Abstract
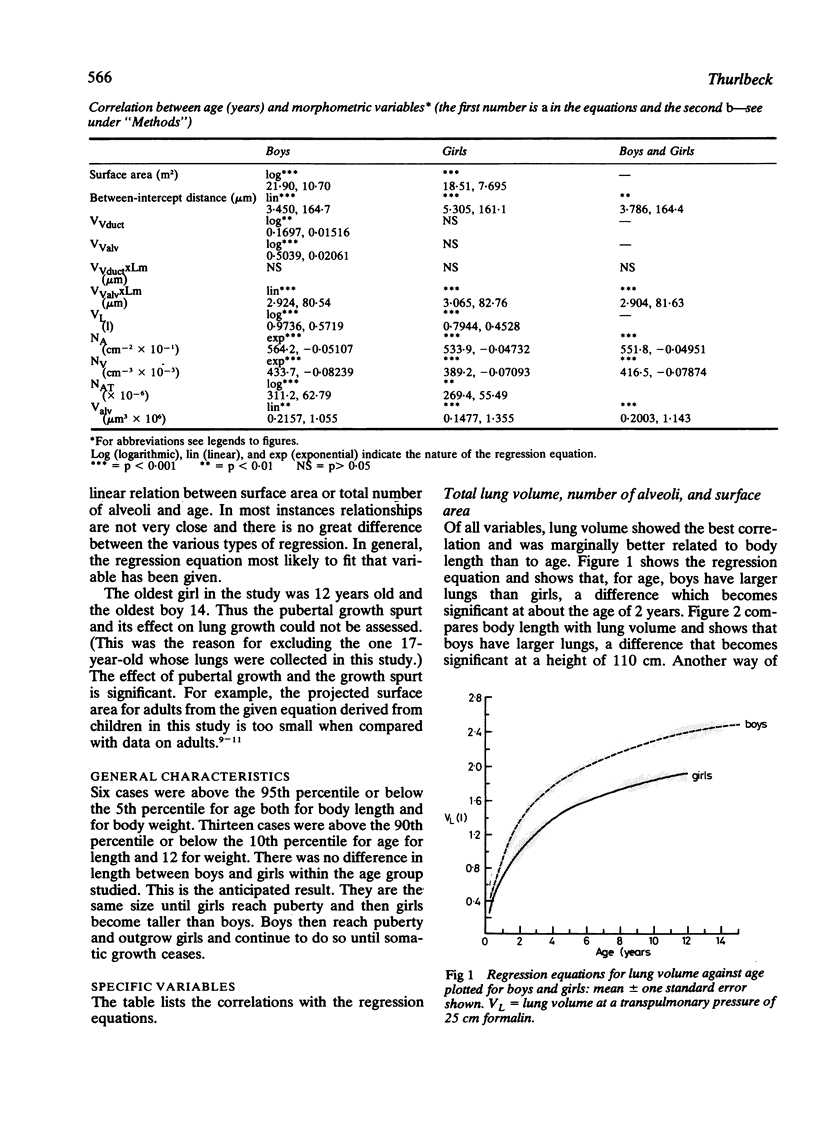
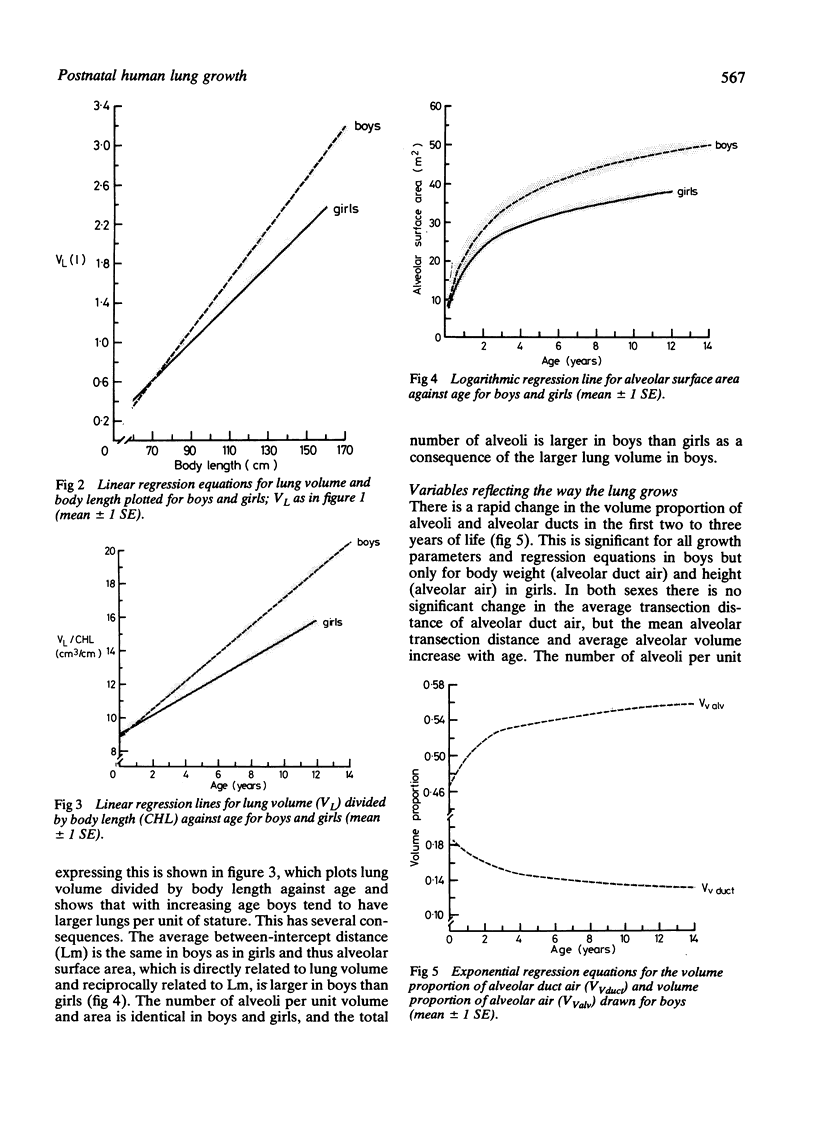
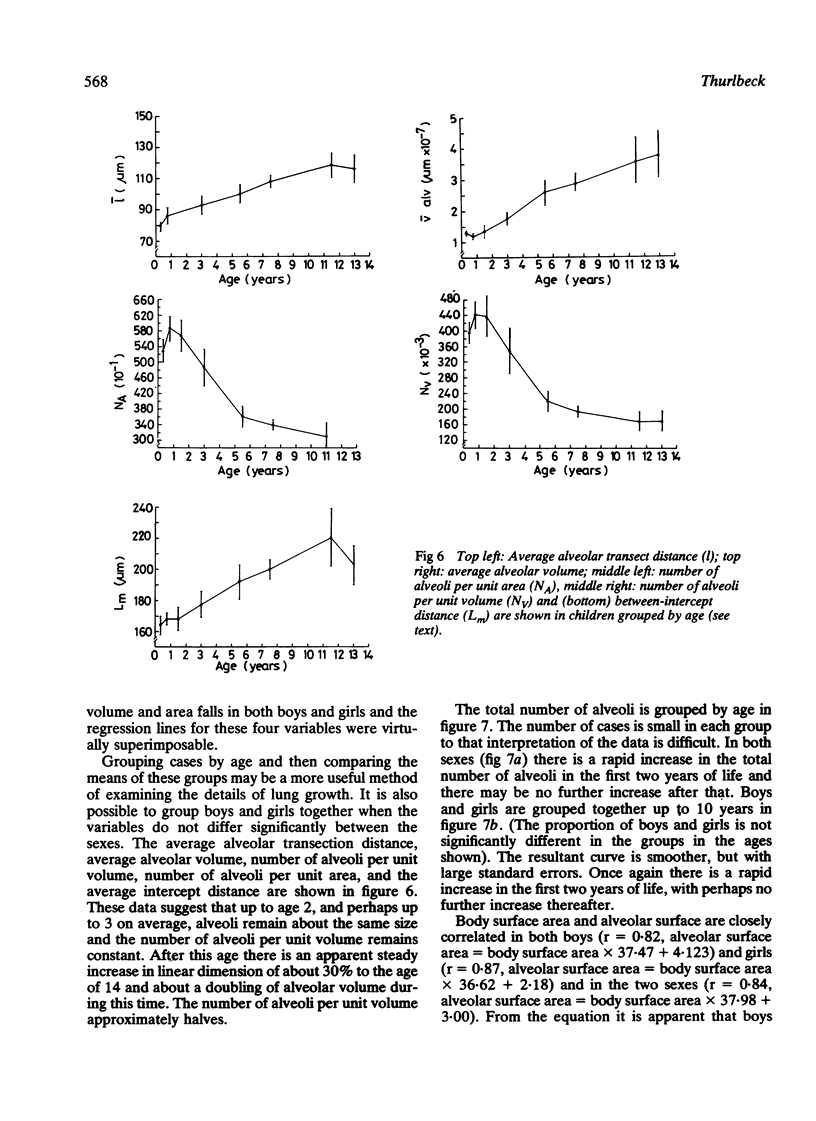
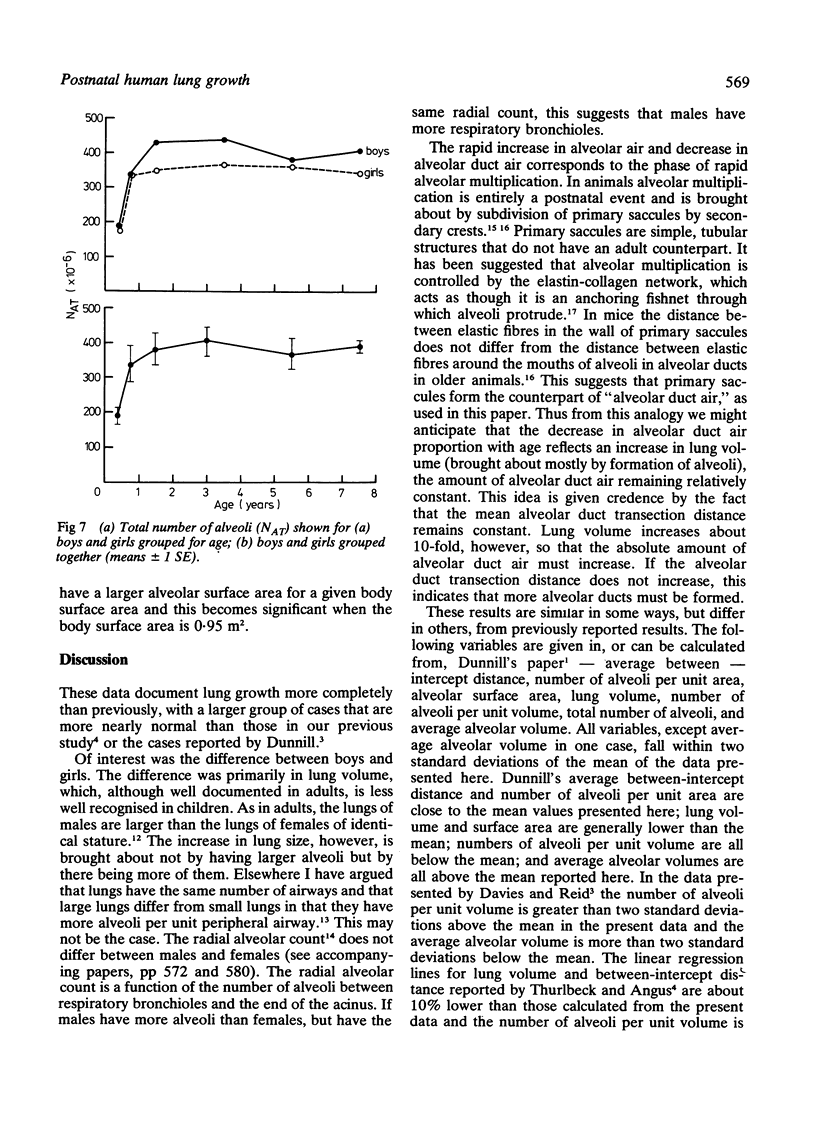
Standard morphometric methods were applied to the lungs of 36 boys and 20 girls aged from 6 weeks to 14 years, dying as a result of trauma or after short illnesses. Individual lung units, alveolar dimensions, and number of alveoli per unit area and volume did not differ between boys and girls, but boys had bigger lungs than girls for the same stature. This resulted in a larger total number of alveoli and a larger aveolar surface area in boys than in girls for a given age and stature. There may be more respiratory bronchioles in boys than girls. There was rapid alveolar multiplication during the first two years of life and alveolar dimensions and number of alveoli per unit area and volume did not change much during this period. There was little or no increase in the total number of alveoli after the age of 2 years but the data are hard to interpret. There is a wide scatter of the total number of alveoli in the growing lung, in keeping with the observation that the total number of alveoli is very variable in adults. Prediction data are given for the various morphometric variables studied.
