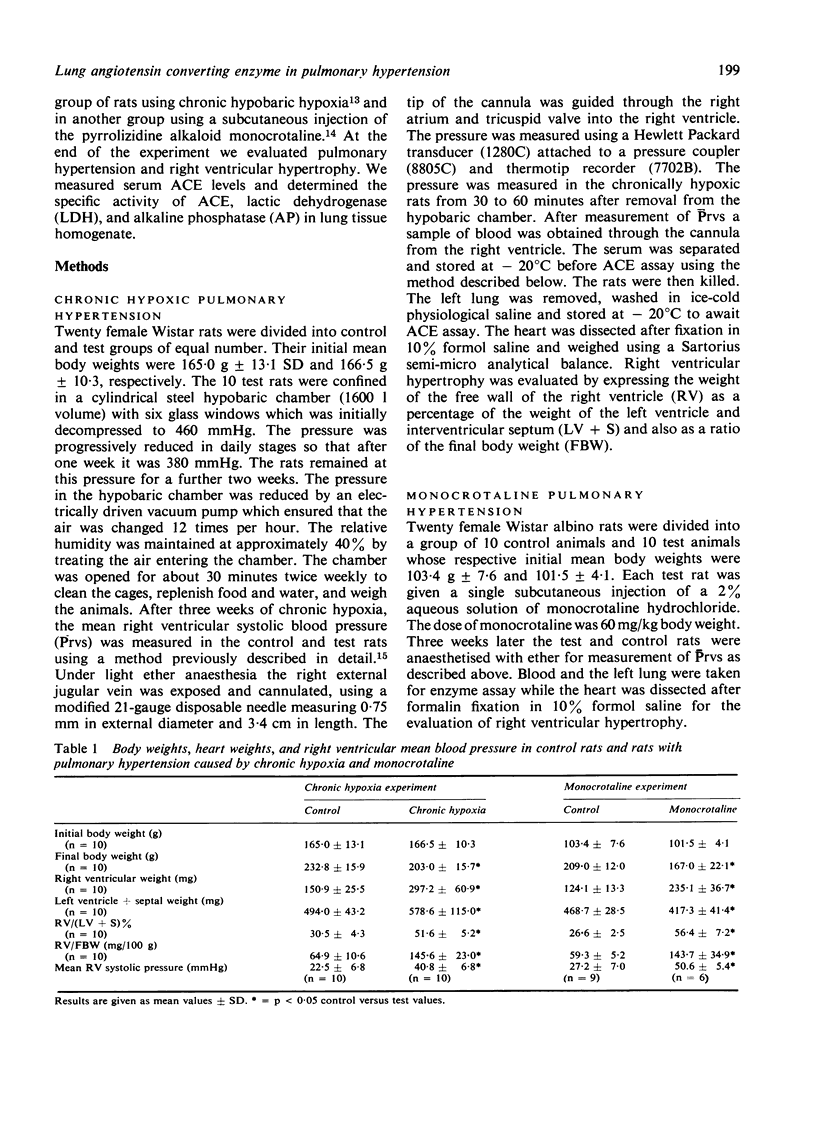
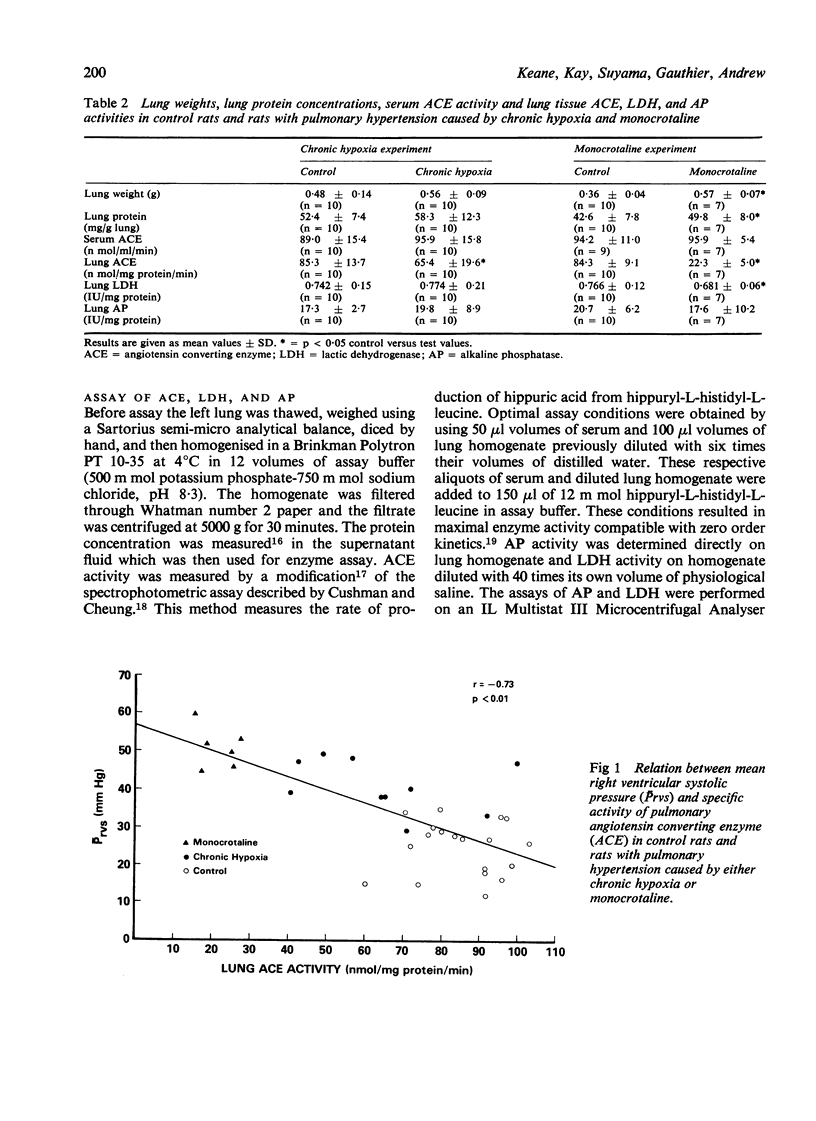
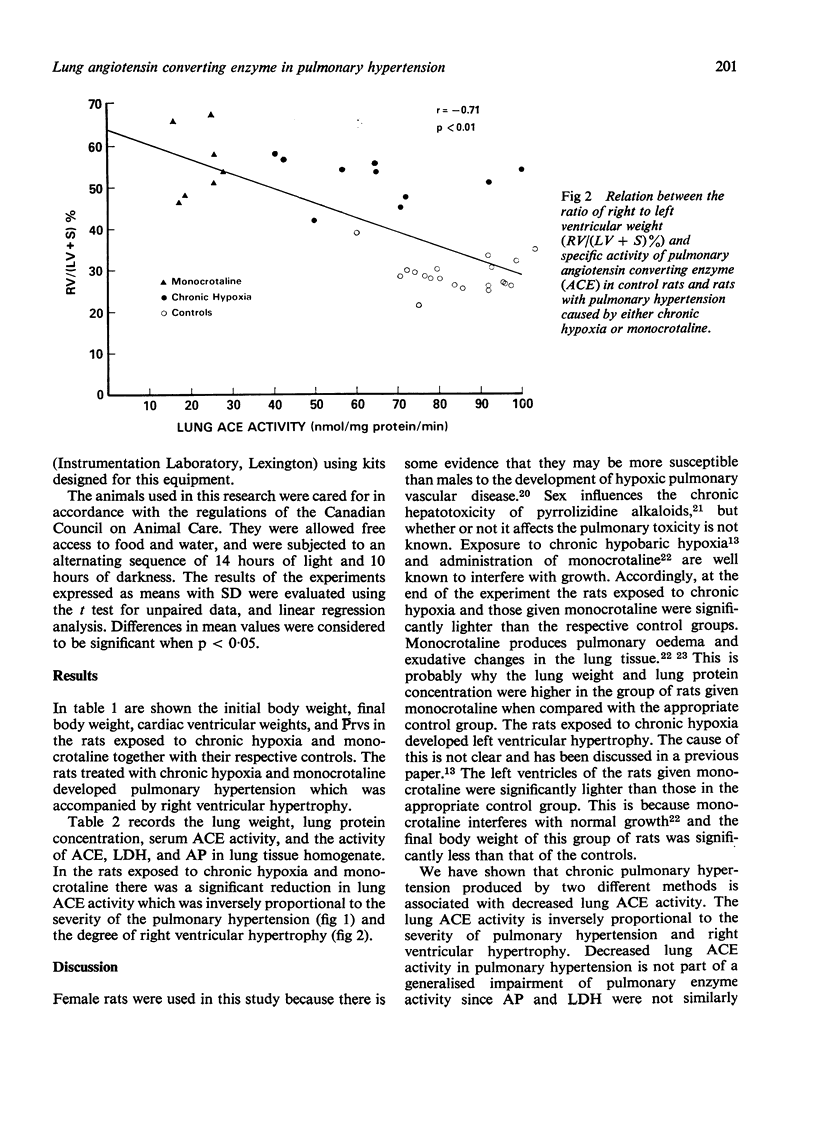
We have studied serum and lung tissue angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity in female Wistar rats with pulmonary hypertension induced by two different methods. Chronic pulmonary hypertension was produced in one group of 10 rats (CH) by confinement in a hypobaric chamber (380 mmHg) for three weeks, and in another group fo 10 rats (M) by a single subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline (60 mg/kg body weight). In these two groups of tests rats and in 20 untreated controls (C), we evaluated right ventricular mean systolic blood pressure (Prvs mmHg), right ventricular hypertrophy, and serum ACE (n mol/ml/min). In lung tissue homogenate, we measured the specific activity of ACE (n mol/mg protein/min), alkaline phosphatase (AP) (IU/mg protein) and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) (IU/mg protein). The Prvs in groups, C, CH, and M was 25 +/- 7 SD, 41 +/- 7, and 51 +/- 5, respectively. The ratio of right ot left ventricular weight (RV/(LV + S)%) in groups, C, CH, and M was 29 +/- 4, 52 +/- 5, and 56 +/- 7, respectively. The lung tissue ACE in groups C, CH, and M was 85 +/- 11, 65 +/- 20, and 22 +/- 5, respectively. In groups CH, and M the Prvs and RV/(LV + S)% were significantly elevated above control values while lung ACE was significant decreased (p less than 0.05). There was a significant inverse relationship between lung ACE on one hand, and Prvs (r = - 0.73) and RV/(LV + S)% (r = - 0.71) on the other hand. Serum ACE and lung AP were unchanged. In group M there was a slight but significant reduction in lung LDH. Chronic pulmonary hypertension, irrespective of its method of production, is associated with decreased lung ACE. The reduction in lung ACE is inversely proportional to the severity of pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;20(7):1637–1648. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G. Angiotensin I converting enzyme. Circ Res. 1975 Feb;36(2):247–255. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanburg B. L., Glazier J. B. Conversion of angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2 in the isolated perfused dog lung. