Abstract
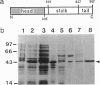
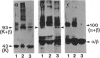
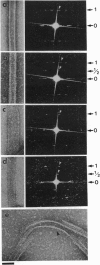
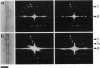
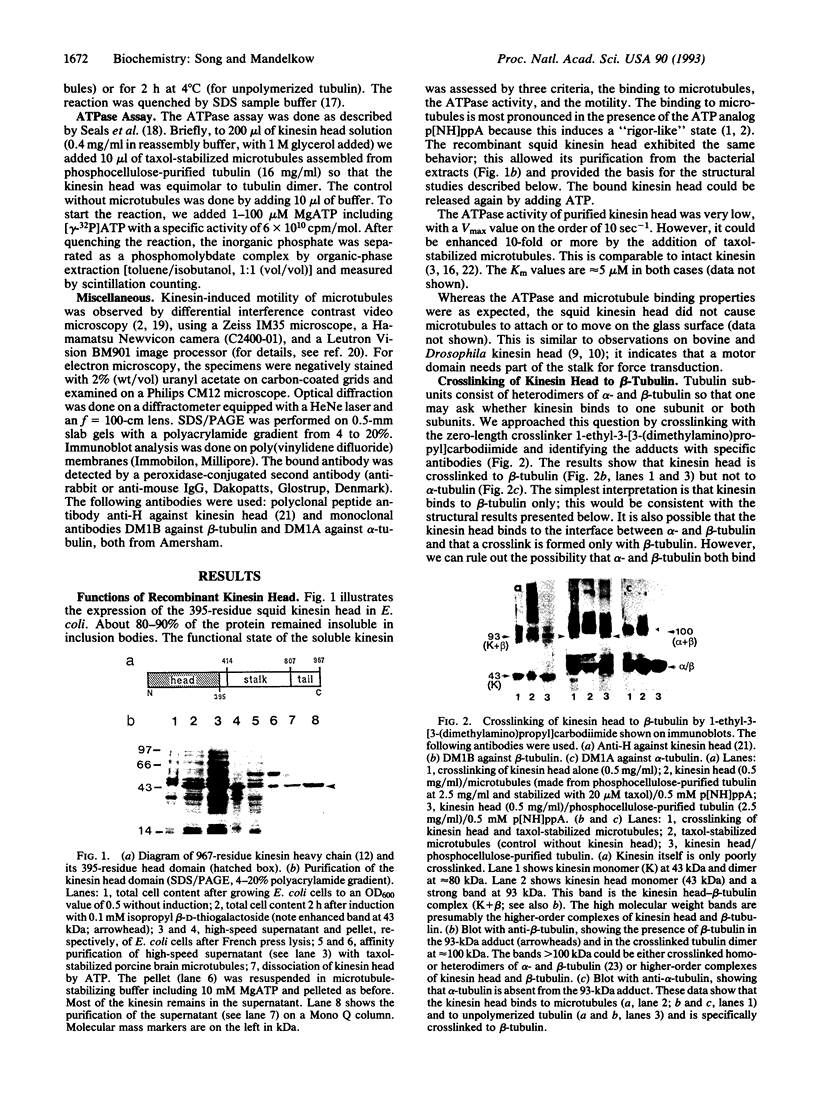
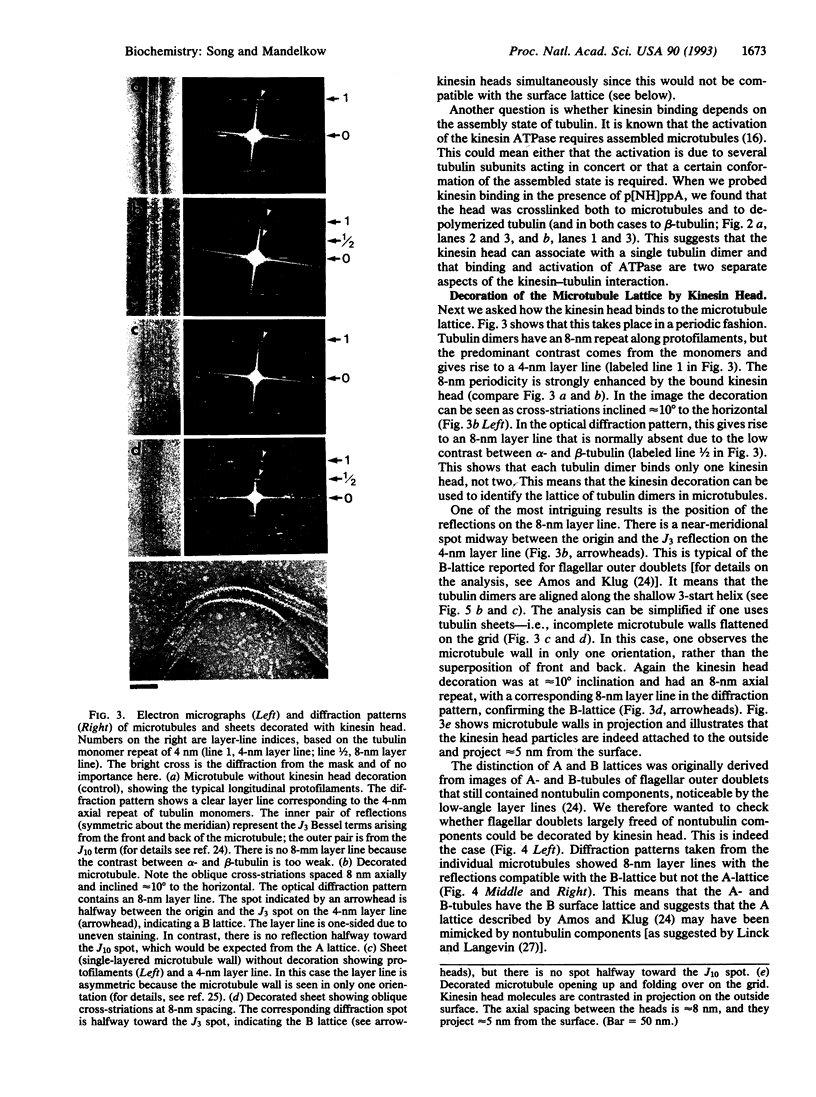
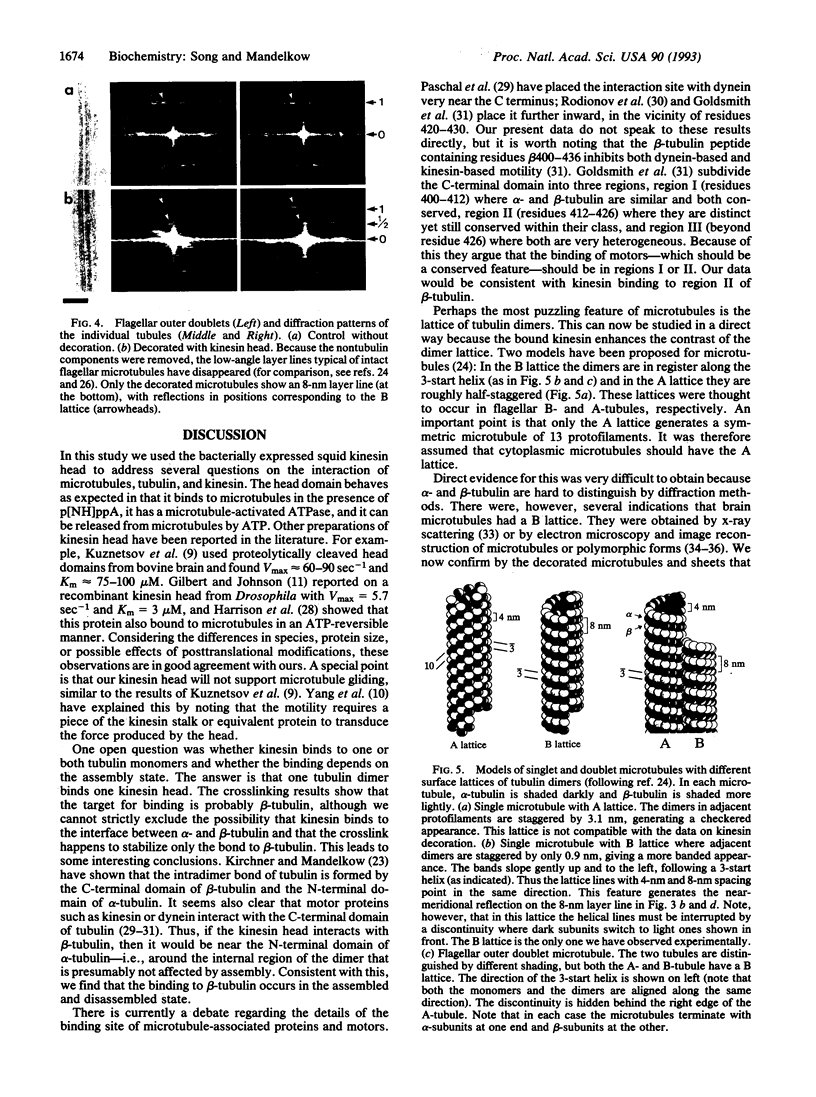
We have expressed the recombinant squid kinesin head domain in Escherichia coli and studied its interaction with microtubules. The head is active as a microtubule-stimulated ATPase and binds to microtubules, but it does not support microtubule gliding by itself. The head binds to both microtubules and depolymerized tubulin. In each case the zero-length crosslinker 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylamino)propyl] carbodiimide induces a bond specifically to beta- but not alpha-tubulin. The head decorates brain microtubules with an 8-nm axial spacing. Thus the stoichiometry is one kinesin head per tubulin dimer. The lattice is that of flagellar B-tubules, implying that reassembled microtubules are not symmetric. Moreover, the A- and B-tubules of intact flagellar outer doublets are both decorated with a B lattice. This suggests that the B lattice is a general property of microtubules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Weiss D. G., Hayden J. H., Brown D. T., Fujiwake H., Simpson M. Gliding movement of and bidirectional transport along single native microtubules from squid axoplasm: evidence for an active role of microtubules in cytoplasmic transport. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1736–1752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos L., Klug A. Arrangement of subunits in flagellar microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1974 May;14(3):523–549. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.3.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. W., Fraser C., Sale W. S., Tang W. J., Gibbons I. R. Preparation and purification of dynein. Methods Cell Biol. 1982;24:373–397. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60666-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S. Motor proteins for cytoplasmic microtubules. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90060-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T. Native structure and physical properties of bovine brain kinesin and identification of the ATP-binding subunit polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3409–3416. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T. A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):73–75. doi: 10.1038/317073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepeau R. H., McEwen B., Edelstein S. J. Differences in alpha and beta polypeptide chains of tubulin resolved by electron microscopy with image reconstruction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5006–5010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P. Microtubule surface lattice and subunit structure and observations on reassembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):153–167. