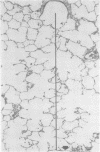
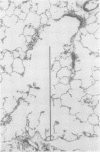
Abstract
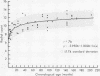
The radial alveolar count method of Emery and Mithal has been re-evaluated on 76 normal postnatal lungs. Results of reproducibility assessments suggest that each observer should establish normal control values when beginning with the method, and should subsequently use control cases to maintain strict reproducibility. The use of 10 fields per case was found to be inadequate to obtain satisfactory reproducibility, even for a single observer. Prior inflation of the lungs significantly increased the radial counts, and this factor may help to explain the large discrepancy between the results of this study and that of Emery and Mithal. The radial counts correlated well with the chronological age of the child (r = +0.76; p less than 0.001). Alveolarization of the acinus occurs primarily between birth and 2 years; significant but slower growth is seen up to 8 years, after which the results plateau, suggesting that alveolarization is complete. The radial count method appears to provide a relatively simple and reasonably satisfactory assessment of alveolar development, as originally proposed by Emery and Mithal.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AREECHON W., REID L. Hypoplasia of lung with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Br Med J. 1963 Jan 26;1(5325):230–233. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5325.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus G. E., Thurlbeck W. M. Number of alveoli in the human lung. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Apr;32(4):483–485. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenazi S. S., Perlman M. Pulmonary hypoplasia: lung weight and radial alveolar count as criteria of diagnosis. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Aug;54(8):614–618. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.8.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berend N., Marlin G. E. Arrest of alveolar multiplication in kyphoscoliosis. Pathology. 1979 Jul;11(3):485–491. doi: 10.3109/00313027909059026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain D., Hislop A., Hey E., Reid L. Pulmonary hypoplasia in babies with severe rhesus isoimmunisation: a quantitative study. J Pathol. 1977 May;122(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/path.1711220108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMERY J. L., MITHAL A. The number of alveoli in the terminal respiratory unit of man during late intrauterine life and childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Dec;35:544–547. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.184.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J., Weibel E. R. Morphological study of pressure-volume hysteresis in rat lungs fixed by vascular perfusion. Respir Physiol. 1972 Jun;15(2):190–213. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. D., Reid L. M. Pulmonary hypoplasia resulting from phrenic nerve agenesis and diaphragmatic amyoplasia. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):282–287. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80496-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. E., Ampaya E. P. Lung morphometry: a fallacy in the use of the counting principle. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Dec;37(6):951–954. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.6.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Hey E., Reid L. The lungs in congenital bilateral renal agenesis and dysplasia. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Jan;54(1):32–38. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. New pathological findings in emphysema of childhood. 1. Polyalveolar lobe with emphysema. Thorax. 1970 Nov;25(6):682–690. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.6.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes C., Thurlbeck W. M. Normal lung growth and response after pneumonectomy in rats at various ages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Nov;120(5):1125–1136. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.5.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Hislop A., Boyden E. A., Reid L. Lung hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. A quantitative study of airway, artery, and alveolar development. Br J Surg. 1971 May;58(5):342–346. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
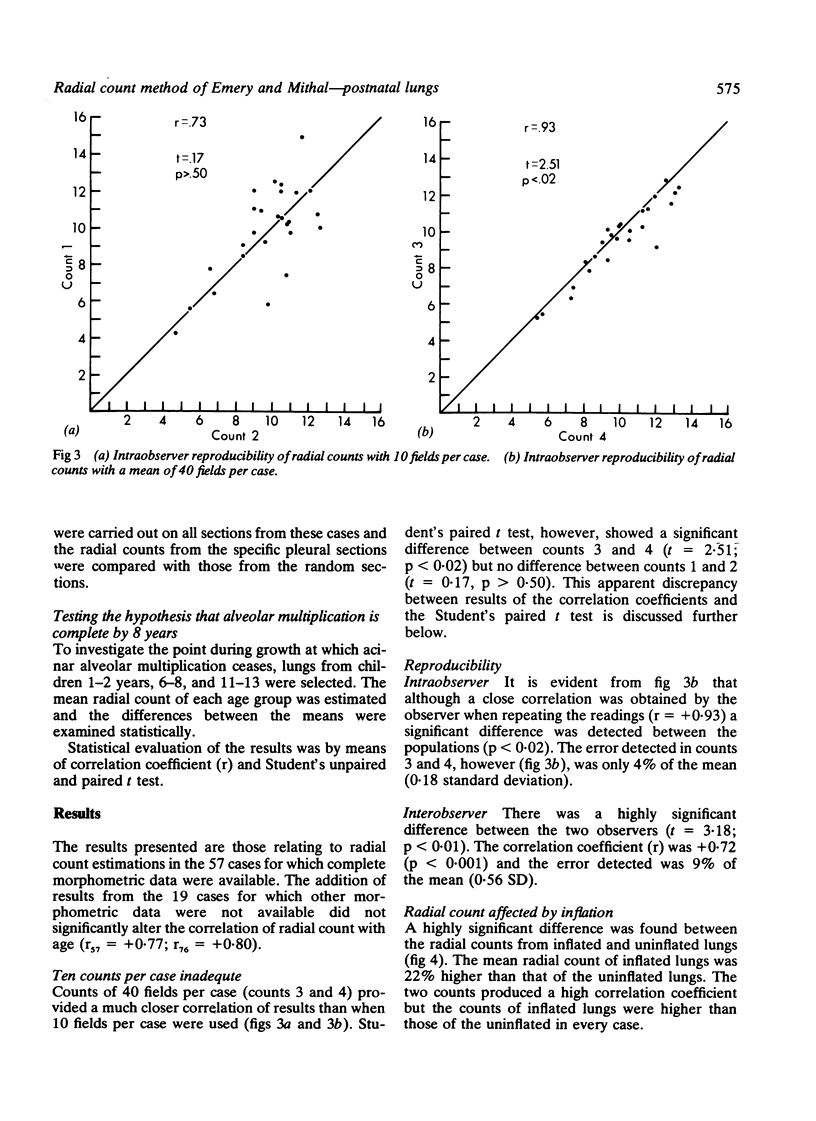
- Langston C., Waszkiewicz E., Thurlbeck W. M. A simple method for the representative sampling of lungs of diverse size. Thorax. 1979 Aug;34(4):527–530. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann A. W., Hum O. S., Francis D. W., Zingg W., van Oss C. J. Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of platelet adhesion from suspension to various substrates. J Biomed Mater Res. 1980 Jul;14(4):499–509. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820140416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Haworth S. G., Vance Z., Vawter G., Castaneda A. R., Nadas A. S., Reid L. M. Early pulmonary vascular changes in congenital heart disease studied in biopsy tissue. Hum Pathol. 1980 Sep;11(5 Suppl):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale F. R., Esterly J. R. Pulmonary hypoplasia: a morphometric study of the lungs of infants with diaphragmatic hernia, anencephaly, and renal malformations. Pediatrics. 1973 Jan;51(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swischuk L. E., Richardson C. J., Nichols M. M., Ingman M. J. Primary pulmonary hypoplasia in the neonate. J Pediatr. 1979 Oct;95(4):573–577. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., GOMEZ D. M. A principle for counting tissue structures on random sections. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Mar;17:343–348. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]