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Sep;35(3):325–331. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. A., Rouse E. T., Kazemi H. Failure of saralasin acetate, a competitive inhibitor of angiotensin II, to diminish alveolar hypoxic vasoconstriction in the dog. Cardiovasc Res. 1977 Nov;11(6):541–546. doi: 10.1093/cvr/11.6.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Patwell S., Zuckerman J. E., Gorin A., Parsons G. Effect of acute lung injury on angiotensin converting enzyme in serum, lung lavage, and effusate. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):373–376. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Patwell S. W., Zuckerman J. E., Gorin A. B., Parsons G., Giri S. N. Effect of paraquat on serum angiotensin converting enzyme. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 May;121(5):795–798. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.5.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxtable R., Ciaramitaro D., Eisenstein D. The effect of a pyrrolizidine alkaloid, monocrotaline, and a pyrrole, dehydroretronecine, on the biochemical functions of the pulmonary endothelium. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):1189–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jago M. V. Factors affecting the chronic hepatotoxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J Pathol. 1971 Sep;105(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/path.1711050102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M. Effect of intermittent normoxia on chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular hypertrophy, and polycythemia in rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jun;121(6):993–1001. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Gillund T. D., Heath D. Mast cells in the lungs of rats fed on Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. Am J Pathol. 1967 Dec;51(6):1031–1044. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Heath D. Observations on the pulmonary arteries and heart weight of rats fed on Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(2):385–394. