Abstract
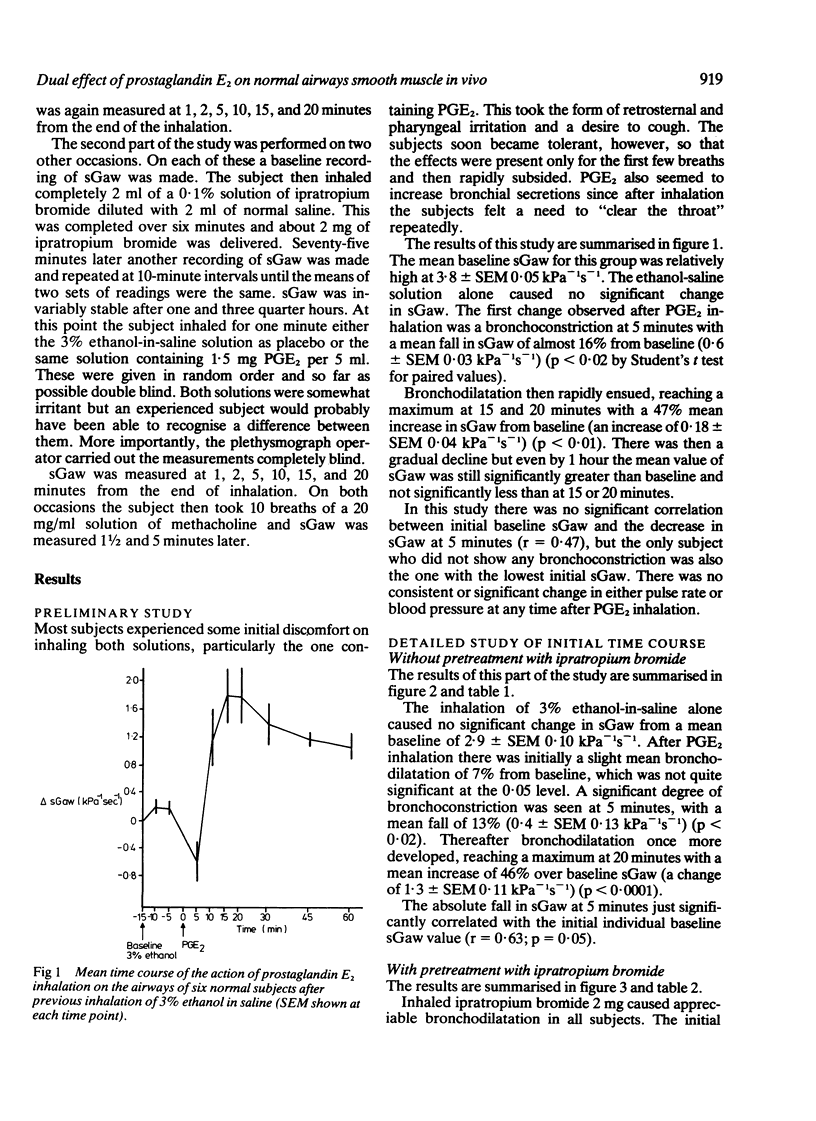
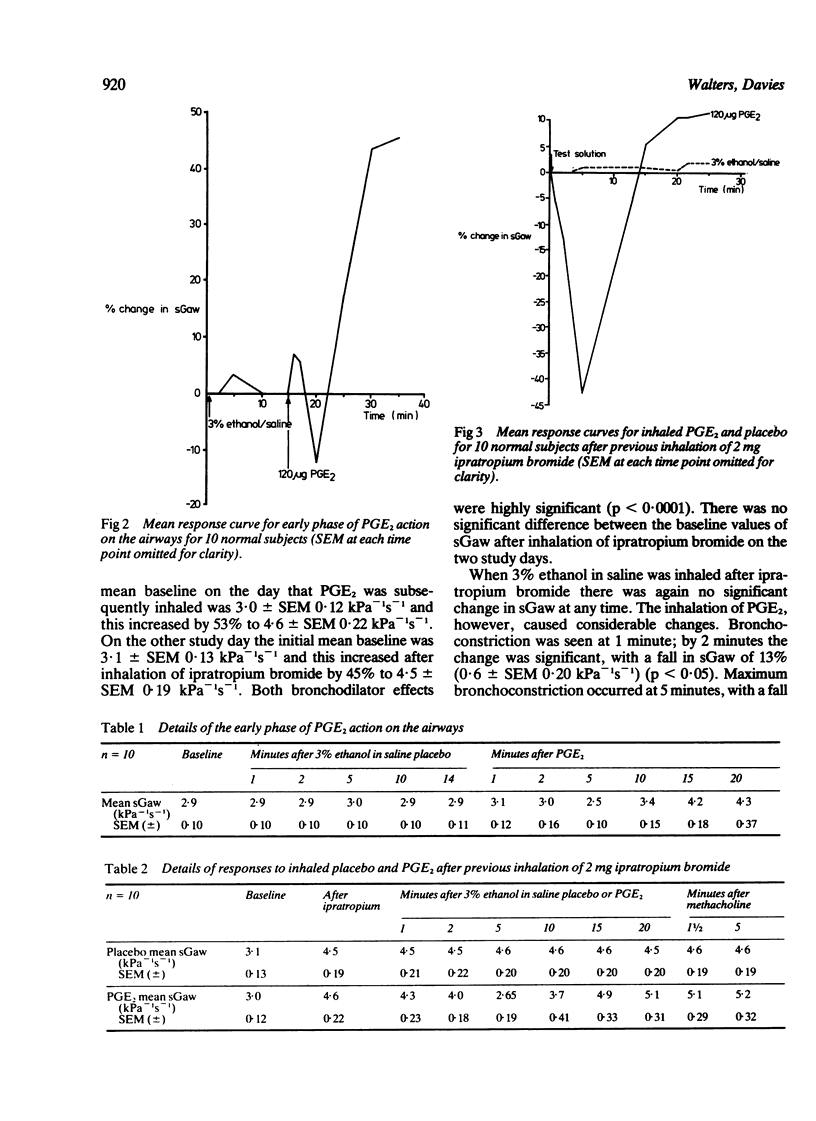
Inhalation of prostaglandin E2 by normal subjects caused initial bronchoconstriction followed by the predominant effect of bronchodilatation, which was maximal by 15 minutes. The degree of bronchoconstriction seen in the early phase appeared to be related to the initial tone of airways smooth muscle and was exaggerated after bronchodilatation with a large dose of ipratropium bromide. Bronchoconstriction induced by prostaglandin E2 is a direct effect on muscle and not secondary to a vagal reflex initiated by airways irritant receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beil M., Wylicil P. Anwendung von Sch 1000 in der Inhalationsbehandlung mit intermittierendem Uberdruck bei chronisch obstruktiven Atemwegserkrankungen. MMW Munch Med Wochenschr. 1975 Feb 28;117(9):357–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. A., Kennedy I. Contractile and relaxant actions of prostaglandins on guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;68(3):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb14569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas N. J., Sudlow M. F., Flenley D. C. Effect of an inhaled atropinelike agent on normal airway function. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Feb;46(2):256–262. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner P. J., Collier H. O. Receptors for E and F prostaglandins in airways. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1980;7:1003–1008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathé A. A., Hedqvist P. Effect of prostaglandins F2 alpha and E2 on airway conductance in healthy subjects and asthmatic patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Mar;111(3):313–320. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathé A. A., Hedqvist P., Holmgren A., Svanborg N. Bronchial hyperreactivity to prostaglandin F 2 and histamine in patients with asthma. Br Med J. 1973 Jan 27;1(5847):193–196. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5847.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsson B. G., Jacobs F. M., Nadel J. A. Role of autonomic nervous system and the cough reflex in the increased responsiveness of airways in patients with obstructive airway disease. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1812–1818. doi: 10.1172/JCI105671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Cuthbert M. F. The response of normal and asthmatic subjects to prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha by different routes, and their significance in asthma. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1976;1:449–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storms W. W., DoPico G. A., Reed C. E. Aerosol Sch 1000. An anticholinergic bronchodilator. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):419–422. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. C., Patel K. R., Kerr J. W. Sodium cromoglycate and ipratropium bromide in exercise-induced asthma. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):694–699. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. H., Bevan C., Parrish R. W., Davies B. H., Smith A. P. Time-dependent effect of prostaglandin E2 inhalation on airway responses to bronchoconstrictor agents in normal subjects. Thorax. 1982 Jun;37(6):438–442. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.6.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. H., Bevan M., Davies B. H. The effects of oral propranolol and indomethacin on the response to inhaled PGE2 in normal human subjects. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1982 Feb;8(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/s0262-1746(82)80006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman M. A. Pharmacologic and therapeutic implications of prostaglandins on airway smooth muscle. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1981;17(4):675–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



