Description
A man presented to his local plastic surgery department, with a history of headache and recurrent abscesses in the soft tissues of the forehead (figure 1). He was initially treated with repeated aspiration and antibiotics, but the lesion failed to resolve. A diagnosis of chronic frontal sinusitis with osteomyelitis, eponymously called Pott's Puffy tumour,1 was made after CT scan (figure 2A) and MRI (figure 2B). The patient was then taken to the theatre for endoscopic sinus surgery and frontal sinus trephines to drain the abscess and ensure adequate sinus ventilation. Microbiological analysis of the abscess pus confirmed growth of Streptococcus anginosus. In total, a 3-month course of metronidazole and moxifloxacin antibiotic therapy was completed to treat the frontal bone osteomyelitis. Repeat CT scan showed well-pneumatised sinuses and no disease recurrence (figure 3). The patient was followed up for 1 year to ensure resolution and remained symptom free.
Figure 1.
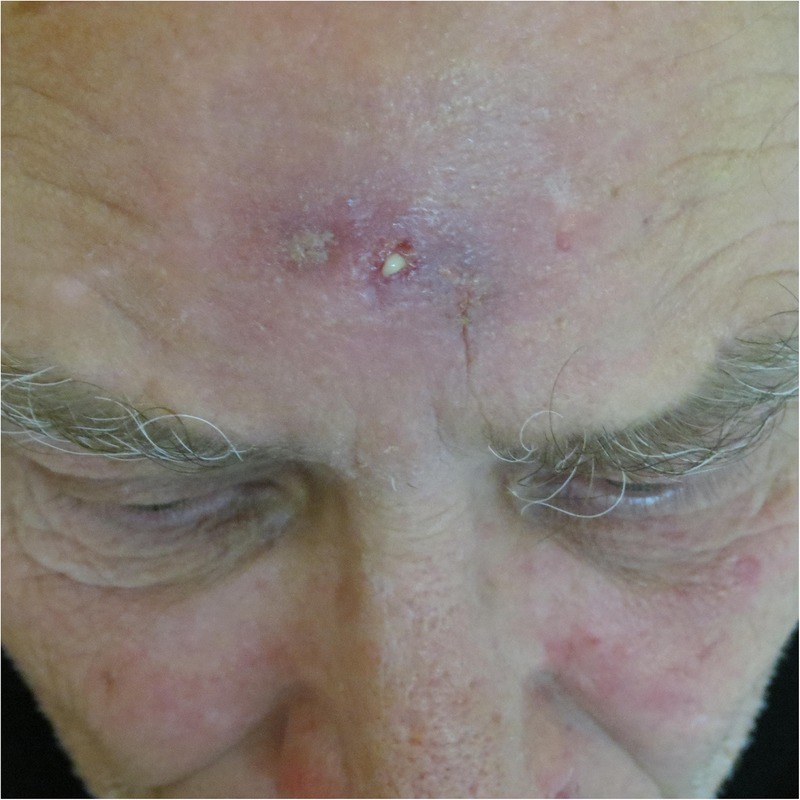
Clinical photograph showing discharging frontal sinus abscess. The surrounding tissues are swollen, erythaematous and boggy.
Figure 2.
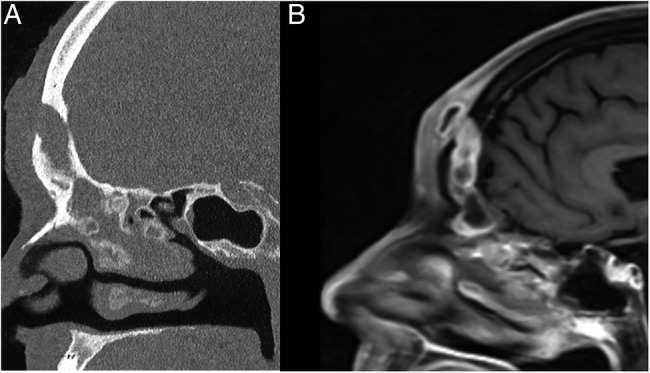
(A) Sagittal CT of the paranasal sinuses demonstrating an opacified frontal sinus, erosion of the anterior wall of the frontal sinus and contiguous abscess of the soft tissues of the forehead. (B) Sagittal T1-weighted MRI with contrast of the paranasal sinuses showing forehead soft tissue abscess with enhancement in continuity with opacified frontal sinus.
Figure 3.
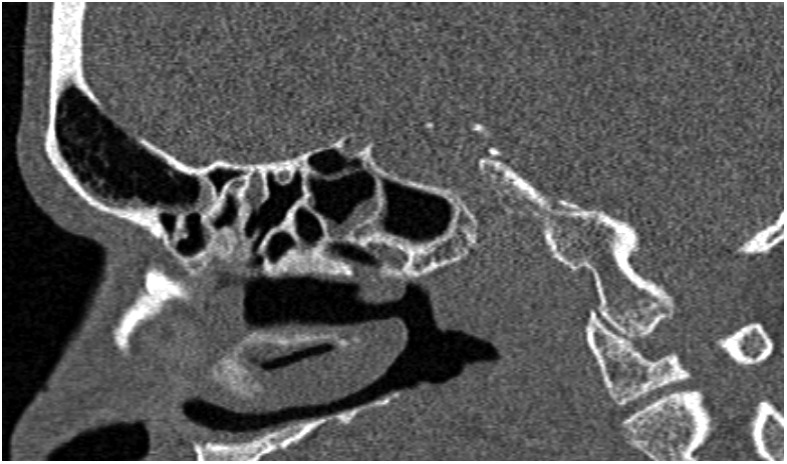
Post-treatment sagittal CT scan demonstrating a well-pneumatised frontal sinus; the other paranasal sinuses are also healthy with no disease recurrence. The imaging improvement can lag behind clinical response, though in this case, a sufficient time window has elapsed between treatment and repeat CT scan.
In the initial stages of Pott's puffy tumour, misdiagnosis of a simple infected skin cyst may occur. Lesions in this region should be referred for an ENT (ear, nose and throat) opinion where endoscopic nasal assessment and cross-sectional radiological imaging will be performed. In the diagnostic work up for potential intracranial complications of rhinosinusitis, a combination of CT scan and MRI are complementary; CT scan provides a better assessment of the bony involvement, and MRI provides better characterisation of soft tissue detail and, importantly, can exclude intracranial involvement of frontal sinusitis. The treatment consists of a combination of long-term antibiotics, with surgical drainage, debridement and reconstruction, depending on disease severity.2
Learning points.
Pott's puffy tumour is a rare complication of frontal sinusitis.
Lesions on the forehead, especially with any sinonasal symptoms or headache, should be referred for an ENT (ear, nose and throat) opinion with nasal endoscopy and cross-sectional imaging.
Treatment of Pott's puffy tumour normally consists of long-term antibiotics, with surgical drainage, debridement and reconstruction, depending on disease severity.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the help and participation of our patient in the preparation and reviewing of the case report.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Pott P. The chirurgical works of Percival Pott, F.R.S. Vol 1 London, UK: Woods and Innes, 1808. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Akiyama K, Karaki M, Mori N. Evaluation of adult Pott's puffy tumor: our five cases and 27 literature cases. Laryngoscope 2012;122:2382–8. doi:10.1002/lary.23490 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