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Smith P., Heath D. Electron microscopy of Crotalaria pulmonary hypertension. Thorax. 1969 Sep;24(5):511–526. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.5.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Smith P., Heath D., Will J. A. Effects of phenobarbitone, cinnarizine, and zoxazolamine on the development of right ventricular hypertrophy and hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease in rats treated with monocrotaline. Cardiovasc Res. 1976 Mar;10(2):200–205. doi: 10.1093/cvr/10.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Waymire J. C., Grover R. F. Lung mast cell hyperplasia and pulmonary histamine-forming capacity in hypoxic rats. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jan;226(1):178–184. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.1.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Treut A., Couliou H., Delbary M., Larzul J. J., De Labarthe B., Le Gall J. Y. Le dosage de l'enzyme de conversion de l'angiotensine I par méthode spectrophotométrique. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Oct 15;98(1-2):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuenberger P. J., Stalcup S. A., Mellins R. B., Greenbaum L. M., Turino G. M. Decrease in angiotensin I conversion by acute hypoxia in dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Sep;158(4):586–589. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijers C. A., Rutten J. C. A simple rapid method for the determination of total nitrogen in urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 May;24(2):308–310. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Gamble W., Reid L. Development of Crotalaria pulmonary hypertension: hemodynamic and structural study. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):H692–H702. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.5.H692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molteni A., Zakheim R. M., Mullis K. B., Mattioli L. The effect of chronic alveolar hypoxia on lung and serum angiotensin I converting enzyme activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):263–265. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. K., Vane J. R. Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Nature. 