Abstract
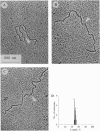
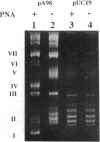
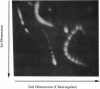
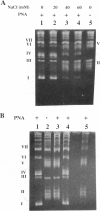
It was recently found that polyamide nucleic acid (PNA) analogues consisting of thymines attached to an aminoethylglycine backbone bind strongly and sequence-selectively to adenine sequences of oligonucleotides and double-stranded DNA [Nielsen, P. E., Egholm, M., Berg, R. H. & Buchardt, O. (1991) Science 254, 1497-1500]. It was concluded that the binding to double-stranded DNA was accomplished via strand displacement, in which the PNA bound to the Watson-Crick complementary adenine-containing strand, whereas the thymine-containing strand was extruded in a virtually single-stranded conformation. This model may provide a general way in which to obtain sequence-specific recognition of any sequence in double-stranded DNA by Watson-Crick hydrogen-bonding base-pair recognition, and it is thus paramount to rigorously establish this binding mode for synthetic DNA-binding ligands. We now report such results from electron microscopy. Furthermore, we show that binding of PNA to closed circular DNA results in unwinding of the double helix corresponding to approximately one turn of the double helix per 10 base pairs. The DNA.PNA complex, which is formed at low salt concentration (only a small portion of DNA molecules show complex formation at NaCl concentration higher than 40 mM), is exceptionally kinetically stable and cannot be dissociated by increasing salt concentration up to 500 mM.
Full text
PDF
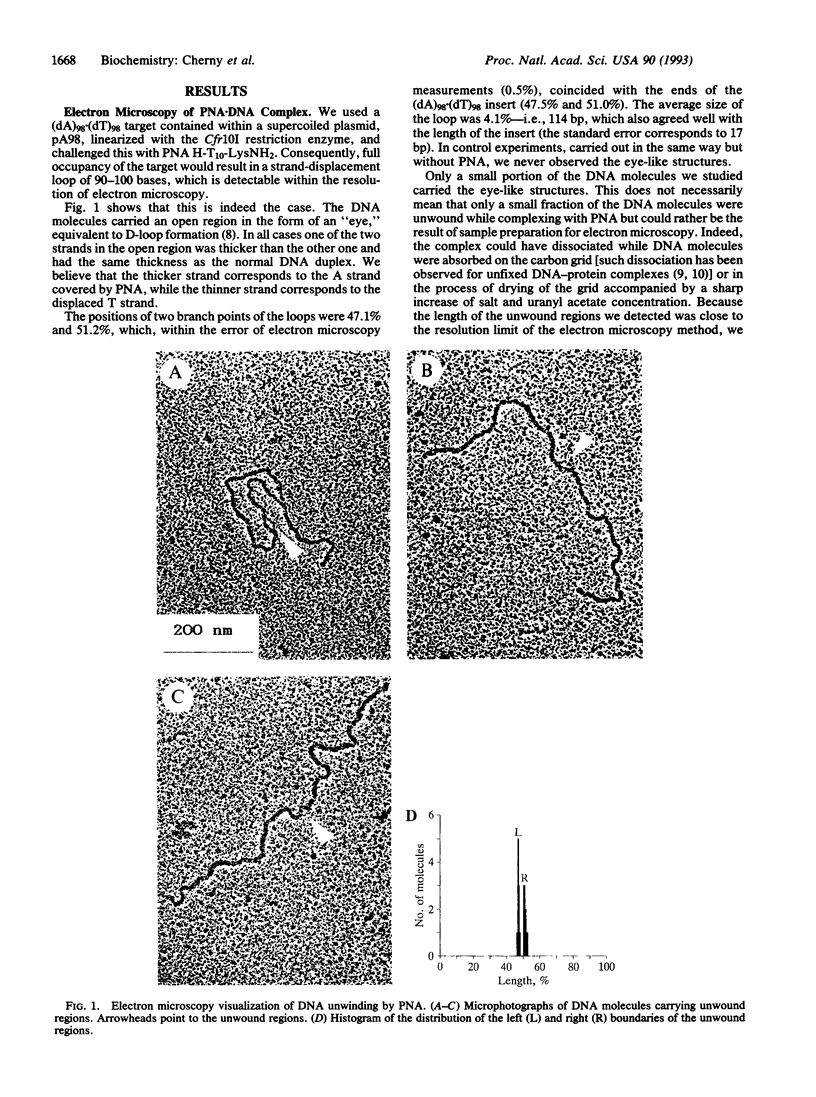