Full text
PDF

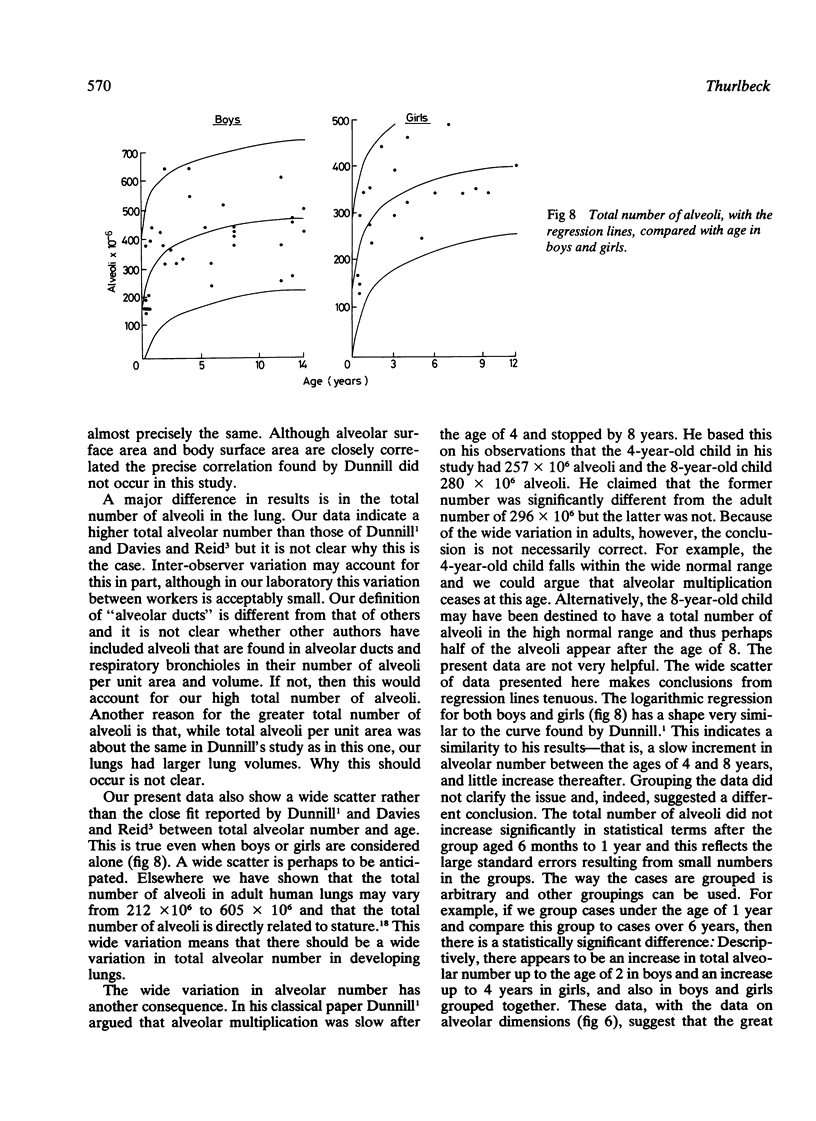

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy R. W., Bowes D., Burri P. H., Haines J., Thurlbeck W. M. Postnatal growth of the mouse lung. J Anat. 1977 Sep;124(Pt 1):131–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus G. E., Thurlbeck W. M. Number of alveoli in the human lung. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Apr;32(4):483–485. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burri P. H. The postnatal growth of the rat lung. 3. Morphology. Anat Rec. 1974 Sep;180(1):77–98. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091800109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. Lung surface area in various morphologic forms of human emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Aug;114(2):347–352. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G., Reid L. Growth of the alveoli and pulmonary arteries in childhood. Thorax. 1970 Nov;25(6):669–681. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMERY J. L., MITHAL A. The number of alveoli in the terminal respiratory unit of man during late intrauterine life and childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Dec;35:544–547. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.184.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery J. L. The post natal development of the human lung and its implications for lung pathology. Respiration. 1970;27(Suppl):41–50. doi: 10.1159/000192718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasleton P. S. The internal surface area of the adult human lung. J Anat. 1972 Sep;112(Pt 3):391–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida K., Thurlbeck W. M. Lack of recovery of lung structure and function after the administration of beta-amino-propionitrile in the postnatal period. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Sep;122(3):467–475. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston C., Waszkiewicz E., Thurlbeck W. M. A simple method for the representative sampling of lungs of diverse size. Thorax. 1979 Aug;34(4):527–530. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuba K., Thurlbeck W. M. The number and dimensions of small airways in nonemphysematous lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Oct;104(4):516–524. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.4.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle W. A simple method for volumetry of organs in quantitative stereology. Mikroskopie. 1970 Jun;26(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M. Post-mortem lung volumes. Thorax. 1979 Dec;34(6):735–739. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.6.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M. The internal surface area of nonemphysematous lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 May;95(5):765–773. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