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelles J., Schnapp B. J., Sheetz M. P. Tracking kinesin-driven movements with nanometre-scale precision. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):450–453. doi: 10.1038/331450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M., Connolly J. A., Kumar N., Wu J., Yarbrough L. R., van der Kooy D. Conserved beta-tubulin binding domain for the microtubule-associated motors underlying sperm motility and fast axonal transport. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;20(3):249–262. doi: 10.1002/cm.970200308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. The kinesin superfamily: tails of functional redundancy. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;1(4):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D. Kinesin ATPase: rate-limiting ADP release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6314–6318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura S., Kamiya R. High-frequency vibration in flagellar axonemes with amplitudes reflecting the size of tubulin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1443–1454. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura S., Mandelkow E. Tubulin protofilaments and kinesin-dependent motility. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):865–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner K., Mandelkow E. M. Tubulin domains responsible for assembly of dimers and protofilaments. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2397–2402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Schnapp B., Inouye H., Neve R. L. The primary structure and analysis of the squid kinesin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3278–3283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Gelfand V. I. Bovine brain kinesin is a microtubule-activated ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8530–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Vaisberg Y. A., Rothwell S. W., Murphy D. B., Gelfand V. I. Isolation of a 45-kDa fragment from the kinesin heavy chain with enhanced ATPase and microtubule-binding activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):589–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W., Langevin G. L. Reassembly of flagellar B (alpha beta) tubulin into singlet microtubules: consequences for cytoplasmic microtubule structure and assembly. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):323–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Herrmann M., Rühl U. Tubulin domains probed by limited proteolysis and subunit-specific antibodies. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):311–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E., Unwin N., Cohen C. Tubulin hoops. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):655–657. doi: 10.1038/265655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Schultheiss R., Rapp R., Müller M., Mandelkow E. On the surface lattice of microtubules: helix starts, protofilament number, seam, and handedness. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1067–1073. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E., Thomas J., Cohen C. Microtubule structure at low resolution by x-ray diffraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3370–3374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B., Edelstein S. J. Evidence for a mixed lattice in microtubules reassembled in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):123–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M. Structure of flagellar microtubules. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;125:47–93. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Obar R. A., Vallee R. B. Interaction of brain cytoplasmic dynein and MAP2 with a common sequence at the C terminus of tubulin. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):569–572. doi: 10.1038/342569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodionov V. I., Gyoeva F. K., Kashina A. S., Kuznetsov S. A., Gelfand V. I. Microtubule-associated proteins and microtubule-based translocators have different binding sites on tubulin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5702–5707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J., Wordeman L. G. Evidence for kinesin-related proteins in the mitotic apparatus using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):303–313. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Heuser J., Yang J. T., Goldstein L. S. Identification of globular mechanochemical heads of kinesin. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):355–357. doi: 10.1038/338355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., McDonald J. M., Bruns D., Jarett L. A sensitive and precise isotopic assay of ATPase activity. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Wright R. W., Swingle D. M. Enhancement by N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide of water-soluble carbodiimide-mediated coupling reactions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):220–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Shpetner H. S. Motor proteins of cytoplasmic microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:909–932. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Laymon R. A., Goldstein L. S. A three-domain structure of kinesin heavy chain revealed by DNA sequence and microtubule binding analyses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):879–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Saxton W. M., Stewart R. J., Raff E. C., Goldstein L. S. Evidence that the head of kinesin is sufficient for force generation and motility in vitro. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):42–47. doi: 10.1126/science.2142332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Massow A., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Interaction between kinesin, microtubules, and microtubule-associated protein 2. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(4):562–571. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]