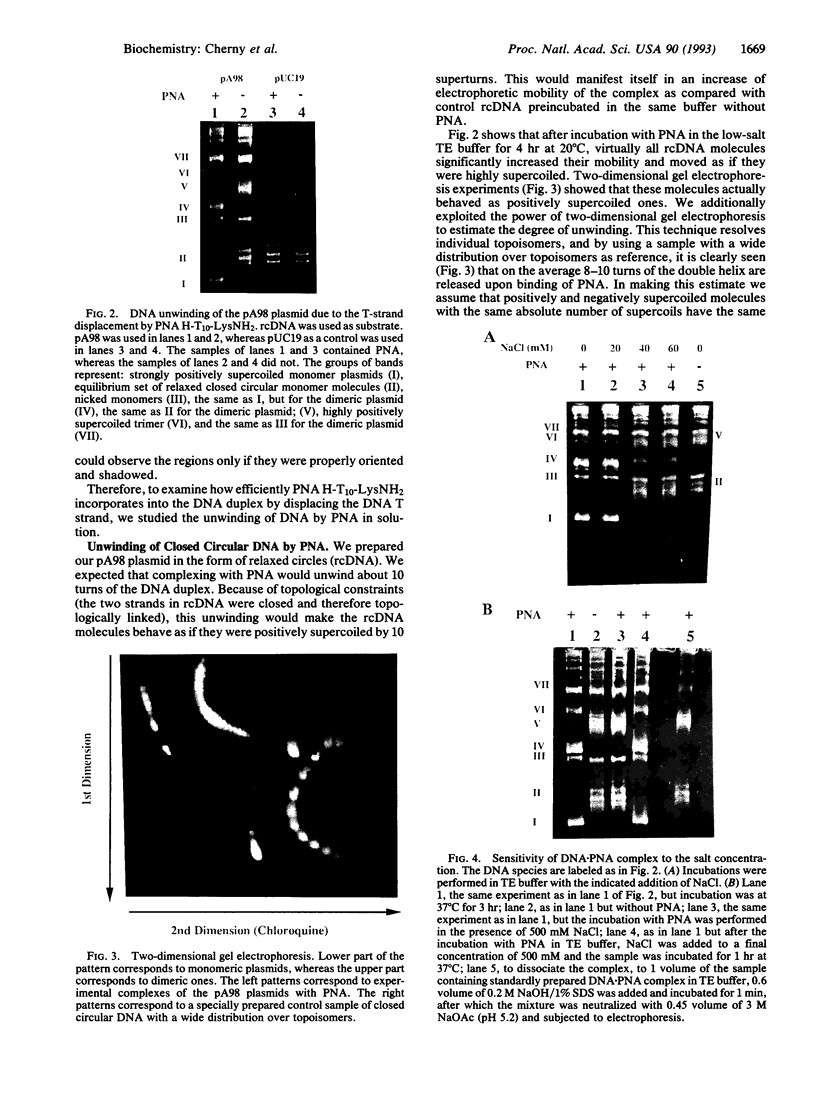

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anshelevich V. V., Vologodskii A. V., Lukashin A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Slow relaxational processes in the melting of linear biopolymers: a theory and its application to nucleic acids. Biopolymers. 1984 Jan;23(1):39–58. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Ducommun M., Zollinger M., Kellenberger E. A new preparation method for dark-field electron microscopy of biomacromolecules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Williams R. C., Chamberlin M. J. Electron microscopic studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. Characterization of the non-specific interactions of holoenzyme with a restriction fragment of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 5;136(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Robberson D. L., Vinograd J. A novel closed-circular mitochondrial DNA with properties of a replicating intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2252–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller T., Kübler O., Portmann R., Sogo J. M. High resolution physical mapping of specific binding sites of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase on the DNA of bacteriophage T7 . J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. A pH-dependent structural transition in the homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):327–338. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Berg R. H., Buchardt O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1962210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]