1967 Nov 25;216(5117):762–766. doi: 10.1038/216762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S., Low J., Koerner T. J. Altered angiotensin I conversion in pulmonary disease. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Dec;51(6):537–543. doi: 10.1042/cs0510537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polsky-Cynkin R., Reichlin S., Fanburg B. L. Angiotensin-1-converting enzyme activity in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Jul;164(3):242–247. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W., Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Whitaker C., Chung A. Subcellular localization of pulmonary antiotensin-converting enzyme (kininase II). Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):497–499. doi: 10.1042/bj1460497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Moosavi H., Winson M., Heath D. The influence of age and sex on the response of the right ventricle, pulmonary vasculature and carotid bodies to hypoxia in rats. J Pathol. 1974 Jan;112(1):11–18. doi: 10.1002/path.1711120104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalcup S. A., Lipset J. S., Woan J. M., Leuenberger P., Mellins R. B. Inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme activity in cultured endothelial cells by hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):966–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI109397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Stalcup S. A., Pang L. M., Lipset J. S., Odya C. E., Goodfriend T. L., Mellins R. B. Gestational changes in pulmonary converting enzyme activity in the fetal rabbit. Circ Res. 1978 Nov;43(5):705–711. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szidon P., Bairey N., Oparil S. Effect of acute hypoxia on the pulmonary conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II in dogs. Circ Res. 1980 Feb;46(2):221–226. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakheim R. M., Mattioli L., Molteni A., Mullis K. B., Bartley J. Prevention of pulmonary vascular changes of chronic alveolar hypoxia by inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme in the rat. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



